Analgesic Effect of Harpagophytum procumbens on Postoperative and Neuropathic Pain in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effects of H. Procumbens Extracts on Mechanical Hyperalgesia Induced by Plantar Incision
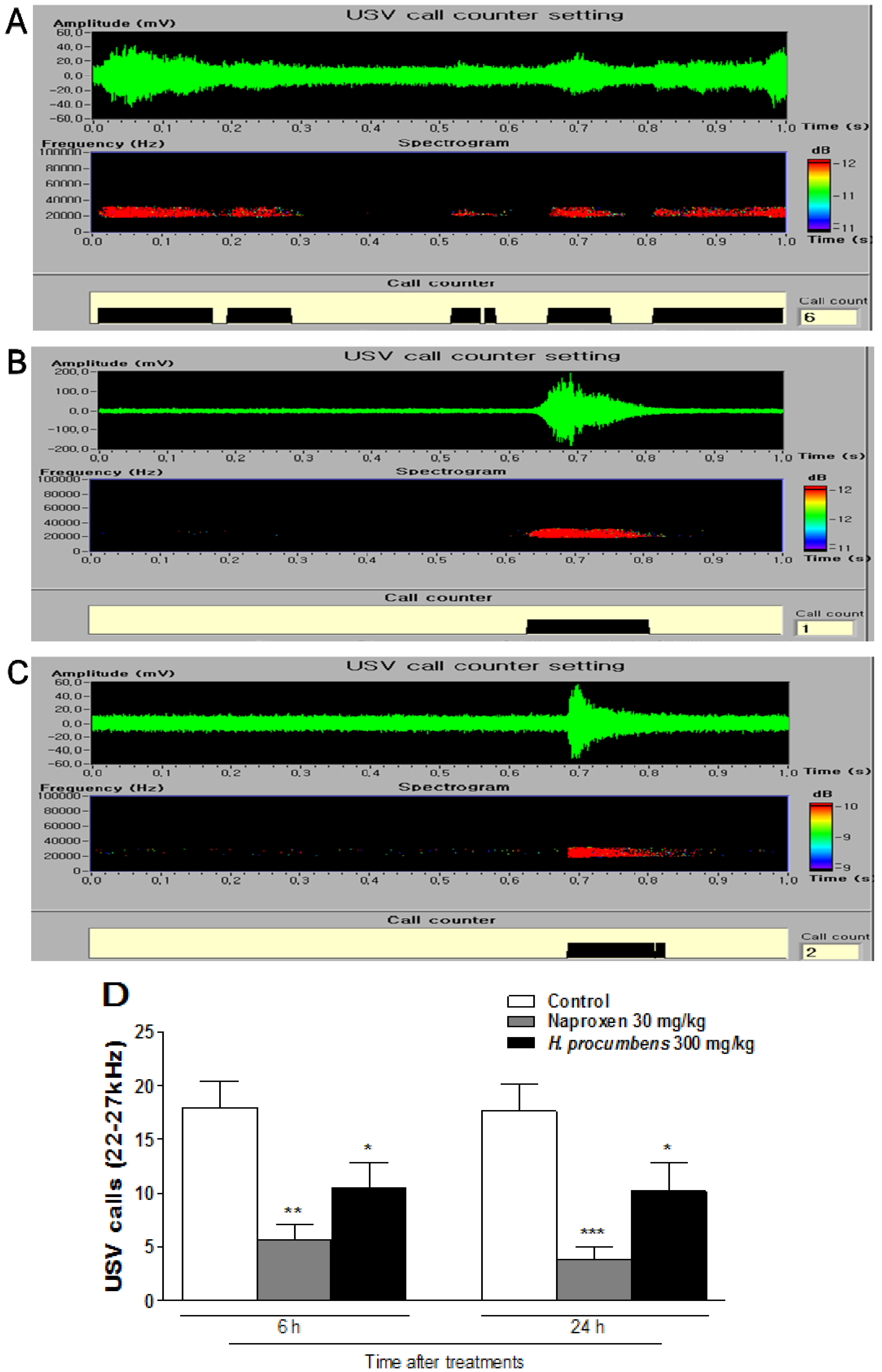
2.2. Effects of H. Procumbens Extracts on Ultrasonic Vocalizations (USVs) Induced by Plantar Incision
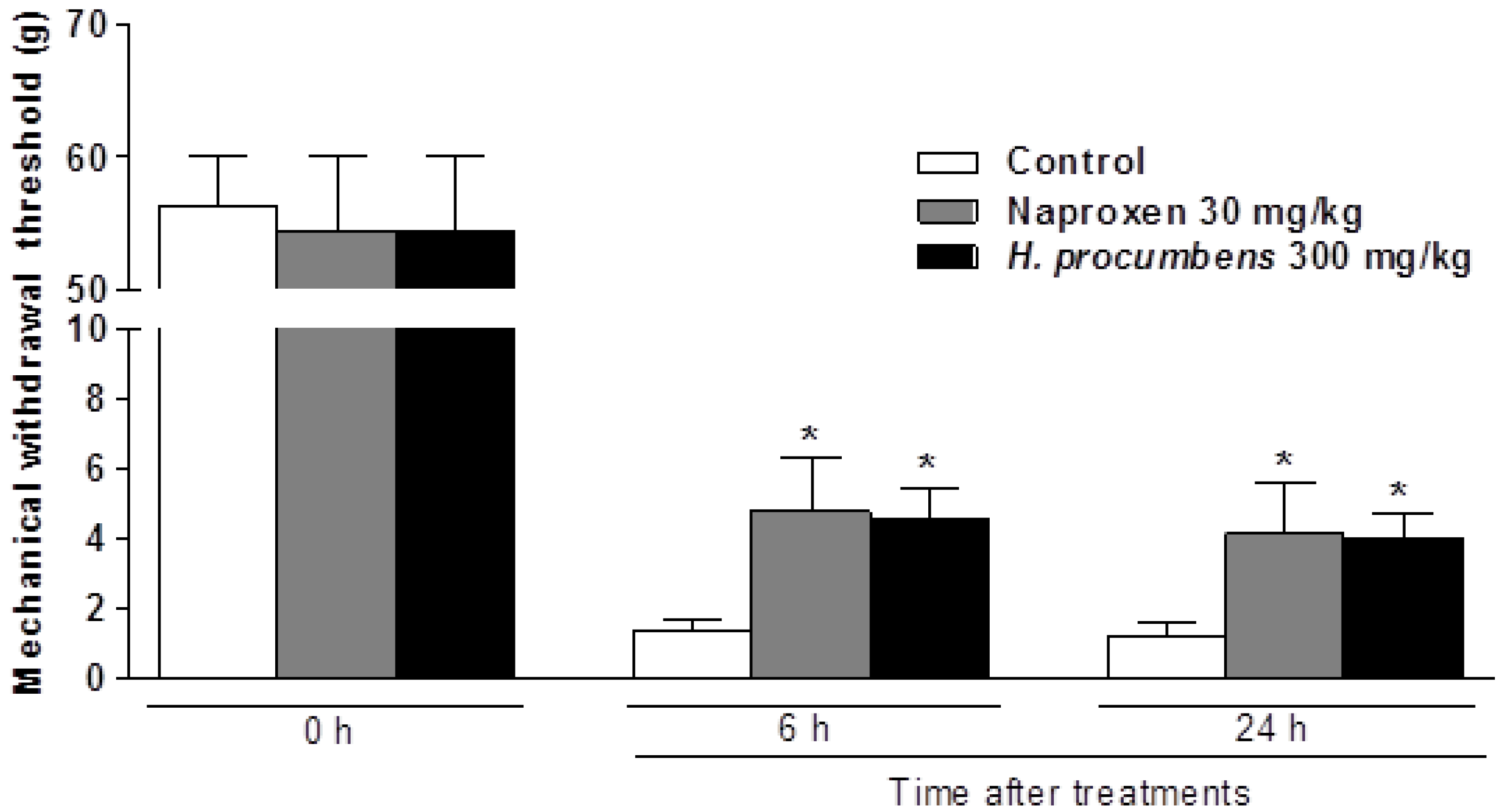
2.3. Effects of H. Procumbens Extracts on Mechanical Allodynia Induced by Spared Nerve Injury (SNI)

3. Experimental
3.1. Preparation of H. Procumbens Extracts
3.2. Animals and Treatments
3.3. Plantar Incision of Postoperative Pain Rat Model
3.4. Spared Nerve Injury (SNI) of Neuropathic Pain Rat Model
3.5. Mechanical Withdrawal Threshold (MWT) Analysis
3.6. Ultrasonic Vocalization (USVs) Analysis
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stewart, W.F.; Ricci, J.A.; Chee, E.; Hahn, S.R.; Morganstein, D. Cost of lost productive work time among us workers with depression. JAMA 2003, 289, 3135–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltzenburg, M.; Scadding, J. Neuropathic pain. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2001, 14, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, C.J.; Doubell, T.P. The pathophysiology of chronic pain--increased sensitivity to low threshold a beta-fibre inputs. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 1994, 4, 525–534. [Google Scholar]
- Dickenson, A.H. Recent advances in the physiology and pharmacology of pain: Plasticity and its implications for clinical analgesia. J. Psychopharmacol. 1991, 5, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilron, I.; Coderre, T.J. Emerging drugs in neuropathic pain. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2007, 12, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.; Knaus, E.E. Evolution of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (nsaids): Cyclooxygenase (cox) inhibition and beyond. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 11, 81s–110s. [Google Scholar]
- Furlan, A.D.; Sandoval, J.A.; Mailis-Gagnon, A.; Tunks, E. Opioids for chronic noncancer pain: A meta-analysis of effectiveness and side effects. Can. Med. Assn. J. 2006, 174, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, K.A.; Manjavachi, M.N.; Paszcuk, A.F.; Pivatto, M.; Viegas, C., Jr.; Bolzani, V.S.; Calixto, J.B. Plant derived alkaloid (-)-cassine induces anti-inflammatory and anti-hyperalgesics effects in both acute and chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain models. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Z.; Hu, C. Analgesic effect of iridoid glycosides from paederia scandens (lour.) merrill (rubiaceae) on spared nerve injury rat model of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 102, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimam, M.; Brownell, L.; Hodges, M.; Jia, Q. Analgesic effects of a standardized bioflavonoid composition from scutellaria baicalensis and acacia catechu. J. Diet. Suppl. 2012, 9, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, M.I.; Alipieva, K.; Orhan, I.E. Cholinesterases inhibitory and antioxidant activities of harpagophytum procumbens from in vitro systems. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendler, T.; Gruenwald, J.; Ulbricht, C.; Basch, E. Devil’s claw (harpagophytum procumbens dc): An evidence-based systematic review by the natural standard research collaboration. J. Herbal Pharmacother. 2006, 6, 89–126. [Google Scholar]
- Lanhers, M.C.; Fleurentin, J.; Mortier, F.; Vinche, A.; Younos, C. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of an aqueous extract of harpagophytum procumbens. Planta Med. 1992, 58, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdikian, B.; Lanhers, M.C.; Fleurentin, J.; Ollivier, E.; Maillard, C.; Balansard, G.; Mortier, F. An analytical study, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of harpagophytum procumbens and harpagophytum zeyheri. Planta Med. 1997, 63, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.L.; Santos, E.H.; Seabra Mde, L.; da Silva, A.A.; Tufik, S. Evaluation of acute and chronic treatments with harpagophytum procumbens on freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 91, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, T.J.; Vandermeulen, E.P.; Gebhart, G.F. Characterization of a rat model of incisional pain. Pain 1996, 64, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourquin, A.F.; Suveges, M.; Pertin, M.; Gilliard, N.; Sardy, S.; Davison, A.C.; Spahn, D.R.; Decosterd, I. Assessment and analysis of mechanical allodynia-like behavior induced by spared nerve injury (sni) in the mouse. Pain 2006, 122, e11–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiergiel, A.H.; Zhou, Y.; Dunn, A.J. Effects of chronic footshock, restraint and corticotropin-releasing factor on freezing, ultrasonic vocalization and forced swim behavior in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 183, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sances, G.; Martignoni, E.; Fioroni, L.; Blandini, F.; Facchinetti, F.; Nappi, G. Naproxen sodium in menstrual migraine prophylaxis: A double-blind placebo controlled study. Headache 1990, 30, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, G.T.; Harrison, J.; Boulet, J.; Mark, L.; Pearson, M.; Gottshall, S.; Walker, K. Pharmacological characterisation of a rat model of incisional pain. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 141, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvin, Y.; Blanchard, D.C.; Blanchard, R.J. Rat 22 khz ultrasonic vocalizations as alarm cries. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 182, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, B.; Burgdorf, J.; Panksepp, J. Ultrasonic vocalizations as indices of affective states in rats. Psychol. Bull. 2002, 128, 961–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudzynski, S.M.; Chiu, E.M. Behavioural responses of laboratory rats to playback of 22 khz ultrasonic calls. Physiol. Behav. 1995, 57, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miczek, K.A.; Weerts, E.M.; Vivian, J.A.; Barros, H.M. Aggression, anxiety and vocalizations in animals: Gabaa and 5-ht anxiolytics. Psychopharmacology 1995, 121, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portfors, C.V. Types and functions of ultrasonic vocalizations in laboratory rats and mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2007, 46, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Richner, M.; Bjerrum, O.J.; Nykjaer, A.; Vaegter, C.B. The spared nerve injury (sni) model of induced mechanical allodynia in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, M.R.; Racis, S.P., Jr.; Vaidya, U. Changes in plasma cytokines associated with peripheral nerve injury. J. Neuroimmunol. 1992, 39, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Myers, R.R. Endoneurial injection of tnf-alpha produces neuropathic pain behaviors. Neuroreport 1996, 7, 2897–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Kawaguchi, M.; Shimada, K.; Konishi, N.; Furuya, H.; Nakashima, T. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in schwann cells and macrophages in the sciatic nerve after single spinal nerve injury in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 363, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebich, B.L.; Heinrich, M.; Hiller, K.O.; Kammerer, N. Inhibition of tnf-alpha synthesis in lps-stimulated primary human monocytes by harpagophytum extract steihap 69. Phytomedicine 2001, 8, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, J.K.; Mossanda, K.S.; Na, H.K.; Surh, Y.J. Inhibitory effects of the extracts of sutherlandia frutescens (l.) r. Br. And harpagophytum procumbens dc. On phorbol ester-induced cox-2 expression in mouse skin: Ap-1 and creb as potential upstream targets. Cancer Lett. 2005, 218, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdos, A.; Fontaine, R.; Friehe, H.; Durand, R.; Poppinghaus, T. Contribution to the pharmacology and toxicology of different extracts as well as the harpagosid from harpagophytum procumbens dc (author’s transl). Planta Med. 1978, 34, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decosterd, I.; Woolf, C.J. Spared nerve injury: An animal model of persistent peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain 2000, 87, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the H. procumbens extracts are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, D.W.; Kim, J.G.; Han, D.; Kim, Y.T. Analgesic Effect of Harpagophytum procumbens on Postoperative and Neuropathic Pain in Rats. Molecules 2014, 19, 1060-1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19011060
Lim DW, Kim JG, Han D, Kim YT. Analgesic Effect of Harpagophytum procumbens on Postoperative and Neuropathic Pain in Rats. Molecules. 2014; 19(1):1060-1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19011060
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Dong Wook, Jae Goo Kim, Daeseok Han, and Yun Tai Kim. 2014. "Analgesic Effect of Harpagophytum procumbens on Postoperative and Neuropathic Pain in Rats" Molecules 19, no. 1: 1060-1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19011060
APA StyleLim, D. W., Kim, J. G., Han, D., & Kim, Y. T. (2014). Analgesic Effect of Harpagophytum procumbens on Postoperative and Neuropathic Pain in Rats. Molecules, 19(1), 1060-1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19011060




