Evidence for the Formation of Difluoroacetic Acid in Chlorofluorocarbon-Contaminated Ground Water
Abstract
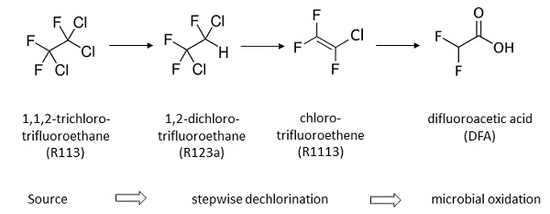
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Determination of the Methyl Esters of Difluoro- and Trifluoroacetic Acid by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
3.4. Sampling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ellis, D.A.; Hanson, M.L.; Sibley, P.K.; Shahid, T.; Fineberg, N.A.; Solomon, K.R.; Muir, D.C.G.; Mabury, S.A. The fate and persistence of trifluoroacetic and chloroacetic acids in pond waters. Chemosphere 2001, 42, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, K.R.; Velders, G.J.M.; Wilson, S.R.; Madronich, S.; Longstreth, J.; Aucamp, P.J.; Bornman, J.F. Sources, fates, toxicity, and risks of trifluoroacetic acid and its salts: Relevance to substances regulated under the Montreal and Kyoto Protocols. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2016, 19, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, B.F.; Macdonald, R.W.; Kannan, K.; Fisk, A.; Witter, A.; Yamashita, N.; Durham, L.; Spencer, C.; Muir, D.C.G. Trifluoroacetate profiles in the Arctic, Atlantic, and Pacific oceans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6555–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, B.F.; Spencer, C.; Marvin, C.H.; MacTavish, D.C.; Muir, D.C.G. Distribution of Haloacetic Acids in the Water Columns of the Laurentian Great Lakes and Lake Malawi. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1893–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCulloch, A. Fluorocarbons in the global environment: A review of the important interactions with atmospheric chemistry and physics. J. Fluor. Chem. 2003, 123, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, H.; Christoph, E.H.; Holm-Hansen, O.; Bullister, J.F. Trifluoroacetate in Ocean Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.W.; Mabury, S.A.; Wong, C.S.; Noventa, F.; Solomon, K.R.; Alaee, M.; Muir, D.C.G. Airborne Haloacetic Acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 2889–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visscher, P.T.; Culbertson, C.W.; Oremland, R.S. Degradation of trifluoroacetate in oxic and anoxic sediments. Nature 1994, 369, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.R.; Suidan, M.T.; Wallington, T.J.; Du, X. Biodegradability of trifluoroacetic acid. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2000, 17, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, D.A.; Mabury, C.A.; Jonathan, W.; Martin, J.W.; Muir, D.C.G. Thermolysis of Fluoropolymers as a potential source of halogenated organic acids in the environment. Nature 2001, 412, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, D.A.; Martin, J.W.; Muir, D.C.G.; Mabury, S.A. The use of 19F NMR and mass spectrometry for the elucidation of novel fluorinated acids and atmospheric fluoroacid precursors evolved in the thermolysis of fluoropolymers. Analyst 2003, 128, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesticide Properties Data Base, University of Hertfordshire. Available online: https://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/Reports/2896.htm (accessed on 12 February 2019).
- Kazil, J.; McKeen, S.; Kim, S.W.; Ahmadov, R.; Grell, G.A.; Talukdar, R.K.; Ravishankara, A.R. Deposition and rainwater concentrations of trifluoroacetic acid in the United States from the use of HFO-1234yf. AGU J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 14059–14079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 20595:2018-01. Water Quality—Determination of Selected Highly Volatile Organic Compounds in Water—Method Using Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry by Static Headspace Technique (HSGC-MS); ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Balsiger, C.; Holliger, C.; Höhner, P. Reductive dechlorination of chlorofluorocarbons and hydrochlorofluorocarbons in sewage sludge and aquifer sediment microcosms. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohn, D.R.; Leininger, J.R.; Lash, L.H.; Quebbemann, A.J.; Anders, M.W. Nephrotoxicity of S-(2-chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethyl)glutathione and S-(2-chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethyl)-L-cysteine, the glutathione and cysteine conjugates of chlorotrifluoroethene. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1985, 235, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morel, G.; Ban, M.; Bonnet, P.; Zissu, D.; Brondeau, M.T. Effect of β-naphthoflavone and phenobarbital on the nephrotoxicity of chlorotrifluoroethylene and 1,1-dichloro-2,2-difluoroethylene in the rat. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2005, 25, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commandeur, J.N.; Oostendorp, R.A.; Schoofs, P.R.; Xu, B.; Vermeulen, N.P. Nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity of 1,1-dichloro-2,2-difluoroethylene in the rat. Indications for differential mechanisms of bioactivation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1987, 24, 4229–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekant, W.; Vamvakas, S.; Berthold, K.; Schmidt, S.; Wild, D.; Henschle, D. Glutathione in bacteria Bacterial β-lyase mediated cleavage and mutagenicity of cysteine conjugates derived from the nephrocarcinogenic alkenes trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene and hexachlorobutadiene. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1986, 60, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifongo, L.L.; Bowden, D.J.; Brimblecombe, P. Thermal degradation of haloacetic acids in water. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2010, 5, 738–747. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228952048_Thermal_degradation_of_haloacetic_acids_in_water (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- Alexandrino, D.A.M.; Ribeiro, I.; Pint, L.M.; Cambra, R.; Oliveira, R.S.; Pereira, F.; Carvalho, M.F. Biodegradation of mono-, di- and trifluoroacetate by microbial cultures with different origins. New Biotechnol. 2017, 43, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oremland, R.S. Microbial Degradation of Atmospheric Halocarbons. In Microbiology of Atmospheric Traces Gases—Sources, Sinks and Global Processes, 1st ed.; Murrell, J.C., Kelly, D.E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; pp. 85–101. ISBN 978-3-642-64693-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, D.J.; Clegg, S.L.; Brimblecombe, P. The Henry’s law constants of the haloacetic acids. J. Atmos. Chem. 1998, 29, 85–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, T.M.; Benesch, J.A.; Gustin, M.S.; Zimmerman, E.J.; Seiber, J.N. Simplified Method for Trace Analysis of Trifluoroacetic Acid in Plant, Soil, and Water Samples Using Headspace Gas Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 4465–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Water Sample | TFA (ng/L) | DFA (ng/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Rainwater 1: 1 h of rainfall after a long dry period | 1556 a | 151 a |
| Rainwater 2: after 12 h of heavy rainfall | 370 (3.7%) | 43 (4.4%) |
| Surface water: Teltow canal | 1908 (0.9%) | n.d. b |
| Surface water: Havel lake | 676 (7.1%) | n.d. b |
| Ground Water Sample | TFA (ng/L) | DFA (ng/L) | R113 (µg/L) | R123a (µg/L) | R1113 (µg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contamination hot spot | 639 (19%) | 2249 (21%) | 4806 (5%) | 27.1 (2%) | 68.4 (3%) |
| Contamination plume | 425 (3.3%) | 1220 (1.8%) | 3315 (3%) | 10.1 (4%) | 28.2 (3%) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dorgerloh, U.; Becker, R.; Kaiser, M. Evidence for the Formation of Difluoroacetic Acid in Chlorofluorocarbon-Contaminated Ground Water. Molecules 2019, 24, 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061039
Dorgerloh U, Becker R, Kaiser M. Evidence for the Formation of Difluoroacetic Acid in Chlorofluorocarbon-Contaminated Ground Water. Molecules. 2019; 24(6):1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061039
Chicago/Turabian StyleDorgerloh, Ute, Roland Becker, and Melanie Kaiser. 2019. "Evidence for the Formation of Difluoroacetic Acid in Chlorofluorocarbon-Contaminated Ground Water" Molecules 24, no. 6: 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061039
APA StyleDorgerloh, U., Becker, R., & Kaiser, M. (2019). Evidence for the Formation of Difluoroacetic Acid in Chlorofluorocarbon-Contaminated Ground Water. Molecules, 24(6), 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061039