Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Hyperlipidemic Activities of Flavonoids from Corn Silk on STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Total Flavonoids and Total Phenolic Content
2.2. Effect of CSFs on Body Weight of Normal and STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice

2.3. Effect of MI and CSFs on Fasting BG of Normal and STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice

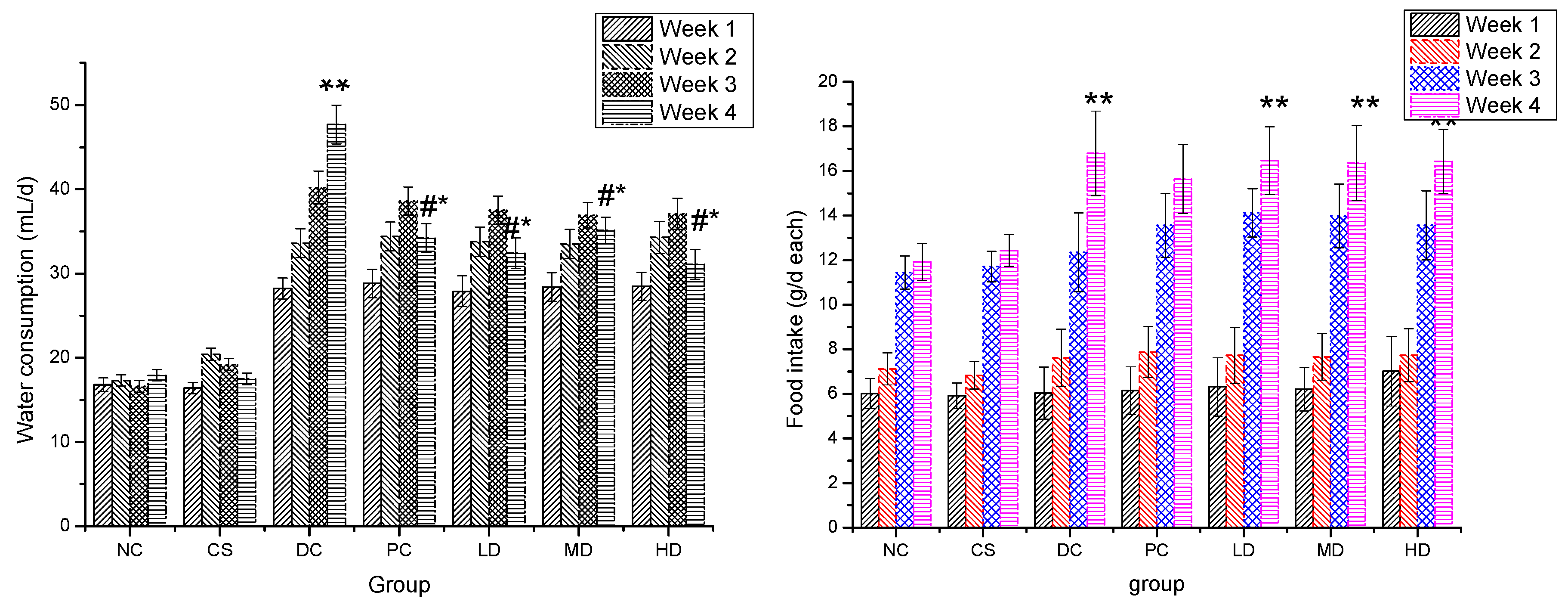
2.4. Effect of CSFs on Water Consumption and Food Intake of Normal and STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice
2.5. Effect of CSFs on Related Organ Weight and Liver Glycogen of Normal and STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice

2.6. Effect of CSFs on Serum SOD and MDA of Normal and STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice

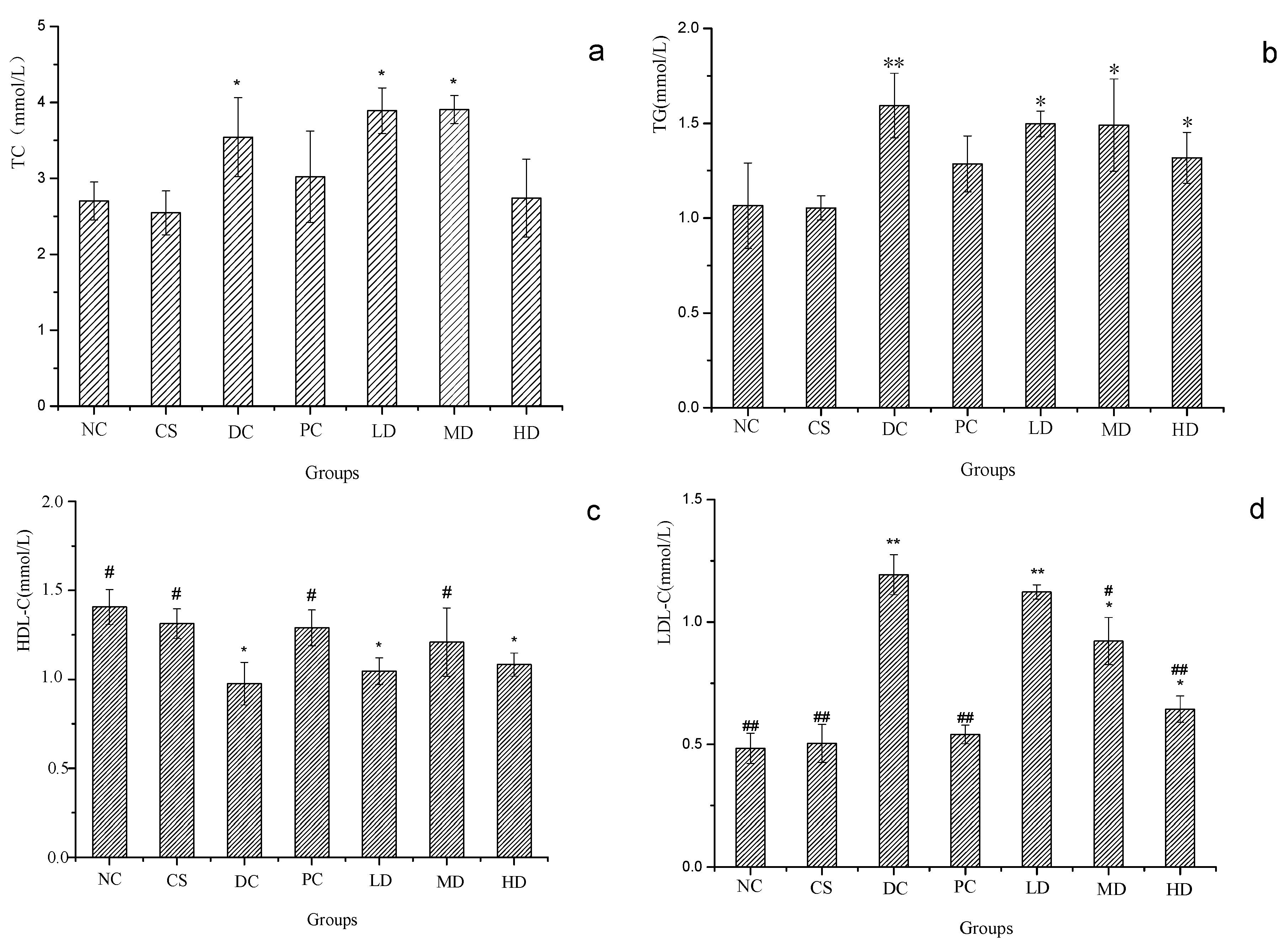
2.7. Effect of CSFs on Serum TC, TG HDL-C and LDL-C of Normal and STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of Corn Silk Flavonoids (CSFs)
3.3. Determination of Total Phenolic Content
3.4. Determination of Total flavonoid Content
3.5. Animals and Diets
3.6. Induction of T2DM model [MI]
3.7. Experimental Design
3.8. Biological Analysis
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Roozendaal, B.W.; Krass, I. Development of an evidence-based checklist for the detection of drug related problems in type 2 diabetes. Pharm. World Sci. 2009, 31, 580–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aladag, I.; Eyibilen, A.; Guven, M.; Atis, O.; Erkorkmaz, U. Role of oxidative stress in hearing impairment in patients with type two diabetes mellitus. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2009, 123, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierckx, N.; Horvath, G.; van Gils, C.; Vertommen, J.; van de Vliet, J.; de Leeuw, I.; Manuel-y-Keenoy, B. Oxidative stress status in patients with diabetes mellitus: Relationship to diet. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 57, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, P.V.; Liu, D.; Gilbert, E.R. Recent advances in understanding the anti-diabetic actions of dietary flavonoids. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1777–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.A.; Islam, M.S. Anti-diabetic effects of the acetone fraction of Senna singueana stem bark in a type 2 diabetes rat model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canivell, S.; Gomis, R. Diagnosis and classification of autoimmune diabetes mellitus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, R.; Morris, G.A. The anti-diabetic potential of polysaccharides extracted from members of the cucurbit family: A review. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2014, 3, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkens, J.A.; Klungel, O.H.; Stolk, R.P.; Spoelstra, J.A. Cardiovascular drug use and hospitalizations attributable to type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Shankar, K.; Ronis, M.J.; Mehendale, H.M. Mechanisms and Outcomes of Drug- and Toxicant-Induced Liver Toxicity in Diabetes. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2007, 37, 413–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Du, P.; An, L.; Yuan, G.; Sun, Z. Anti-diabetic effect of Coptis Chinensis polysaccharide in high-fat diet with STZ-induced diabetic mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 55, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girija, K.; Lakshman, K.; Udaya, C.; Sabhya Sachi, G.; Divya, T. Anti–diabetic and anti–cholesterolemic activity of methanol extracts of three species of Amaranthus. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 1, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, S.; Salam, A.D.; Tomy, D.V.; Carla, B.; Kumar, R.A.; Sunil, C. Diabetes mellitus and medicinal plants—A review. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2014, 4, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, X.; Xue, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, W. Anti-hepatoma activity and mechanism of corn silk polysaccharides in H22 tumor-bearing mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 64, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Lu, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, E.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. Subchronic toxicity study of corn silk with rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lin, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, E.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. Supercritical fluid extraction of flavonoids from Maydis stigma and its nitrite-scavenging ability. Food Bioprod. Process. 2011, 89, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.A.; Wan Rosli, W.I. Nutritional compositions and antioxidative capacity of the silk obtained from immature and mature corn. J. King Saud Uni. Sci. 2014, 26, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.R.; Niture, N.T.; Ansari, A.A.; Shah, P.D. Anti-diabetic activity of embelin: Involvement of cellular inflammatory mediators, oxidative stress and other biomarkers. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Xiong, H.; Wang, J.; Ding, X.; Shu, G.; Mei, Z. Antidiabetic effect of total flavonoids from Sanguis draxonis in type 2 diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.S.; Chen, C.P.; Xiao, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Min, Q.X.; Yue, Y.; Chen, J. In vitro and in vivo anti-diabetic activity of Swertia kouitchensis extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 147, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, P.; Paul, P.; Mudgal, J.; Nayak, P.G.; Pannakal, S.T.; Priyadarsini, K.I.; Unnikrishnan, M.K. Antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant effects of the flavonoid rich fraction of Pilea microphylla (L.) in high fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetes in mice. Exp. Toxicol Pathol. 2012, 64, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksimovic, Z.A.; Kovacevic, N. Preliminary assay on the antioxidative activity of Maydis stigma extracts. Fitoterapia 2003, 74, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-E.; Xu, D.-P. Study on the chemical constituents of flavones from corn silk. Zhong Yao Cai 2007, 30, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Lu, S.; Liu, J. The antioxidant and free-radical scavenging activities of extract and fractions from corn silk (Zea mays L.) and related flavone glycosides. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Ahmed, D.; Gupta, P.S.; Anwar, F.; Mujeeb, M. Anti-diabetic, anti-oxidant and anti-hyperlipidemic activities of Melastoma malabathricum Linn. leaves in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Yin, Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, F. Comparison of anti-diabetic effects of polysaccharides from corn silk on normal and hyperglycemia rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. In Oxidants and Antioxidants, Pt A; Packer, L., Ed.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 1999; Volume 299, pp. 152–178. [Google Scholar]
- Dewanto, V.; Wu, X.Z.; Adom, K.K.; Liu, R.H. Thermal processing enhances the nutritional value of tomatoes by increasing total antioxidant activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3010–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Yang, M.H.; Wen, H.M.; Chern, J.C. Estimation of total flavonoid content in propolis by two complementary colorimetric methods. J. Food Drug Anal. 2002, 10, 178–182. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council. Guide of the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; The National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; p. 125. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of crude flavonoids from corn silk (CSFs) are available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Ma, Z.; Cheng, J.; Liu, J. Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Hyperlipidemic Activities of Flavonoids from Corn Silk on STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice. Molecules 2016, 21, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21010007
Zhang Y, Wu L, Ma Z, Cheng J, Liu J. Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Hyperlipidemic Activities of Flavonoids from Corn Silk on STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice. Molecules. 2016; 21(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yan, Liying Wu, Zhongsu Ma, Jia Cheng, and Jingbo Liu. 2016. "Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Hyperlipidemic Activities of Flavonoids from Corn Silk on STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice" Molecules 21, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21010007
APA StyleZhang, Y., Wu, L., Ma, Z., Cheng, J., & Liu, J. (2016). Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Hyperlipidemic Activities of Flavonoids from Corn Silk on STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice. Molecules, 21(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21010007




