Foods 2023, 12(11), 2139; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112139 - 25 May 2023
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3620
Abstract
As a result of the increasing focus on alternative protein sources which are ideally still sustainable, the yellow mealworm, Tenebrio molitor, has come into focus. To verify its suitability as a food source in relation to human health, an analysis of the
[...] Read more.
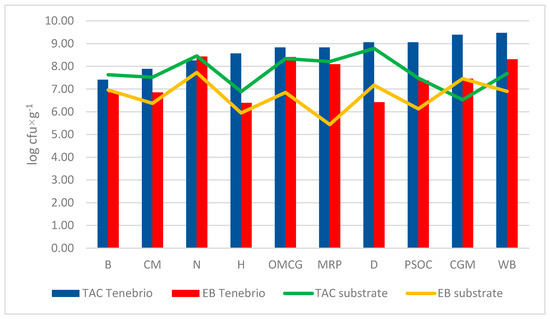
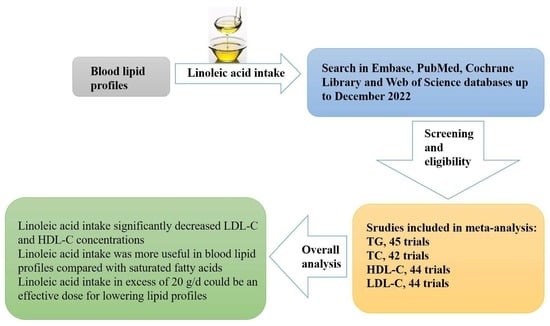
As a result of the increasing focus on alternative protein sources which are ideally still sustainable, the yellow mealworm, Tenebrio molitor, has come into focus. To verify its suitability as a food source in relation to human health, an analysis of the microbiome of larvae of T. molitor is pertinent. Subsequently, the focus of this study was, on the one hand, to analyze the influence of the substrate on the microbial load of the larvae microbiome, and, on the other hand, to determine which processing methods ensure the risk-free consumption of mealworms. For this purpose, mealworms were grown on 10 different substrates derived from by-products of food production (malt residual pellets, corn germ meal, chestnut breakage and meal, wheat bran, bread remains, draff, nettle, hemp seed oil cake, oyster mushrooms with coffee grounds, pumpkin seed oil cake) and microbial loads were analyzed using different selective media. Further starvation/defecation and heating (850 W for 10 min) methods were used to investigate how the reduction of microorganisms is enabled by these methods. The results showed that there was no significant relationship between the microbial load of the substrate and the mealworm. Starvation and defecation led to a lower stock of microorganisms. Heating led to a significant microbial reduction in non-defecated mealworms. The group of defecated and heated mealworms showed no detectable microbial load. In conclusion, firstly, the choice of substrate showed no effect on the microbial load of larvae of Tenebrio molitor and secondly, heating and starvation allow risk-free consumption. This study makes an important contribution for evaluating the safety of mealworms as a sustainable protein source in human nutrition.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microorganisms and Their Importance in the Food Industry: Safety, Quality and Health Properties)
►
Show Figures