Sensors 2018, 18(9), 2784; https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092784 - 24 Aug 2018
Cited by 78 | Viewed by 7902
Abstract
With the fast development and expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT), billions of smart devices are being continuously connected, and smart homes, as a typical IoT application, are providing people with various convenient applications, but face security and privacy issues. The idea
[...] Read more.
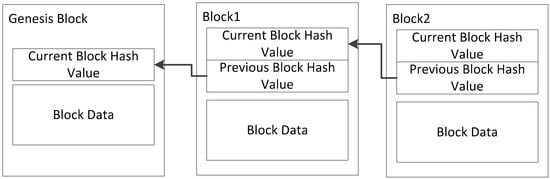
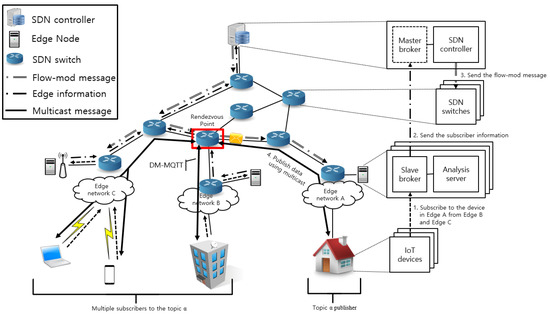
With the fast development and expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT), billions of smart devices are being continuously connected, and smart homes, as a typical IoT application, are providing people with various convenient applications, but face security and privacy issues. The idea of Blockchain (BC) theory has brought about a potential solution to the IoT security problem. The emergence of blockchain technology has brought about a change of decentralized management, providing an effective solution for the protection of network security and privacy. On the other hand, the smart devices in IoT are always lightweight and have less energy and memory. This makes the application of blockchain difficult. Against this background, this paper proposes a blockchain model based on hypergraphs. The aims of this model are to reduce the storage consumption and to solve the additional security issues. In the model, we use the hyperedge as the organization of storage nodes and convert the entire networked data storage into part network storage. We discuss the design of the model and security strategy in detail, introducing some use cases in a smart home network and evaluating the storage performance of the model through simulation experiments and an evaluation of the network.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sensor Networks for Collaborative and Secure Internet of Things)
►
Show Figures