Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(6), 5952; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065952 - 21 Mar 2023
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 2399
Abstract
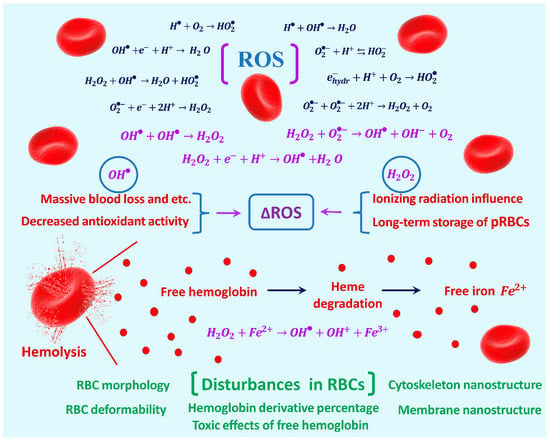
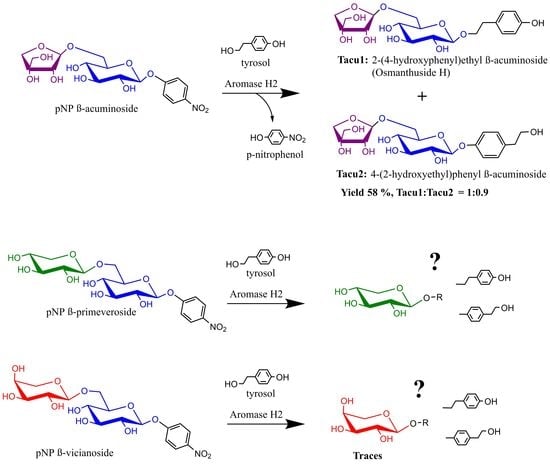
The influences of various factors on blood lead to the formation of extra reactive oxygen species (ROS), resulting in the disruption of morphology and functions of red blood cells (RBCs). This study considers the mechanisms of the mechanochemical synergism of
The influences of various factors on blood lead to the formation of extra reactive oxygen species (ROS), resulting in the disruption of morphology and functions of red blood cells (RBCs). This study considers the mechanisms of the mechanochemical synergism of
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Roles of Erythrocytes in Human Health and Disease 2.0)
►
Show Figures