Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23(7), 3829; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073829 - 30 Mar 2022
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 5051
Abstract
Autoimmune demyelinating diseases—including multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder, anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-associated disease, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-associated meningoencephalomyelitis—are a heterogeneous group of diseases even though their common pathology is characterized by neuroinflammation, loss of myelin, and reactive astrogliosis.
[...] Read more.
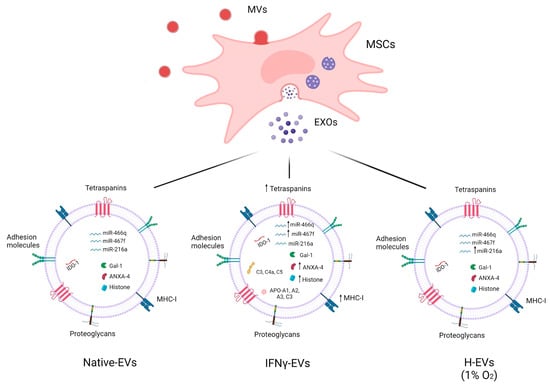
Autoimmune demyelinating diseases—including multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder, anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-associated disease, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-associated meningoencephalomyelitis—are a heterogeneous group of diseases even though their common pathology is characterized by neuroinflammation, loss of myelin, and reactive astrogliosis. The lack of safe pharmacological therapies has purported the notion that cell-based treatments could be introduced to cure these patients. Among stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), obtained from various sources, are considered to be the ones with more interesting features in the context of demyelinating disorders, given that their secretome is fully equipped with an array of anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective molecules, such as mRNAs, miRNAs, lipids, and proteins with multiple functions. In this review, we discuss the potential of cell-free therapeutics utilizing MSC secretome-derived extracellular vesicles—and in particular exosomes—in the treatment of autoimmune demyelinating diseases, and provide an outlook for studies of their future applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Mechanisms of an Aberrant Specific Immune Response: Role in Pathogenesis of Infectious, Autoimmune Diseases and Cancer)
►
Show Figures