1
Department of Airframe and Powerplant Maintenance, Faculty of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Eskişehir Technical University—ESTU, Tepebaşı, Eskişehir 26555, Turkey
2
Sustainable Aviation Research Society—SARES, International Sustainable Aviation and Energy Society, ATAP Technopark No:210, Tepabaşı, Eskişehir 26470, Turkey
3
Department of Civil Aviation Management, School of Civil Aviation, Suleyman Demirel University, Merkez, Isparta 32260, Turkey
4
Department of Aeronautics, and Naval Architecture, Faculty of Transportation Engineering and Vehicle Engineering, Budapest University of Technology and Economics, 1111 Budapest, Hungary
5
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Dunaújváros, 2400 Dunaújváros, Hungary
6
HAVEN, Aviation Energy Engineering Ind. Trade. Co., Ltd., ATAP Technopark No:210, Tepebaşı, Eskişehir 26470, Turkey
Sustainability 2021, 13(9), 5251; https://doi.org/10.3390/su13095251 - 7 May 2021
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 5101
Abstract
Rubber is one of the rare materials that can be used in many sectors and for multiple purposes. It can be used in a wide range of frameworks, from very simple coating materials to very complex spacecraft parts. Apart from natural rubber, compounds
[...] Read more.
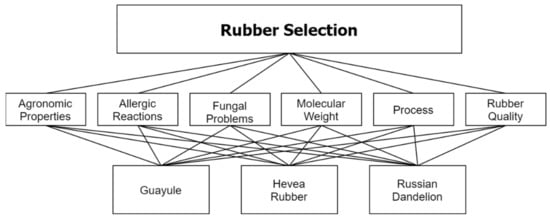
Rubber is one of the rare materials that can be used in many sectors and for multiple purposes. It can be used in a wide range of frameworks, from very simple coating materials to very complex spacecraft parts. Apart from natural rubber, compounds are also used for different purposes in rubber production. For a product with such a wide range of uses, the sustainability of its compounds is particularly important. The objective of this study is to investigate environmentally friendly and sustainable alternatives for rubber and some compounds, such as fillers and softeners. By doing this research with an academic method, the most suitable option is determined by taking the weights of the factors affecting this decision into consideration. As a result, the most suitable rubber, filler, and softener options are presented.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainable Materials)
▼
Show Figures