Sustainability 2020, 12(22), 9516; https://doi.org/10.3390/su12229516 - 16 Nov 2020
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 4373
Abstract
This editorial introduces the Special Issue “Metabolism of Islands”. It makes a case why we should care about islands and their sustainability. Islands are hotspots of biocultural diversity, and home to 600 million people that depend on one-sixth of the earth’s total area,
[...] Read more.
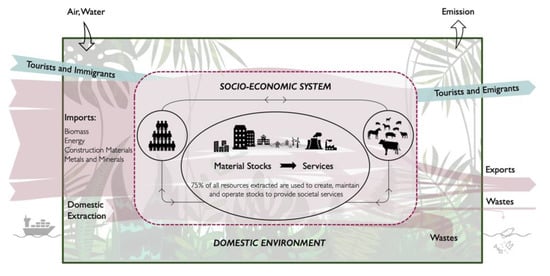
This editorial introduces the Special Issue “Metabolism of Islands”. It makes a case why we should care about islands and their sustainability. Islands are hotspots of biocultural diversity, and home to 600 million people that depend on one-sixth of the earth’s total area, including the surrounding oceans, for their subsistence. Today, they are on the frontlines of climate change and face an existential crisis. Islands are, however, potential “hubs of innovation” and are uniquely positioned to be leaders in sustainability and climate action. We argue that a full-fledged program on “island industrial ecology” is urgently needed with the aim to offer policy-relevant insights and strategies to sustain small islands in an era of global environmental change. We introduce key industrial ecology concepts, and the state-of-the-art in applying them to islands. Nine contributions in this Special Issue are briefly reviewed to highlight the metabolic risks inherent in the island cases. The contributors explore how reconfiguring patterns of resource use will allow island governments to build resilience and adapt to the challenges of climate change.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Metabolism of Islands)
►
Show Figures