Isojacareubin from the Chinese Herb Hypericum japonicum: Potent Antibacterial and Synergistic Effects on Clinical Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Plant Materials
3.2. Bacterial Strains and Media
3.3. Antibacterial Agents
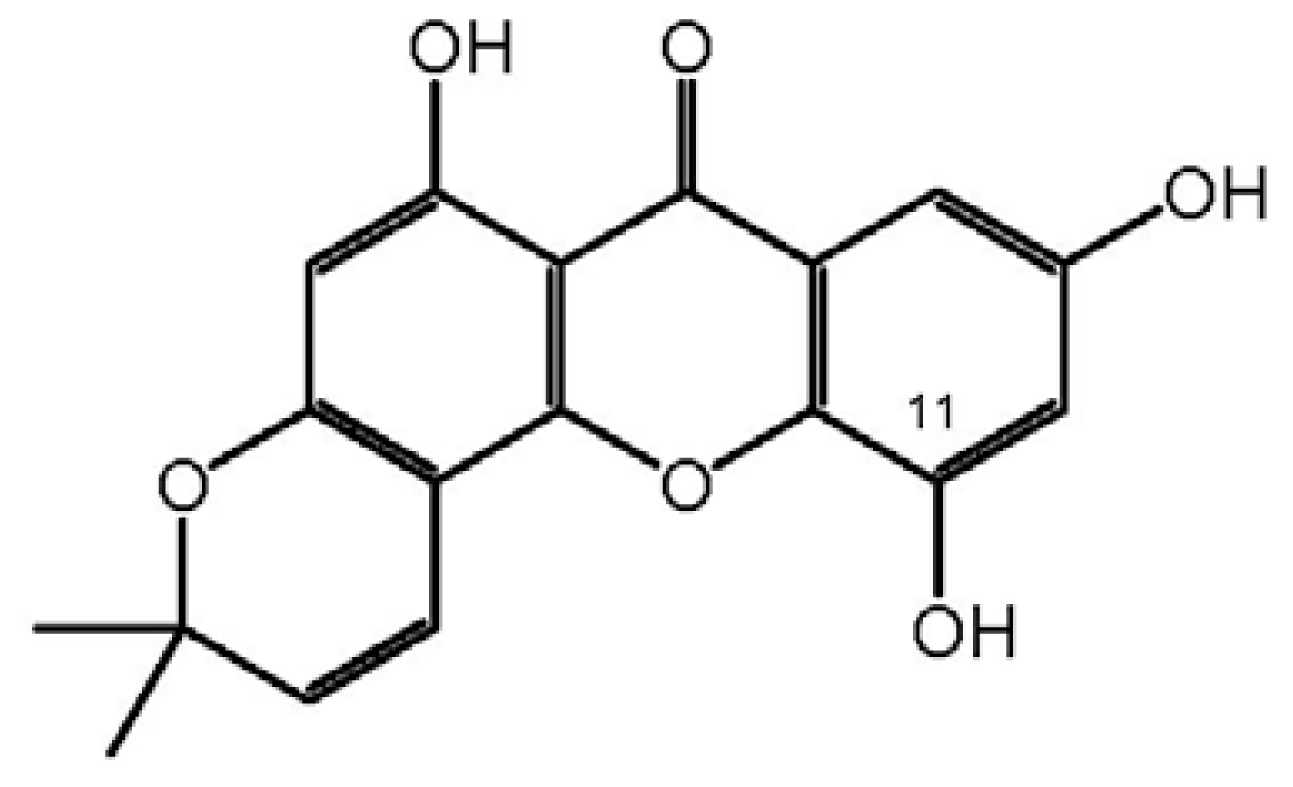
3.4. Bioassay-Guided Isolation and Identification of ISJ
3.5. Susceptibility Testing
3.6. Synergy Testing
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
- Conflict of InterestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chang, S.; Sievert, D.M.; Hageman, J.C.; Boulton, M.L.; Tenover, F.C.; Downes, F.P.; Shah, S.; Rudrik, J.T.; Pupp, G.R.; Brown, W.J.; et al. Infection with vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus containing the vanA resistance gene. N. Engl. J. Med 2003, 348, 1342–1347. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, H.; Ulrich-Merzenich, G. Synergy research: Approaching a new generation of phytopharmaceuticals. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 97–110. [Google Scholar]
- Hemaiswarya, S.; Kruthiventi, A.K.; Doble, M. Synergism between natural products and antibiotics against infectious diseases. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 639–652. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, G.Y.; Wang, G.C.; Zhao, Y.B.; Xu, G.L.; Hao, X.Y.; Han, J.; Zhao, Q. Screening of Chinese medicinal plants for inhibition against clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). J. Ethnopharmacol 2008, 120, 287–290. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, G.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Yang, C.X.; Han, J.; Wang, G.C.; Bian, Z.Q. Evaluation of traditional Chinese medicinal plants for anti-MRSA activity with reference to the treatment record of infectious diseases. Molecules 2012, 17, 2955–2967. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, G.Y.; Meng, F.Y.; Hao, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, G.C.; Xu, G.L. Antibacterial Alkaloids from Chelidonium majus Linn (Papaveraceae) against clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci 2008, 11, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, G.Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Han, J.; Wang, G.C.; Zhang, Y.L.; Pan, W.D. Synergistic antibacterial and antibiotic effects of bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids on clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Molecules 2011, 16, 9819–9826. [Google Scholar]
- An, J.; Zuo, G.Y.; Hao, X.Y.; Wang, G.C.; Li, Z.S. Antibacterial and synergy of a flavanonol rhamnoside with antibiotics against clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 990–993. [Google Scholar]
- Tian-ji-huang, Selected Yunnan Traditional Chinese Herbs; Tianjin People’s Press: Tianjin, China, 1970; Volume I, pp. 30–31.
- Di-er-cao, Dictionary of Chinese Materia Medica; Shanghai Scientific Technical Press: Shanghai, China, 1977; Volume I, pp. 813–814.
- Ishiguro, K.; Nagata, S.; Fukumoto, H.; Yamaki, M.; Isoi, K.; Oyama, Y. An isopentenylated flavonol from Hypericum japonicum. Phytochemistry 1993, 32, 1583–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; McClure, J.A.; Elsayed, S.; Louie, T.; Conly, J.M. Novel multiplex PCR assay for characterization and concomitant subtyping of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec types I to V in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol 2005, 43, 5026–5033. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.Q.; Zhao, W.H.; Asano, N.; Yoda, Y.; Hara, Y.; Shimamura, T. Epigallocatechin gallate synergistically enhances the activity of carbapenems against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother 2002, 46, 558–560. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing—17th Informational Supplement; Approved Standard M100-S17; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2007.
- Petersen, P.J.; Labthavikul, P.; Jones, C.H.; Bradford, P.A. In vitro antibacterial activities of tigecycline in combination with other antimicrobial agents determined by chequerboard and time-kill kinetic analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother 2006, 57, 573–576. [Google Scholar]
- National Pharmacopoeia Committee of China, Tianjihuang zhusheye (Injectio Hyperici Japonici). In Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (Part 1); Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1977; pp. 199–200.
- Di Carlo, G.; Borrelli, F.; Izzo, A.A.; Ernst, E. St John’s wort: Prozac from the plant kingdom. Trends Pharmacol. Set 2001, 22, 292–297. [Google Scholar]
- Chomnawang, M.T.; Surassmo, S.; Wongsariya, K.; Bunyapraphatsara, N. Antibacterial activity of Thai medicinal plants against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Fitoterapia 2009, 80, 102–104. [Google Scholar]
- Sukpondma, Y.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Phongpaichit, S. Antibacterial caged-tetraprenylated xanthones from the fruits of Garcinia hanburyi. Chem. Pharm. Bull 2005, 53, 850–852. [Google Scholar]
- Yasunaka, K.; Abe, F.; Nagayama, A.; Okabe, H.; Lozada-Perez, L.; Lopez-Villafranco, E.; Muniz, E.E.; Aguilar, A.; Reyes-Chilpa, R. Antibacterial activity of crude extracts from Mexican medicinal plants and purified coumarins and xanthones. J. Ethnopharmacol 2005, 97, 293–299. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests; Approved standard M02-A10; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2006.
- Kloos, W.K.; Bannerman, T.L. Staphylococcus and Micrococcus. In Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 7th ed; Murray, P.R., Baron, E.J., Pfaller, M.A., Tenover, F.C., Yolken, R.H., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington DC, USA, 1999; pp. 264–282. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically, 7th ed; Approved standard M7–A7; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2006.
- Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), Methods for Determining Bactericidal Activity of Antimicrobial Agents; Document M26-A; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 1999.
- Orhan, G.; Bayram, A.; Zer, Y.; Balci, I. Synergy tests by E test and chequerboard methods of antimicrobial combinations against Brucella melitensis. J. Clin. Microbiol 2005, 43, 140–143. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, J.N.; Jones, R.N.; Sader, H.S.; Savage, P.B.; Rybak, M.J. Potential synergy activity of the novel ceragenin, CAS-13, against clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, including multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa. J. Antimicrob. Chemother 2008, 61, 365–370. [Google Scholar]
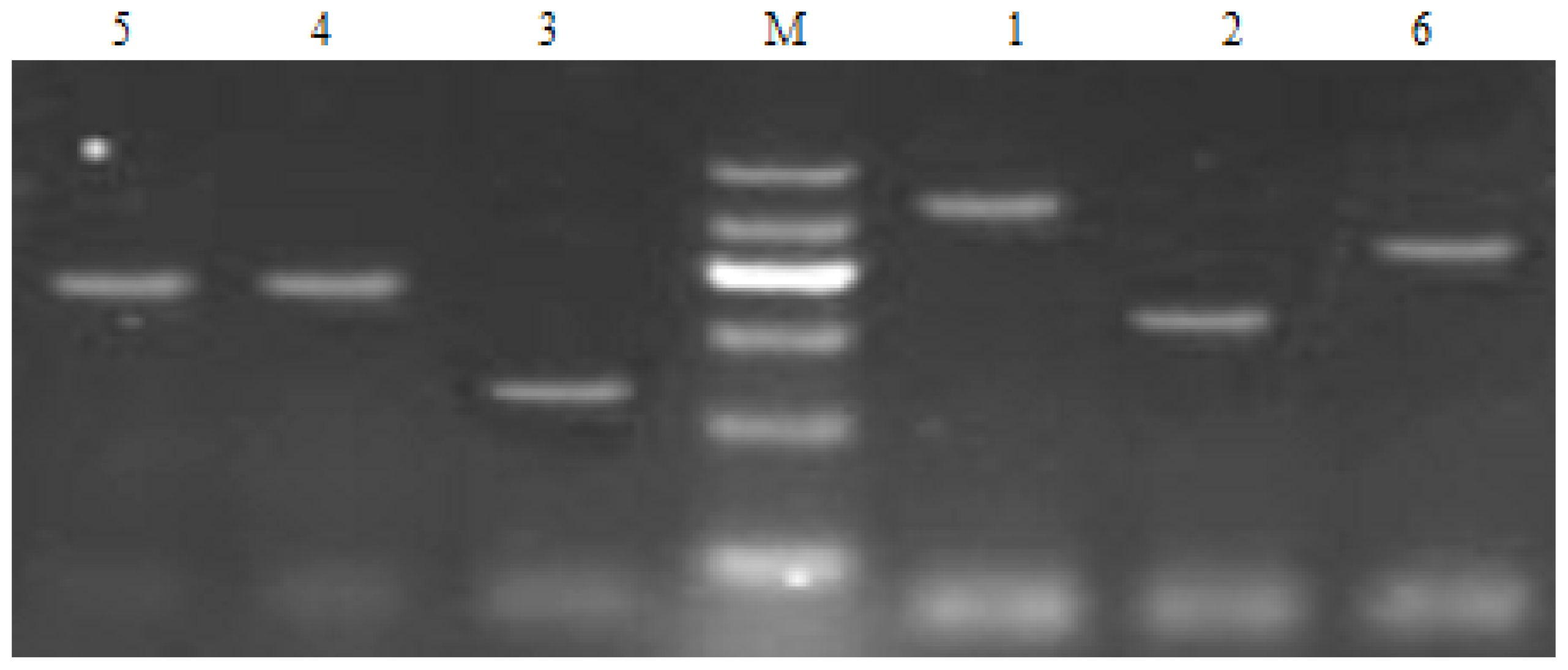

| Strainsa | MSSA (ATCC25923) | MRSA 004 |
|---|---|---|
| Petroleum ether part | 29 | 23 |
| Ethyl acetate part | 22 | 23 |
| Sub-ethyl acetate fraction-A (Fr. A) | 17 | 23 |
| Sub-ethyl acetate fraction-B (Fr. B) | 20 | 15 |
| Sub-ethyl acetate fraction-C (Fr. C2) | 30 | 29 |
| n-Butanol part | 15 | 17 |
| Water part | 15 | 12 |
| Vancomycin | 30 | 30 |
| Agents | ISJa | AMP | CAZ | LEV | AZM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alone | Alone | Combb | Alone | Comb | Alone | Comb | Alone | Comb | |
| Ranges of MIC (/MBC) (μg/mL)c | 4(/16)~ 16(/64) | 16(/64)~ 128(/512) | 4~16 + 1~4 | 128(/128)~ 512(/ex) + 32~128 | 32~128 + 1~4 | 4(/8)~ 16(/64) | 1~4 + 1~4 | ex | 512~1024 + 4~16 |
| MIC50c | 8 | 64 | 8 + 4 | 512 | 32 + 1 | 16 | 2 + 2 | - | 1024 + 8 |
| MIC90 | 16 | 128 | 16 + 4 | 512 | 64 + 4 | 16 | 4 + 4 | - | 1024 + 16 |
| Ranges of FICId | - | - | 0.37~0.62 | - | 0.25~0.5 | - | 0.25~0.5 | - | 1~1.5 |
| FICI50 | - | - | 0.37 | - | 0.25 | - | 0.37 | - | 1.5 |
| FICI90 | - | - | 0.62 | - | 0.37 | - | 0.37 | - | 1.5 |
| Effect (%)e | - | - | ad(30) sn(70) | - | sn(100) | - | sn(100) | - | id(100) |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuo, G.-Y.; An, J.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Wang, G.-C.; Hao, X.-Y.; Bian, Z.-Q. Isojacareubin from the Chinese Herb Hypericum japonicum: Potent Antibacterial and Synergistic Effects on Clinical Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8210-8218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13078210
Zuo G-Y, An J, Han J, Zhang Y-L, Wang G-C, Hao X-Y, Bian Z-Q. Isojacareubin from the Chinese Herb Hypericum japonicum: Potent Antibacterial and Synergistic Effects on Clinical Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(7):8210-8218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13078210
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuo, Guo-Ying, Jing An, Jun Han, Yun-Ling Zhang, Gen-Chun Wang, Xiao-Yan Hao, and Zhong-Qi Bian. 2012. "Isojacareubin from the Chinese Herb Hypericum japonicum: Potent Antibacterial and Synergistic Effects on Clinical Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 7: 8210-8218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13078210




