Pharmaceutics 2022, 14(4), 827; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14040827 - 10 Apr 2022
Cited by 27 | Viewed by 6183
Abstract
The transdermal administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is a valuable and safer alternative to their oral intake. However, most of these drugs display low water solubility, which makes their incorporation into hydrophilic biopolymeric drug-delivery systems difficult. To overcome this drawback, aqueous solutions
[...] Read more.
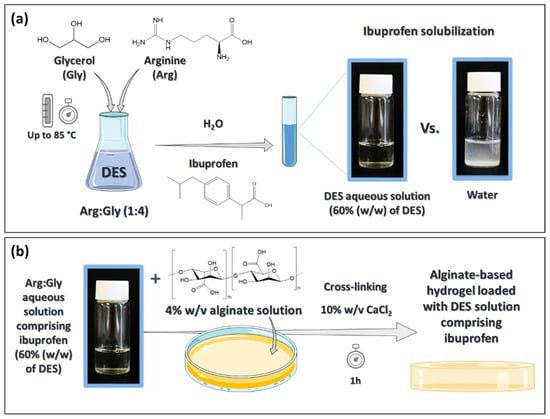
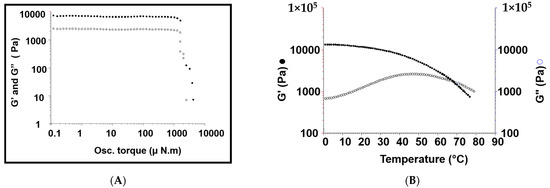
The transdermal administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is a valuable and safer alternative to their oral intake. However, most of these drugs display low water solubility, which makes their incorporation into hydrophilic biopolymeric drug-delivery systems difficult. To overcome this drawback, aqueous solutions of bio-based deep eutectic solvents (DES) were investigated to enhance the solubility of ibuprofen, a widely used NSAID, leading to an increase in its solubility of up to 7917-fold when compared to its water solubility. These DES solutions were shown to be non-toxic to macrophages with cell viabilities of 97.4% (at ibuprofen concentrations of 0.25 mM), while preserving the anti-inflammatory action of the drug. Their incorporation into alginate-based hydrogels resulted in materials with a regular structure and higher flexibility. These hydrogels present a sustained release of the drug, which is able, when containing the DES aqueous solution comprising ibuprofen, to deliver 93.5% of the drug after 8 h in PBS. Furthermore, these hydrogels were able to improve the drug permeation across human skin by 8.5-fold in comparison with the hydrogel counterpart containing only ibuprofen. This work highlights the possibility to remarkably improve the transdermal administration of NSAIDs by combining new drug formulations based on DES and biopolymeric drug delivery systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Polymer-Based Matrices for Drug Delivery: In Vitro, In Vivo and In Silico Approaches)
►
Show Figures