1
Department of Materials and Optoelectronic Science, National Sun Yat-Sen University, Kaohsiung 80424, Taiwan
2
Ningbo Institute of Material Technology and Engineering, Key Laboratory of Graphene Technologies and Applications of Zhejiang Province, Chinese Academy of Science, Zhongguan West Road 1219, Ningbo 315201, China
3
Department of Medicinal and Applied Chemistry, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung 80424, Taiwan
Polymers 2017, 9(10), 503; https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100503 - 12 Oct 2017
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 7012
Abstract
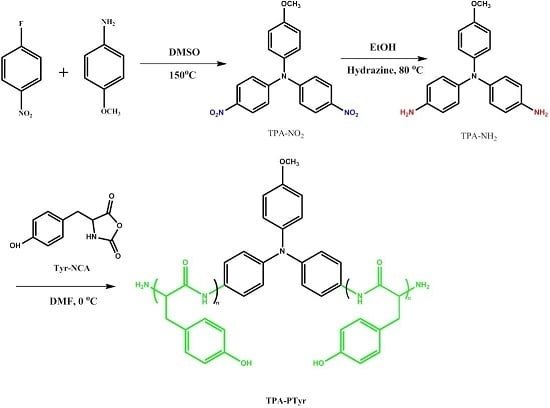
In this study, we synthesized a triphenylamine-functionalized polytyrosine (PTyr-TPA) through living ring opening polymerization with 4,4′-diamino-4″-methoxytriphenylamine (TPA-NH2) as an initiator, and used Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to confirm the chemical structure. Photoluminescence spectroscopy revealed the photophysical
[...] Read more.
In this study, we synthesized a triphenylamine-functionalized polytyrosine (PTyr-TPA) through living ring opening polymerization with 4,4′-diamino-4″-methoxytriphenylamine (TPA-NH2) as an initiator, and used Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to confirm the chemical structure. Photoluminescence spectroscopy revealed the photophysical properties of TPA-NH2 and PTyr-TPA and suggested that TPA-NH2 exhibited aggregation-caused quenching; in contrast, attaching the initiator to the rigid rod conformation of the PTyr segments caused PTyr-TPA to display aggregation-induced emission behavior. Differential scanning calorimetry revealed single glass transition temperatures for miscible PTyr-TPA/P4VP blends, the result of intermolecular hydrogen bonding between the pyridine units of P4VP and the phenolic OH units of PTyr-TPA, as confirmed through FTIR spectroscopic analyses. Furthermore, the chain behavior of PTyr-TPA transformed from a β-sheet conformation to random coils after blending with P4VP, as determined using wide-angle X-ray diffraction. These findings suggest that the decreased emission intensity of PTyr-TPA resulted from release of the restricted intramolecular rotation of the triphenylamine moiety in the polypeptide center.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Polymers)
▼
Show Figures