Reply to the Letter to the Editor by A. Schwelm and S. Neuhauser: “Detection of Ribosomal DNA Sequence Polymorphisms in the Protist Plasmodiophora brassicae for the Identification of Geographical Isolates”
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laila, R.; Robin, A.H.K.; Yang, K.; Choi, G.J.; Park, J.I.; Nou, I.S. Detection of ribosomal DNA sequence polymorphisms in the protist Plasmodiophora brassicae for the identification of geographical isolates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwelm, A.; Berney, C.; Dixelius, C.; Bassc, D.; Neuhauser, S. The large subunit rDNA sequence of plasmodiophora brassicae does not contain intra-species polymorphism. Protist 2016, 167, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, R.; Kawahara, A.; Murakami, H.; Tanaka, S.; Ezawa, T. Complete structure of nuclear rDNA of the obligate plant parasite Plasmodiophora brassicae: Intraspecific polymorphisms in the exon and group I intron of the large subunit rDNA. Protist 2011, 162, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
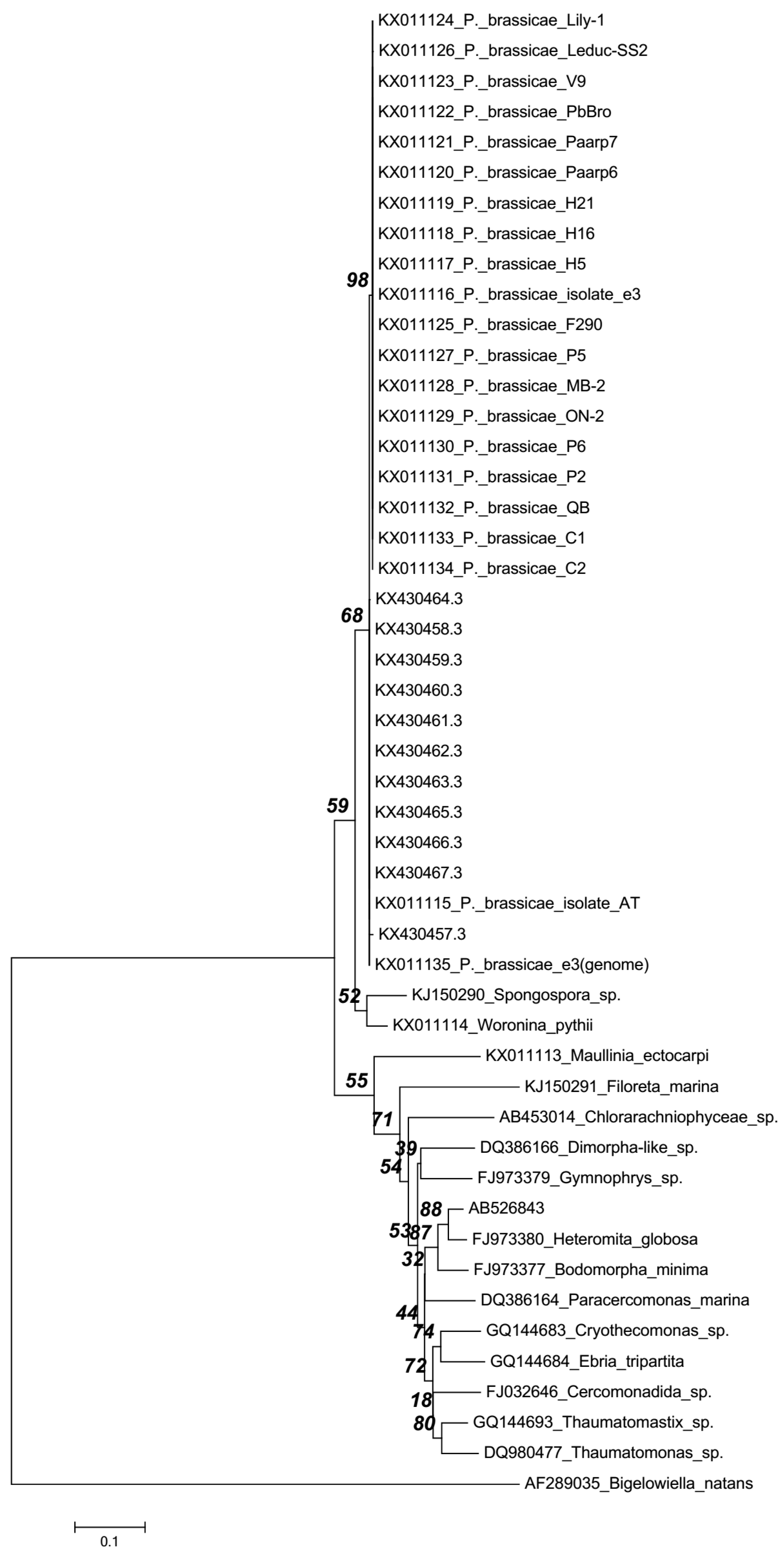
| Different Geographic Isolates | Accession No. | Sequence Length (bp) | Sequence Encoding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gangneung1 | KX430457.3 | 7421 | Partial ribosomal RNA, both small and large subunits |
| Yeoncheon | KX430458.3 | 7421 | |
| Daejon | KX430459.3 | 7425 | |
| Haenam2 | KX430460.3 | 7426 | |
| Seosan | KX430461.3 | 7423 | |
| Pyeongchang | KX430462.3 | 7424 | |
| Gangneung2 | KX430463.3 | 7421 | |
| Haenam1 | KX430464.3 | 7425 | |
| Hoengseong | KX430465.3 | 7425 | |
| Geumsan | KX430466.3 | 7424 | |
| Goesan | KX430467.3 | 7424 |
| Primer Name | Target Region | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSU1 | 5391–5671 | GAACCAGGACGTGGATATTGTATGG | CCGACTTCCCTTACCTACATTGTT | 281 |
| LSU2 | 5648–6639 | CATTGATTCTCCCGCTGGGCCC | GCTGTGGTTTCGCTAGATAGTAGA | 1185 |
| LSU3 | 6549–7459 | GGAGTTCGAACAGCTCTTAAGGTA | GTATAGTATGATGCCCGACCCATT | 911 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laila, R.; Park, J.-I.; Robin, A.H.K.; Yang, K.; Choi, G.J.; Nou, I.-S. Reply to the Letter to the Editor by A. Schwelm and S. Neuhauser: “Detection of Ribosomal DNA Sequence Polymorphisms in the Protist Plasmodiophora brassicae for the Identification of Geographical Isolates”. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071455
Laila R, Park J-I, Robin AHK, Yang K, Choi GJ, Nou I-S. Reply to the Letter to the Editor by A. Schwelm and S. Neuhauser: “Detection of Ribosomal DNA Sequence Polymorphisms in the Protist Plasmodiophora brassicae for the Identification of Geographical Isolates”. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(7):1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071455
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaila, Rawnak, Jong-In Park, Arif Hasan Khan Robin, Kiwoung Yang, Gyung Ja Choi, and Ill-Sup Nou. 2017. "Reply to the Letter to the Editor by A. Schwelm and S. Neuhauser: “Detection of Ribosomal DNA Sequence Polymorphisms in the Protist Plasmodiophora brassicae for the Identification of Geographical Isolates”" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 7: 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071455






