Chemical Characterization of Enteromorpha prolifera Extract Obtained by Enzyme-Assisted Extraction and Its Influence on the Metabolic Activity of Caco-2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Multielemental Composition of Algal Biomass, Enzymatic Extract and Post-Extraction Residue
2.2. Enzyme-Assisted Extraction of Algae
Extraction Yield
2.3. Total Phenolic Content
2.4. Antibacterial Activity of Algal Extracts
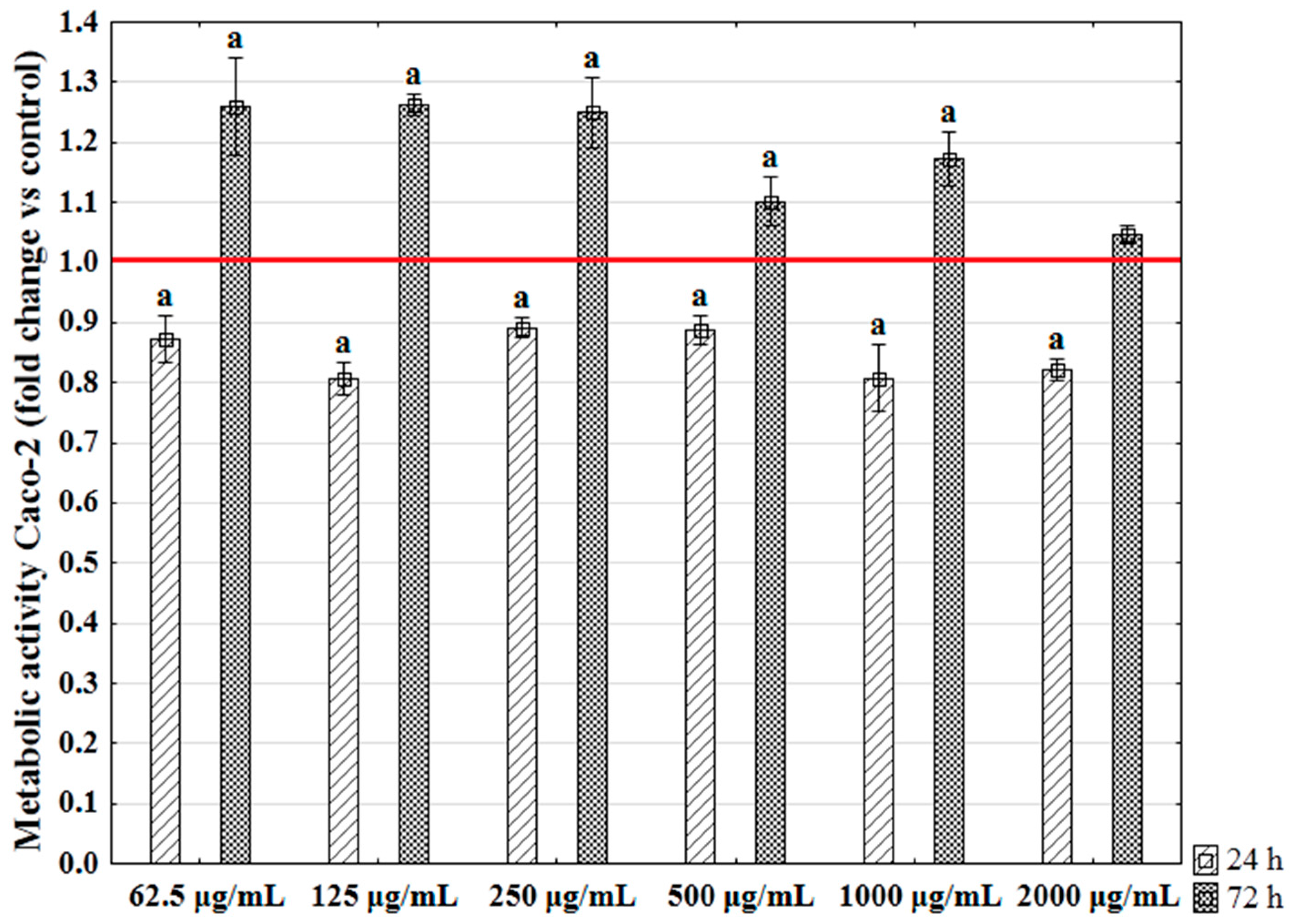
2.5. The Influence of Enteromorpha prolifera Enzymatic Extracts on the Metabolic Activity of Human Colon Epithelial Cells (Caco-2)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Algal Biomass
3.2. Multielemental Analysis of Algal Biomass
3.3. Selection of Hydrolysis System for Preparation of Enzymatic Extracts
3.3.1. Hydrolysis Experiments
3.3.2. Glucose Assay by 3,5-Dinitrosalicylic Acid Colorimetric Method
3.3.3. Selection of Proper Hydrolysis System—Calculations
3.4. Measurement of Extraction Yield
3.5. Total Phenolic Content in Enzymatic Hydrolysates
3.6. Antibacterial Activity of Algal Extracts
3.7. The Influence of Enteromorpha prolifera Enzymatic Extracts on the Metabolic Activity of Human Colon Epithelial Cells (Caco-2)
3.7.1. Propagation of Cells/Cell Culture
3.7.2. Determination of Proliferative Activity—Alamar Blue Test
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michalak, I.; Chojnacka, K. Algal extracts: Technology and advances. Eng. Life Sci. 2014, 14, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Web of Knowledge. Available online: http://login.webofknowledge.com/ (accessed on 2 September 2016).
- Wijesinghe, W.A.J.P.; Jeon, Y.J. Enzyme-assistant extraction (EAE) of bioactive components: A useful approach for recovery of industrially important metabolites from seaweeds: A review. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adalbjörnsson, B.V.; Jónsdóttir, R. Enzyme-enhanced extraction of antioxidant ingredients from algae. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1308, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, P.J.; Shahidp, F.; Jeon, Y.J. Antioxidant activities of enzymatic extracts from an edible seaweed Sargassum horneri using ESR spectrometry. J. Food Lipids 2004, 11, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulila, A.; Hassen, I.; Haouari, L.; Mejri, F.; Amor, I.B.; Casabianca, H.; Hosni, K. Enzyme-assisted extraction of bioactive compounds from bay leaves (Laurus nobilis L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 74, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.C.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, G.; Kim, K.N.; Cha, S.H.; Kim, S.K.; Jeon, B.T.; Park, P.J.; Lee, K.W.; Jeon, Y.J. Effect of enzyme-assisted extract of Sargassum coreanum on induction of apoptosis in HL-60 tumor cells. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, S.U.; Tiwari, B.K.; O’Donnell, C.P. Application of novel extraction technologies for bioactives from marine algae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4667–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, K.; Murthy, G.S. Enzymatic Degradation of Microalgal Cell Walls; Paper Number: 1035636; ASABE: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Cong, W. Enzyme-assisted aqueous extraction of lipid from microalgae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11771–11776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardouin, K.; Bedoux, G.; Burlot, A.S.; Nyvall-Collén, P.; Bourgougnon, N. Enzymatic recovery of metabolites from seaweeds: Potential applications. Adv. Bot. Res. 2014, 71, 281–323. [Google Scholar]
- Siriwardhana, N.; Jeon, Y.J.; Kim, S.H.; Ha, J.H.; Heo, S.J.; Lee, K.W. Enzymatic hydrolysis for effective extraction of antioxidative compounds from Hizikia fusiformis. Algae 2004, 19, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, I.; Chojnacka, K. Algae as production systems of bioactive compounds. Eng. Life Sci. 2015, 15, 160–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billakanti, J.M.; Catchpole, O.J.; Fenton, T.A.; Mitchell, K.A.; MacKenzie, A.D. Enzyme-assisted extraction of fucoxanthin and lipids containing polyunsaturated fatty acids from Undaria pinnatifida using dimethyl ether and ethanol. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 1999–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardouin, K.; Burlot, A.-S.; Umami, A.; Tanniou, A.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Widowati, I.; Bedoux, G.; Bourgougnon, N. Biochemical and antiviral activities of enzymatic hydrolysates from different invasive French seaweeds cells. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 1029–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulshreshtha, G.; Burlot, A.S.; Marty, C.; Critchley, A.; Hafting, J.; Bedoux, G.; Bourgougnon, N.; Prithiviraj, B. Enzyme-Assisted Extraction of bioactive material from Chondrus crispus and Codium fragile and its effect on Herpes simplex Virus (HSV-1). Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 558–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heo, S.J.; Park, P.J.; Park, E.J.; Kim, S.K.; Jeon, Y.J. Antioxidant activity of enzymatic extracts from a brown seaweed Ecklonia cava by electron spin resonance spectrometry and comet assay. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 221, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.J.; Park, E.J.; Lee, K.W.; Jeon, Y.J. Antioxidant activities of enzymatic extracts from brown seaweeds. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, S.J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.T.; Lee, K.W. Antioxidant effect of enzymatic hydrolyzate from a Kelp, Ecklonia cava. Algae 2003, 18, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, N.; Gupta, V.; Reddy, C.R.K.; Jha, B. Enzymatic hydrolysis and production of bioethanol from common macrophytic green alga Ulva fasciata Delile. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 150, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.B.; Park, P.J.; Je, J.Y. Preparation and biological evaluation of enzyme-assisted extracts from edible seaweed (Enteromorpha prolifera) as antioxidant, anti-acetylcholinesterase and inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in murine macrophages. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 63, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalak, I.; Miller, U.; Tuhy, Ł.; Sówka, I.; Chojnacka, K. Characterization of biological properties of co-composted Baltic seaweeds in germination tests. Eng. Life Sci. 2016, 17, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Morales, M.; Casas-Valdez, M.; Carrillo-Domínguez, S.; González-Acosta, B.; Pérez-Gil, F. Chemical composition and microbiological assays of marine algae Enteromorpha spp. as a potential food source. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2005, 18, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, A.M.; Szaniawska, A.; Normant, M.; Janas, U. The biochemical composition of Enteromorpha spp. from the Gulf of Gdańsk coast on the southern Baltic Sea. Oceanologia 2000, 42, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Dodson, J.R.; Aronson, J.M. Cell wall composition of Enteromorpha intestinalis. Bot. Mar. 1978, 21, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiloglu, S.; Capanoglu, E.; Grootaert, C.; Van Camp, J. Anthocyanin absorption and metabolism by human intestinal Caco-2 cells—A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 6, 21555–21574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michalak, I.; Górka, B.; Wieczorek, P.P.; Rój, E.; Lipok, J.; Łęska, B.; Messyasz, B.; Wilk, R.; Schroeder, G.; Dobrzyńska-Inger, A.; et al. Supercritical fluid extraction of algae enhances levels of biologically active compounds promoting plant growth. Eur. J. Phycol. 2016, 51, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, I.; Tuhy, Ł.; Chojnacka, K. Seaweed extract by microwave assisted extraction as plant growth biostimulant. Open Chem. 2015, 13, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.J.; Lee, K.W.; Song, C.B.; Jeon, Y.J. Antioxidant activity of enzymatic extracts from brown seaweeds. Algae 2003, 18, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, T.K. Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure Appl. Chem. 1986, 59, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Tsai, W.S.; Chiu, T.H. Antioxidant properties of seven cultivated and natural edible seaweed extracts from Taiwan. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2012, 21, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, J.Y.; Park, P.J.; Kim, E.K.; Park, J.S.; Yoon, H.D.; Kim, K.R.; Ahn, C.B. Antioxidant activity of enzymatic extracts from the brown seaweed Undaria pinnatifida by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 874–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Lamsal, B.P.; Stepien, V.; Johnson, L.A.; Murphy, P.A. Functionality of soy protein produced by enzyme-assisted extraction. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2006, 83, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitiratsakul, B.; Anprung, P. Prebiotic activity score and bioactive compounds in Longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.): Influence of pectinase in enzyme-assisted extraction. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 1947–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzesiak, J.; Marycz, K.; Wrzeszcz, K.; Czogała, J. Isolation and morphological characterisation of ovine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in culture. Int. J. Stem Cells 2011, 4, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhein-Knudsen, N.; Ale, M.T.; Meyer, A.S. Seaweed hydrocolloid production: An update on enzyme assisted extraction and modification technologies. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3340–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, D.; Sousa, S.; Silva, A.; Amorim, M.; Pereira, L.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P.; Gomes, A.M.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Freitas, A.C. Impact of enzyme- and ultrasound-assisted extraction methods on biological properties of red, brown, and green seaweeds from the central west coast of Portugal. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3177–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, L.F.; Kolling, D.; Camassola, M.; Dillon, A.J.P.; Ramos, L.P. Comparison of Penicillium echinulatum and Trichoderma reesei cellulases in relation to their activity against various cellulosic substrates. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stengel, D.B.; Connan, S.; Popper, Z. Algal chemodiversity and bioactivity: Sources of natural variability and implications for commercial application. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, E.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Antibacterial derivatives of marine algae: An overview of pharmacological mechanisms and applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J. Antibacterial Effect of Extracts from Two Icelandic Algae (Ascophyllum nodosum and Laminaria digitata). UNU-Fisheries Training Programme, University of Akureyri: Reykjavik, Iceland, 2010. Available online: http://www.unuftp.is/static/fellows/document/jin-proofread-caitlin-and-ski-mfd.pdf (accessed on 22 January 2017).
- Olejnik, A.; Lewandowska, M.; Grajek, W.; Czaczyk, K. New rapid method of Caco-2 cell differentiation. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2003, 12, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, M.L.; Potin, P.; Craigie, J.S.; Raven, J.A.; Merchant, S.S.; Helliwell, K.E.; Smith, A.G.; Camire, M.E.; Brawley, S.H. Algae as nutritional and functional food sources: Revisiting our understanding. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlot, A.-S.; Bedoux, G.; Bourgougnon, N. Response surface methodology for enzyme-assisted extraction of water-soluble antiviral compounds from the proliferative macroalga Solieria chordalis. Enz. Eng. 2016, 5, 1000148. [Google Scholar]
- Rizo, W.F.; Ferreira, L.E.; Colnaghi, V.; Martins, J.S.; Franchi, L.P.; Takahashi, C.S.; Beleboni, R.O.; Marins, M.; Pereira, P.S.; Fachin, A.L. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of coronaridine from Tabernaemontana catharinensis A.DC in a human laryngeal epithelial carcinoma cell line (Hep-2). Genet. Mol. Biol. 2013, 36, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, U.; Sivasubramanian, V.; Niranjali Devaraj, S. In vitro cytotoxic activity of aqueous extract of Chlorococcum humicola and ethylacetate extract of Desmococcus olivaceus on Hep 2 cells of human lung cancer. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 5, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Press, B. Optimization of the Caco-2 permeability assay to screen drug compounds for intestinal absorption and efflux. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 763, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lillie, R.D. Histopathologic Technique, 1st ed.; The Blakiston Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Dashtban, M.; Maki, M.; Leung, K.T.; Mao, C.; Qin, W. Cellulase activities in biomass conversion: Measurement methods and comparison. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2010, 30, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.S. Glucose Assay by Dinitrosalicylic Colorimetric Method. University of Maryland. Available online: http://www.eng.umd.edu/~nsw/ench485/lab4a.htm (accessed on 3 November 2016).
- Shetty, K.; Curtis, O.F.; Levin, R.E.; Witkowsky, R.; Ang, V. Prevention of vitrification associated with the in vitro shoot culture of oregano (Origanum vulgare) by Pseudomonas spp. J. Plant Physiol. 1995, 147, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marycz, K.; Pazik, R.; Zawisza, K.; Wiglusz, K.; Marędziak, M.; Sobierajska, P.; Wiglusz, R.J. Multifunctional nanocrystalline calcium phosphates loaded with Tetracycline antibiotic combined with human adipose derived mesenchymal stromal stem cells (hASCs). Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 69, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
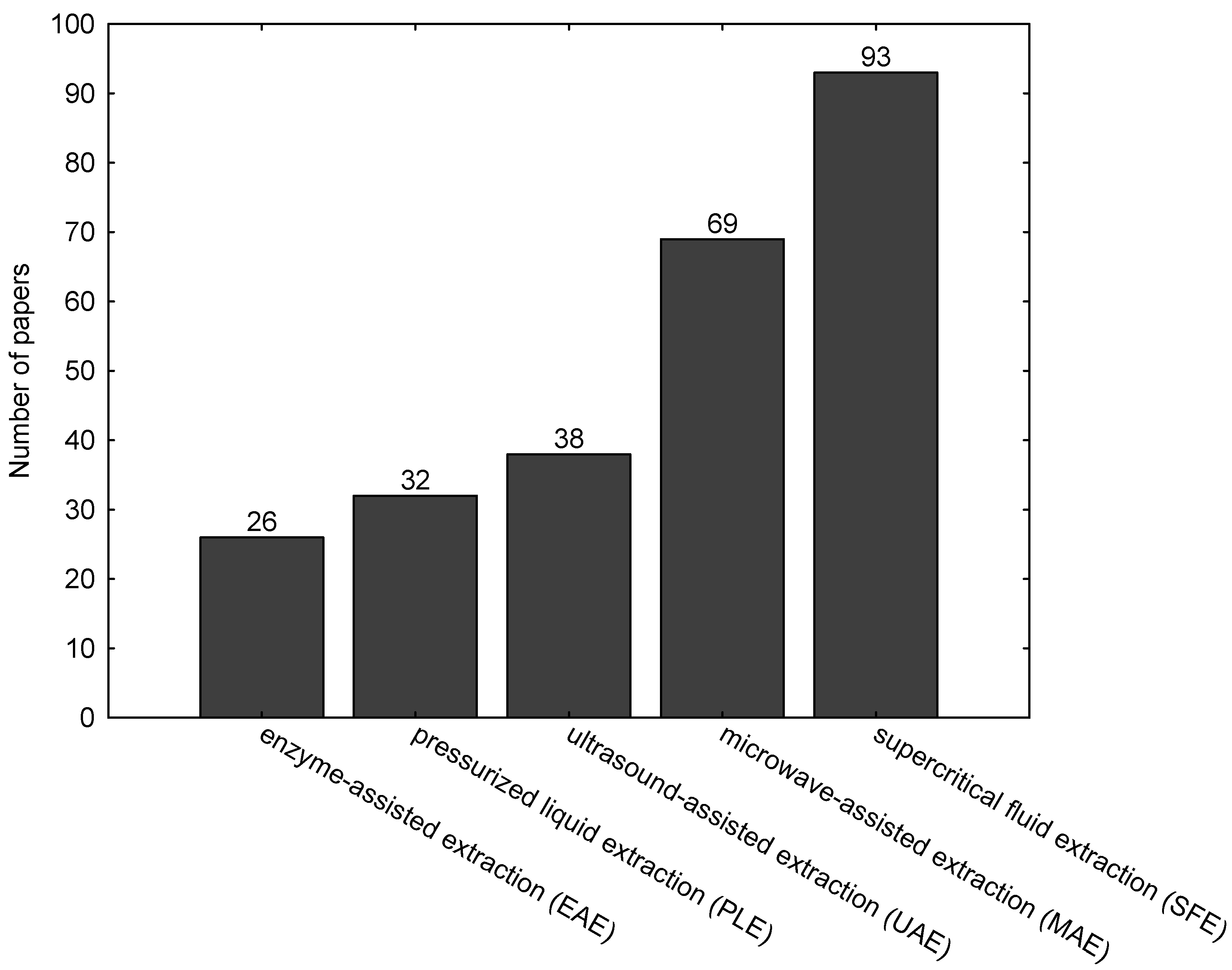
| Enzyme | Alga | Extracted Compound | Method | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutrase 0.8 L (endoprotease—neutral Bacillus amyloliquefaciens protease) | Sargassum coreanum (B) | crude polysaccharide (fucose, galactose, and glucose) | 50 g A, 5 g E, 0.2 M PB, pH 8, 50 °C, 12 h | inhibitory activities against cancer cell growth, induction of apoptosis in HL-60 tumor cells | [7] |
| Alginate lyase (combined extraction method: enzyme pre-treated Undaria after centrifugation was used to extract fucoxanthin and lipids using organic solvents) | Undaria pinnatifida (B) | fucoxanthin, lipids containing polyunsaturated fatty acid | 0.05% (v/w) A, 10 mg/mL E, 0.1 M PB, pH 6.2, 37 °C, 2 h | possible alternative to ethanol for the extraction of fucoxanthin from U. pinnatifida | [14] |
| Carbohydrases (cellulase, xylanase, arabanase, β-glucanase); Proteases (endopeptidase, endoprotease) | Ulva sp. (G) Sargassum muticum (B) Solieria chordalis (R) | soluble protein, polyphenol, neutral sugars, uronic acids, sulphated polysaccharides | 500 g A, 0.5% (w/w) E, 500 mL H2O, 50 °C, 5 h (example for Ulva sp.) | antiviral activity without cytotoxicity effect–tested Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) | [15] |
| Carbohydrase (cellulase, β-glucanase, Ultaflo (heat-stable multi-active β-glucanase)); Protease | Chondrus crispus (R) Codium fragile (G) | protein, neutral sugars, uronic acids, and sulfates | 1 and 10 g A, 0.5% E, 200 mL H2O, 50 °C, 3 h | functional food and antiviral drug discovery—the enzymatic hydrolysates exhibited significant activity against HSV-1 | [16] |
| Carbohydrases: Celluclast (β-glucanase), exo-1,4-α-d-glucosidase (AMG), Termantyl (heat-stable α-amylase), Ultaflo, Viscozyme (arabanase, cellulase, β-glucanase, hemicellulase and xyianase); Proteases: Alcalase (endoprotease), Protamex (endoprotease), Neutrase, Flavourzyme (endoprotease and exopeptidase activities), Kojizyme (endo/exopeptidase) | Sargassum horneri (B) | 1 g A, 100 µL (or mg) E, 100 mL of buffer (AB for Viscozyme, AMG, Celluclast, for the rest—PB), 12 h | antioxidant activity (use in different food formulations and pharmaceutical industry) | [5,17,18] | |
| Carbohydrases: Celluclast (β-glucanase), exo-1,4-α-d-glucosidase (AMG), Termantyl (heat-stable α-amylase), Ultaflo, Viscozyme (arabanase, cellulase, β-glucanase, hemicellulase and xyianase); Proteases: Alcalase (endoprotease), Protamex (endoprotease), Neutrase, Flavourzyme (endoprotease and exopeptidase activities), Kojizyme (endo/exopeptidase) | Ecklonia cava (B) | antioxidant compounds | 1 g A, 100 µL (or mg) E, 100 mL of buffer (AB for Viscozyme, AMG, Celluclast, for the rest—PB), 12 h | antioxidant activity (use in different food formulations and pharmaceutical industry) | [19] |
| Viscozyme L (cellulase) | Ulva fasciata (G) | - | 1 g A, 1%, 2% and 5% (v/v) E, 20 mL of sodium acetate buffer (pH 4.8), 45 °C, 42 h | production of bioethanol | [20] |
| Carbohydrases (amyloglucosidase 300 L (AMG), Celluclast 1.5 L FG, Dextrozyme, Maltogenase, Promozyme, Viscozyme L and Termamyl); Proteases (Alcalase 2.4 L FG, Flavourzyme 500 MG, Neutrase 0.8 L, Protamex) | Enteromorpha prolifera (G) | - | 1 g A, 20 mg E, 60 mL of H2O, 8 h | antioxidant, anti-acetylcholinesterase and anti-inflammatory activity | [21] |
| Carbohydrases (Viscozyme, Celluclast, Termamyl and Ultraflo); Proteases (Protamex, Kojizyme, Neutrase, Flavourzyme and Alcalase) | Hizikia fusiformis (B) | antioxidant compounds—polyphenols | 1 g A, 100 mL of distilled water, 5%—enzyme/substrate ratio, 3 days, final pH 7.0 | antioxidant activity | [12] |
| Element | Wavelength (nm) | Algae before Extraction (mg/kg of Dry Mass (d.m.)) | Algal Extract—EAE (mg/L) | Post-Extraction Residue of Algae (mg/kg of d.m.) | Algal Extract—SFE * (mg/L) [27] | Algal Extract—MAE ** (mg/L) [28] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 188.980 | <LLD | <LLD | <LLD | 0.72 ± 0.09 (EP: 7.4%) | 0.198 ± 0.025 (EP: 5.1%) |
| B | 249.772 | 231 ± 35 | 4.69 ± 0.70 (EP: 2.0%) | 37.2 ± 5.6 | <LLD | 4.74 ± 0.71 (EP: 4.8%) |
| Ba | 455.403 | 26.9 ± 4.0 | 1.04 ± 0.16 (EP: 3.9%) | 26.4 ± 4.0 | - | - |
| Ca | 315.887 | 16,540 ± 3308 | 381 ± 57 (EP: 7.4%) | 9412 ± 1882 | 1060 ± 210 (EP: 7.4%) | 365 ± 54 (EP: 0.9%) |
| Cd | 228.802 | 0.260 ± 0.039 | <LLD | 0.010 ± 0.002 | <LLD | 0.001 ± 0.000 (EP: 0.14%) |
| Co | 228.615 | 2.41 ± 0.36 | 0.035 ± 0.009 (EP: 1.6%) | 1.49 ± 0.22 | 0.026 ± 0.004 (EP: 0.54%) | 0.0135 ± 0.0034 (EP: 0.47%) |
| Cr | 267.716 | 3.79 ± 0.57 | 0.022 ± 0.006 (EP: 0.58%) | 3.65 ± 0.55 | 0.31 ± 0.05 (EP: 2.4%) | - |
| Cu | 324.754 | 7.09 ± 1.06 | 0.23 ± 0.03 (EP: 3.2%) | 6.50 ± 0.97 | 6.3 ± 0.9 (EP: 22%) | 0.108 ± 0.016 (EP: 0.85%) |
| Fe | 259.940 | 2440 ± 488 | 17.3 ± 2.6 (EP: 0.71%) | 2114 ± 423 | 9.2 ± 1.4 (EP: 0.1%) | 4.47 ± 0.70 (EP: 0.07%) |
| K | 766.491 | 2705 ± 541 | 42.3 ± 6.3 (EP: 1.6%) | 1293 ± 259 | 52 ± 8 (EP: 1.1%) | 951 ± 142 (EP: 19%) |
| Mg | 285.213 | 5993 ± 1199 | 142 ± 21 (EP: 2.4%) | 5180 ± 1036 | 406 ± 61 (EP: 10%) | 322 ± 48 (EP: 10%) |
| Mn | 257.61 | 322 ± 48 | 7.09 ± 1.06 (EP: 2.2%) | 281 ± 42 | 6.6 ± 1.0 (EP: 2.4%) | 3.07 ± 0.46 (EP: 1.3%) |
| Na | 588.995 | 2586 ± 517 | 1593 ± 319 (EP: 62%) | 1887 ± 377 | 965 ± 145 (EP: 17%) | 1250 ± 250 (EP: 20%) |
| Ni | 231.604 | 9.01 ± 1.35 | 0.255 ± 0.038 (EP: 2.8%) | 6.29 ± 0.94 | 0.27 ± 0.04 (EP: 3.0%) | 0.132 ± 0.019 (EP: 2.5%) |
| P | 213.618 | 1168 ± 234 | 15.1 ± 2.3 (EP: 1.3%) | 923 ± 138 | 43 ± 6 (EP: 2.8%) | 32.9 ± 4.9 (EP: 2.8%) |
| S | 181.972 | 18,381 ± 3676 | 292 ± 44 (EP: 1.6%) | 10,890 ± 2178 | 9300 ± 1900 (EP: 92%) | 702 ± 105 (EP: 8.1%) |
| Si | 251.611 | 668 ± 100 | 6.65 ± 0.99 (EP: 1.0%) | 682 ± 102 | - | 11.9 ± 1.8 (EP: 1.3%) |
| Zn | 213.857 | 227 ± 34 | 3.70 ± 0.56 (EP: 1.6%) | 64.3 ± 9.6 | 5.2 ± 0.8 (EP: 3.0%) | 0.169 ± 0.025 (EP: 0.26%) |
| Enzyme Dose (μL) Time (h) | 10 | SSDD | 20 | SSDD | 50 | SSDD | 100 | SSDD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Control Point) | |||||||||
| 6 (1st) | Mean glucose concentration ± standard deviation (mg/mL) | ||||||||
| SSDT | 0.998 a,b,A,c,d,e,f ± 0.005 | A | 0.969 g,h,i,j,k,B,l,m,n,o ± 0.005 | b | 1.02 p,q,r ± 0.01 | e,f,g | 1.03 s,C,t ± 0.01 | i,j,B | |
| 8 (2nd) | - | - | - | - | |||||
| SSDT | 1.09 g,u,w,D ± 0.01 | A,a | 1.08 x,y ± 0.01 | b,c,d | 1.20 a,h,s,z,α,β,γ,δ,ε,ζ ± 0.01 | e,h | 1.20 b,i,p,η,θ,ι,κ,λ,μ,ξ ± 0.02 | i,k | |
| 10 (3rd) | a,b | c,d | a,c | b,d | |||||
| SSDT | 1.03 z,η,E,F,π,ρ ± 0.03 | 0.976 u,α,θ,ς,σ,τ,υ ± 0.008 | c | 1.09 A,j,ι,φ,χ,ψ ± 0.04 | h | 1.08 k,β,ω,G ± 0.05 | k,m | ||
| 12 (4th) | e,f | e | f | ||||||
| SSDT | 1.06 B,γ,κ,H,ä ± 0.02 | 1.03 δ,λ,ë,ï ± 0.02 | 1.12 c,l,C,E,ς,ö,ø ± 0.00 | f | 1.12 d,m,q,F,σ,ü,ÿ ± 0.02 | j | |||
| 24 (5th) | A,B | A | B | ||||||
| SSDT | 0,976 x,ε,μ,φ,ω,ö,ü ± 0.024 | a | 0,980 w,ζ,ξ,χ,G,ø,ÿ ± 0.024 | d | 1.15 e,n,t,π,τ,H,ë ± 0.05 | g | 1.19 f,o,r,D,y,ρ,υ,ψ,ä,ï ± 0.07 | B,m | |
| 6 (1st) | g,h | i,j | g,i | h,j | |||||
| Enzyme Dose (μL) Time (h) | 10 | SSDD | 20 | SSDD | 50 | SSDD | 100 | SSDD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Control Point) | |||||||||
| Total enzyme activity (U) | |||||||||
| 6 (1st) | 1.54 ± 0.01 | a,b,c,d | 1.49 ± 0.01 | k,l,m,n | 1.58 ± 0.01 | u,v,w,x | 1.59 ± 0.01 | ε,ζ,η,θ | |
| SSDT | a,b | a | b | ||||||
| 8 (2nd) | 1.26 ± 0.01 | a,e,f,g | 1.24 ± 0.01 | k,o,p,q | 1.38 ± 0.02 | u,y,z,α | 1.38 ± 0.02 | ε,ι,κ,λ | |
| SSDT | c,d | e,f | c,e | d,f | |||||
| 10 (3rd) | 0.939 ± 0.031 | b,e,h,i | 0.894 *,** ± 0.007 | l,o,r,s | 0.999 ± 0.040 | v,y,β,γ | 0.987 ± 0.042 | ζ,ι,μ,ξ | |
| SSDT | A | g,h | A,g | h | |||||
| 12 (4th) | 0.796 ± 0.015 | c,f,h,j | 0.777 ± 0.013 | m,p,r,t | 0.844 * ± 0.003 | w,z,β,δ | 0.844 ** ± 0.012 | η,κ,μ,π | |
| SSDT | B,i | B | i | ||||||
| 24 (5th) | 0.365 ± 0.009 | d,g,i,j | 0.366 ± 0.009 | n,q,s,t | 0.429 ± 0.018 | x,α,γ,δ | 0.446 ± 0.024 | θ,λ,ξ,π | |
| SSDT | C,j | D,k | C,D | j,k | |||||
| Absolute enzyme activity (U/mL) | |||||||||
| 6 (1st) | 154 A,B ± 1 | 74.7 ± 0.4 | 31.5 ± 0.2 | 15.9 ± 0.1 | |||||
| 8 (2nd) | 127 C ± 1 | 62.4 ± 0.5 | 27.8 ± 0.3 | 13.9 ± 0.2 | |||||
| 10 (3rd) | 94.8 ± 3.1 | 45.1 ± 0.4 | 20.2 ± 0.8 | 10.0 ± 0.4 | |||||
| 12 (4th) | 81.6 ± 1.5 | 39.8 ± 0.7 | 17.3 ± 0.1 | 8.66 A ± 0.12 | |||||
| 24 (5th) | 37.6 ± 0.9 | 18.9 ± 0.5 | 8.85 ± 0.38 | 4.60 B,C ± 0.25 | |||||
| Enzyme concentration (%, v/v) | 1 × 10−2 | * |
| 2 × 10−2 | * | |
| 5 × 10−2 | * | |
| 9.99 × 10−2 | [19,29] | |
| Biomass:medium ratio | 1 g:100 mL (each enzyme dose) | [19,29] |
| 4 g:200 mL (selected enzyme dose) | [21] (1 g:60 mL) | |
| Medium, pH | Citrate buffer, pH 4.8 | [30] |
| Temperature | 50 °C | [19] |
| Efficacy—enhancing action | Rotary shaking, 200 rpm | * |
| Time | 6 h | * |
| 8 h | [21] | |
| 10 h | * | |
| 12 h | [19,29] | |
| 24 h | * |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Michalak, I.; Dmytryk, A.; Śmieszek, A.; Marycz, K. Chemical Characterization of Enteromorpha prolifera Extract Obtained by Enzyme-Assisted Extraction and Its Influence on the Metabolic Activity of Caco-2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030479
Michalak I, Dmytryk A, Śmieszek A, Marycz K. Chemical Characterization of Enteromorpha prolifera Extract Obtained by Enzyme-Assisted Extraction and Its Influence on the Metabolic Activity of Caco-2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(3):479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030479
Chicago/Turabian StyleMichalak, Izabela, Agnieszka Dmytryk, Agnieszka Śmieszek, and Krzysztof Marycz. 2017. "Chemical Characterization of Enteromorpha prolifera Extract Obtained by Enzyme-Assisted Extraction and Its Influence on the Metabolic Activity of Caco-2" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 3: 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030479
APA StyleMichalak, I., Dmytryk, A., Śmieszek, A., & Marycz, K. (2017). Chemical Characterization of Enteromorpha prolifera Extract Obtained by Enzyme-Assisted Extraction and Its Influence on the Metabolic Activity of Caco-2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(3), 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030479







