Sustainability 2023, 15(7), 5934; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075934 - 29 Mar 2023
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2875
Abstract
Authentication protocol is a critical part of any application to manage the access control in many applications. A former research recently proposed a lightweight authentication scheme to transmit data in an IoT subsystem securely. Although the designers presented the first security analysis of
[...] Read more.
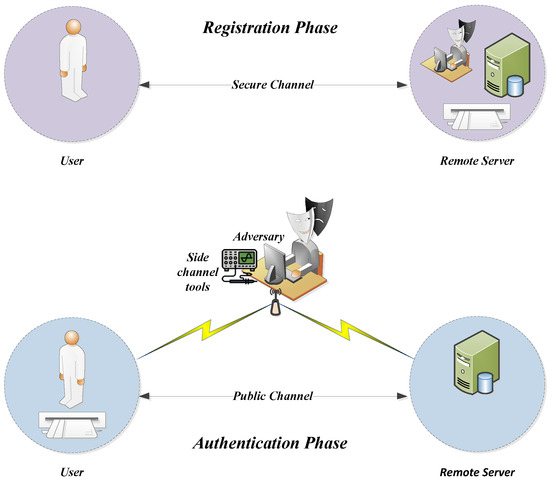
Authentication protocol is a critical part of any application to manage the access control in many applications. A former research recently proposed a lightweight authentication scheme to transmit data in an IoT subsystem securely. Although the designers presented the first security analysis of the proposed protocol, that protocol has not been independently analyzed by third-party researchers, to the best of our knowledge. On the other hand, it is generally agreed that no cryptosystem should be used in a practical application unless its security has been verified through security analysis by third parties extensively, which is addressed in this paper. Although it is an efficient protocol by design compared to other related schemes, our security analysis identifies the non-ideal properties of this protocol. More specifically, we show that this protocol does not provide perfect forward secrecy. In addition, we show that it is vulnerable to an insider attacker, and an active insider adversary can successfully recover the shared keys between the protocol’s entities. In addition, such an adversary can impersonate the remote server to the user and vice versa. Next, the adversary can trace the target user using the extracted information. Finally, we redesign the protocol such that the enhanced protocol can withstand all the aforementioned attacks. The overhead of the proposed protocol compared to its predecessor is only 15.5% in terms of computational cost.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Technologies, Sustainable Engineering and Cybersecurity in the Digital Age)
►
Show Figures