Appl. Sci. 2022, 12(24), 12746; https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412746 - 12 Dec 2022
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2638
Abstract
In China, the Ministry of Transport stressed the need to “Strengthen the application of active safety technology”. The transportation of hazardous chemicals represented by LNG, LPG, and liquefied hydrocarbons is the weak link in traffic safety. The aim of this study is to
[...] Read more.
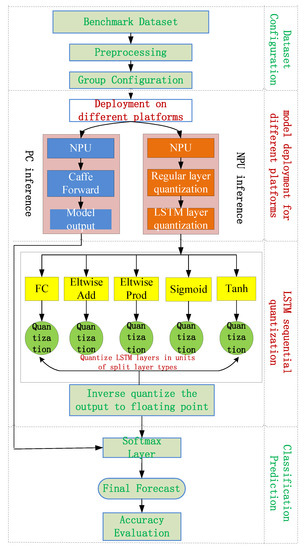
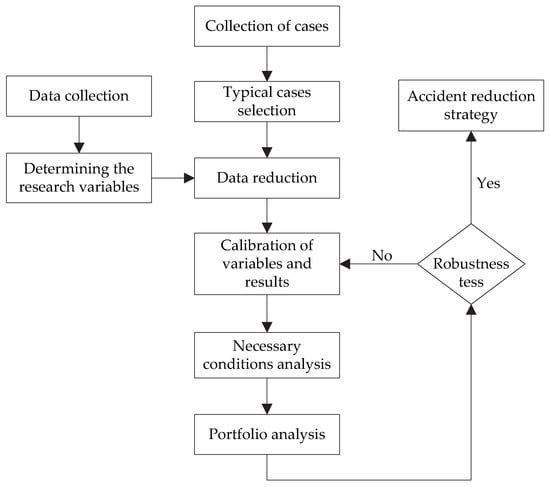
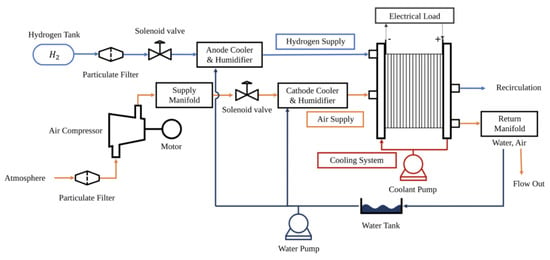
In China, the Ministry of Transport stressed the need to “Strengthen the application of active safety technology”. The transportation of hazardous chemicals represented by LNG, LPG, and liquefied hydrocarbons is the weak link in traffic safety. The aim of this study is to apply digital twin (hereinafter referred to as DT) technology to the whole process of handling (including loading and unloading) and transportation of hazardous chemicals to help improve the anti-risk ability of road networks at all levels. The method is intended to design a monitoring system covering operation visualization, information fusion, cargo tracking, and hazard source monitoring that is based on DT technology and multi-source data acquisition technology. First, DT technology in the areas of hazardous chemicals handling and transportation is discussed. Then, the DT system is designed, including the system construction, functions, and the means of achieving these functions. Finally, taking the procedure in LNG road transportation as an example, we illustrate the application of DT in its four stages. This system is used to present the evolutionary path of accidents that occur in different links and assist in testing the rationality of the comprehensive disposal plan.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Applied Industrial Technologies)
►
Show Figures