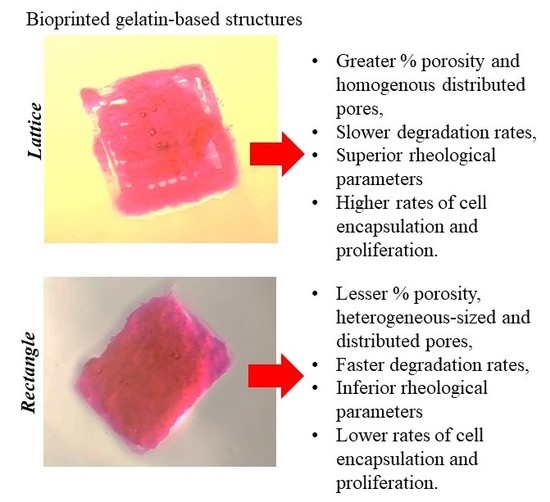
A Comparative Study of a 3D Bioprinted Gelatin-Based Lattice and Rectangular-Sheet Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
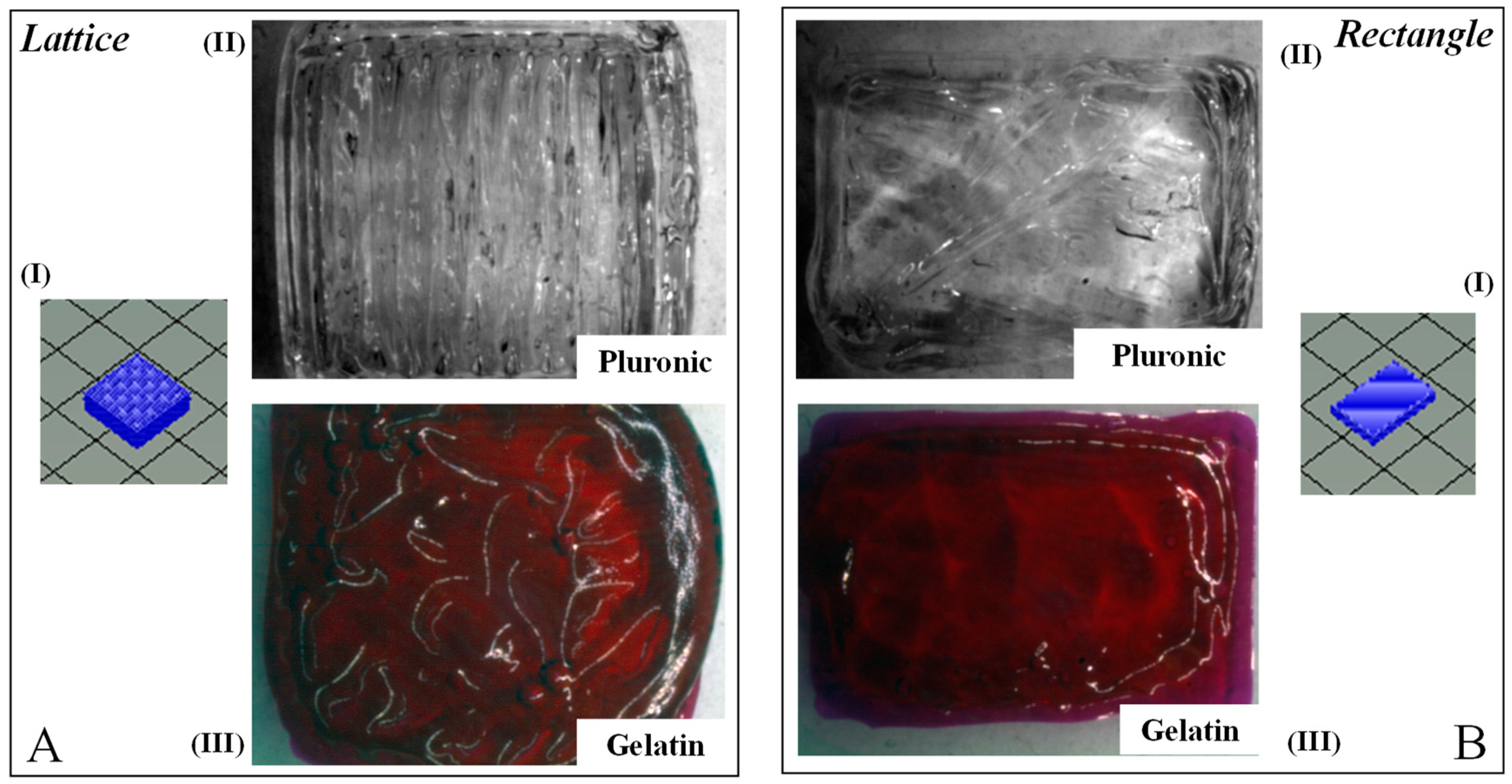
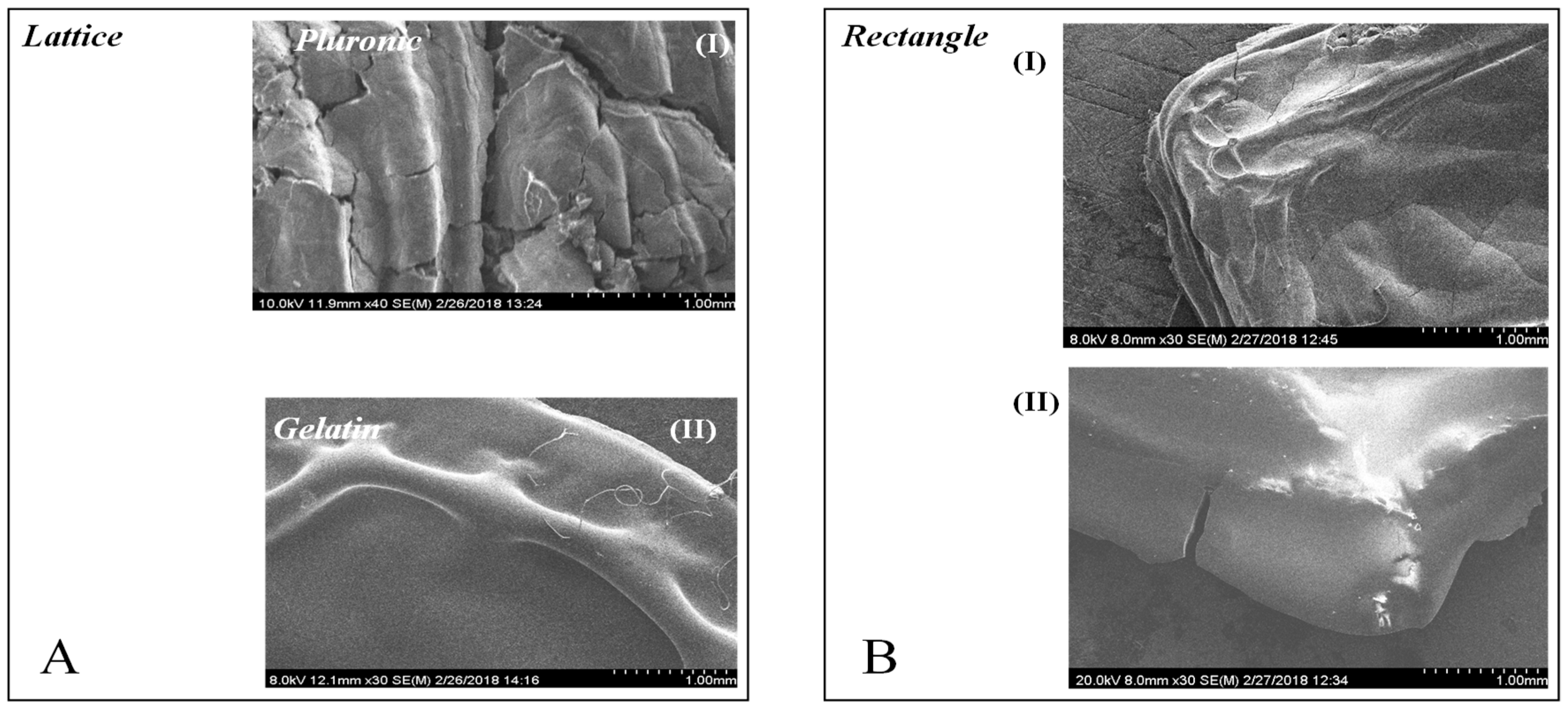
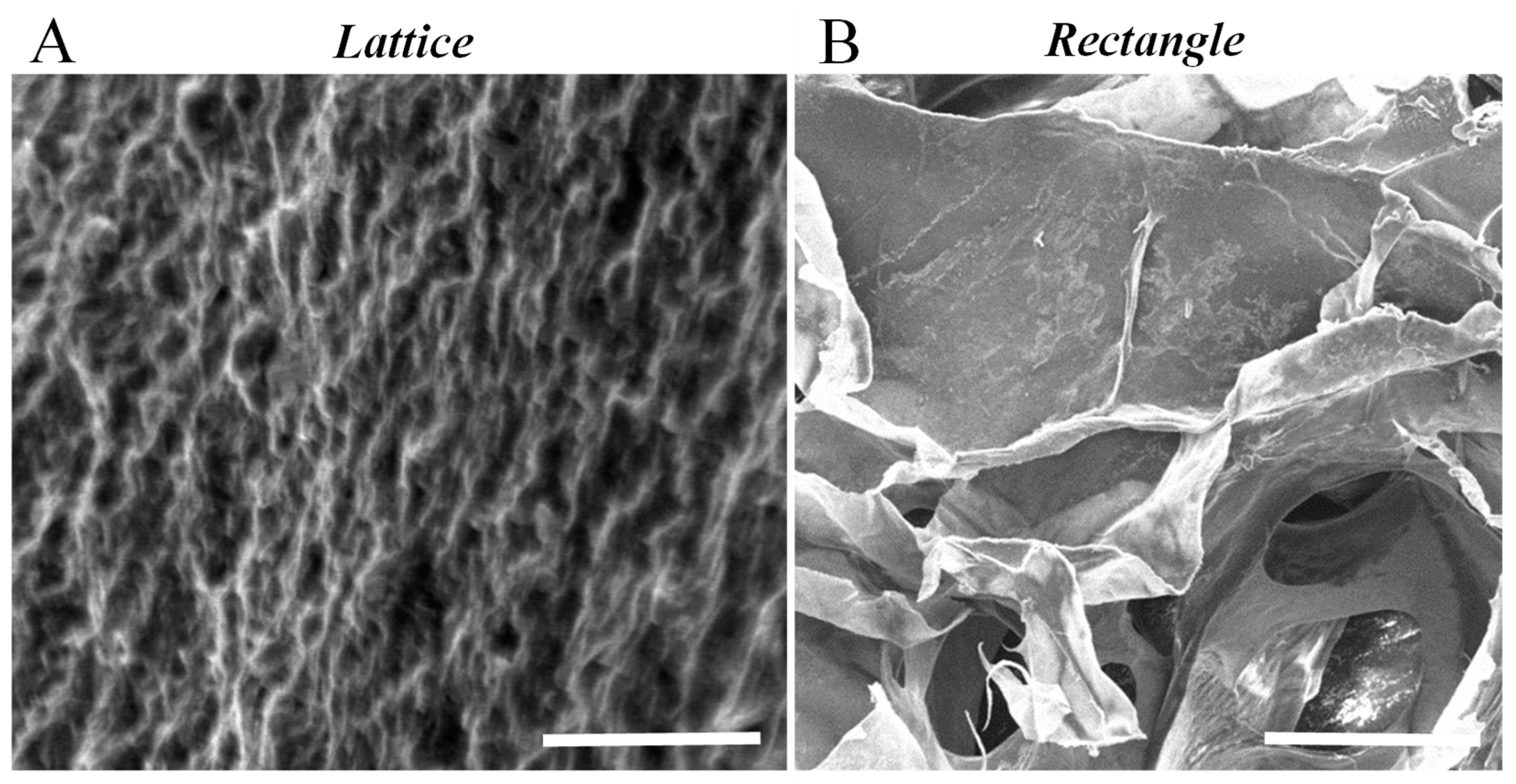
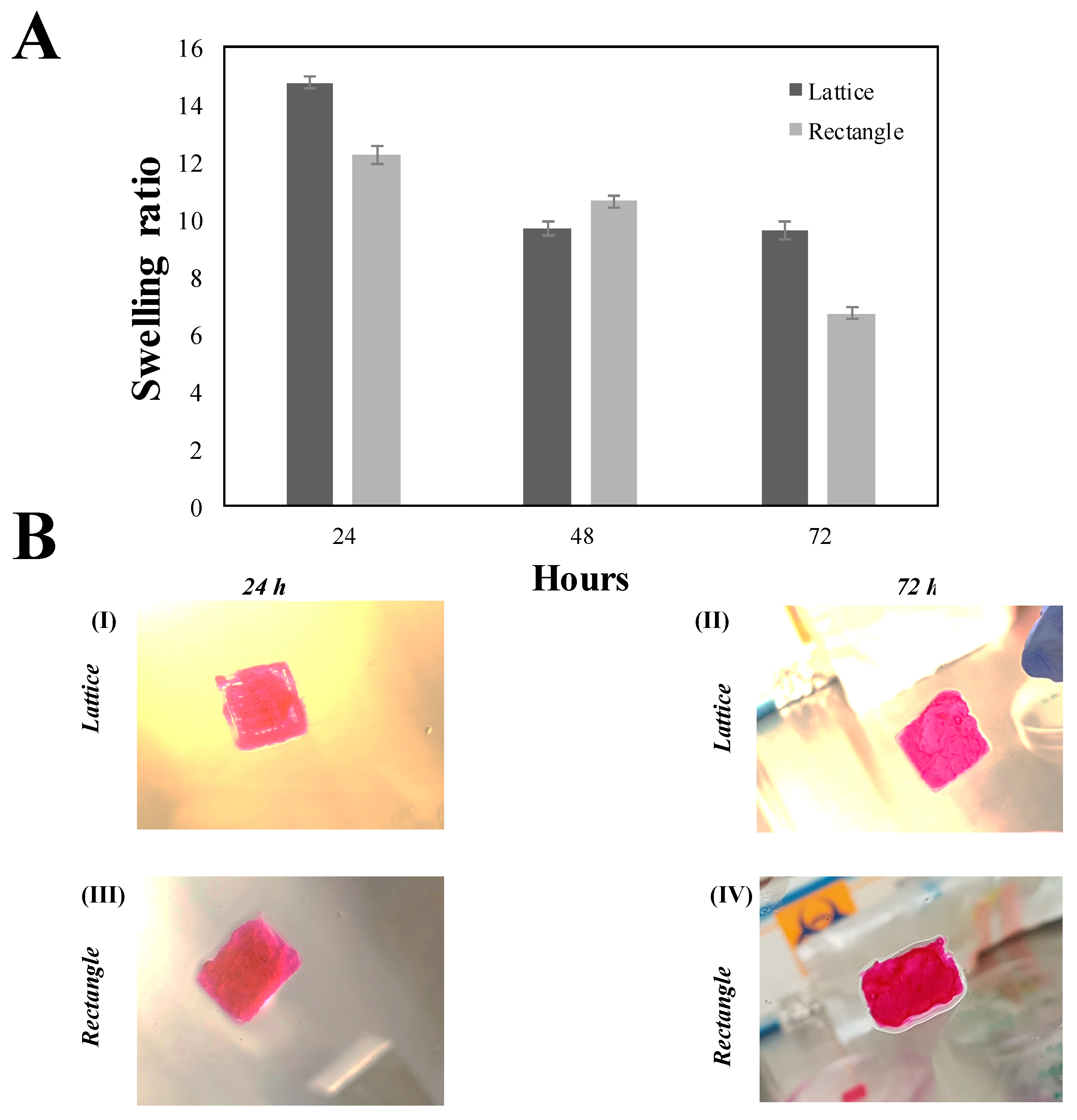
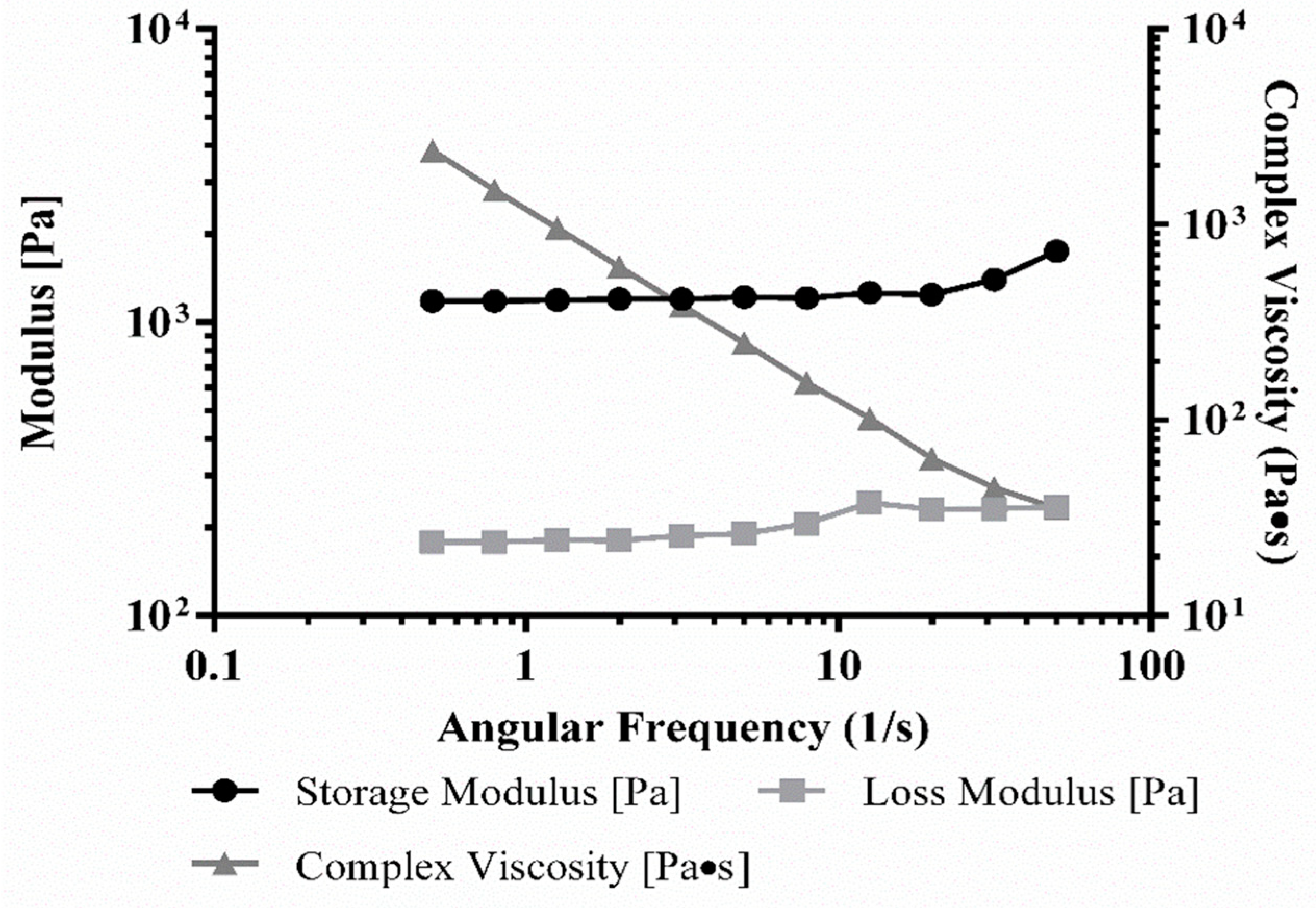
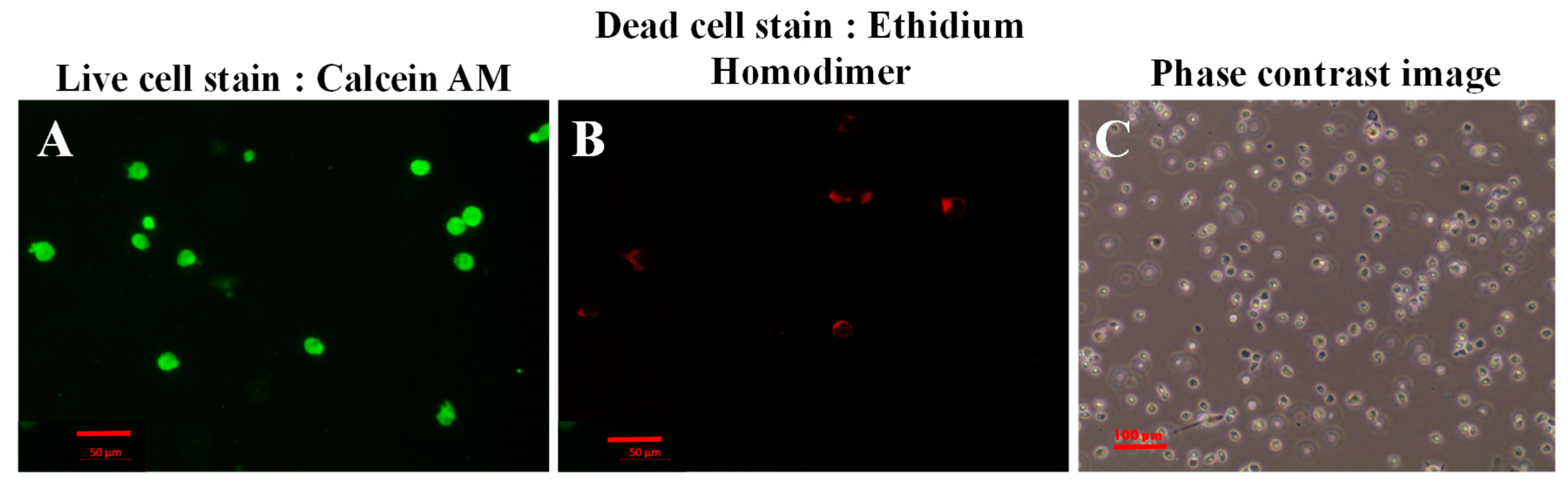
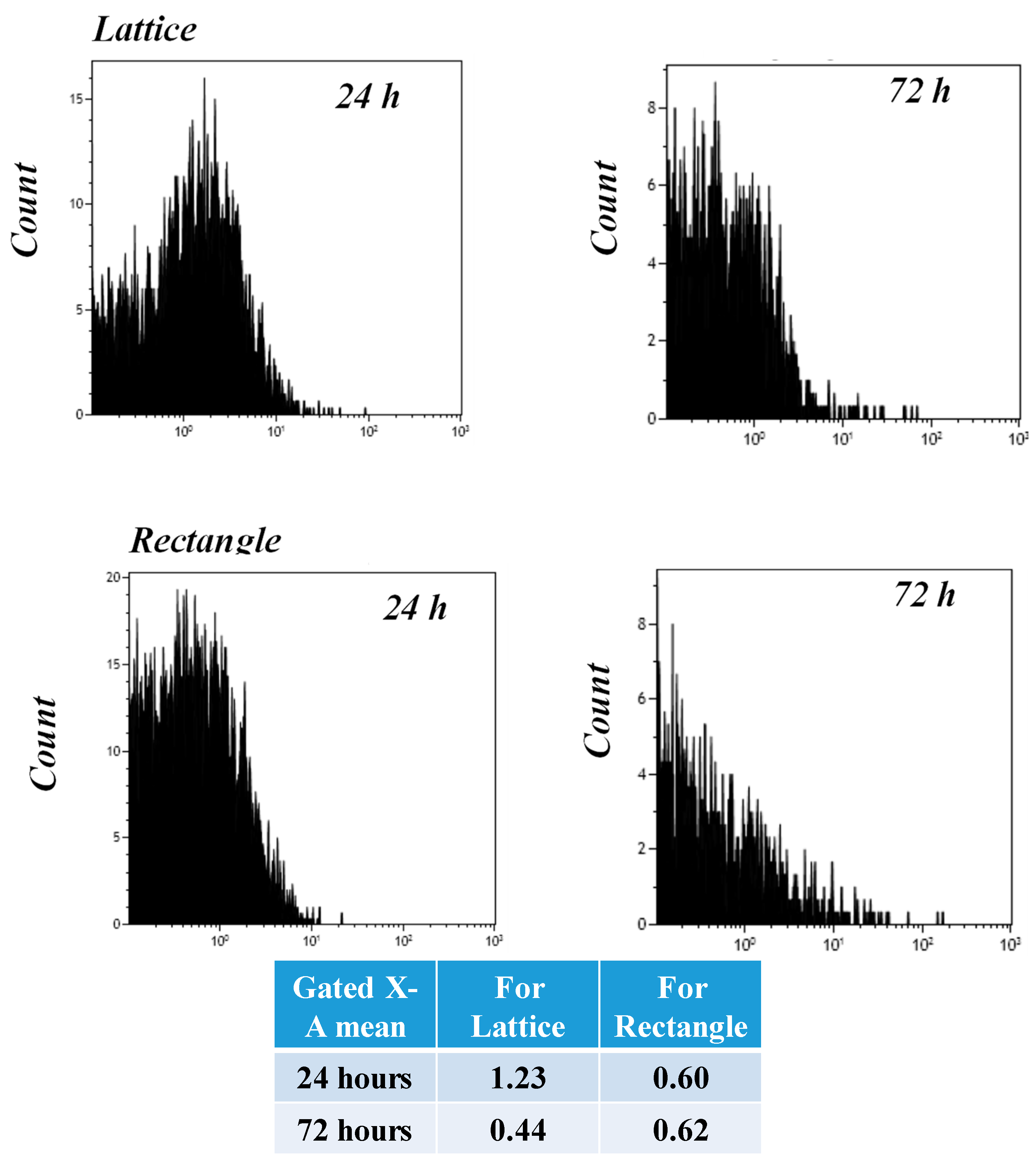
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Cells and Growth Medium
3.3. Biofabrication
3.4. Gross Morphology
3.5. Rheology of Bioink
3.6. In-Vitro Culture Conditions for the Cell-Laden Constructs
3.7. Live/Dead Cytotoxicity Assay
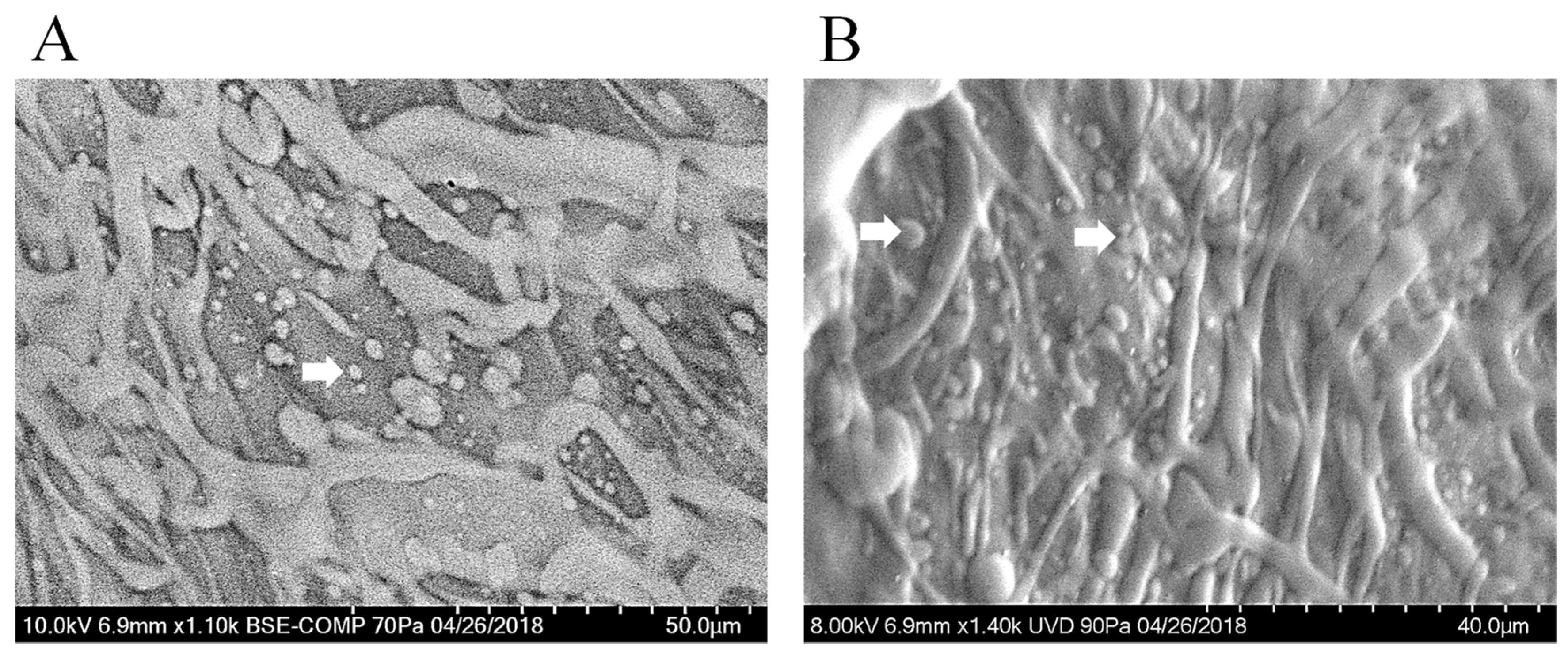
3.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.9. Swelling Behaviour
3.10. Cell Proliferation
3.11. Flow Cytometry (FACS) Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murphy, S.V.; Atala, A. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigi, A.; Cojazzi, G.; Panzavolta, S.; Roveri, N.; Rubini, K. Stabilization of gelatin films by crosslinking with genipin. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4827–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimene, D.; Lennox, K.K.; Kaunas, R.R.; Gaharwar, A.K. Advanced bioinks for 3D printing: A materials science perspective. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 2090–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Yi, H.-G.; Kim, S.-W.; Cho, D.-W. 3D cell printed tissue analogues: A new platform for theranostics. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3118–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.J.; Choi, J.; Park, Y.D.; Hong, S.; Lee, J.J.; Ahn, C.B.; Choi, H.; Sun, K. Sodium alginate hydrogel-based bioprinting using a novel multinozzle bioprinting system. Artif. Organs 2011, 35, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AnilKumar, S.; Allen, S.C.; Tasnim, N.; Akter, T.; Park, S.; Kumar, A.; Chattopadhyay, M.; Ito, Y.; Suggs, L.J.; Joddar, B. The applicability of furfuryl-gelatin as a novel bioink for tissue engineering applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Richards, D.J.; Pollard, S.; Tan, Y.; Rodriguez, J.; Visconti, R.P.; Trusk, T.C.; Yost, M.J.; Yao, H.; Markwald, R.R.; et al. Engineering alginate as bioink for bioprinting. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4323–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; Li, P.; Huang, G.; Feng, S.; Shen, C.; Han, B.; Zhang, X.; Jin, F.; Xu, F.; et al. Bioinspired engineering of honeycomb structure—Using nature to inspire human innovation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 74, 332–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, K.; Gandhi, M.; Khalil, S.; Yan, K.C.; Marcolongo, M.; Barbee, K.; Sun, W. Characterization of cell viability during bioprinting processes. Biotechnol. J. 2009, 4, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, J.; Day, W.; Henderson, C.; Purewal, S.; Cerveira, J.; Summers, H.; Rees, P.; Davies, D.; Filby, A. A method for evaluating the use of fluorescent dyes to track proliferation in cell lines by dye dilution. Cytometry Part A 2013, 83, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filby, A.; Perucha, E.; Summers, H.; Rees, P.; Chana, P.; Heck, S.; Lord, G.M.; Davies, D. An imaging flow cytometric method for measuring cell division history and molecular symmetry during mitosis. Cytometry Part A 2011, 79, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joddar, B.; Garcia, E.; Casas, A.; Stewart, C.M. Development of functionalized multi-walled carbon-nanotube-based alginate hydrogels for enabling biomimetic technologies. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pati, F.; Jang, J.; Ha, D.-H.; Kim, S.W.; Rhie, J.-W.; Shim, J.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Cho, D.-W. Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pati, F.; Shim, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Cho, D.W. 3D printing of cell-laden constructs for heterogeneous tissue regeneration. Manuf. Lett. 2013, 1, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Shim, J.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Cho, D.-W. Preparation of photocured azidophenyl-fish gelatin and its capturing of human epidermal growth factor on titanium plate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Seo, S.; Na, H.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.; Woo, H.; Lee, J.; Seok, H.; Lee, J.; Chung, S.; et al. Preparation of a visible light-reactive low molecular-O-carboxymethyl chitosan (LM-O-CMCS) derivative and applicability as an anti-adhesion agent. Macromol. Res. 2011, 19, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaki, T.; Shiozaki, Y.; Yamane, K.; Yoshida, A.; Nakamura, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Zhou, D.; Kitajima, T.; Tanaka, M.; Ito, Y.; et al. A novel, visible light-induced, rapidly cross-linkable gelatin scaffold for osteochondral tissue engineering. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, T.I.; Sakuragi, M.; Takahashi, S.; Obuse, S.; Kang, J.; Fujishiro, M.; Matsushita, H.; Gong, J.; Shimizu, S.; Tajima, Y.; et al. Visible light-induced crosslinkable gelatin. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 4005–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stowers, R.S.; Allen, S.C.; Suggs, L.J. Dynamic phototuning of 3D hydrogel stiffness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1953–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaetani, R.; Feyen, D.A.; Verhage, V.; Slaats, R.; Messina, E.; Christman, K.L.; Giacomello, A.; Doevendans, P.A.; Sluijter, J.P. Epicardial application of cardiac progenitor cells in a 3D-printed gelatin/hyaluronic acid patch preserves cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Biomaterials 2015, 61, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornelas, A.; Williams, K.N.; Hatch, K.A.; Paez, A.; Aguilar, A.C.; Ellis, C.C.; Tasnim, N.; Ray, S.; Dirk, C.W.; Boland, T.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of a photocleavable collagen-like peptide. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 1000–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrado, A.R.; Roberson, D.A. Failure analysis and anisotropy evaluation of 3D-printed tensile test specimens of different geometries and print raster patterns. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2016, 16, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anil Kumar, S.; Tasnim, N.; Dominguez, E.; Allen, S.; Suggs, L.J.; Ito, Y.; Joddar, B. A Comparative Study of a 3D Bioprinted Gelatin-Based Lattice and Rectangular-Sheet Structures. Gels 2018, 4, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4030073
Anil Kumar S, Tasnim N, Dominguez E, Allen S, Suggs LJ, Ito Y, Joddar B. A Comparative Study of a 3D Bioprinted Gelatin-Based Lattice and Rectangular-Sheet Structures. Gels. 2018; 4(3):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4030073
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnil Kumar, Shweta, Nishat Tasnim, Erick Dominguez, Shane Allen, Laura J. Suggs, Yoshihiro Ito, and Binata Joddar. 2018. "A Comparative Study of a 3D Bioprinted Gelatin-Based Lattice and Rectangular-Sheet Structures" Gels 4, no. 3: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4030073
APA StyleAnil Kumar, S., Tasnim, N., Dominguez, E., Allen, S., Suggs, L. J., Ito, Y., & Joddar, B. (2018). A Comparative Study of a 3D Bioprinted Gelatin-Based Lattice and Rectangular-Sheet Structures. Gels, 4(3), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4030073