Readings of spaces and places in terms of emotion go hand in hand with the creation of maps that function like a visual memory-cloth and concern issues like the personal, the underground, belonging, and longing. Here emotional mapping extends itself by going deeper, to become, indeed, deep mapping, and, in that sense, map-making becomes world-making.
1. Deep Mapping the Harbour as a Liminal, Spatial-Social Body
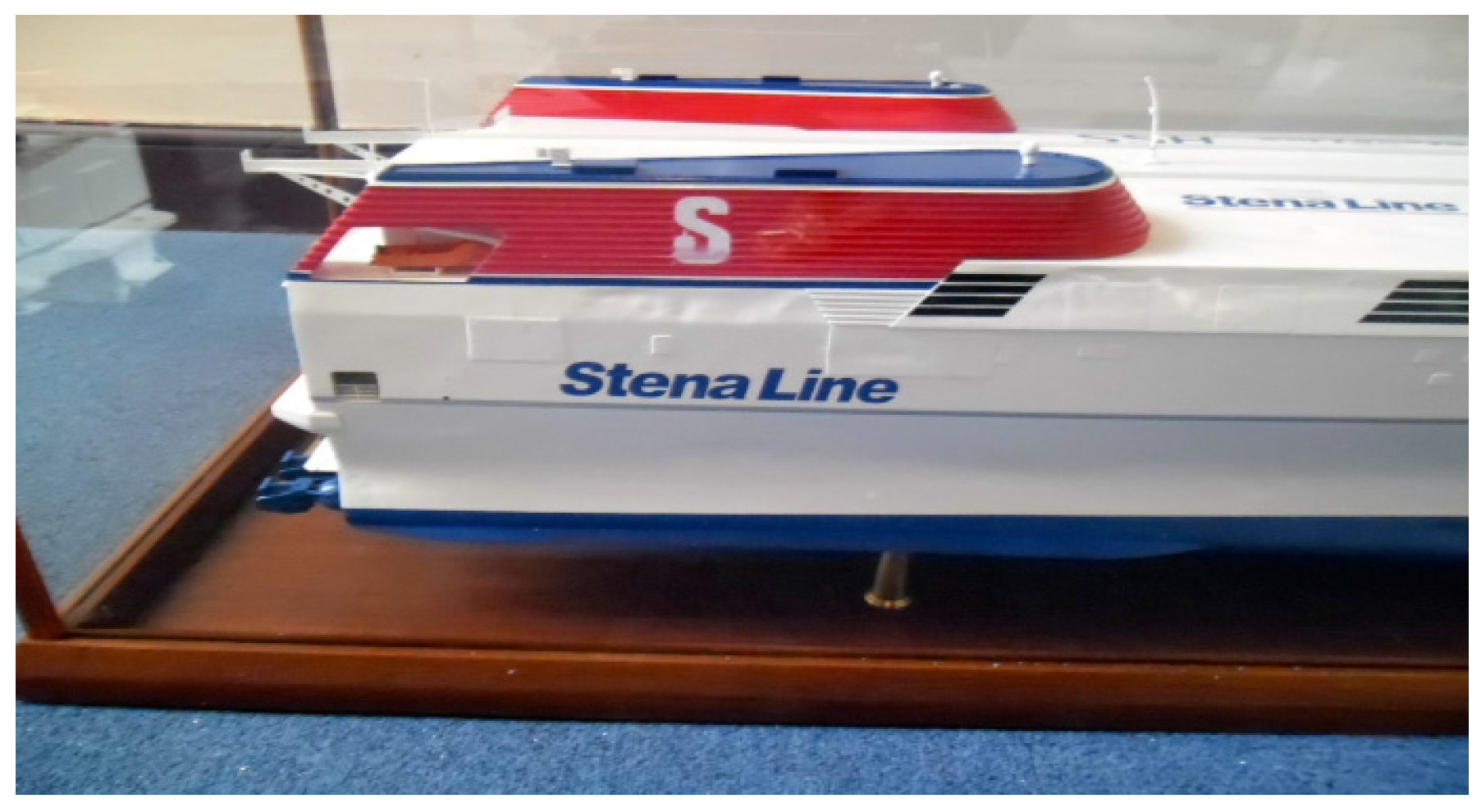
Dún Laoghaire, a small seaside town situated 12 kilometres outside Dublin, as a geographical place underwent dramatic changes in its development from the tiny 18th century fishing village of Dunlary or Dunleary to the imperial Kingstown of 1821 to 1920, which boasted a royal harbour and a magnificent railway line. The town’s name after Irish Independence reverted back to Dún Laoghaire, and it became a thriving ferry hub in the 1990s. With the aviation industry already having taken over the leading role in global passenger transport, Dún Laoghaire, like the rest of Ireland, was hit hard by the economic crash in 2008, and when the Stena Line announced the final closing of its ferry service from Dún Laoghaire to Holyhead in February 2015, which had been operating since 1835, it felt like yet another ending with no new beginning.
The ferry boat model of the HSS Stena Explorer depicted in
Figure 2 was donated by the Dún Laoghaire Harbour Company to the Maritime Museum of Ireland, where it has been restored and is to be part of the museum display. The particular image features as a fragment for the Ferry Terminal book in the
Glas Journal series—because of the boat’s obvious historical connection to the operational procedures in the harbour, but also because its containment in a glass vitrine mirrors the frozen quality of melancholia, where, in the attempt of evading psychic pain, without containment, there would be leaking.
Figure 2.
Ferry Terminal fragment, 2015. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
Figure 2.
Ferry Terminal fragment, 2015. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
Current trends of rejuvenation, as part of a master plan to tackle Dún Laoghaire’s ghost town status, include significant investment into cruise line business, the planned building of a Berlin-inspired urban pool/beach and a diaspora centre to attract visitors. The plans have been perceived as problematic in scale and validity to be of local benefit, and have consequently been contested by voluntary citizen initiatives and community organisations like Save Our Seafront (SOS) [
2].
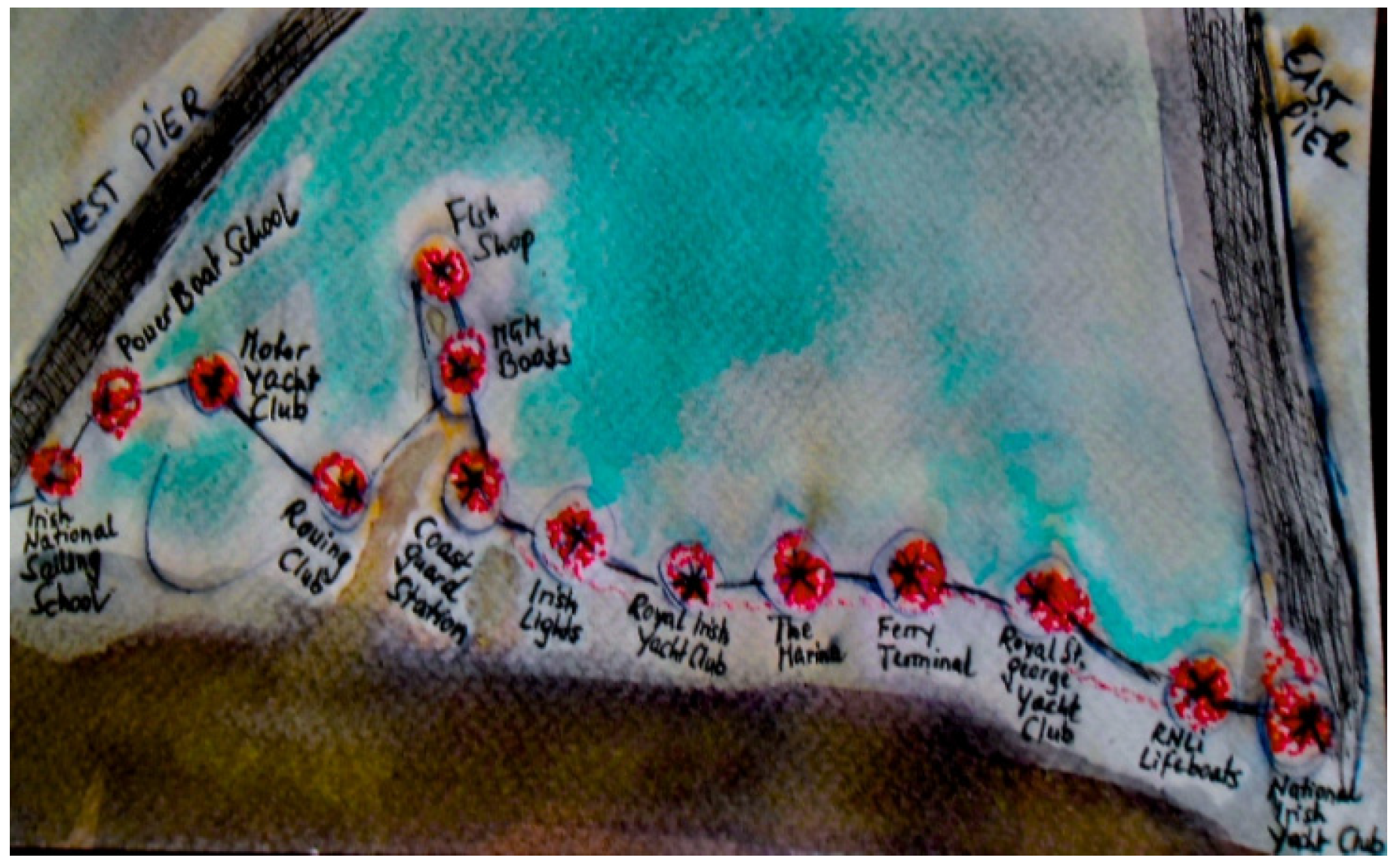
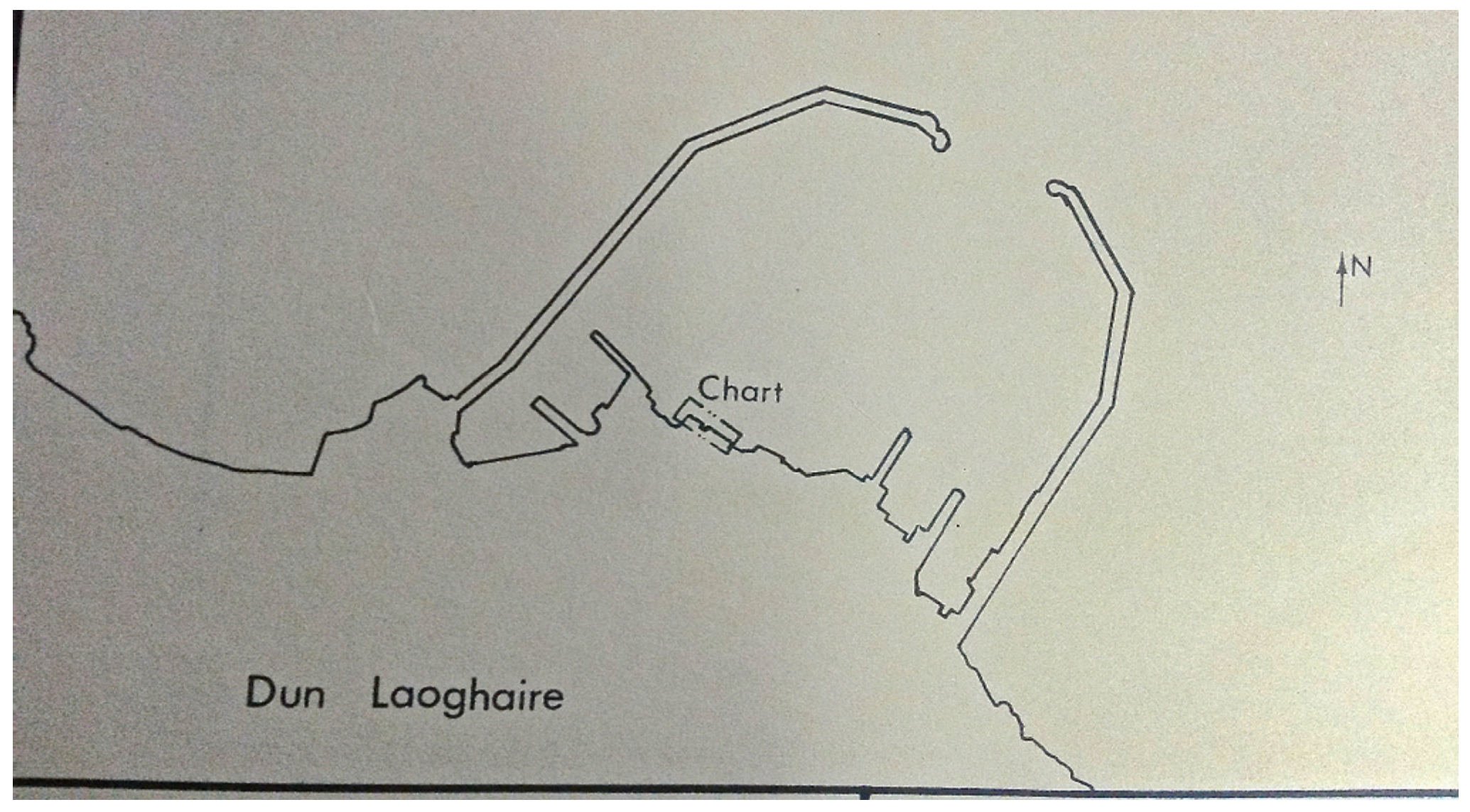
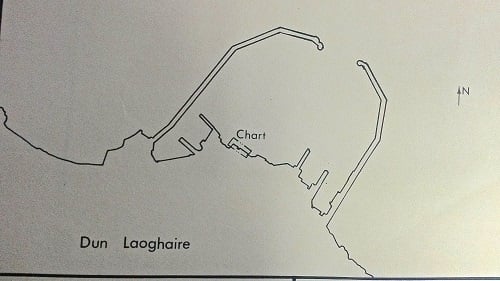
Glas Journal hopes to reflect these recent developments in the sense that residents and workers may evoke life cycles of birth, decay, destruction and resurrection, distinct from Dublin’s phases of investment and its recent cultural and financial crisis. In addition to this attention to the socio-economic context, the project also reflects the physical landscape of the two harbour piers forming a space of protection, as the physical structure of the two piers (West and East) may be described as two arms that reach out to sea to guide naval vessels into the safety of land, as depicted in
Figure 3.
Figure 3.
Map fragment, 2015 [1983]. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
Figure 3.
Map fragment, 2015 [1983]. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
The original map fragment showing Dún Laoghaire Harbour in
Figure 3 is property of the Dún Laoghaire Harbour Company, who kindly allowed me to photograph their “old” maps in storage. The elegant minimalist fragment originally served as a hydrographic map and also has a stamp from the engineering office of the Commissioners of Irish Lights on it, which dates back to 8 June 1983 (the 1980s being another era of economic depression and mass emigration in Ireland). In 2015, the fragment stands for an almost pathological desire for the map to be reconstructed or to be coloured in.
The concept of liminality thus applies to times of transition, historical shifts and the emergence of new social and cultural paradigms. To cross the threshold into a new aeon, spaces themselves are required to shed their skin and to adapt a new identity. Liminality as a concept of cultural hybridity often refers to the disruptive nature of inbetween-ness and the interstitial pathways or passages that constitute the body of territorial maps and their spatial divisions. The threshold space in-between boundaries was called
limen or threshold by the Belgian anthropologist Arnold van Gennep in
Rites of Passage (1909). Liminality as a concept has been used by Mircea Eliade [
3] to divide the human experience of what is sacred and what is profane, whereas liminal space was regarded as transformative by Victor Turner, the ritualistic passageway from one state to another [
4].
If we consider these various conceptualisations of the threshold or liminal space in relation to harbours, we understand that they are not just nodes in a network. Rather they are places and localities that emerge from numerous threshold crossings to recount the diverse social lives of the harbour as border space providing a rich source of information about the rituals
and buildings, homes
and docks, myths
and quantitative measures of the sea. Harbours are often seen as sites of recreation (boat docking, fishing, sailing or waterside redevelopment) or as export nodes of a global economy. However, in Allan Sekula’s photographic ethnography,
Fish Story (1995), harbours are not havens any longer because the sea now equals money [
5]. In support of Sekula’s findings about the effects of an excessive capitalist economy on the sea-faring industries, Michael Taussig elaborated on how ports have become gentrified, how museums contain the objects that were once vital for survival, and how luxury housing with a “sea view” replaced working class areas. But when describing his personal relationship to waves, Taussig also mentions a “fragile freedom, always already lost” ([
6], p. 260) which brings us to the magic of liminal spaces inbetween commodified agendas and to the multiple meanings of threshold, where we pass from one phase to another in terms of ritual and initiation, historically and personally, as well as spatially.
Mikhail Bakhtin’s literary concept of the chronotope [
7], which refers to the cross-section of time and space in the novel that determines the plot, may be used to map historical and geographical changes that bring about the various in-between states that building structures find themselves in. The relevance of mapping in-between or liminal spaces lies in the exploration of psychological meanings of spatial attachment to and/or detachment from places of home and work. A cyclical theme that appears to emerge again and again in the context of home, exile and belonging is how tightly interlinked mappings of home are with feelings of safety within the community and the role that spaces of protection play in everyday life. Inspired by Walter Benjamin’s staccato methods of mapping the everyday that culminated in the fragmented form of a collage or montage of cultural meanings [
8],
Glas Journal seeks to explore the emotional dimensions of spatial attachment to a harbour, which, by its nature, is a space of protection.
Drawing upon a methodology then that is based on a visio-textual bricolage consisting of fragments to survey forms of life, as Benjamin would have it, Glas Journal looks at how the themes of care and intimacy are interwoven in a complex contained public space such as the harbour. By seeking to emphasise how individual stories, performances, and emotional geographies are intertwined with the physicality of a built maritime environment, the first series of 14 hand-size and hand-made artist books that document 14 corresponding harbour spaces is created by me in my studio in the Coast Guard Cottages. This process of making allows for a positioning of the subject matter of deep maps in the fragmented form of artist books as well as for a positioning of myself as the initiator and participant of the project. The second series of books will be based on 14 journals made in collaboration with the residents and workers of the given spaces between West and East Pier, in order to map how they relate to the sea as a border space and what the harbour as a space of protection means to them. A form of emotional mapping that deals with the harbour as an allegory creates a cartography of intimacy that serves as an antidote to the sharp distinctions of borders and separation lines as used in the classified western mapping system to define territories.
3. Tender and Chaotic Mappings
The field of emotional mapping offers a new form of power to maps—it is an engagement of spatial practices with the human condition, and, in that sense, it seeks to redeem the calculating and colonising tactics of forms of cartography that feed into the fantasy of territorial sovereignty. The focus on emotional responses to space, how one interacts with the public sphere in private and intimate ways, shifts the investigation of the city as a web of streets defined by their architectural setting into a search for possible alternative interpretations of what it might mean to navigate through a city visually and emotionally.
Numerous important aspects of emotional mapping can be grasped in the poem “Your Street Again” by Sophie Hannah [
13]:
- “Guess who I saw last night’, was all she said.
- That, and the answer (you), was all it took,
- And now I’m leafing through my A–Z
- To find your street again. I had to look
- Four years ago, and memorize the way:
- Palatine, Central, Burton—halfway there.
- I don’t intend to visit you today
- As I did then, and so I shouldn’t care
- Which road comes after which and where they lead.
- I do though. I repeat them name by name
- My house is here and yours there. I need
- To prove the space between them stays the same.”
A connection between places, signs and emotions has been established, a connection that has been hinted at, and thoughts that may fleetingly cross our mind—yes we know what it means to look for someone’s street, we can relate to that—although it is rather difficult if not impossible to express what Sophie Hannah really meant by “Palatine, Central, Burton—halfway there”. What does her mapping stand for? Is it an allegory for a doomed relationship, someone departed she does not want to cross paths with ever again, a spatial mind exercise of how long it takes from Palatine to Central to Burton? Hannah’s poem evokes a deeply intimate process of mapping, something so important in her spatial memory that, in order to get it right, she needs to get her A–Z (because someone has been seen, so he or she is still visible and creates an impact) and “Palatine, Central, Burton—halfway there” act as her emblems to make sense of the situation (“I need to prove the space between them stays the same”).
The Situationist International movement operating in Paris in the 1950s and 1960s created collage-based maps representing psychological influences and playful associations with space. The Situationists’ maps asked to be examined in their function as a resistance to space that was determined by the ideology of a hegemonic state apparatus, with its focus on capitalist market values and consumer-orientated forms of representation. They called for an exploration of the concept of “public intimacy”, which relates to the entanglement of personalised expressions in public space and their possible meanings. One of the major influences for the Situationists was Madame de Scudéry and her tender map about intimacy and the discourse of love, which goes back to the 17th century. In 1654, Madeleine de Scudéry published her novel
Clélie. She designed a
Carte de Tendre or Map of Tenderness and created an emotional topography with roads called Friendship to cities with names like Tenderness, Great Wit or, negatively, Submission—all concerning the affairs of the heart, with the hope of ending up in The City of New Friendship. At first hearing this may not sound extraordinary, but de Scudéry’s use of an exterior that expresses an interior landscape opens up new approaches to the mapping of space ([
14], p. 264).
De Scudéry’s form of mapping may be compared to the workings of cathedral space, where an inner sanctum is created through gothic shape, the sound of music and the smell of candle wax, transporting the praying person into an inner refuge [
15]; or, on the opposite end of the emotional scale, to the works of Rainer Maria Rilke, who consistently wrote about the chaos of inner space translated into the terminology of an outer world in his works. In Rilke’s only novel,
The Notebooks of Malte Laurids Brigge (1910), the protagonist is not aiming at a detailed description of modern life in metropolitan Paris but isolates certain places and injects them with personal meaning [
16]. Malte is not concerned about depictions of urban “realities” but rather projects his own inner psychological space into the outside of the city. His experiences with urban decay and his encounters with the city-dwellers and their fear of poverty and death result in moments of paranoia for Malte. Malte’s wanderings through Paris are a form of becoming. The city becomes his emotional states and his emotional states become the city.
Another example for an emotional mapping of the city is Wim Wenders’
Wings of Desire (1987), which refers to Berlin’s post-war void. Dealing with spatial erasures and the despair of modern city life, this film can be seen as “an architectural document of a city that no longer exists” [
17]. The work’s moving images dissolve the frozen quality of melancholy by paying tribute to discoloured urban space with care and empathy. Wender’s inserts a poetic discourse into everyday language by deploying an angelic phantasmagoria as a perspective that allows one to view the modern city in psychological terms. In the film, urban angels, that yearn to become human, offer a perspective from above: an angelic perception onto the everyday activities of humans. The aerial perspective of the city is offered to the viewer and this contributes to a voyeuristic feeling of witnessing the intimacy of people’s lives and by being provided with a bird’s eye view the viewer looks into people’s apartments, into their thoughts.
Himmel über Berlin (the film’s original title) can be considered a cinematic memory cloth of 1980s Berlin because of its interlinking of personal stories with the topography of the city, black and white and bleak in representation changing into colour, once the protagonist of the film, an angel, turns human and is able to live the city experience of the here-and-now, the city to becoming a space that “could be characterised by the experience of procession and movement, of appearance and spectacle, of progress and the new, of dreams and ghosts” [
18].
Opposed to the Situationists’ disillusion with modern urban life expressed in Guy Debord’s final statements that
logos had triumphed over
eros by turning the city into nothing more than cheap-thrill commodity zones, Wenders’ film is leading to the act of “logos redeeming eros” [
19]. In that sense phantasmagoria as an inherently fluid concept was used to map the threshold experiences of a city in transition, whereby its liminality was reflected back and forth in the corporeal metamorphosis of the film’s protagonist as well as in the film’s layered narrative of belonging and longing. This kind of layered or liquid mapping, whether it is expressed in tender ways in de Scudéry fashion or more chaotic and dreamlike, is the essence of
Glas Journal, where 14 artist books covered and stained by ink layers reflect the colour of the Irish Sea, as illustrated in
Figure 4, and serve as the basis for a contemporary map of shelter and protection, of navigation and connection, and of processes of anchoring and homecoming. The books are located in a refuge inbetween two scenographic harbour arms, but the exhibition venue (the former Mariners’ Church now housing the National Maritime Museum of Ireland, which is about ten minutes walking distance from the East Pier of Dún Laoghaire Harbour) in itself may be described as a space of guidance, and, possibly, healing.
Figure 4.
Glas Journal installation, Maritime Museum of Ireland, 2015. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
Figure 4.
Glas Journal installation, Maritime Museum of Ireland, 2015. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
4. Cartographies of Intimacy
In terms of gendered place-making, the issue arises as to how emotional mapping and a form of writing that does not exclude women and their spaces can be created. If the social functions of artistic production and presentation are being viewed from a feminist viewpoint, past history has rarely included women artists. Geography as well as fiction is a discourse that has been shaped by male dominance for a long time and created disciplines that Rosalyn Deutsche calls a “boys town” [
20]. In
Atlas of Emotion (2002), Bruno extends Virginia Woolf’s concept that a woman must be able to call a room her own and to have some money in order to write fiction to processes of emotional mapping. Bruno refers to Gertrude Stein’s literary-geographic path, where geography stands for a way of writing that Bruno calls “tender cartography”. Spatial representations that include women in the field of geography become a “room of one’s own” ([
14], p. 209).
The use of elements of oral history in
Glas Journal to map difficult threshold experiences in a handmade book is fundamentally different to the traditional western cartography from the 17th century onwards, which was based on spatial representations that depicted the development of European nation-states and defined territorial claims of ownership. When Mei-Po Kwan used geographical information systems (GIS) to map the levels of fear that are prevalent in the everyday lives and quotidian routes of Muslim women in the US post-September 11, she challenged the concept of a binary us-versus-them opposition that is conveyed by single-voiced authoritarian narratives [
21]. In her study of 2008, Kwan pointed out the importance of oral history accounts, where participants tell about their threshold experiences in terms of their memories and emotional connections to events, people and places. In order to construct her geo-visualised multi-media narrative of the life paths of a Muslim woman based in Columbus with the fictitious name “Nada”, Kwan used daily activity data and emotional coding to identify “Nada”s levels of fear. Kwan made the important point that women, who have been made
Other through a dominant anti-Muslim narrative by being associated with the category of “terrorists and anti-American foreigners” ([
20], pp. 666–67), suffered from significant fear on their daily routes and in public places in particular, and that there needs to be a shift of perspective as to how these fears are being constructed. Kwan also asked for a more careful examination of the life paths of Muslim women in the US, rather than creating yet another homogenous category for their experiences.
In questioning traditional cartographic models and their alleged objectivity, an aesthetic of failure of how we read representational as well as experiential maps may be necessary, in order to enter different paradigms of thinking. Juxtaposing, or, perhaps, complimenting Kwan’s representation of post-September 11 experiences of Muslim women in the US, Iranian born artist Shirin Neshat’s oeuvre, in particular her black-and-white portrait series of
Women of Allah from the 1990s, is based upon an orchestrated rebellious fearlessness within dogmatic social and cultural systems that aim at keeping women contained in the domestic sphere. Neshat, who has been living in American exile since the mid-1970s, uses several layers to construct her fantasy of the Muslim woman as a revolutionary. In Neshat’s early photographs, “woman” always wears a chador, often points a gun, its barrel sometimes appears to be in the place of earrings. And then there are the layers of Persian calligraphy. At first glance the Farsi poems of contemporary Iranian women appear to be neatly inked on to the face of “woman”, her hands or her feet. On closer inspection the viewer realises that the writings are meticulously applied to the prints, rather than directly tattooed on to exposed skin. The inky calligraphy writings are confusing mappings that create barriers for non-Farsi speaking viewers, who may be forced into perceiving these texts in their graphic beauty as mere decoration, or as cultural codes that are incomprehensible [
22], beyond grasp of their meanings, and hence experience feelings of failure and a longing “to understand the map”.
Glas Journal is an organically growing multi-layered project that allows the participants and myself to deal with writing as a source of cure and poison simultaneously, in order to come to terms with moments of crisis, whether economic, personal or spiritual, and to overcome the binary oppositions of remembering/forgetting. Deep Mapping processes relate to unstable states and ambivalent emotions that may lead to the discovery of fragments that are confusing. However, as deep maps allow for multiple expressions and interpretations, they cannot “go wrong”.
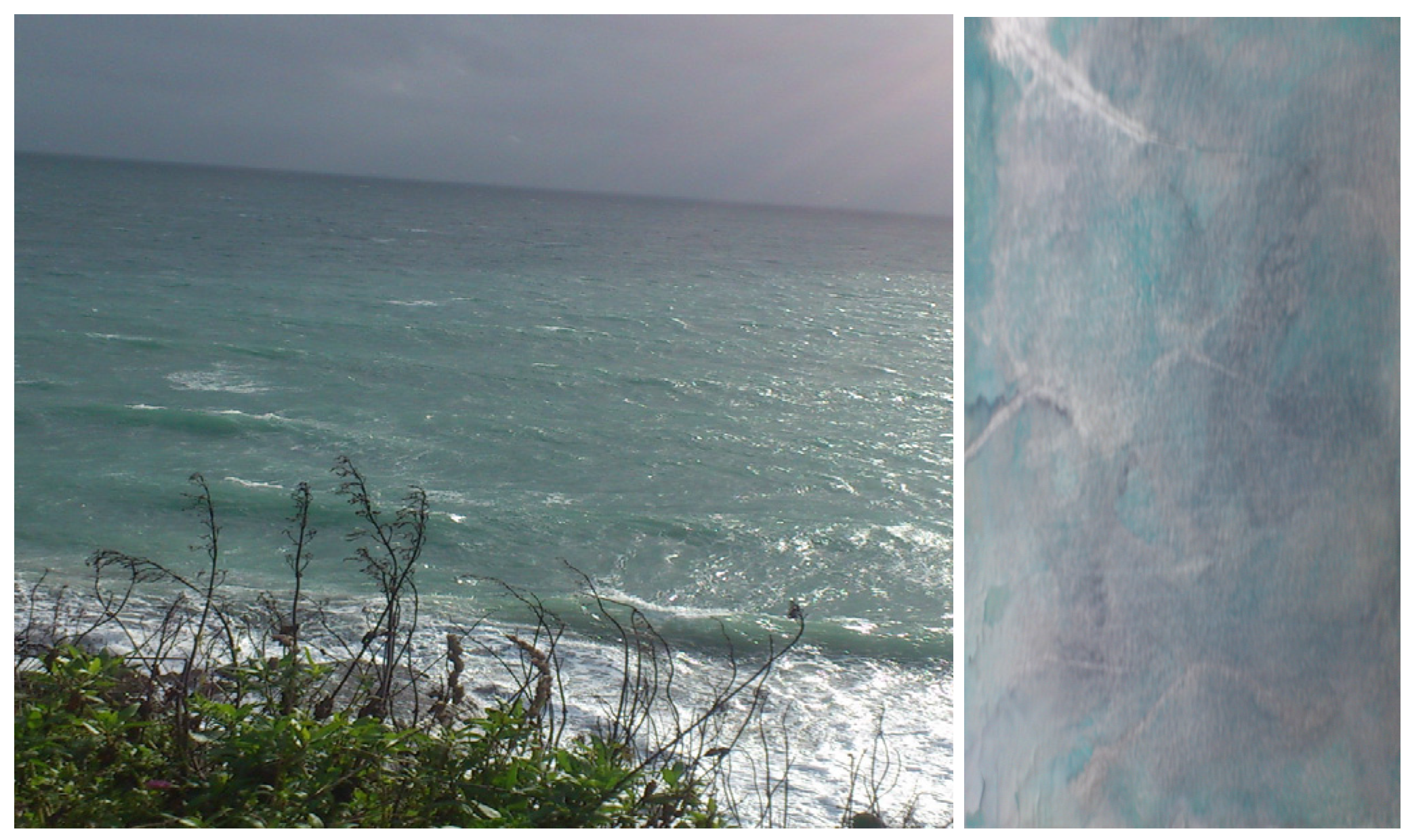
5. Liquid-Coloured Mappings of Belonging and Longing
In Irish, the word
glas is reserved for the indefinite shades of green, blue and grey that are present in the sea. I take this chromatic generosity as a marker for
Glas Journal. By using layered colour occurrences as a metaphor for the multiple processes that occur in works of deep mapping framed by artistic narratives, I seek to transform binary oppositions of spatial laws and their fixed regularity into a fluid and performative discourse. A “translation” of colour semantics taking place, as suggested in
Figure 5, where
glas as a colour of nature and the Irish Sea in particular becomes a visio-cultural register for cultural liquidity in
Glas Journal.
Figure 5.
Glas coloured Irish Sea and glas on paper, 2014. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
Figure 5.
Glas coloured Irish Sea and glas on paper, 2014. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
Glas as a colour in old Irish and in Welsh is also used for grassy patches and the skin tone of dead animals, both rather confined, opposed to the general idea of “the boundless, infinite sea” [
23], but in its liquid function it could not be applied to the Pacific, for instance, or to the Mediterranean Sea, which Homer described as “winedark” in
The Illiad.
Homer’s sea, whether háls, thálassa, or póntos, is described as misty, darkly troubled, black-dark, and grayish, as well as bright, deep, clashing, tumultuous, murmuring, and tempestuous—but it is never blue. The Greek word for blue, kuáneos, was not used of the sea until the late sixth or early fifth century BC, in a poem by the lyric poet Simonides—and even here, it is unclear if “blue” is strictly meant, and not, again, “dark”.
The Roman word
locus (deriving from “to stand”) equates to the Greek
topos. The ancient Greeks used
topos for any kind of place, if it were to be found in a book, body, landscape or any other kind of discourse.
Chora, the Greek used for larger settlements, relates to the verbal description of places. In Hellenistic Greece, chorography referred to the quality of place, to the description of a given area and all its particularities. Traditional cartographers, like surveyors, aim at an exact visual reproduction of space, whereas chorographers create a medley of geography, topography and history of a place that is based on a heteroglossic narrative. Joseph Rykwert describes chorophilia as an archaic expression that may be used to describe the relationship between an exile and their homeland, and states that Joyce’s
Ulysses is “one of the grandest monuments to the non-returning exile”s chorophiliac nostalgia’ ([
25], pp. 14–16). Contrasting colour references of the sea are found in numerous literary accounts of aquatic locations. A sense of familiarity, the taste and smell of a place, its climate and its colours, contribute to emotional stability and security. If one is deprived of this sense, nostalgia comes into being. How do personal ties to specific locations come to be understood as signifiers that encompass the human desire to feel safe in landscapes that were formerly shaped by high productivity, but now appear to have been taken over by notions of emptiness, melancholia and ghosts from the past?
Whereas Homer talked about the “winedark” sea in a Greek context, Joyce did neither use “glas” nor “winedark” but “snot green” for the Irish Sea. Joyce’s reference in
Ulysses, where he describes “the mailboat clearing the harbour mouth of Kingstown” (Dún Laoghaire’s name when it was part of the British Empire) brings up once more the fact that places in transition phases often change colour as well as names.
He mounted to the parapet again and gazed out over Dublin bay, his fair oakpale hair stirring slightly.
God, he said quietly. Isn’t the sea what Algy calls it: a great, sweet mother? The snot green sea. The scrotum tightening sea. Epi oinopa ponton. Ah Daedalus, the Greeks. I must teach you. You should read them in the original. Thalatta! Thalatta! She is our great, sweet mother. Come and look.
Stephen stood up and went over to the parapet. Leaning on it he looked down on the water and on the mailboat clearing the harbour mouth of Kingstown.
The original map fragment of Kingstown shown in
Figure 6 is property of the Dún Laoghaire Harbour Company and currently in storage in the Ferry Terminal. It is a beautifully drawn drainage map that depicts a winedark border line marking a “proposed intercepting sewer” and dates back to 29 September 1873, a year when Joyce was not even born yet, and Kingstown/Dún Laoghaire basked in the afterglow of a building boom, having ten years previously been described as “the wealthiest and most popular township in Ireland” ([
27], p. 99).
Figure 6.
Map fragment, 2015 [1873]. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
Figure 6.
Map fragment, 2015 [1873]. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
The use of a dark red borderline leads to a contemporary interpretation of Homer’s use of “winedark” as an aquatic colour and brings up notions of the blood red of water because of the death of thousands of migrants on maritime borders. The winedark sea ties in with passages across the water to reach the place one may call home, and to belong. Given the humanitarian disasters of boat people in the Mediterranean Sea and in South East Asia, the term “Asylum Harbour”, which is what Dún Laoghaire Harbour was historically called before it became the “Royal Harbour of George IV at Kingstown” ([
27], pp. 20–21, 26), takes on new meanings of large-scale global dimensions. Mapping the theme of belonging asks, perhaps more than anything, to put displacement on to a map, and to give it a name and a home in a space of protection.
“What is a space of protection?”, “Who am I in it?”, and “Who is the Other?” are main research questions in
Glas Journal in order to establish a model of cultural practice that attempts to create a broader understanding of visual and spatial experiences on a local level in Dún Laoghaire Harbour. The enquiry does not focus on the mastery of a certain historio-geographical discourse, but stresses the importance of the bricolage, the fragmentation and the in-between in its production of meanings. One of the concerned harbour spaces that is being deep-mapped for
Glas Journal and evokes feelings of stability and safety but has undergone profound changes on liquid ground is Dún Laoghaire’s old coastguard station with the adjacent coastguard cottages. Renowned maritime historian John de Courcy Ireland stated that one of the functions of the British Coast Guard service operating in Ireland from the 1830s onwards until independence was to help vessels in distress, and that the service, which “was normally manned by former naval men and worked under semi-military discipline” [
28], was strongly successful in saving lives, albeit the local population was inclined to support smugglers and opponents of British Rule.
Dún Laoghaire’s Coast Guard Station, as shown in the map fragment of
Figure 7, the original being stored by the Dún Laoghaire Harbour Company and dating back to 1911, a year where the township of Kingstown was still on the rise, echoes the boundary status and dialectic of the liquid threshold in its spatial representation.
Figure 7.
Map fragment, 2015 [1911]. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
Figure 7.
Map fragment, 2015 [1911]. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
Currently only three of the eight residential units are occupied. Two units are family homes, and one cottage is home to the Dún Laoghaire Arts Centre downstairs, and three individual artist studios upstairs (one taken over by myself). Some of the empty units are used as storage space, and, occasionally, as a film set.
All throughout Ireland there are similar styles to “my” Coast Guard Station. The watchtower stands tall over the residential units that were initially intended for crew members and their families. The layout itself is a reminder of Jeremy Bentham’s
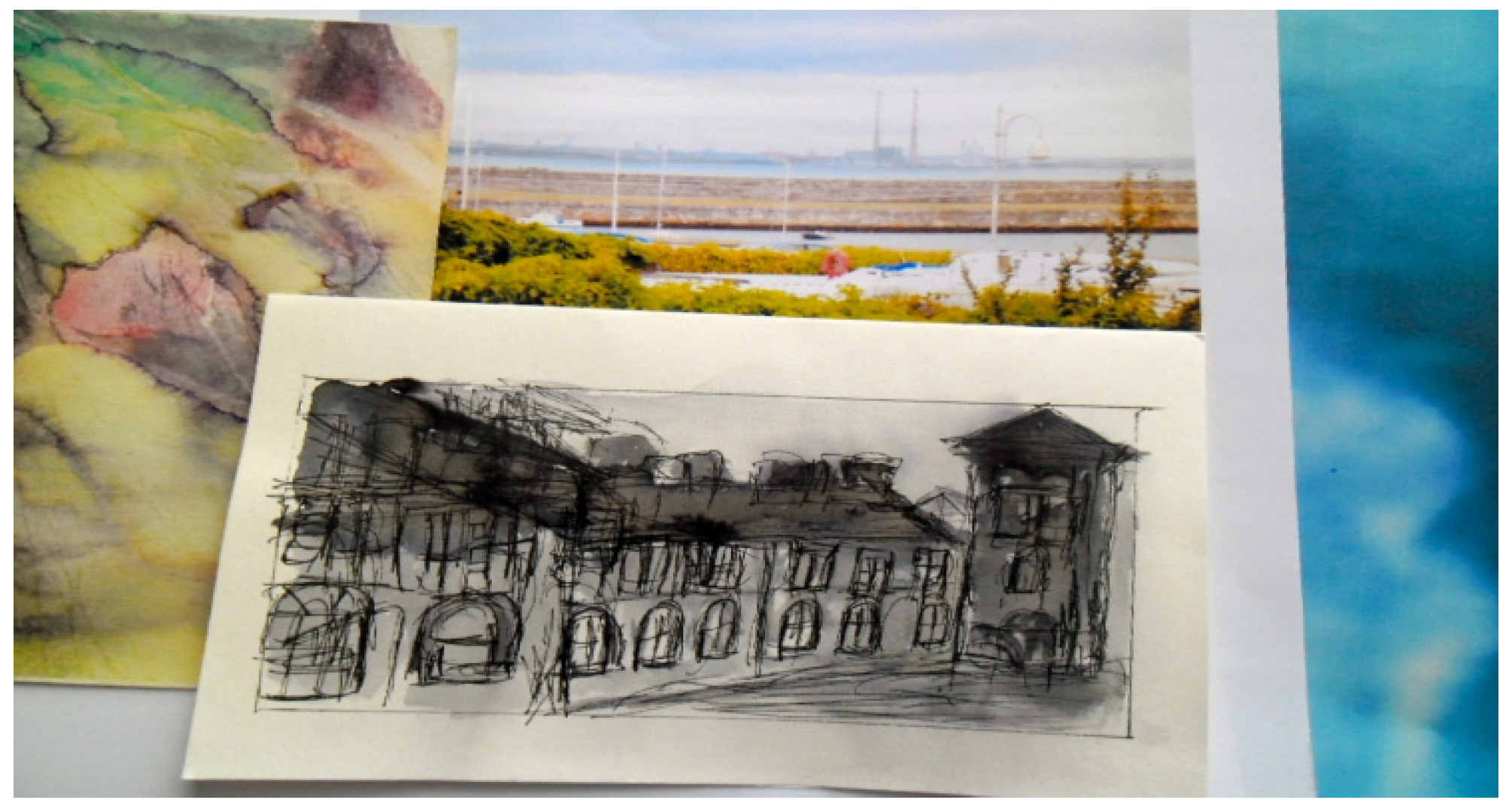
panopticon used for institutional architecture, like the asylum, the hospital, and the prison. Yet I love this building, the fragments depicted in
Figure 8 paying only small homage to its magic. I have been working in the Coast Guard Cottages for three years. I feel the building’s solidity and peace, its proximity to the sea. Its severe structure is softened by the lush gardens and wildly changeable coastal weather. I often look out of my studio window over the gardens to the West Pier and into Dublin Port and wonder who has had that view before me.
Figure 8.
Coast Guard Station fragments, 2015. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
Figure 8.
Coast Guard Station fragments, 2015. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
Allen, artist son of a sea captain, and his group of painters, the Dún Laoghaire Art Centre, have occupied several locations in the harbour throughout the years and have been based in the Coast Guard Cottages for almost a decade, first in Number One, and now in Number Three. Miriam, one of the fellow artists and a local of Dún Laoghaire, kept a communion certificate that she found at the time when the studios were based in Number One. The document conveys that a resident who lived in the Coast Guard Cottages approximately one hundred years ago, a little girl called Maisie McDonald, made her Holy Communion on 27 May 1916, one month after the Easter Rising, when an independent Irish state was established. As it happens, 27 May is also the birth date of Miriam’s daughter, who is now the guardian of the fragment of Number One, Coast Guard Cottages, which is depicted in
Figure 9.
Figure 9.
Coast Guard Cottages fragment, 2015. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
Figure 9.
Coast Guard Cottages fragment, 2015. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
One of the central issues of linguistic anthropology is the importance of language and place names, the use of metaphor as well as the uses of silence, blank spaces and gaps, which help us to define our modes of belonging on liquid grounds, and
Glas Journal hopes to open the doors to spaces we knew nothing of before we were handed a snippet of random information. When describing his study of Western Apache senses of place, Keith Basso points out that the ways in which native people communicate about their landscape “may shed light on matters other than geography” ([
29], pp. 101–2). “Belonging” in the English language originally had spatial implications rather than referring to possession or ownership. Boullata compares this meaning to the word’s Arabic roots. In Arabic “belonging” (
intima) refers to an activity—to develop, to make progress, and its original English meaning refers to a relationship between two things that “may be equally long and run parallel”, they share something significant, require each other. The Yanomami, a semi-nomadic tribe in the Amazon, on the border between Brazil and Venezuela, perceive themselves as belonging to the land, as opposed to the land belonging to them. They consider their territory as alive, in constant change and movement and do not live with the concept of the border as a line that is not to be crossed [
30].
When contemporary Islamic artist, Emily Jacir, an American-Palestinian, who is able to travel freely where displaced Palestinians are not allowed to go, collected people’s wishes that were mostly of a mundane nature, she went about to look for somebody’s house, visit somebody’s mother’s grave, and pay a phone bill for a man in the post office of Jerusalem. Jacir followed in Walter Benjamin’s footsteps to trace life, in her case, the vanished life of others, to negotiate meanings of home. Whereas Mona Hatoum’s maps and spheres often relate to objects of domesticity (like colanders, graters, soap bars and neon tubes), and where the objects extend themselves to being unstable maps because they are objects without belonging to a place, Jacir’s approach to people who live in exile was to weave their fragments of meanings of home into a metaphorical tapestry of connections. She acted on behalf of the exiled person’s desires and travelled to Jerusalem or Haifa to carry out their wishes, brought very mundane things back and forth, or attended events on their behalf, and as such gave a narrative to the history of displaced individuals whose former home in its physicality is unattainable to them. By collecting these fragments to document
Where We Come From, 2001–2003, which first appeared as a magazine publication on Palestinian territory [
31], Jacir’s work deals with mapping others’ (and perhaps her own) up-rootedness. When Jacir crossed geographical borders for those who are not allowed to do so freely, she also crossed boundaries between arts practice, individual life histories and politics by producing a cultural work that emphasises the multi-faceted textures of spatiality, travelling and belonging.
In her work
Atlas of Emotion (2002), Giuliana Bruno insists on the entwined nature of seeing and travelling. She connects “emotion” with “motion”, “sight” with “site” and metaphorically draws polyphonic interdisciplinary maps that are based on cultural life. In accordance with Bruno’s work, a creative form of mapping that gives information about places and spaces in a visual context, and that differs from traditional cartographic and architectural models, was chosen as the topic of enquiry for
Glas Journal. To elaborate upon mapping techniques that defy the box-ticking systems of control of classified western cartography, and to integrate forms of belonging and displacement on a deep map, also means to integrate forms of longing. The hand-made artist books in
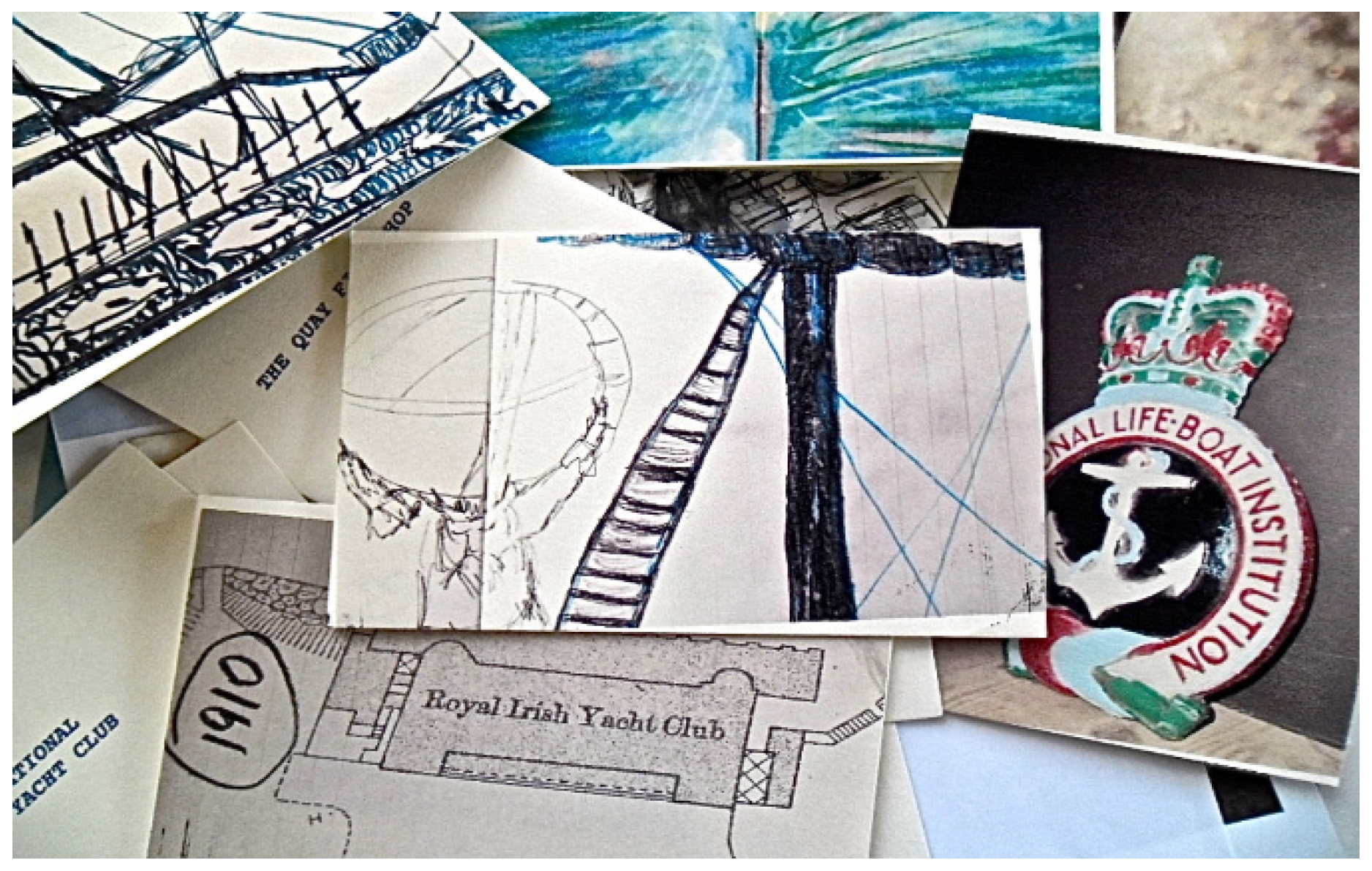
Glas Journal that are currently in the process of being made, as demonstrated in
Figure 10, stand for individual places in the harbour and are included as a valuable source of information for the visual emotional vocabulary that constitutes urban palimpsests (the palimpsest referring to the multiple possible readings of public space as a text), wherein arts research practice criss-crosses with cultural geography, visual culture and critical theory.
Figure 10.
Glas Journal fragments, 2015. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
Figure 10.
Glas Journal fragments, 2015. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
The idea to put a spatial discourse into books goes back to the idea of inner space, of finding a way to express an inner infrastructure that captures modes of being. The books reveal themselves as sites of emotional habitat, bearing to stay with the spaces of the present that differ from a colonial past, but still carry its heritage. A liquid or deep way of mapping may expose some aspects of this patrimony, but has no interest in “fixing” history. Rather, the attempt is being made to relate “the story” or “the image” to pictures, scenes and sounds of everyday life and to bring a fragmented discourse, where dispersal and disintegration are woven into places, home.
6. Conclusions: Journeys and Journals as Wayfinders
Multi-sited or hybrid explorations of ethnographic space asks for new cultural productions of spatial meanings. In order to create such an alternative cultural production that concerns the public sphere of the harbour with a narrative that is built upon a multiplicity of different voices, I am looking at places “through discovered metaphorical associations”, as Marcus terms it ([
32], p. 108). The artist books in
Glas Journal stand not only for places but also for representational forms of feelings that constitute a fluid and multi-sensory map of the harbour. I chose for a hybrid assemblage of narrative structures because the patching together of a varied amount of cultural material allows for an exploration of intimacy with public space in a way that I could not have grasped with the objectively structured methods of a scientific analysis, resulting in a map that is “to be trusted”.
As shown in Emily Jacir’s working to produce memory cloth of Palestine for exiles, where she interweaved spatial attachment strands of individuals to a homeland that only exists in memory, an emotional mapping of spaces that includes wishes and desires cannot be easily understood through questionnaires or public opinion surveys. Instead, fragments from personal narratives provide insights about difficult feelings that circuit around loss, change and insecurity. Gaps, errors and discontinuities of an emotional discourse will also offer significant “data” about the atmosphere of a place, including its mood and energy. From these materials, a map can be created that situates local knowledge through the space-times of cultural myths, local icons, and shared histories.
The hybrid forms of how we make sense of places are muddled, contrary and in-between by its nature, and prove difficult to be pressed into a specific typology of rigid parameters. If experiential explorations of being in a space, and of subsequently creating a journal that functions like a memory trail by extracting personalised symbols of oral history accounts are dealt with as patchwork pieces, the fragmented narrative allows for a circular-structured investigation and randomness that addresses the ambiguity of threshold spaces. This kind of approach leaves it up to “the participants”, “the creators”, “the travellers of their own spaces” to inject their journals with cultural meaning. It also functions as a tool to critique the linear concept of borderlines that divide A from B, and, in this way, to simultaneously question the satisfaction that the Social Sciences derive from finite and neat chronological narration models.
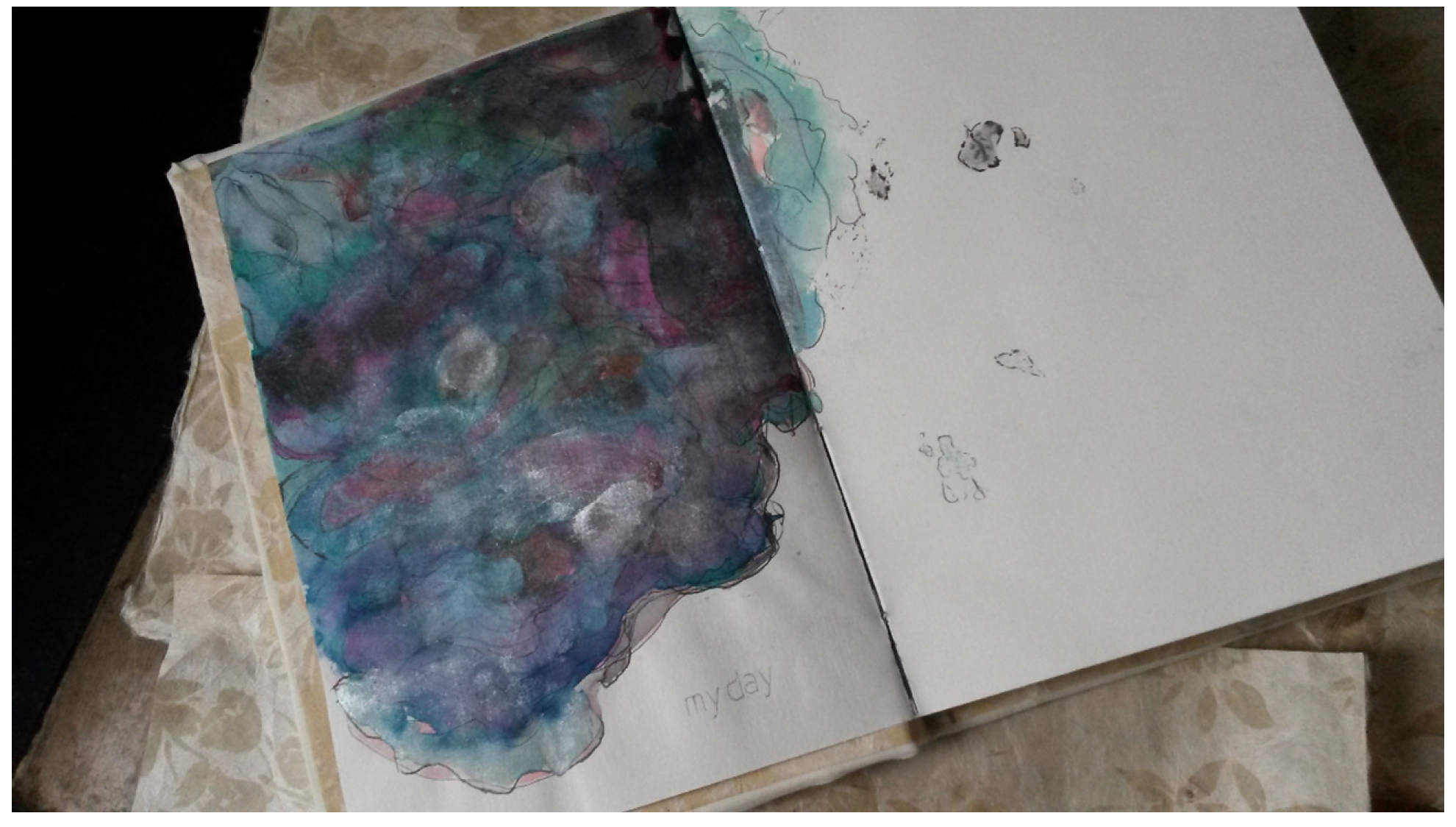
Writing enables self-reflection, but by putting the Self on to a map that is always unfinished, incomplete and contradictory, the writer has to face up to the ambivalence of intimacy, in order to reveal what their day may literally and visually be like. Sometimes, it is not possible to put feelings or memories on a map, particularly if meant for public display, and so the page stays empty, and, perhaps, left to the viewer’s imagination, like in
Figure 11.
Figure 11.
My day fragment, 2015. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
Figure 11.
My day fragment, 2015. © Silvia Loeffler, Glas Journal, 2015.
Deep mapping is the process of collecting fragments in order to gain understanding of liminal spaces. In the creation of
Glas Journal, the participants and myself make artist books that contain map segments, drawings, paintings, photographs, sound recordings, and objects, showing puzzling connections and intersections, exciting loose bits and frustrating gaps that form a different kind of topography—a deep map. My mapping of Dún Laoghaire Harbour hopes to make visible a larger story about place, belonging and public intimacy, contributing to interdisciplinary debates where space is more than a “flat surface” that we travel across. It co-constitutes the social through the simultaneous, unfolding pathways of life stories ([
33], p. 5). Deep Mapping is very often about rituals of space. Iain Biggs introduces Anthony Lyons’ deep mapping project of the Quantock Hills in Britain, which was called
Quantock Dreaming. Secret Mappings and Mapping Secrets (2008), and which he conducted with members of the public and in co-operation with poet Ralph Hoyte, as a “slow residency” [
34]. The term resonates with Werner Hamacher’s philological treatise and his notions of waiting. Before the expectations waiting was there all along, which in German is a lovely word play: “Vor der Erwartung war das Warten” [
35]. Waiting for Hamacher appears to be the space where one is holding back as well as holding open. The space of waiting is full of hidden meanings, and it is liminal.
Glas Journal reflects meanings of the sea, of home, of harbour. The deep mapping work for Glas Journal in the form of a slow residency intertwined with waiting happens in the Coast Guard Cottages (the studio site), on the harbour stretch between West and East Pier (the work site), in the Maritime Museum (the archival site), and—literally—in the Irish Sea (the swimming site). In connecting all these sites spatially, physically and artistically on a daily basis, several crossings take place that relate to historical and individual passages, almost pilgrim-like constructs of journeys at times. By looking at the community function of “containing” wholesome internal space, as opposed to the fragmented and uncontained, which is accompanied by the melancholia of loss and nostalgia for a Golden Age, the harbour as a womb-like space may also be interpreted as a sacred space that has the translucent quality of water leading from darkness to light.
The creation of an artistic harbour installation as a space of protection with artist books that form the reference points of maps speaks of the possibility to accommodate multiple narratives about meanings of liquidity as well as of solidity and shelter. Even though all structures are unstable, public intimacy as a concept for the empathetic exploration of spaces is very exciting because it relates to a powerful public engagement concerning the production of space by looking at its performative elements. Deep mapping is also about the re-claiming of ownership of living and work places by creating a many-faceted framework of spatial understanding and weaving it into a rich multi-sensual narrative by posing the crucial question of “How do you feel connected to this place?”