Molecules 2014, 19(3), 3181-3192; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19033181 - 17 Mar 2014
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 7494
Abstract
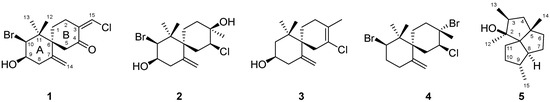
Two new chamigrane sesquiterpenes 1–2 and three known compounds 3–5 were isolated from a lipophilic extract of the red alga Laurencia dendroidea collected from the Southeastern Brazilian coast. Dendroidone (1) and dendroidiol (2) were isolated
[...] Read more.
Two new chamigrane sesquiterpenes 1–2 and three known compounds 3–5 were isolated from a lipophilic extract of the red alga Laurencia dendroidea collected from the Southeastern Brazilian coast. Dendroidone (1) and dendroidiol (2) were isolated from samples collected at Biscaia Inlet, Angra dos Reis, Rio de Janeiro and at Manguinhos Beach, Serra, Espírito Santo, respectively. Debromoelatol (3), obtusane (4) and (1S*,2S*,3S*,5S*,8S*,9S*)-2,3,5,9-tetramethyltricyclo[6.3.0.01.5]undecan-2-ol (5) were obtained from specimens collected at Vermelha Beach, Parati, Rio de Janeiro. The structures of new compounds were elucidated by extensive NMR (1H-, 13C-, COSY, HSQC, HMBC and NOESY) and high resolution mass spectrometry analysis. Additionally, the absolute configuration of compound 2 was assigned by X-ray analysis. Full spectroscopic data is described for the first time for compound 3. Anti-inflammatory and antimycobacterial activities of compounds 2–5 were evaluated. Compounds 3–5 inhibited the release of inflammatory mediator NO while TNF-α levels were only affected by 3. All compounds tested displayed moderate antimycobacterial action.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Natural Products Chemistry)
►
Show Figures