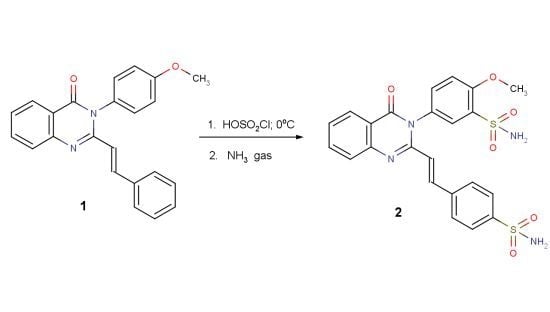
2-Methoxy-5-{4-oxo-2-[(E)-2-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)ethenyl-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-3-yl]benzene-1-sulfonamide
Abstract
:Experimental
Supplementary materials
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2Supplementary File 3Acknowledgments
References
- Connolly, D.J.; Cusack, D.; O’Sulivan, T.P.; Guiry, P.J. Synthesis of quinazolinones and quinazolines. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 10153–10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.S.; Kamel, M.M.; Abotaleb, N.; Nofal, S.M.; Ahmed, M.F. Novel 3-(p-Substituted-phenyl)-6-bromo-4(3H)-quinazolinone derivatives of promising anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2009, 67, 487–500. [Google Scholar]
- Hitkari, A.; Bhalla, M.; Saxena, A.K.; Verma, M.; Gupta, M.P.; Shanker, K. Substituted quinazolinones and their anti-inflammatory activity. Boll. Chim. Farm. 1995, 134, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kurumbail, R.G.; Stevens, A.M.; Gierse, J.K.; McDonald, J.J.; Stegeman, R.A.; Pak, J.Y.; Gildehaus, D.; Miyashiro, J.M.; Pening, T.D.; Seibert, K.; et al. Structural basis for selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 by anti-inflammatory agents. Nature 1996, 384, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.J.; Rao, P.N.P.; Knaus, E.E. Design and synthetis of novel celecoxib analogues as selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors: Replacement of sulfonamido pharmacophore by a sulfonylazide bioisostere. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 5273–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayun; Yanuar, A.; Hanafi, M.; Hudiyono, S. Virtual screening of 2,3-disubstituted-4(3H)-quinazolinones possessing benzenesulfonamide moiety for COX-2 inhibitor. Bioinformation 2011, 7, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, J.S.; Kramer, S.; Talley, J.J.; Penning, T.; Collins, P.; Graneto, M.J.; Seibert, K.; Koboldt, C.M.; Masferrer, J.; Zweifel, B. Synthesis and activity of sulfonamide-substituted 4,5-Diaryl thiazoles as selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errede, L.A. Acylanthranils.1. The pathway of quinazolinone formation in the reaction of acylanthranils with anilines. J. Org. Chem. 1976, 41, 1763–1765. [Google Scholar]
- Varma, R.S.; Bahadur, S.; Agnihotri, A.K. Synthesis of some 6-bromo-3-[(arylamino)methyl]- and 2-styryl-3-[4'-(carboalkoxy)phenyl]-4(3H)-quinazolinones. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1981, 26, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Kashaw, S.K.; Jatav, V.; Mishra, P. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of some new 3-[5-(4-substituted)phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-yl]-2-styrylquinazoline-4(3H)-ones. Med. Chem. Res. 2008, 17, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Webster, F.X.; Kiemle, D.J. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]

© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hayun; Hanafi, M.; Yanuar, A.; Hudiyono, S. 2-Methoxy-5-{4-oxo-2-[(E)-2-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)ethenyl-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-3-yl]benzene-1-sulfonamide. Molbank 2012, 2012, M765. https://doi.org/10.3390/M765
Hayun, Hanafi M, Yanuar A, Hudiyono S. 2-Methoxy-5-{4-oxo-2-[(E)-2-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)ethenyl-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-3-yl]benzene-1-sulfonamide. Molbank. 2012; 2012(3):M765. https://doi.org/10.3390/M765
Chicago/Turabian StyleHayun, Muhammad Hanafi, Arry Yanuar, and Sumi Hudiyono. 2012. "2-Methoxy-5-{4-oxo-2-[(E)-2-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)ethenyl-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-3-yl]benzene-1-sulfonamide" Molbank 2012, no. 3: M765. https://doi.org/10.3390/M765