A Kernel-Based Intuitionistic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Using a DNA Genetic Algorithm for Magnetic Resonance Image Segmentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets (IFSs)
2.2. Fuzzy C-Means
- is a model parameter that determines the amount of fuzziness in the clustering.
- is the set of cluster centroids.
- is the Euclidean distance between and .
- is the membership degree of data in the fuzzy cluster with centroid .
- is the membership matrix, which satisfies two conditions: (a) for each row k, and (b) for each column .
2.3. DNA Genetic Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: Generic DNA-GA |
| Input: : the objective function : the number of variables in : domains of the n variables : the size of initial population Output: The value of that optimizes Method:
|
3. Related Work
4. Problem Formulation
4.1. Local Intensity Variance
4.2. Intuitionistic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering
4.3. Kernel Intuitionistic FCM (KIFCM)
5. The DNA Genetic Algorithm
| Algorithm 2: KIFCM-DNAGA |
| Input: : convergence threshold : maximum number of iterations : the number of fuzzy clusters : a kernel function : an MRI image : the size of the population Output: : the membership matrix : the centroids of fuzzy clusters Method:
|
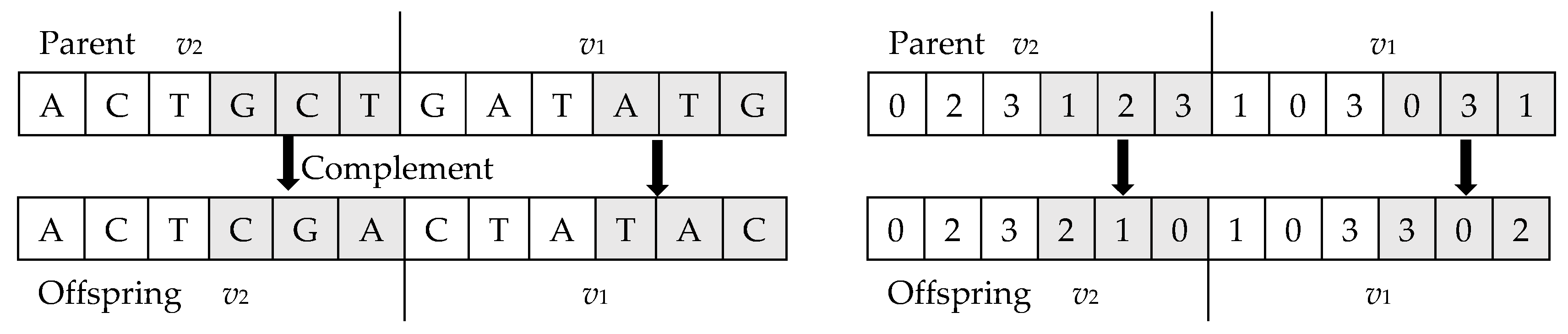
5.1. DNA Encoding and Decoding
5.2. The Initialization
5.3. Selection Operator
5.4. DNA Genetic Operators
5.4.1. Crossover Operator
5.4.2. Mutation Operator
5.4.3. Reconstruction Operator
6. Experiments and Results
6.1. Experiment Setup
- The Jaccard Similarity is defined by:where S1 is the segmented volume and S2 is the ground truth volume.
- AMI is defined as follows:where , are the entropies for and , respectively. Mutual information MI quantifies the value of information shared between the two random variables and can be defined using the entropy definitions. .
- ARI is defined as follows:where N11 denotes the number of pairs that are in the same cluster in both U and V, N00 denotes the number of pairs that are in different clusters in both U and V, N01 denotes the number of pairs that are in the same cluster in U but in different clusters in V, and N10 denotes the number of pairs that are in different clusters in U but in the same cluster in V.
6.2. Results on UCI Datasets
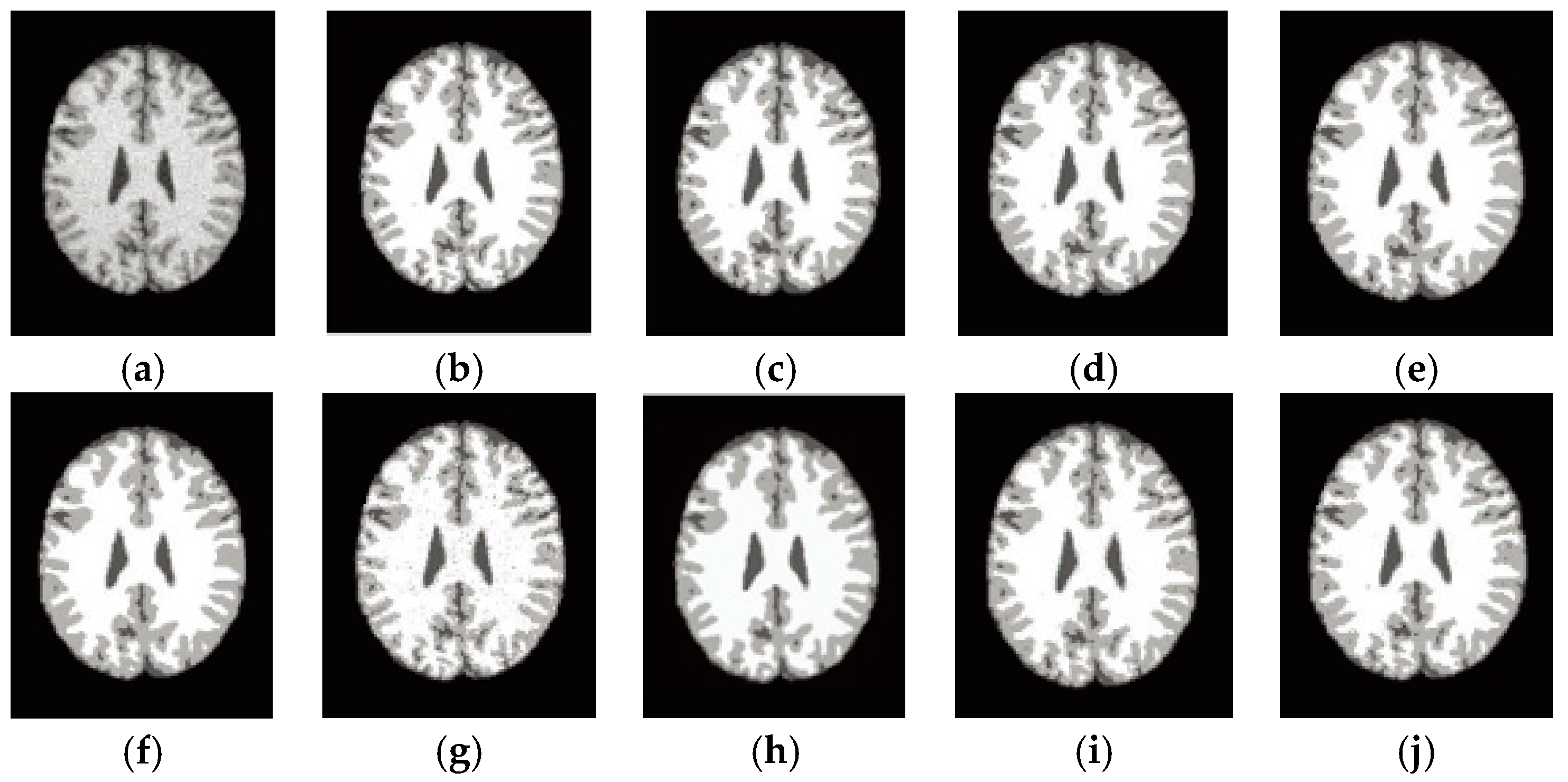
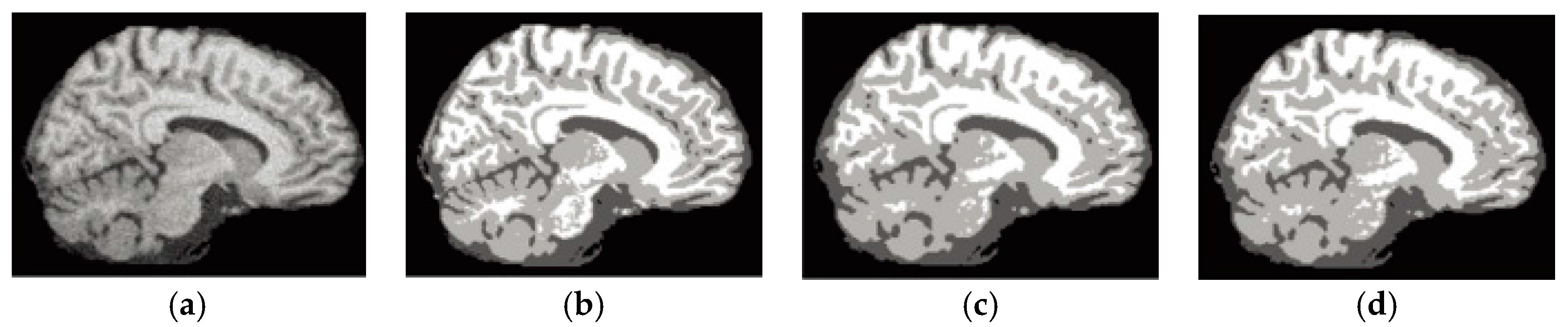
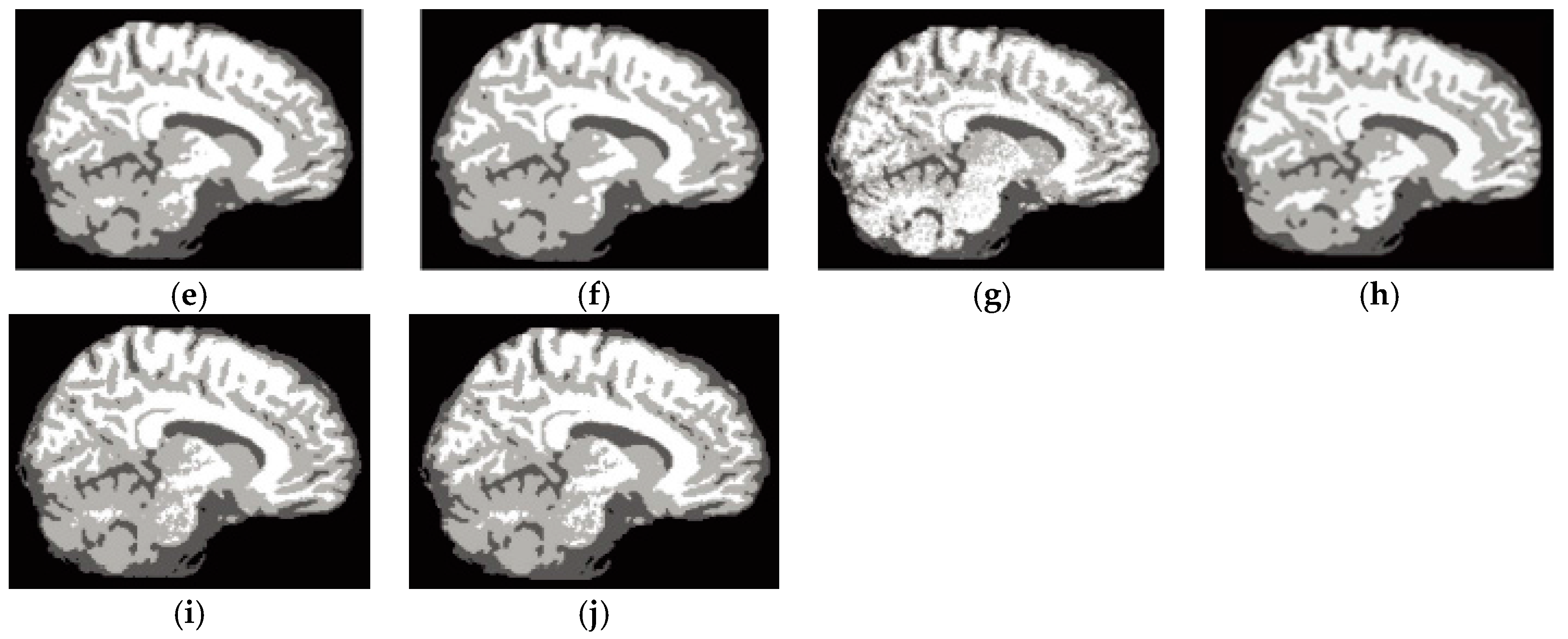
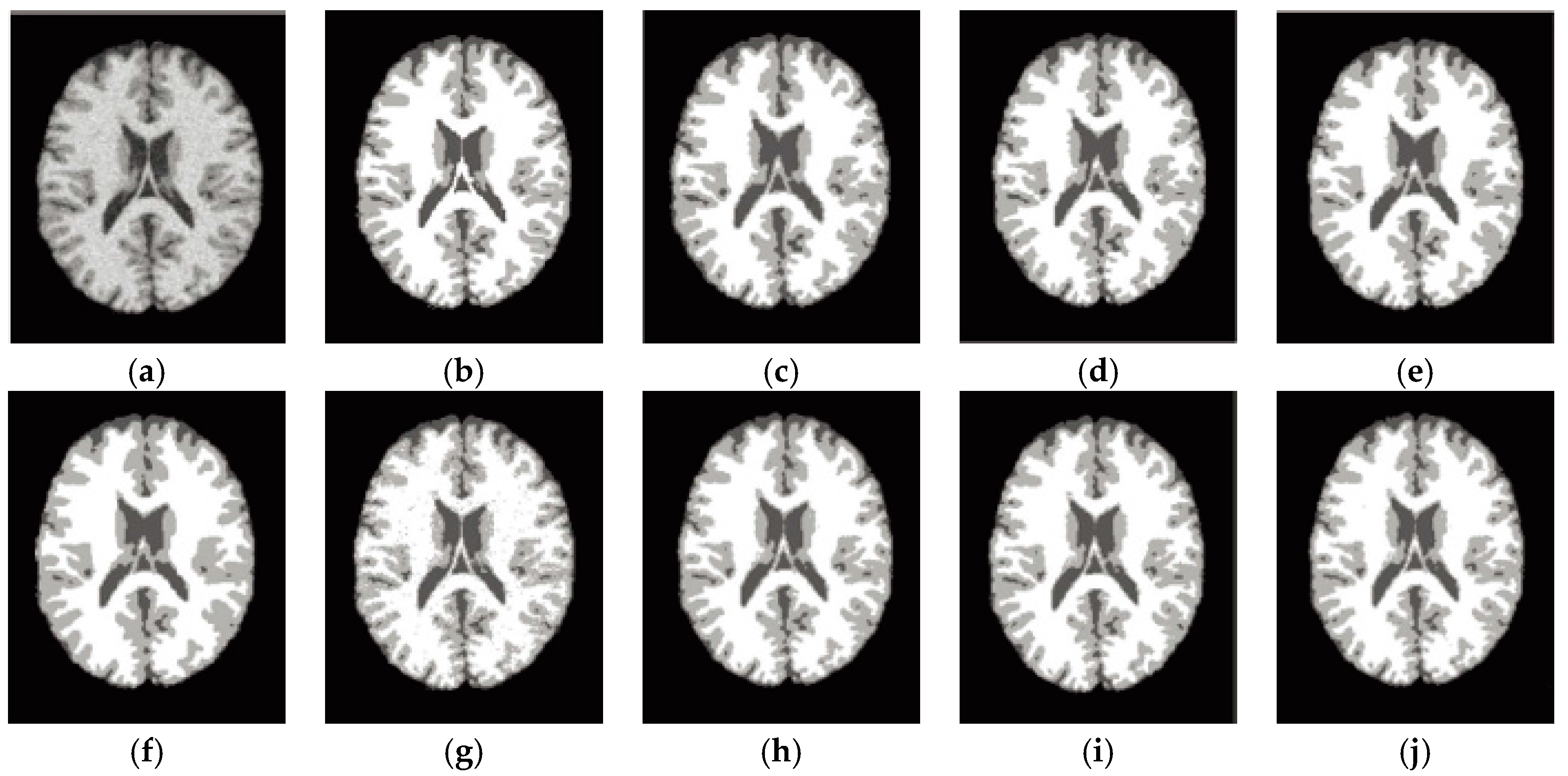
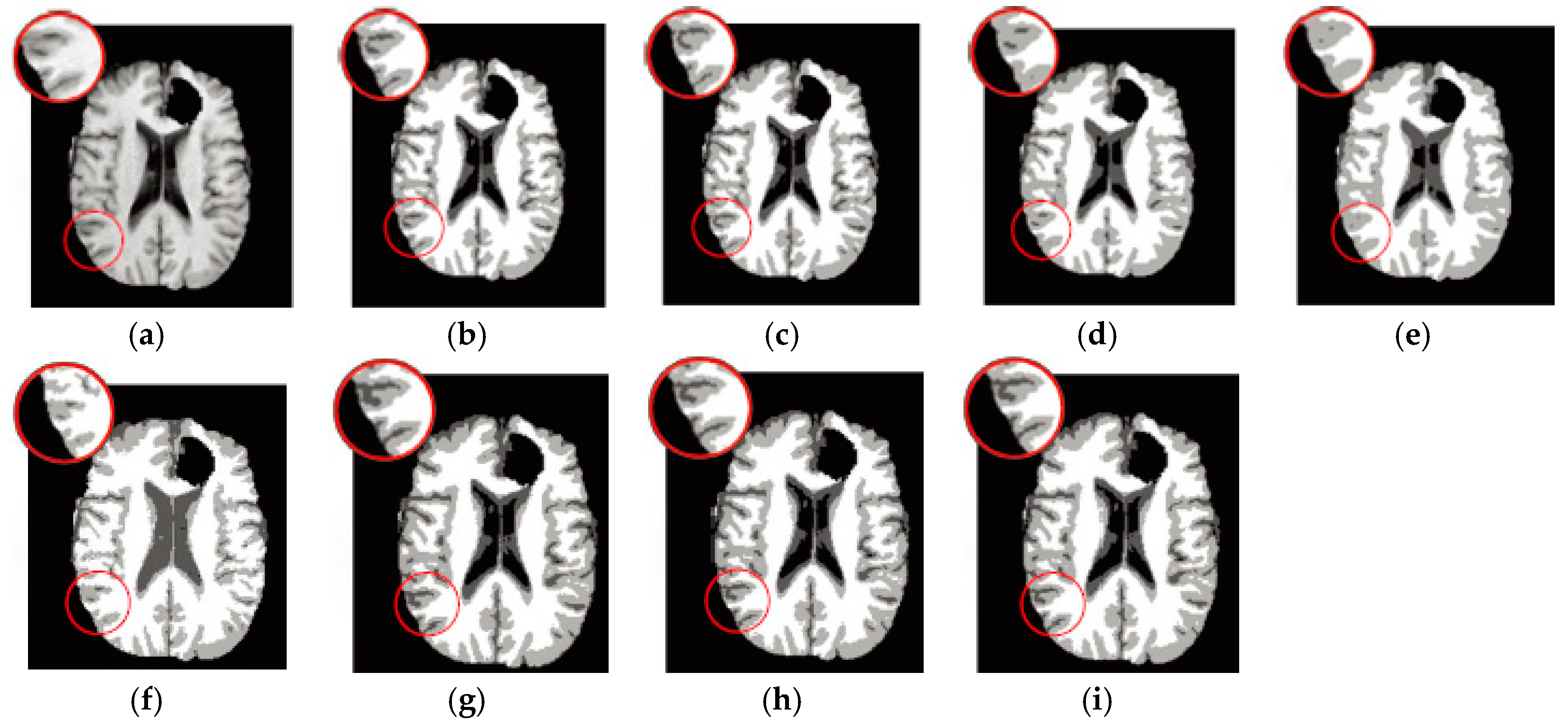
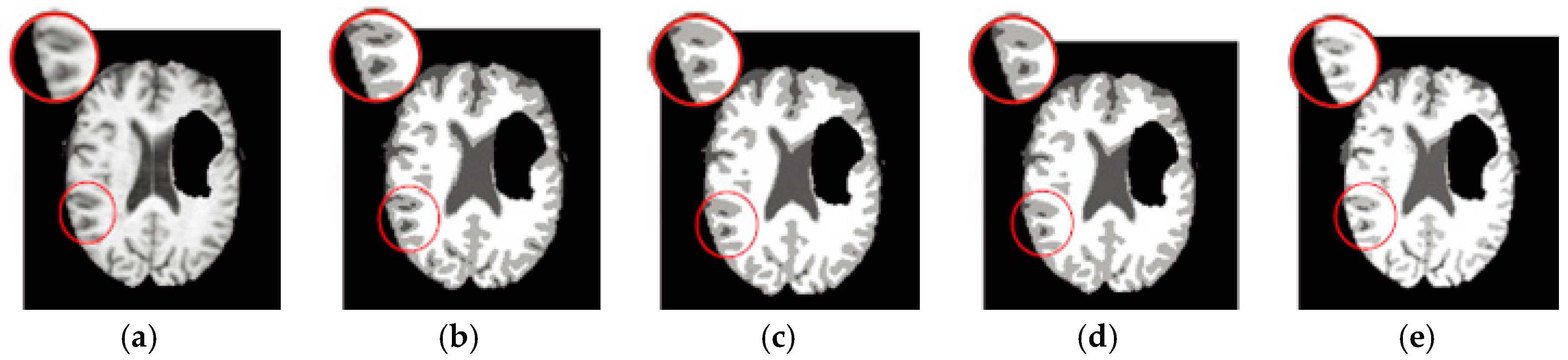
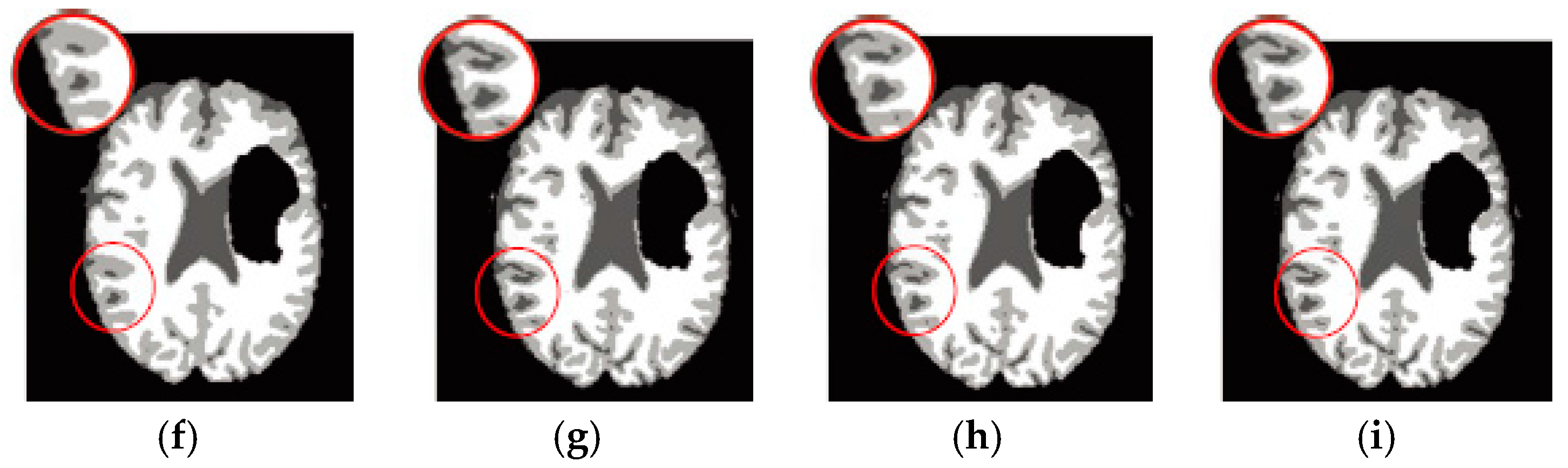
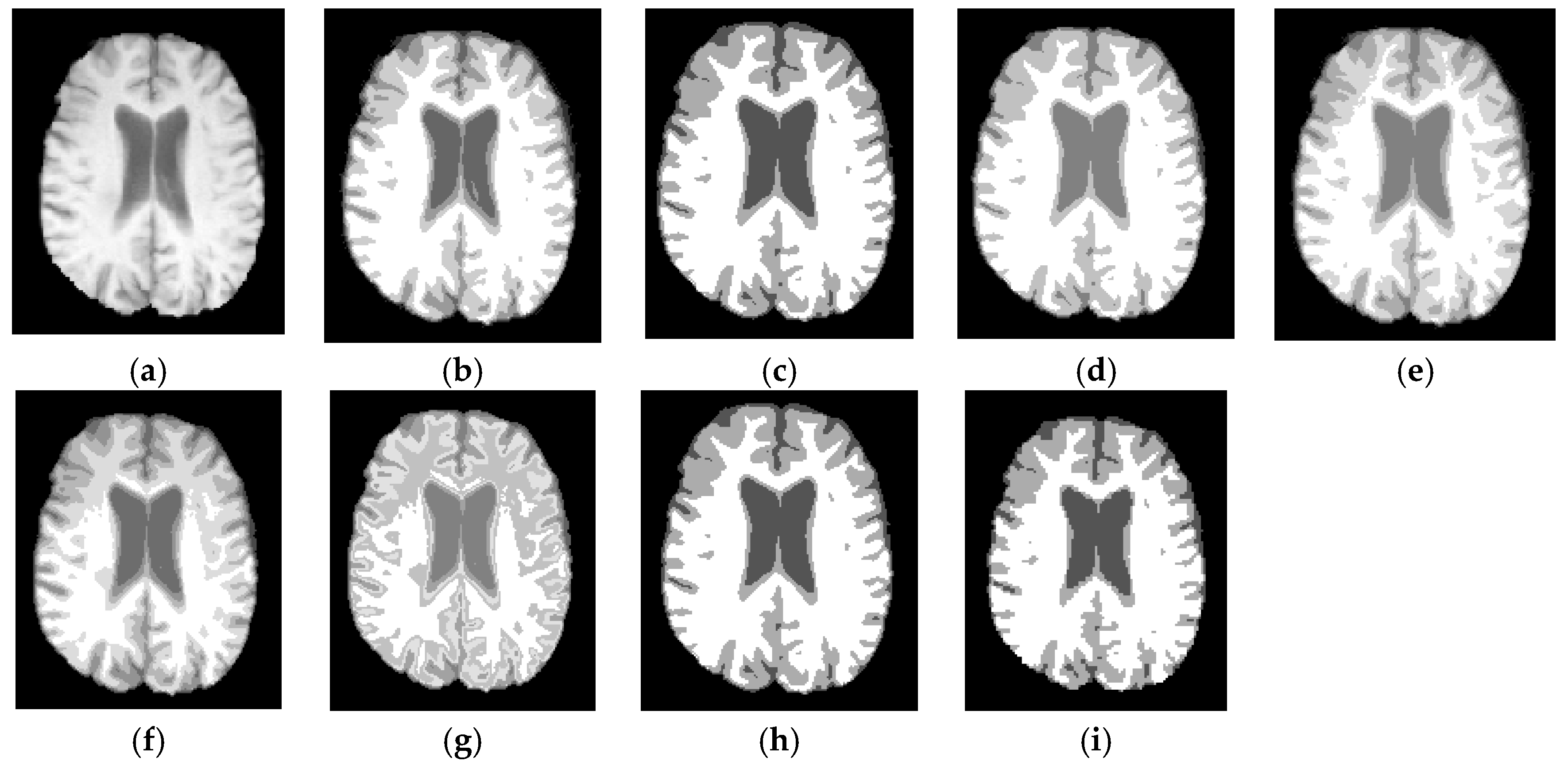
6.3. Results on Synthetic Brain MR Images
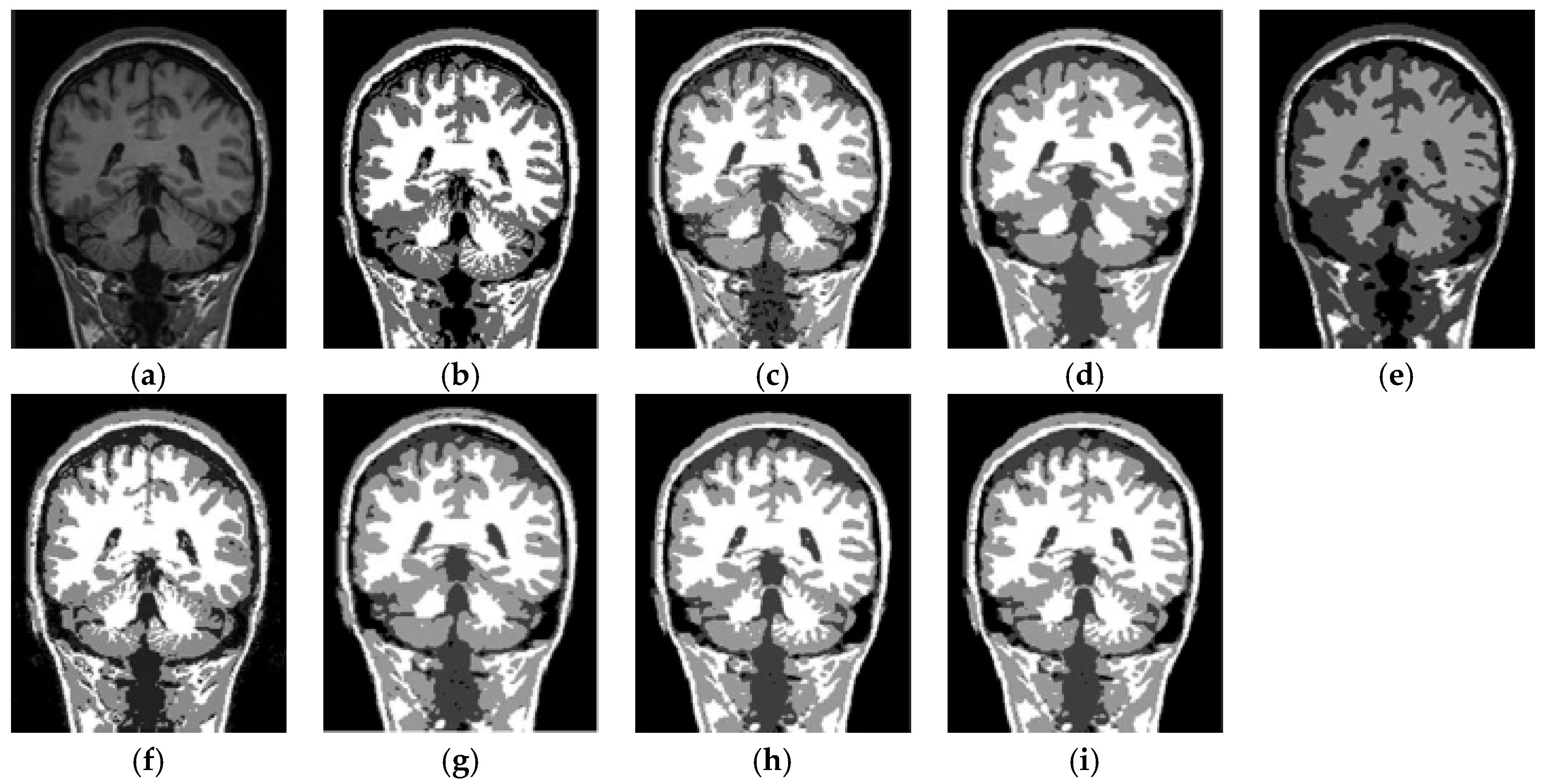
6.4. Results on Clinical Brain MR Images
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elazab, A.; AbdulAzeem, Y.M.; Wu, S.; Hu, Q. Robust kernelized local information fuzzy C-means clustering for brain magnetic resonance image segmentation. J. X-ray Sci. Technol. 2016, 24, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krinidis, S.; Chatzis, V. A Robust Fuzzy Local Information C-Means Clustering Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikou, C.; Galatsanos, N.P.; Likas, A.C. A class-adaptive spatially variant mixture model for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.L.; Chen, S.C.; Zhang, D.Q. Fast and robust fuzzy c-means clustering algorithms incorporating local information for image segmentation. Pattern Recogn. 2007, 40, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.M.; Gore, J.C.; Davatzikos, C. Multiplicative intrinsic component optimization (MICO) for MRI bias field estimation and tissue segmentation. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 32, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.X.; Liu, J.Y.; Cao, G.; Sun, Q.S.; Chen, Q. Robust spatially constrained fuzzy c-means algorithm for brain MR image segmentation. Pattern Recogn. 2014, 47, 2454–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despotovic, I.; Goossens, B.; Philips, W. MRI Segmentation of the Human Brain: Challenges, Methods, and Applications. Comput. Math. Method Med. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezdek, J.C.; Ehrlich, R.; Full, W. FCM: The fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Comput. Geosci. 1984, 10, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Dong, W.S.; Xie, X.M.; Shi, G.M.; Bai, X. Mixed Noise Removal via Laplacian Scale Mixture Modeling and Nonlocal Low-Rank Approximation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3171–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, R.M.; Kumari, R.S.S. Spatial Fuzzy C Means and Expectation Maximization Algorithms with Bias Correction for Segmentation of MR Brain Images. J. Med. Syst. 2017, 41, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iakovidis, D.K.; Pelekis, N.; Kotsifakos, E.; Kopanakis, I. Intuitionistic Fuzzy Clustering with Applications in Computer Vision. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2008, 5259, 764–774. [Google Scholar]
- Chaira, T. A novel intuitionistic fuzzy C means clustering algorithm and its application to medical images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 1711–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, R.; Tripathy, B.; Tripathy, A.; Dhull, R.; Verma, E.; Swarnalatha, P. Rough intuitionistic fuzzy C-means algorithm and a comparative analysis. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM India Computing Convention, Vellore, India, 22–25 August 2013; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Atanassov, K.T. Intuitionistic Fuzzy-Sets. Fuzzy Set. Syst. 1986, 20, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruna Kumar, S.; Harish, B. A Modified Intuitionistic Fuzzy Clustering Algorithm for Medical Image Segmentation. J. Intell. Syst. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, H.; Agrawal, R.; Sharan, A. An improved intuitionistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm incorporating local information for brain image segmentation. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 46, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-Q.; Chen, S.-C. Clustering incomplete data using kernel-based fuzzy C-means algorithm. Neural Process. Lett. 2003, 18, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-Q.; Chen, S.-C. A novel kernelized fuzzy c-means algorithm with application in medical image segmentation. Artif. Intell. Med. 2004, 32, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, C.R. Kernel functions for machine learning applications. Creat. Commons Attrib. Noncommer. Share Alike 2010, 3, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.-P. A novel evolutionary kernel intuitionistic fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 22, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.S.; Tsai, H.S. A Gaussian kernel-based fuzzy c-means algorithm with a spatial bias correction. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2008, 29, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adleman, L.M. Molecular Computation of Solutions to Combinatorial Problems. Science 1994, 266, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, D.E. Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization, and Machine Learning; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.; Wang, N. DNA computing based RNA genetic algorithm with applications in parameter estimation of chemical engineering processes. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2007, 31, 1602–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X. A Genetic Algorithm Using Triplet Nucleotide Encoding and DNA Reproduction Operations for Unconstrained Optimization Problems. Algorithms 2017, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, W.; Ren, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X. Automatic Density Peaks Clustering Using DNA Genetic Algorithm Optimized Data Field and Gaussian Process. Int. J. Pattern Recogn. 2017, 31, 1750023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, W.; Jiang, Z.; Ren, L. Improved spectral clustering based on density combining DNA genetic algorithm. Int. J. Pattern Recogn. 2017, 31, 1750010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, W.; Sun, M.; Jiang, Z. A DNA genetic algorithm inspired by biological membrane structure. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2016, 13, 3763–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.N.; Yamany, S.M.; Mohamed, N.; Farag, A.A.; Moriarty, T. A modified fuzzy C-means algorithm for bias field estimation and segmentation of MRI data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2002, 21, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.C.; Zhang, D.Q. Robust image segmentation using FCM with spatial constraints based on new kernel-induced distance measure. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 2004, 34, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elazab, A.; Wang, C.; Jia, F.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; Hu, Q. Segmentation of brain tissues from magnetic resonance images using adaptively regularized kernel-based fuzzy-means clustering. Comput. Math. Method Med. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.G.; Liang, Y.; Shi, J.; Ma, W.P.; Ma, J.J. Fuzzy C-Means Clustering With Local Information and Kernel Metric for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillonetto, G.; Dinuzzo, F.; Chen, T.S.; De Nicolao, G.; Ljung, L. Kernel methods in system identification, machine learning and function estimation: A survey. Automatica 2014, 50, 657–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, K.R.; Mika, S.; Ratsch, G.; Tsuda, K.; Scholkopf, B. An introduction to kernel-based learning algorithms. IEEE Trans. Neural Networ. 2001, 12, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, D.; Pedrycz, W. Kernel-based fuzzy clustering and fuzzy clustering: A comparative experimental study. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2010, 161, 522–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X. Bioinformatics. Available online: http://www.lmbe.seu.edu.cn/chenyuan/xsun/bioinfomatics/web/CharpterFive/5.4.htm (accessed on 27 October 2017).
- Zhang, L.; Wang, N. A modified DNA genetic algorithm for parameter estimation of the 2-Chlorophenol oxidation in supercritical water. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhauser, C.; Krone, S.M. The genealogy of samples in models with selection. Genetics 1997, 145, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.; Hock, M.; Paschke, M. Low genetic variation reduces cross-compatibility and offspring fitness in populations of a narrow endemic plant with a self-incompatibility system. Conserv. Genet. 2003, 4, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.D.; Crick, F.H. A structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid. Nature 1953, 171, 737–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asuncion, A.; Newman, D.J. UCI Machine Learning Repository; University of California: Irvine, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gousias, I.S.; Edwards, A.D.; Rutherford, M.A.; Counsell, S.J.; Hajnal, J.V.; Rueckert, D.; Hammers, A. Magnetic resonance imaging of the newborn brain: Manual segmentation of labelled atlases in term-born and preterm infants. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vovk, U.; Pernus, F.; Likar, B. A review of methods for correction of intensity inhomogeneity in MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2007, 26, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinh, N.X.; Epps, J.; Bailey, J. Information Theoretic Measures for Clusterings Comparison: Variants, Properties, Normalization and Correction for Chance. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 2837–2854. [Google Scholar]
- Cocosco, C.A.; Kollokian, V.; Kwan, R.K.-S.; Pike, G.B.; Evans, A.C. Brainweb: Online Interface to a 3D MRI Simulated Brain Databas; CiteSeerX: State College, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.L.; Greenshields, I.R. A Nonlocal Maximum Likelihood Estimation Method for Rician Noise Reduction in MR Images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2009, 28, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Fritts, J.E.; Goldman, S.A. An entropy-based objective evaluation method for image segmentation. SPIE 2004, 5307, 38–49. [Google Scholar]
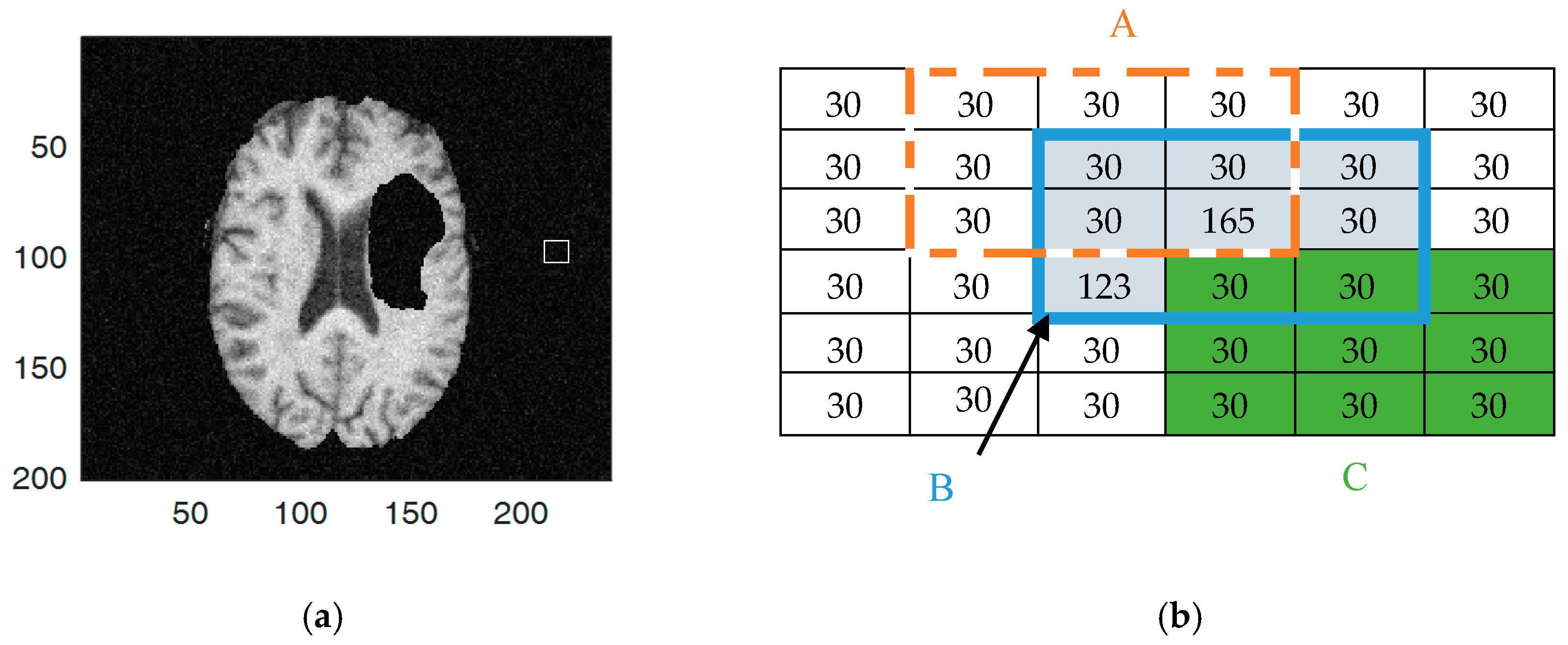
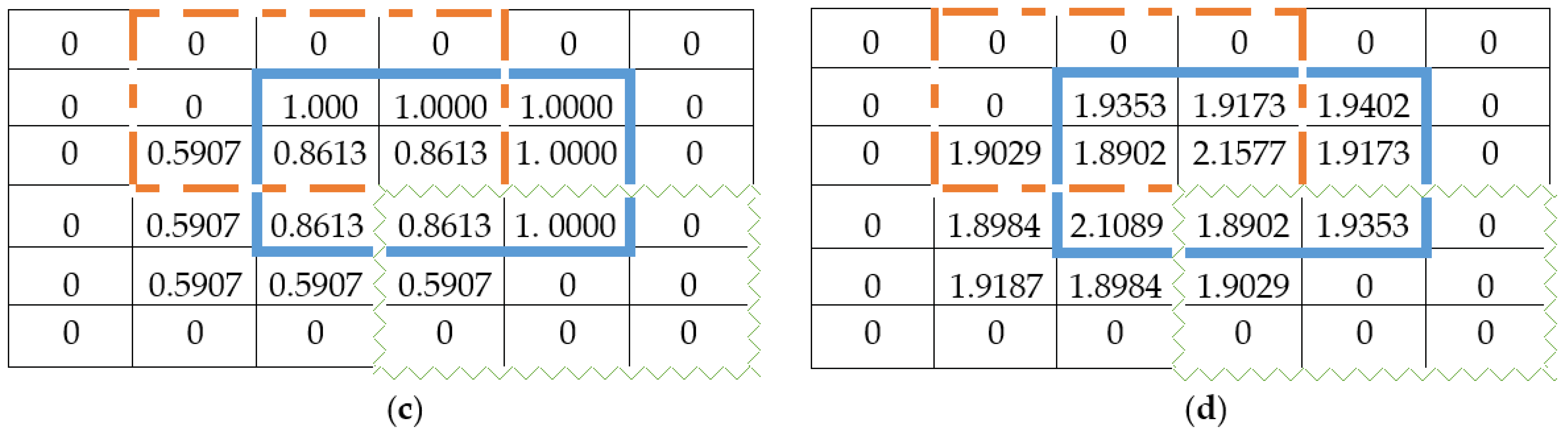
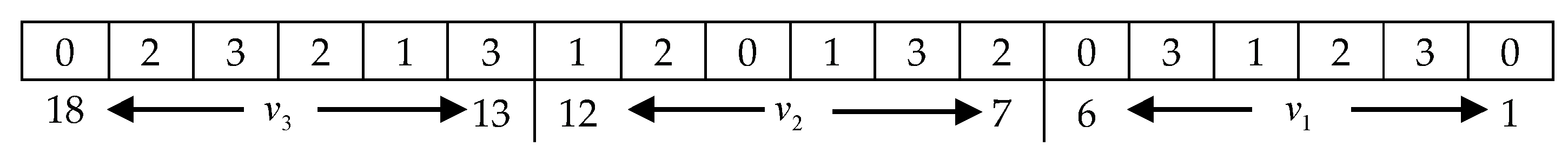
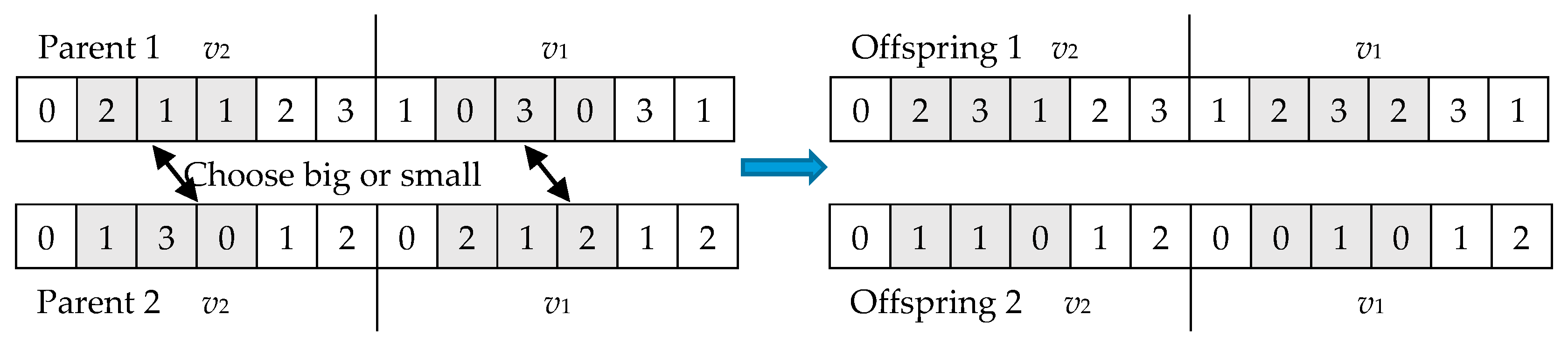

| Datasets | Number of Instances | Number of Attributes | Number of Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Haberman’s Surviva1 Data | 306 | 3 | 2 |
| Contraceptive Method Choice | 1473 | 9 | 3 |
| Wisconsin Prognostic Breast Cancer | 198 | 34 | 2 |
| SPECT Heart Data | 267 | 22 | 2 |
| Title | Method | Parameters | AMI | ARI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haberman’s Surviva1 Data | GKFCM1 | 0.7263 | 0.6430 | |
| GKFCM2 | 0.7221 | 0.6332 | ||
| FLICM | 0.9509 | 0.8620 | ||
| KWFLICM | 0.9386 | 0.8497 | ||
| MICO | 0.7319 | 0.6430 | ||
| RSCFCM | 0.9406 | 0.8587 | ||
| KIFCM1-DNAGA | 0.9704 | 0.8815 | ||
| Contraceptive Method Choice | GKFCM1 | 0.6534 | 0.6544 | |
| GKFCM2 | 0.6525 | 0.6525 | ||
| FLICM | 0.7366 | 0.7366 | ||
| KWFLICM | 0.7577 | 0.7577 | ||
| MICO | 0.6477 | 0.6477 | ||
| RSCFCM | 0.6853 | 0.7515 | ||
| KIFCM1-DNAGA | 0.7991 | 0.8021 | ||
| Wisconsin Prognostic Breast Cancer | GKFCM1 | 0.9708 | 0.9687 | |
| GKFCM2 | 0.9665 | 0.9644 | ||
| FLICM | 0.9451 | 0.9430 | ||
| KWFLICM | 0.9771 | 0.9750 | ||
| MICO | 0.9808 | 0.9787 | ||
| RSCFCM | 0.9832 | 0.9815 | ||
| KIFCM1-DNAGA | 0.9865 | 0.9844 | ||
| SPECT Heart Data | GKFCM1 | 0.6365 | 0.7039 | |
| GKFCM2 | 0.7264 | 0.7264 | ||
| FLICM | 0.8350 | 0.8350 | ||
| KWFLICM | 0.8915 | 0.8915 | ||
| MICO | 0.7339 | 0.7339 | ||
| RSCFCM | 0.8488 | 0.8500 | ||
| KIFCM1-DNAGA | 0.9174 | 0.9213 |
| Algorithm | GKFCM1 | GKFCM2 | FLICM | KW FLICM | MICO | RSCFCM | KIFCM1-DNAGA | KIFCM2-DNAGA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WM | 0.930 | 0.933 | 0.941 | 0.937 | 0.894 | 0.898 | 0.940 | 0.941 |
| GM | 0.822 | 0.855 | 0.860 | 0.852 | 0.782 | 0.842 | 0.864 | 0.868 |
| CSF | 0.781 | 0.847 | 0.829 | 0.805 | 0.860 | 0.882 | 0.863 | 0.867 |
| Average | 0.844 | 0.879 | 0.876 | 0.865 | 0.845 | 0.874 | 0.889 | 0.892 |
| Time (s) | 0.911 | 0.586 | 3.403 | 139.470 | 0.673 | 2.530 | 0.356 | 0.282 |
| Algorithm | GKFCM1 | GKFCM2 | FLICM | KWFLICM | MICO | RSCFCM | KIFCM1-DNAGA | KIFCM2-DNAGA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WM | 0.773 | 0.775 | 0.771 | 0.765 | 0.672 | 0.702 | 0.785 | 0.788 |
| GM | 0.796 | 0.806 | 0.794 | 0.791 | 0.669 | 0.743 | 0.815 | 0.816 |
| CSF | 0.834 | 0.852 | 0.835 | 0.824 | 0.869 | 0.813 | 0.871 | 0.872 |
| Average | 0.801 | 0.811 | 0.800 | 0.794 | 0.736 | 0.753 | 0.824 | 0.825 |
| Time (s) | 1.377 | 1.797 | 5.392 | 166.717 | 0.751 | 0.786 | 0.348 | 0.329 |
| Algorithm | GKFCM1 | GKFCM2 | FLICM | KWFLICM | MICO | RSCFCM | KIFCM1-DNAGA | KIFCM2-DNAGA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WM | 0.931 | 0.921 | 0.929 | 0.927 | 0.885 | 0.891 | 0.926 | 0.925 |
| GM | 0.804 | 0.827 | 0.831 | 0.821 | 0.777 | 0.803 | 0.838 | 0.840 |
| CSF | 0.826 | 0.872 | 0.861 | 0.846 | 0.889 | 0.876 | 0.887 | 0.892 |
| Average | 0.854 | 0.873 | 0.874 | 0.865 | 0.850 | 0.857 | 0.884 | 0.886 |
| Time (s) | 1.836 | 1.869 | 2.953 | 124.922 | 0.649 | 0.781 | 0.218 | 0.220 |
| Image | Measure | GKFCM1 | GKFCM2 | FLICM | KWFLICM | MICO | RSCFCM | KIFCM1-DNAGA | KIFCM2-DNAGA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brats1 | E | 1.311 | 1.288 | 1.392 | 1.424 | 1.309 | 1.314 | 1.274 | 1.270 |
| Time (s) | 2.591 | 1.516 | 9.510 | 6.354 | 1.747 | 12.622 | 1.185 | 1.111 | |
| Brats2 | E | 1.307 | 1.297 | 1.336 | 1.340 | 1.298 | 1.307 | 1.273 | 1.271 |
| Time (s) | 1.576 | 1.115 | 5.170 | 4.002 | 1.546 | 1.674 | 1.091 | 0.827 | |
| Brats3 | E | 1.295 | 1.285 | 1.324 | 1.328 | 1.286 | 1.295 | 1.261 | 1.259 |
| Time (s) | 1.564 | 1.103 | 5.158 | 4.002 | 1.534 | 1.662 | 1.079 | 0.815 | |
| Brats4 | E | 1.425 | 1.415 | 1.454 | 1.458 | 1.416 | 1.424 | 1.391 | 1.389 |
| Time (s) | 6.099 | 4.301 | 20.116 | 15.611 | 5.982 | 6.481 | 4.2081 | 3.1785 |
| Algorithm | GKFCM1 | GKFCM2 | FLICM | KWFLICM | MICO | RSCFCM | KIFCM1-DNAGA | KIFCM2-DNAGA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall complexity |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zang, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X. A Kernel-Based Intuitionistic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Using a DNA Genetic Algorithm for Magnetic Resonance Image Segmentation. Entropy 2017, 19, 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19110578
Zang W, Zhang W, Zhang W, Liu X. A Kernel-Based Intuitionistic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Using a DNA Genetic Algorithm for Magnetic Resonance Image Segmentation. Entropy. 2017; 19(11):578. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19110578
Chicago/Turabian StyleZang, Wenke, Weining Zhang, Wenqian Zhang, and Xiyu Liu. 2017. "A Kernel-Based Intuitionistic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Using a DNA Genetic Algorithm for Magnetic Resonance Image Segmentation" Entropy 19, no. 11: 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19110578
APA StyleZang, W., Zhang, W., Zhang, W., & Liu, X. (2017). A Kernel-Based Intuitionistic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Using a DNA Genetic Algorithm for Magnetic Resonance Image Segmentation. Entropy, 19(11), 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19110578





