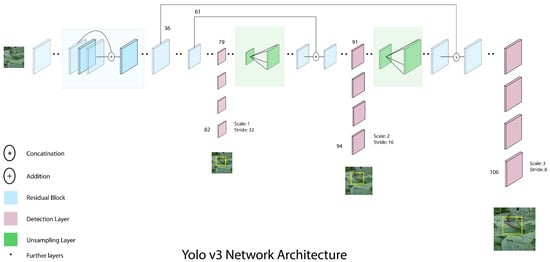
Sustainability 2023, 15(8), 6924; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086924 - 20 Apr 2023
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 7855
Abstract
We introduce a simple yet efficient approach to optimize the modal fleet size of urban public transportation services, considering both user- and operator-oriented factors. This is envisaged to enhance the potential for achieving sustainable urban transportation systems and, eventually, opportunities to create sustainable
[...] Read more.
We introduce a simple yet efficient approach to optimize the modal fleet size of urban public transportation services, considering both user- and operator-oriented factors. This is envisaged to enhance the potential for achieving sustainable urban transportation systems and, eventually, opportunities to create sustainable cities. The presented constraint optimization approach can be described as follows. First, the expected passenger demand and the cycle time for the public transportation service are estimated. Next, the desired constraints and parameters, such as those related to the headway and seat supply, are determined. Finally, the optimal combination of different vehicle classes and the number of trips satisfying all the defined constraints are determined. The case of an urban area in a developing country is considered. The resulting solution determines the optimal numbers of public transportation trips and vehicles, by mode, required to meet the expected passenger demand, provide a high-quality service with acceptable headways for passengers, and, at the same time, reduce the service providers’ costs as well as the environmental impacts. It is also concluded that a fleet composed of different modes can better facilitate the achievement of the optimal solution for passengers and service providers compared with the one-mode fleet.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Towards Sustainable and Inclusive Smart Cities: Challenges and Opportunities)
►
Show Figures