A Biosorption Isotherm Model for the Removal of Reactive Azo Dyes by Inactivated Mycelia of Cunninghamella elegans UCP542
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Kinetics of Adsorption of Azo Dyes
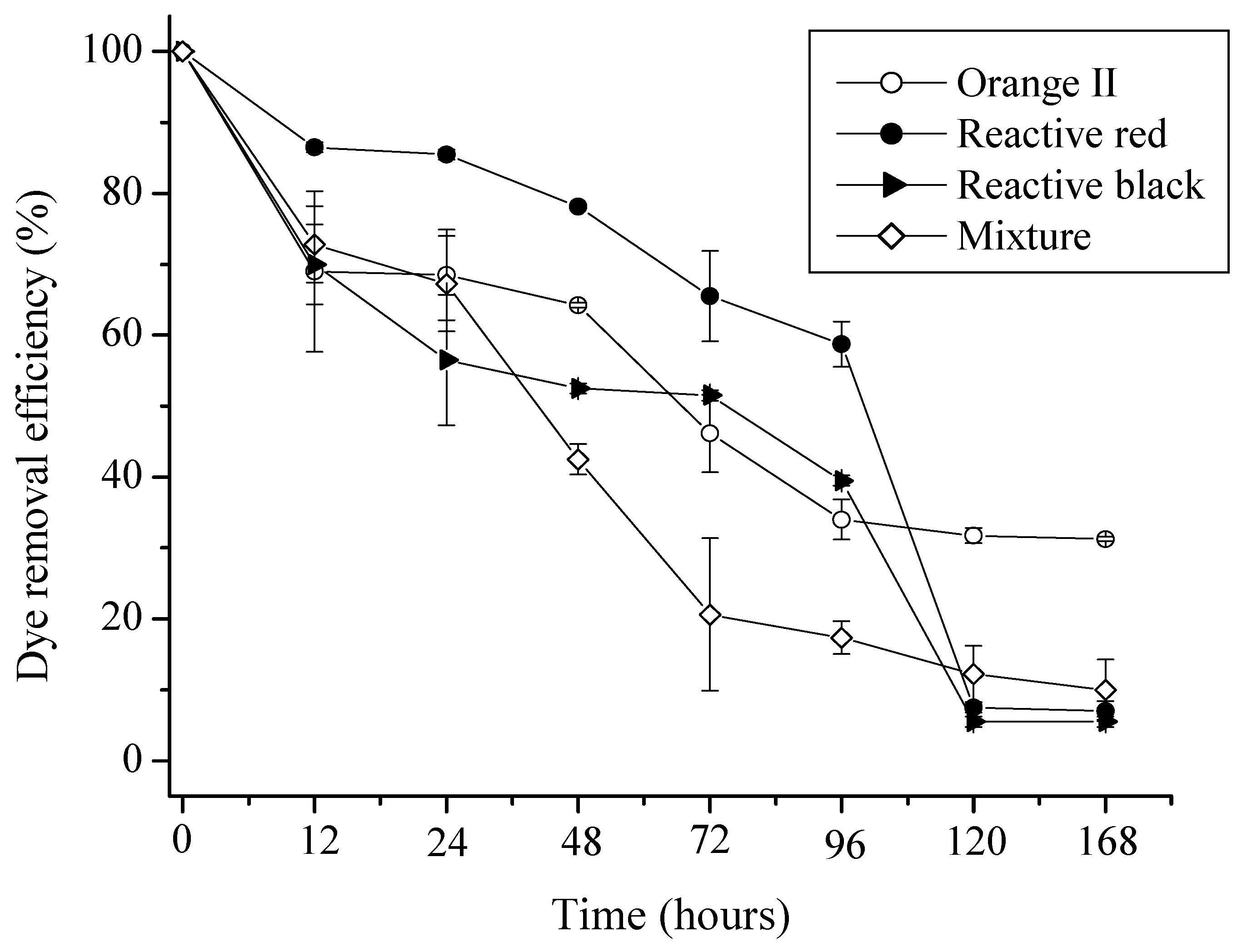
2.2. The Langmuir and Freundlich Isotherms



| b | Langmuir affinity adsorption constant (mg/L) |
| Ceq | Concentration at equilibrium of non-adsorbed dye (mg/L) |
| C0 | Initial dye concentration (mg/L) |
| KF | Proportionality Freundlich adsorption constant |
| n | Exponent Freundlich adsorption constant |
| qeq | Amount of adsorbed dye per unit weight of mycelium at equilibrium (mg/g) |
| Q0 | Limiting Langmuir adsorption constant (mg/g) |
| R2 | Linear correlation coefficient |
| X | Mycelium concentration (g/L) |
| Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | |||||
| Dyes | Q0 (mg/g) | b (mg/L) | R2 | KF | n | R2 |
| Orange | 6.94 | 1.52 | 0.983 | 3.71 | 2.43 | 0.993 |
| Red | 23.5 | 2.41 | 0.980 | 6.86 | 2.16 | 0.996 |
| Black | 4.18 | 1.96 | 0.980 | 2.71 | 1.37 | 0.995 |
| Mixture | 48.4 | 0.20 | 0.980 | 10.5 | 2.23 | 0.995 |
2.3. Ultrastructural Analyses
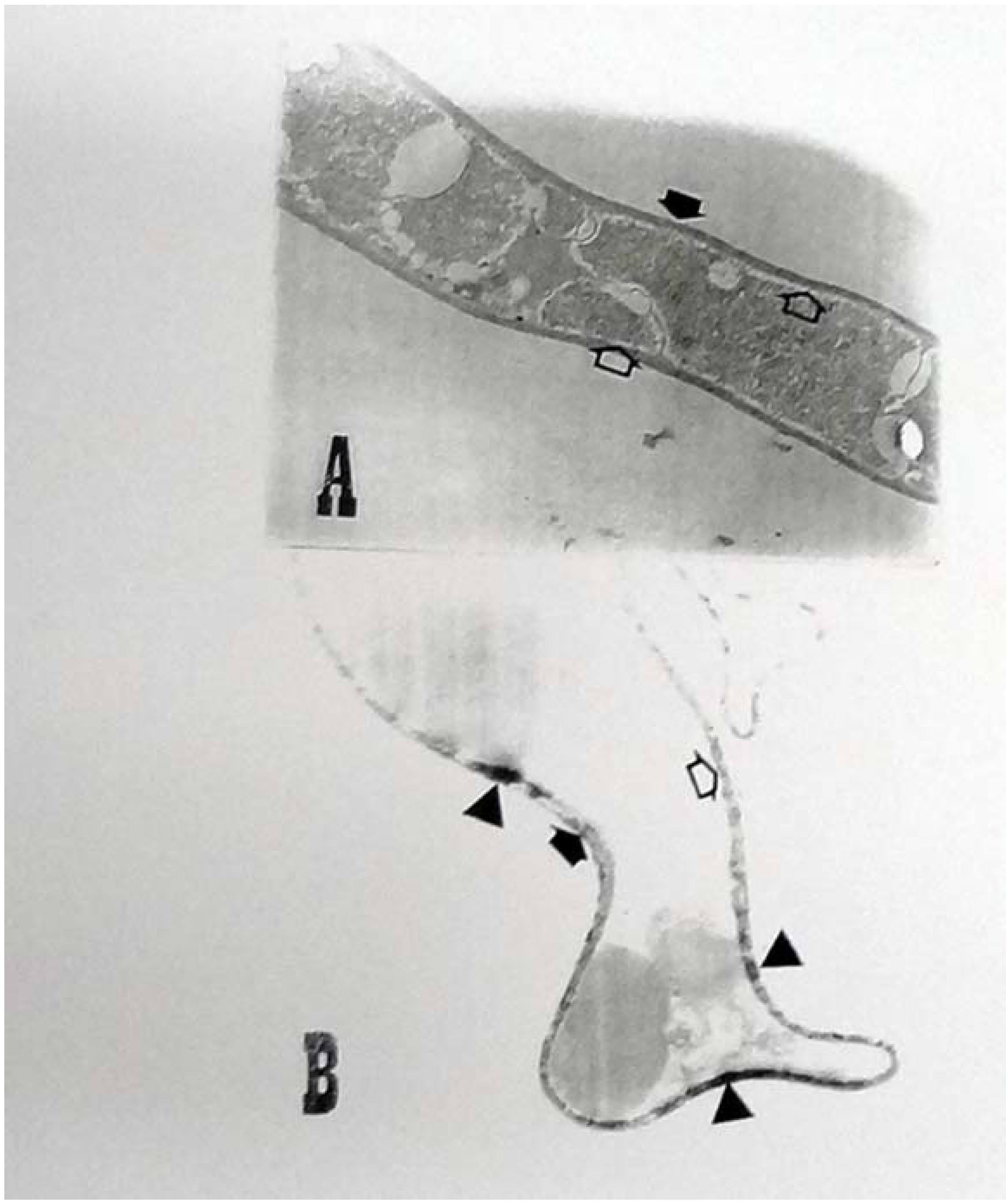
3. Experimental
3.1. Microorganism
3.2. Dyes
| Dyes | MM | lmax | Classification | Chemical structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orange II | 350 | 485 | Anionic monoazo | 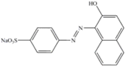 |
| Black-5 | 992 | 597 | Anionic diazo | 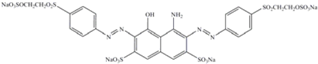 |
| Red-198 | 1470 | 517 | Anionic monoazo | 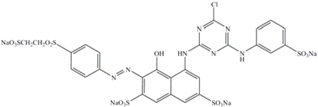 |
3.3. Biomass Preparation
3.4. Mycelium Inactivation
3.5. Adsorption Kinetics
3.6. Adsorption Isotherms
3.7. Color Reduction Measurements
3.8. Ultrastructural Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Zanoni, M.V.B.; Carneiro, P.A. O descarte dos corantes têxteis. Ciência Hoje 2001, 29, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Bumpus, J.A. Microbial degradation of azo dyes. In Biotransformations: Microbial Degradation of Health-Risk Compounds; Singh, V.P., Ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 157–175. [Google Scholar]
- Kumaran, N.S.; Dharani, G. Decolorization of textile dyes by white rot fungi Phanerocheate chrysosporium and Pleurotus sajor-caju. J. Appl. Technol. Environ. Sanit. 2011, 1, 361–370. [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishnan, R.; Sellappa, S. Decolourisation of methyl orange and methyl red by live and dead biomass of fungi. Asian J. Exp. Biol. Sci. 2011, 2, 569–574. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Viraraghavan, T. Fungal decolorization of dye watewaters: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 79, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Viraraghavan, T.; Cullimore, R.D. Removal of heavy metals using the fungus Aspergillus niger. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 70, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartinick-Garcia, S. Cell wall chemistry, morphogenesis and taxonomy of fungi. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1968, 22, 98–108. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrósio, S.T.; Campos-Takaki, G.M. Decolorization of reactive azo dyes by Cunninghamella elegans UCP 542 under co-metabolic conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 91, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Viraraghavan, T. Dye biosorption sites in Aspergillus niger. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 82, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, A.; Peralta-Zamora, P.; Moraes, S.G.; Durán, N. Novas tendências no tratamento de efluentes têxteis. Quim. Nova 2002, 25, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, R.; Sundaran, S.K.; Maheswari, K.U. Aerobic biodecolorization of mixture of azo dye containing textile effluent using adaptated microbial strains. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 4, 568–578. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Degs, Y.; Khraisheh, S.J.; Allen, S.J.; Ahmad, M.N. Effect of carbon surface chemistry on the removal of reactive dyes from textile effluent. Water Res. 2000, 34, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slockar, Y.M.; Le Marechal, A.M. Methods of decoloration of textile. Dyes Pigm. 1998, 37, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyis, I.; Subasioglu, T. Comparison of live and dead biomass of fungi on decolorization of methyl orange. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 2212–2216. [Google Scholar]
- Aksu, Z.; Tezer, S. Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of biosorption of Remazol Black B by Rhizopus arrhizus in a batch system: Effect of temperature. Process Biochem. 2000, 36, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z.; Çalik, A.; Dursun, A.Y.; Demircan, Z. Biosorption of iron (III)—Cyanide complex anions to Rhizopus arrhizus: Applications of adsorption isotherms. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 483–491. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, K.M.G.; Compart, L.C.A.; Morais, R.R.O.; Santos, M.H. Biodegradation of reactive textile dyes by basidiomycetous fungi from Brazilian ecosystems. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2006, 37, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onat, T.A.; Gümüşdere, H.T.; Güvenç, A.; Dönmez, G.; Mehmetoğlu, U. Decolorization of textile azo dyes by ultrasonication and microbial removal. Desalination 2010, 255, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Liu, G; Xu, Z.; Tao, W. Decolorization of a dye industry effluent by Aspergillus fumigatus XC6. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 74, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, W. Técnicas Básicas de Microscopia Eletrônica Aplicadas às Ciências Biológicas; Sociedade Brasileira de Microscopia Eletrônica: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kapdan, I.K.; Kargi, F.; McMullan, G.; Marchant, R. Effect of environmental conditions on biological of textile dye by Coriolus versicolor. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2000, 26, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesiladalı, S.; Pekin, G.; Bermek, H.; Arslan-Alaton, I.; Orhon, D.; Tamerler, C. Bioremediation of textile azo dyes by Trichophyton rubrum LSK-27. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 22, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyis, I.; Subasioglu, T. Comparison of live and dead biomass of fungi on decolorization of methyl orange. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 7, 2212–2216. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, G.; Weatherley, L.R. Biodegradation and biosorption of acid anthraquinone dye. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 108, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.J.; Mckay, G.; Khader, K.Y.H. Multicomponent sorption isotherms of basic dyes onto peat. Environ. Pollut. 1988, 52, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.R.; Viraraghavan, T. Biosorption of phenol from an aqueous solution by Aspergillus niger. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 85, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyis, I.; Subasioglu, T. Comparison of live and dead biomass of fungi on decolorization of methyl orange. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 2212–2216. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.L. Sorption of reactive dyes by Aeromonas biomass. Water Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- Aretxaga, A.; Romero, S.; Montserrat, S.; Vicent, T. Adsorption step in the biological degradation of a textile dye. Biotechnol. Prog. 2001, 17, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, C.J.; Mims, C.W.; Blackwell, M. Introductory Mycology; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kunz, A.; Peralta-Zamora, P.; Moraes, S.G.; Durán, N. Novas tendências no tratamento de efluentes têxteis. Quim. Nova 2002, 25, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdal, S.; Taskin, M. Uptake of textile dye Reactive Black-5 by Penicillium chrysogenum MT-6 isolated from cement-contaminated soil. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 4, 618–625. [Google Scholar]
- Sing, C.; Yu, J. Copper adsorption and removal from water by living mycelium of white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2746–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Thakur, I.S. Biosorption potency of Aspergillus niger for removal of chromium (VI). Curr. Microbiol. 2006, 53, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhinotti, E.; Pozza, F.; Furlan, L.; Sanchez, M.N.M.; Klug, M.; Laranjeira, M.C.M.; Fávere, V.T. Adsorption of anionic dyes on the biopolymer chitin. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 1998, 9, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraco, V.; Pezzella, C.; Giardina, P.; Piscitelli, A.; Vanhulle, S.; Sannia, G. Decolourization of textile dyes by the white-rot fungi Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Pleurotus ostreatus. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahony, T.O.; Guibal, E.; Tobin, J.M. Reactive dye biosorption by Rhizopus arrhizus biomass. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2002, 31, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, V.M.; Stephenson, T.; Judd, S. Characterization of textile wastewaters – a review. Environ. Technol. 1994, 15, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Strain Cunninghamella elegans UCP542 are available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ambrósio, S.T.; Vilar Júnior, J.C.; Da Silva, C.A.A.; Okada, K.; Nascimento, A.E.; Longo, R.L.; Campos-Takaki, G.M. A Biosorption Isotherm Model for the Removal of Reactive Azo Dyes by Inactivated Mycelia of Cunninghamella elegans UCP542. Molecules 2012, 17, 452-462. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17010452
Ambrósio ST, Vilar Júnior JC, Da Silva CAA, Okada K, Nascimento AE, Longo RL, Campos-Takaki GM. A Biosorption Isotherm Model for the Removal of Reactive Azo Dyes by Inactivated Mycelia of Cunninghamella elegans UCP542. Molecules. 2012; 17(1):452-462. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17010452
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmbrósio, Sandra T., José C. Vilar Júnior, Carlos A. Alves Da Silva, Kaoru Okada, Aline E. Nascimento, Ricardo L. Longo, and Galba M. Campos-Takaki. 2012. "A Biosorption Isotherm Model for the Removal of Reactive Azo Dyes by Inactivated Mycelia of Cunninghamella elegans UCP542" Molecules 17, no. 1: 452-462. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17010452
APA StyleAmbrósio, S. T., Vilar Júnior, J. C., Da Silva, C. A. A., Okada, K., Nascimento, A. E., Longo, R. L., & Campos-Takaki, G. M. (2012). A Biosorption Isotherm Model for the Removal of Reactive Azo Dyes by Inactivated Mycelia of Cunninghamella elegans UCP542. Molecules, 17(1), 452-462. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17010452




