Buildings 2021, 11(6), 233; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11060233 - 29 May 2021
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 4817
Abstract
Previous studies have shown that indoor environmental quality (IEQ) parameters may have a considerable effect on office employees’ comfort, health and performance. Therefore, we initiated a research program to help occupants identify IEQ parameters they perceive as risk factors for their health in
[...] Read more.
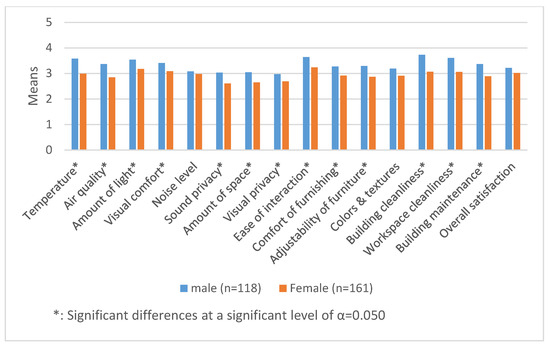
Previous studies have shown that indoor environmental quality (IEQ) parameters may have a considerable effect on office employees’ comfort, health and performance. Therefore, we initiated a research program to help occupants identify IEQ parameters they perceive as risk factors for their health in an office and enhance their comfort levels in an office environment. Since we assumed that office employees might have different indoor environmental quality expectations related to their work area and that these differences could be measured, our objective was to develop an office ‘comfort map’ based on occupants’ individual IEQ preferences. Thus, the goal of the comfort map would be to help tailor office spaces to their occupants’ health and comfort expectations. The comfort survey was developed to assess the comfort-related opinions of the occupants, based on IEQ parameters (visual comfort, acoustic comfort, air quality and thermal comfort) of a chosen open-plan office building. The survey also assessed the degree to which the given IEQ parameter was considered a health risk factor by occupants or caused a negative comfort sensation for them. The survey was filled in by 216 occupants. The answers were then analyzed with the help of a frequency table depicting relative frequency. The measurements of IEQ parameters took place in an open-plan office in the chosen office building (a Hungarian subsidiary’s office building belonging to an international company in Budapest). The occupants had different opinions regarding the perceived effects of the IEQ parameters on their health and comfort. Almost two-thirds of the respondents (64.8%) were dissatisfied with the adjustability of the noises and sounds IEQ parameter at their workstation. Furthermore, half of the respondents (50.1%) were dissatisfied with the adjustability of ventilation. Most of the occupants (45.8%) considered noises and sounds as the IEQ parameter that had a negative effect on their health. There were also IEQ differences between different areas of the office space. Based on these results, a comfort map was developed for the office. The comfort map contains information about the IEQ characteristics of each workstation by depicting the thermal comfort, carbon dioxide, visual comfort and acoustic comfort characteristics of a given workstation on a relative scale. Based on the thermal, air, acoustic, and lighting differences between the workstations, occupants can select their preferred workstations when a desk-sharing system works. Although still in its pilot phase, the comfort map could increase the chances for office employees to find the workstation best suited to their IEQ expectations. This could improve occupants’ overall comfort level, which could in turn enhance occupants’ productivity and mental as well as physical health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Architectural Design, Urban Science, and Real Estate)
►
Show Figures