Molecules 2020, 25(20), 4720; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204720 - 14 Oct 2020
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 7659
Abstract
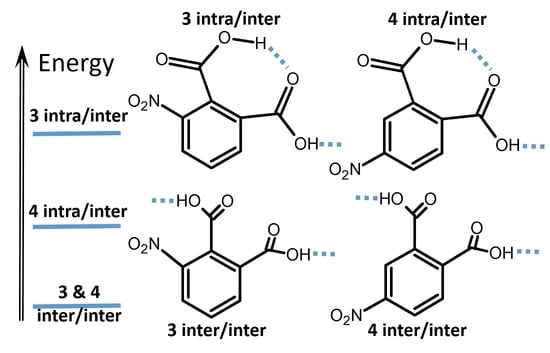
Noncovalent interactions are among the main tools of molecular engineering. Rational molecular design requires knowledge about a result of interplay between given structural moieties within a given phase state. We herein report a study of intra- and intermolecular interactions of 3-nitrophthalic and 4-nitrophthalic
[...] Read more.
Noncovalent interactions are among the main tools of molecular engineering. Rational molecular design requires knowledge about a result of interplay between given structural moieties within a given phase state. We herein report a study of intra- and intermolecular interactions of 3-nitrophthalic and 4-nitrophthalic acids in the gas, liquid, and solid phases. A combination of the Infrared, Raman, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, and Incoherent Inelastic Neutron Scattering spectroscopies and the Car–Parrinello Molecular Dynamics and Density Functional Theory calculations was used. This integrated approach made it possible to assess the balance of repulsive and attractive intramolecular interactions between adjacent carboxyl groups as well as to study the dependence of this balance on steric confinement and the effect of this balance on intermolecular interactions of the carboxyl groups.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Gulliver in the Country of Lilliput: An Interplay of Noncovalent Interactions)
►
Show Figures