Micromachines 2019, 10(12), 797; https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10120797 - 20 Nov 2019
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 4860
Abstract
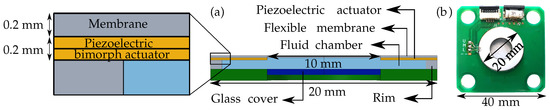
In this paper, we present a finite-element simulation of an adaptive piezoelectric fluid-membrane lens for which we modelled the fluid-structure interaction and resulting membrane deformation in COMSOL Multiphysics®. Our model shows the explicit coupling of the piezoelectric physics with the fluid
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we present a finite-element simulation of an adaptive piezoelectric fluid-membrane lens for which we modelled the fluid-structure interaction and resulting membrane deformation in COMSOL Multiphysics®. Our model shows the explicit coupling of the piezoelectric physics with the fluid dynamics physics to simulate the interaction between the piezoelectric and the fluid forces that contribute to the deformation of a flexible membrane in the adaptive lens. Furthermore, the simulation model is extended to describe the membrane deformation by additional fluid forces from the fluid thermal expansion. Subsequently, the simulation model is used to study the refractive power of the adaptive lens as a function of internal fluid pressure and analyze the effect of the fluid thermal expansion on the refractive power. Finally, the simulation results of the refractive power are compared to the experimental results at different actuation levels and temperatures validating the coupled COMSOL model very well. This is explicitly proven by explaining an observed positive drift of the refractive power at higher temperatures.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Piezoelectric Transducers: Materials, Devices and Applications)
►
Show Figures