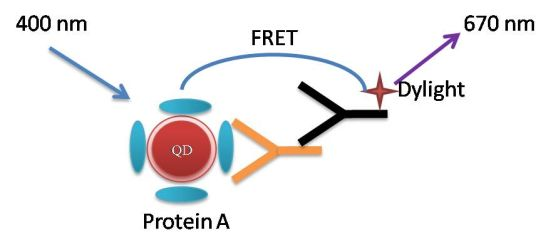
Probing Antigen-Antibody Interaction Using Fluorescence Coupled Capillary Electrophoresis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
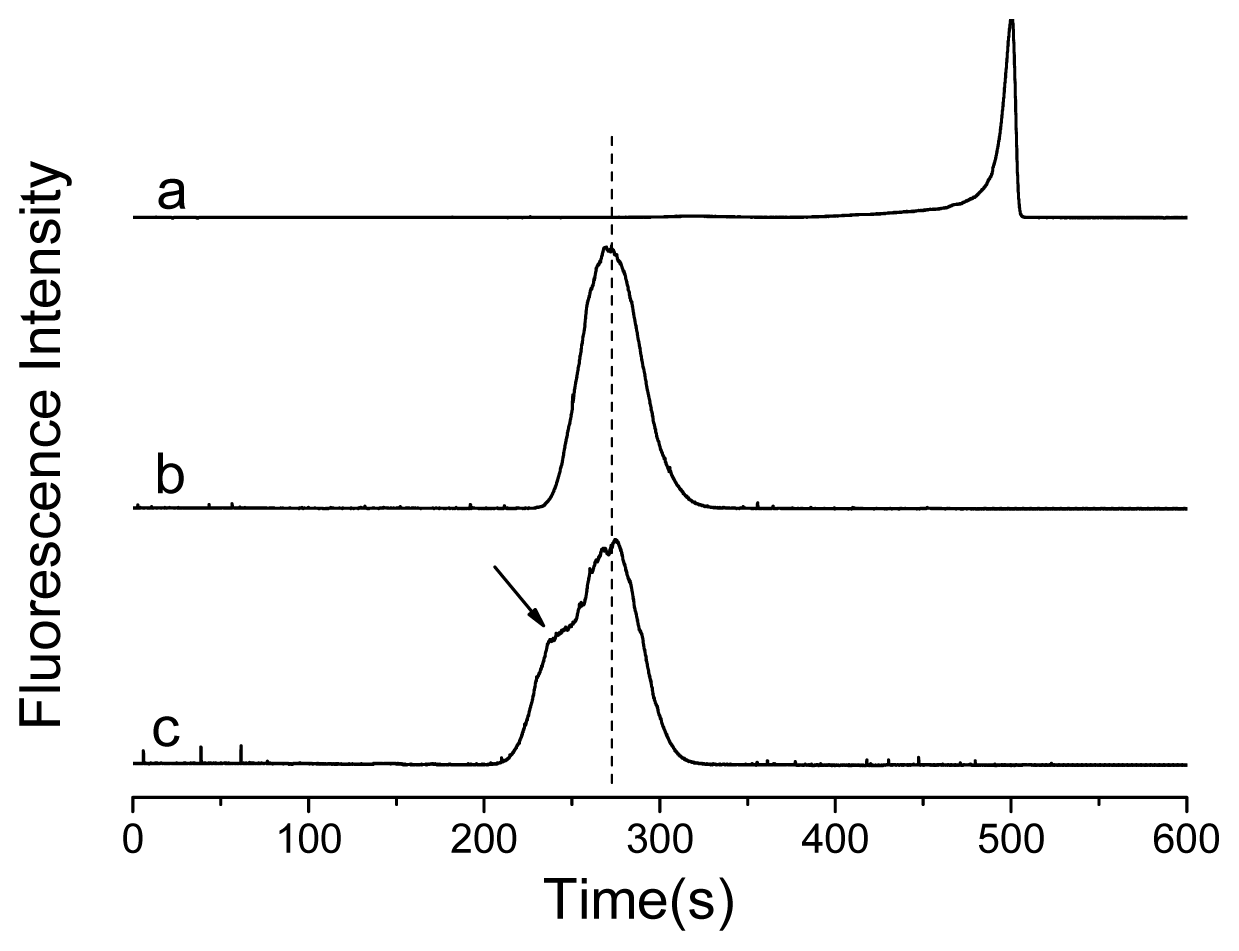
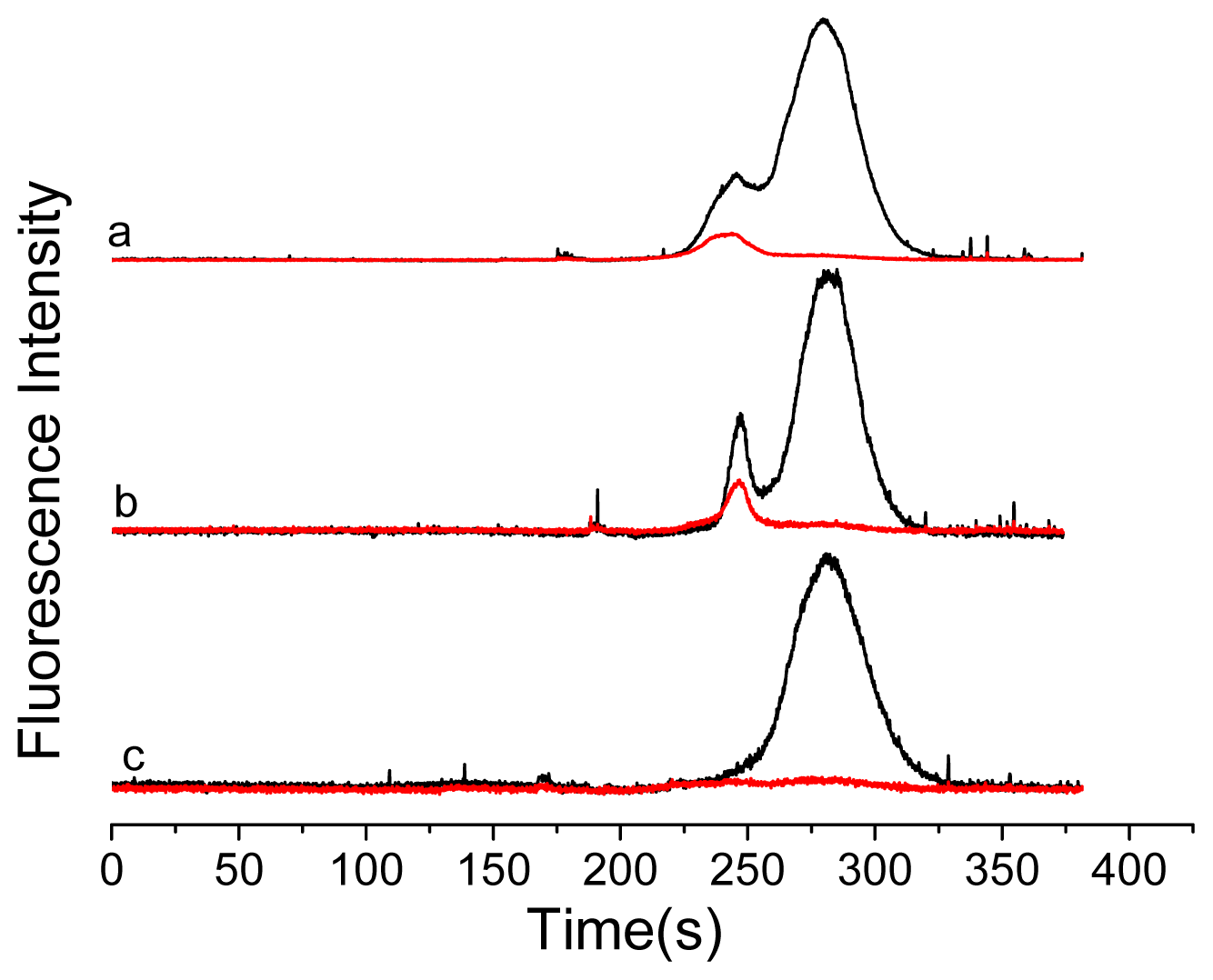
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Instruments
3.2. Preparation of GSH Stabilized QDs
3.3. Preparation of QDs-Protein A and QDs-IgG Conjugates
3.4. Procedure of Capillary Electrophoresis
3.5. Agarose Electrophoresis
3.6. Preparation of QDs-Immunocomplex
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alivisatos, A.P. Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science 1996, 271, 933–937. [Google Scholar]
- Bruchez, M.; Moronne, M.; Gin, P.; Weiss, S.; Alivisatos, A.P. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 1998, 281, 2013–2016. [Google Scholar]
- Medintz, I.L.; Uyeda, H.T.; Goldman, E.R.; Mattoussi, H. Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labeling and sensing. Nat. Mater 2005, 4, 435–446. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, R.E.; Smith, A.M.; Nie, S. Quantum dots in biology and medicine. Physica E 2004, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Michalet, X.; Pinaud, F.F.; Bentolila, L.A.; Tsay, J.M.; Doose, S.; Li, J.J.; Sundaresan, G.; Wu, A.M.; Gambhir, S.S.; Weiss, S. Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 2005, 307, 538–544. [Google Scholar]
- Algara, W.R.; Tavaresa, A.J.; Krull, U.J. Beyond labels: A review of the application of quantum dots as integrated components of assays, bioprobes, and biosensors utilizing optical transduction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 673, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, R.; Zayats, M.; Willner, I. Semiconductor quantum dots for bioanalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2008, 47, 7602–7625. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Haley, K.N.; Treadway, J.A.; Larson, J.P.; Ge, N.; Peale, F.; Bruchez, M.P. Immunofluorescent labeling of cancer marker Her2 and other cellular targets with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol 2002, 21, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, W.C.W.; Nie, S. Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 1998, 281, 2016–2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Cui, Y.; Levenson, R.M.; Chung, L.W.K.; Nie, S. In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol 2004, 22, 969–976. [Google Scholar]
- Clapp, A.R.; Goldman, E.R.; Mattoussi, H. Capping of CdSe-ZnS quantum dots with DHLA and subsequent conjugation with proteins. Nat. Protoc 2006, 1, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Jawaid, A.M.; Snee, P.T. Poly(ethylene glycol) carbodiimide coupling reagents for the biological and chemical functionalization of water-soluble nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 915–923. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Nakatani, E.; Gronenberg, L.S.; Tokimoto, T.; Wirth, M.J.; Hruby, V.J.; Roberts, A.; Lynch, R.M.; Ghosh, I. Peptide-labeled quantum dots for imaging GPCRs in whole cells and as single molecules. Bioconjugate Chem 2007, 18, 323–332. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Thakar, R.; Snee, P.T. Imparting nanoparticle function with size-controlled amphiphilic polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2008, 130, 3744–3745. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, W.; Chen, X. Preparation of peptide-conjugated quantum dots for tumor vasculature-targeted imaging. Nat. Protoc 2008, 3, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Schieber, C.; Bestetti, A.; Lim, J.P.; Ryan, A.D.; Nguyen, T.L.; Eldridge, R.; White, A.R.; Gleeson, P.A.; Donnelly, P.S.; Williams, S.J.; et al. Conjugation of transferrin to azide-modified CdSe/ZnS core-shell quantum dots using cyclooctyne click chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2012, 51, 10523–10527. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.S.; Phipps, W.S.; Loh, K.H.; Howarth, M.; Ting, A.Y. Quantum dot targeting with lipoic acid ligase and HaloTag for single-molecule imaging on living cells. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 11080–11087. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, X.; Bartley, L.; Babcock, H.; Russell, R.; Ha, T.; Herschlag, D.; Chu, S. A Single-molecule study of RNA catalysis and folding. Science 2000, 288, 2048–2051. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, J.; Cheung, H.C. Internal movement in myosin subfragment 1 detected by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 6475–6487. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, L.E. Time-resolved detection of energy transfer: Theory and application to immunoassays. Anal. Biochem 1988, 174, 101–120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Guan, L.; Chen, H.; Luo, Q.; Zhao, Y. High-sensitivity quantum dot-based fluorescence resonance energy transfer bioanalysis by capillary electrophoresis. Biosens. Bioelectron 2010, 25, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Cao, L.H.; Xu, K.H.; Zhuo, L.H.; Ge, J.H.; Li, Q.F.; Yu, L.J. A new nanobiosensor for glucose with high sensitivity and selectivity in serum based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between CdTe quantum dots and Au nanoparticles. Chem. Eur. J 2008, 14, 3637–3644. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.P.; Park, S.; Oh, E.; Oh, Y.H.; Kim, H.S. On-chip detection of protein glycosylation based on energy transfer between nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron 2009, 24, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Willard, D.M.; Carillo, L.L.; Jung, J.; van Orden, A. CdSe-ZnS quantum dots as resonance energy transfer donors in a model protein-protein binding assay. Nano Lett 2001, 1, 469–474. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Johnson, L.W. Quantum-dot-based nanosensor for RRE IIB RNA-Rev peptide interaction assay. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2006, 128, 5324–5325. [Google Scholar]
- Pholphana, N.; Rangkadilok, N.; Thongnest, S.; Ruchirawat, S.; Ruchirawat, M.; Satayavivad, J. Determination and variation of three active diterpenoids in Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Nees. Anal. Biochem 2004, 333, 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, F.; Djavadi-Ohaniance, L.; Goldberg, M.E. Measurement of antibody/antigen association rate constants in solution by a method based on the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Immunol. Methods 1997, 200, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, M.M.; Raman, C.S.; Nall, B.T. Isothermal titration calorimetry of protein-protein interactions. Methods 1999, 19, 213–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Gao, T.; Yan, Y.; Chen, G.; Li, G. Probing into the interaction of β-amyloid peptides with bilayer lipid membrane by electrochemical techniques. Electrochem. Commun 2013, 30, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Zan, F.; Guo, C.G.; Cao, C.; Ren, J. Studies on bioconjugation of quantum dots using capillary electrophoresis and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 1987–1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wolcott, A.; Gerion, D.; Visconte, M.; Sun, J.; Schwartzberg, A.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.Z. Silica-coated CdTe quantum dots functionalized with thiols for bioconjugation to IgG proteins. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 5779–5789. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, R.; Finder, T.; Gill, R.; Willner, I. Probing protein kinase (CK2) and alkaline phosphatase with CdSe/ZnS quantum dots. Nano Lett 2010, 10, 2192–2196. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.W.; Qu, L.; Guo, W.; Peng, X. Experimental determination of the extinction coefficient of CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals. Chem. Mater 2003, 15, 2854–2860. [Google Scholar]


© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Qiu, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Xia, J.; Jiang, P. Probing Antigen-Antibody Interaction Using Fluorescence Coupled Capillary Electrophoresis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 19146-19154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140919146
Wang J, Qiu L, Wang C, Zhang Y, Li J, Xia J, Jiang P. Probing Antigen-Antibody Interaction Using Fluorescence Coupled Capillary Electrophoresis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(9):19146-19154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140919146
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jianhao, Lin Qiu, Cheli Wang, Yue Zhang, Jingyan Li, Jiang Xia, and Pengju Jiang. 2013. "Probing Antigen-Antibody Interaction Using Fluorescence Coupled Capillary Electrophoresis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 9: 19146-19154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140919146
APA StyleWang, J., Qiu, L., Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Li, J., Xia, J., & Jiang, P. (2013). Probing Antigen-Antibody Interaction Using Fluorescence Coupled Capillary Electrophoresis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(9), 19146-19154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140919146