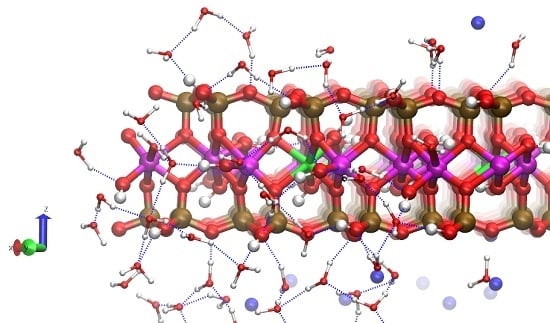
Na-Montmorillonite Edge Structure and Surface Complexes: An Atomistic Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.2. Density Functional Theory (DFT) Geometry Optimizations
3. Results
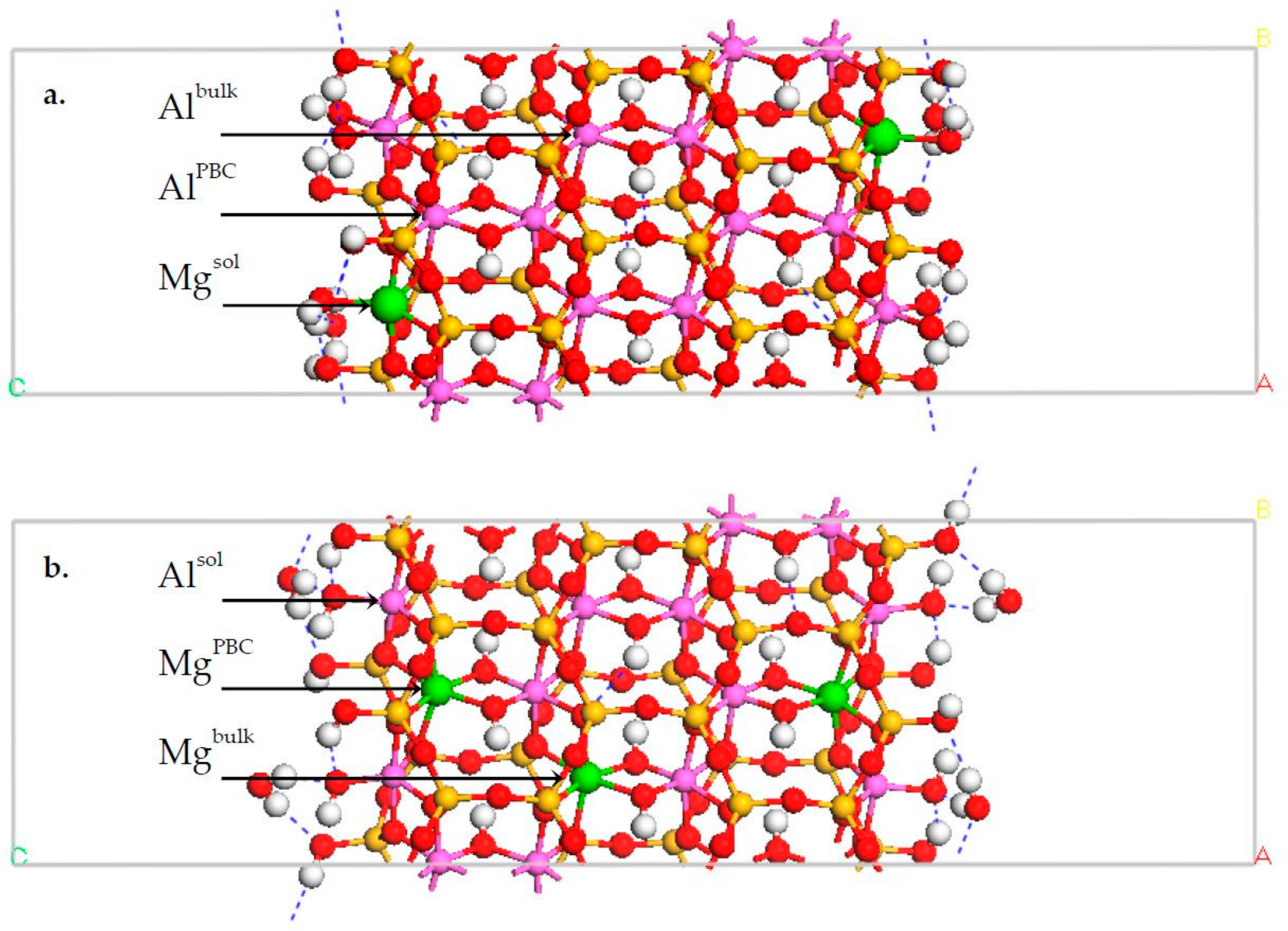
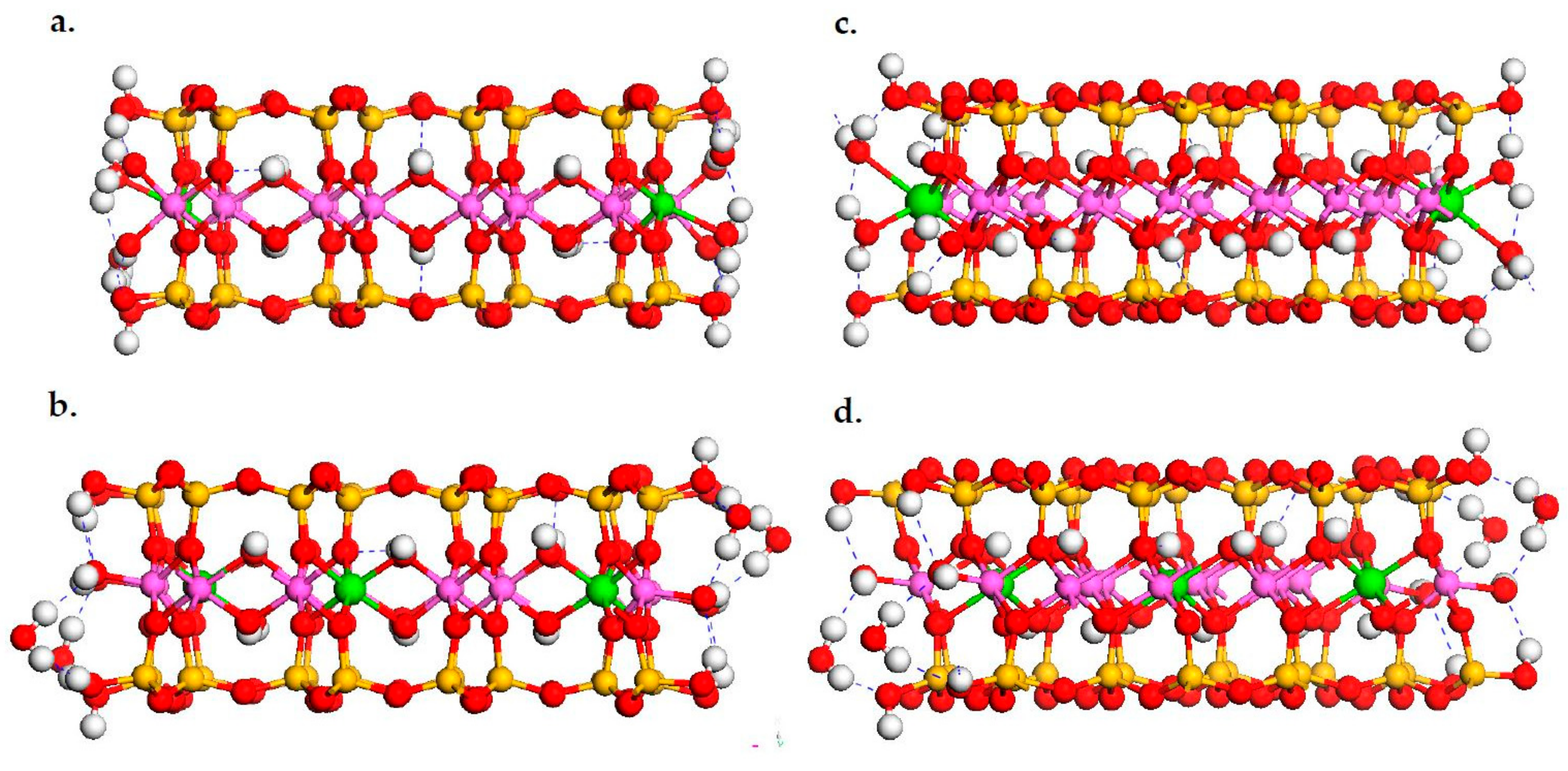
3.1. DFT Calculation Results
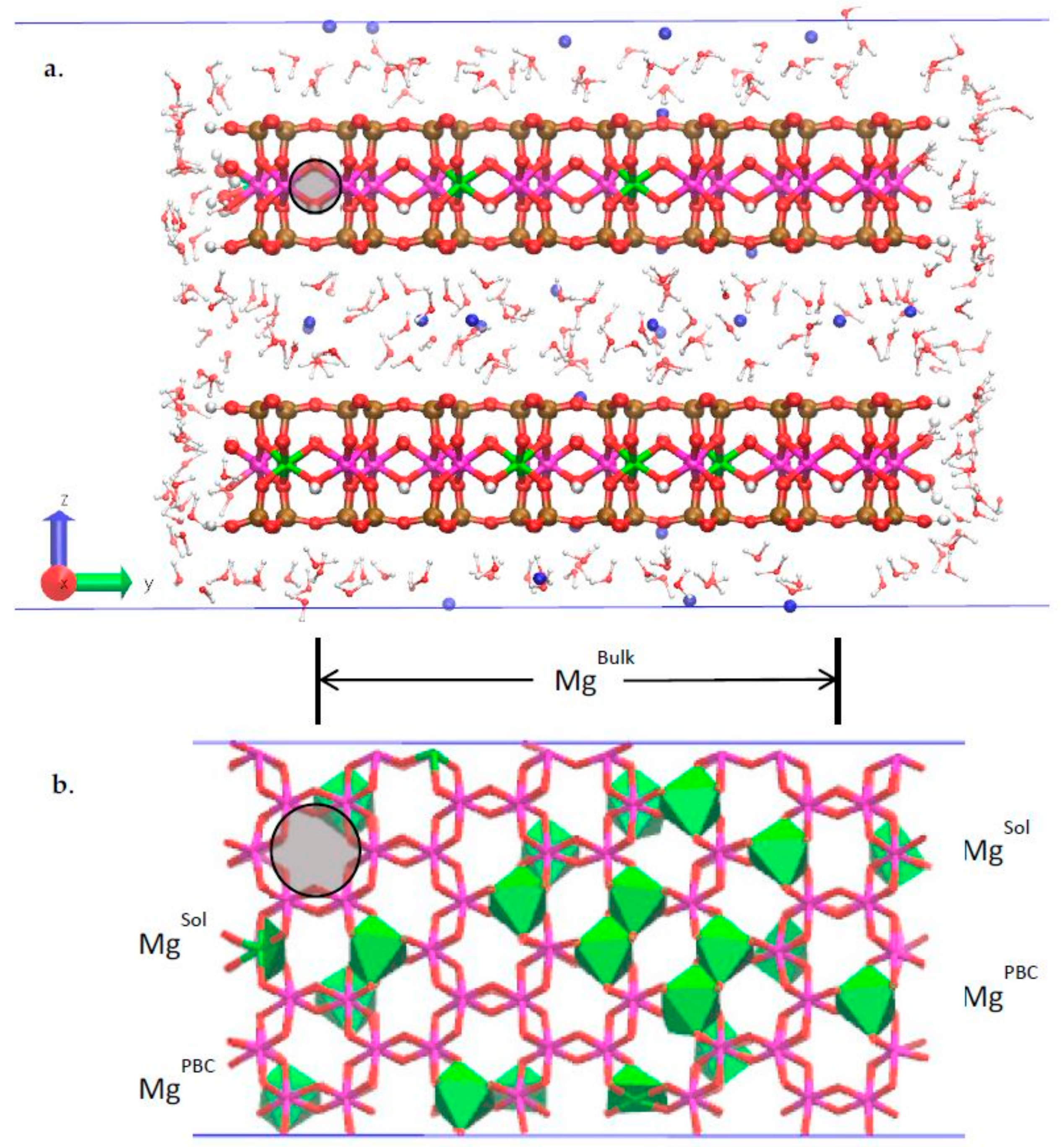
3.2. Classical MD Simultion Results
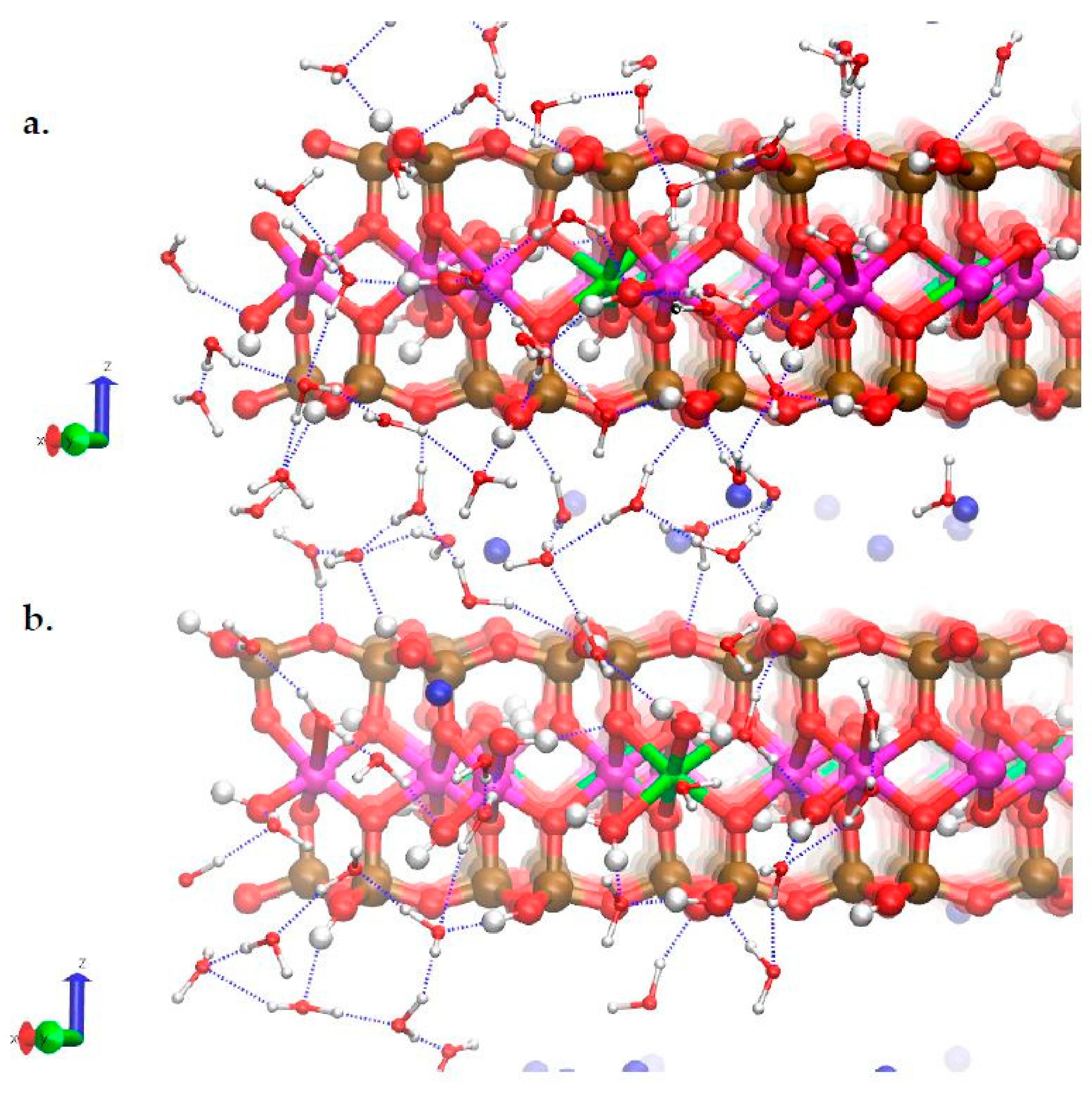
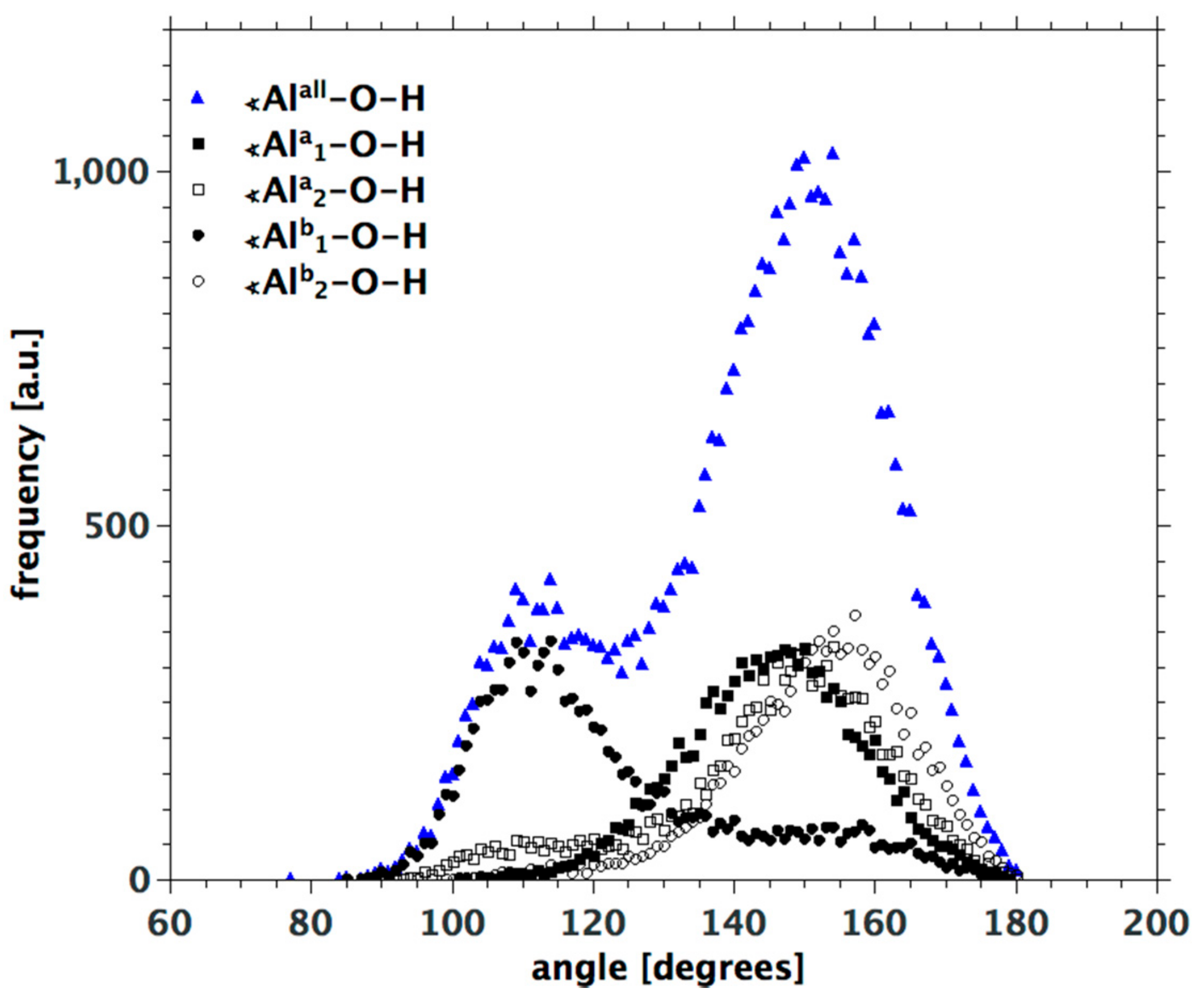
3.3. H-Bond Network at the Na-Montmorillonite B Edge
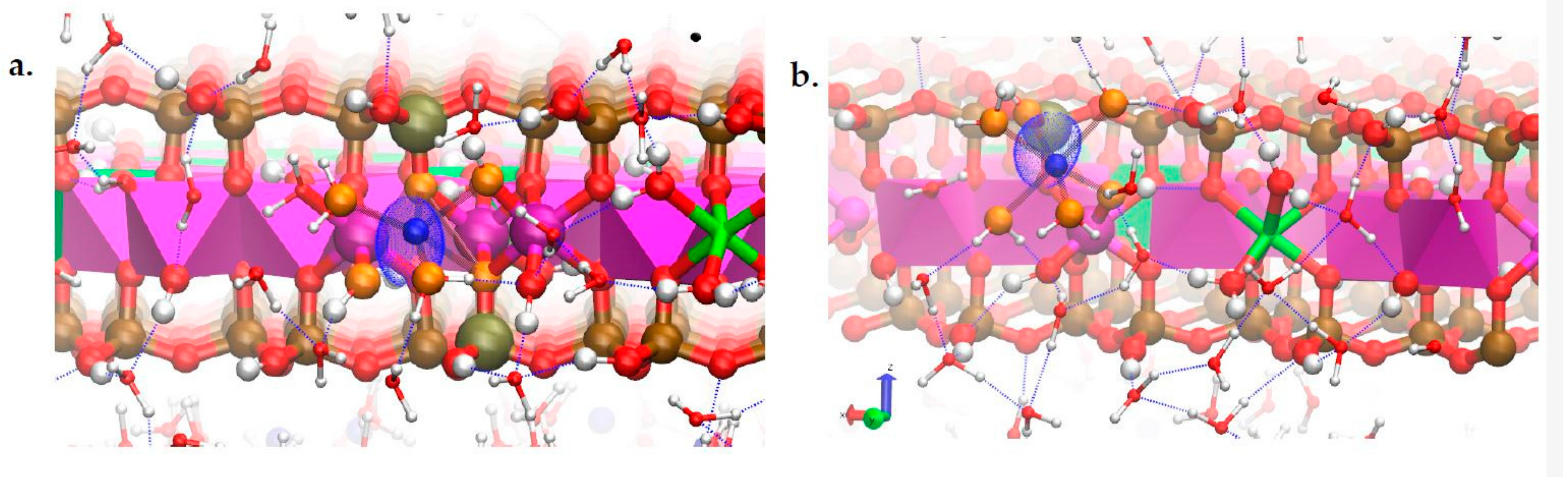
3.4. Na-Montmorillonite B Edge Adsorption Sites
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sposito, G. The Chemistry of Soils, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A.W.; Wang, Y. Radionuclide interaction with clays in dilute and heavily compacted systems: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1981–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusch, R.; Karnland, O. Physico chemical stability of smectite clays. Eng. Geol. 1996, 41, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournassat, C.; Bourg, I.C.; Steefel, C.I.; Bergaya, F. Natural and engineered clay barriers. In Developments in Clay Science 6; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 6, pp. 5–432. [Google Scholar]
- Boulet, P.; Coveney, P.V.; Stackhouse, S. Simulation of hydrated Li+-, Na+- and K+-montmorillonite/polymer nanocomposites using large-scale molecular dynamics. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 389, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.D.; Lu, X.C.; Wang, R.C.; Zhou, H.Q.; Xu, S.J. Interlayer structure and dynamics of alkylammonium-intercalated smectites with and without water: A molecular dynamics study. Clays Clay Miner. 2007, 55, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.R.; Yang, X.N. Molecular simulation of swelling and interlayer structure for organoclay in supercritical CO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Choi, G.; Elzatahry, A.; Vinu, A.; Choy, Y.B.; Choy, J.H. Review of clay-drug hybrid materials for biomedical applications: Administration routes. Clays Clay Miner. 2016, 64, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, E.; Baeyens, B.; Maes, A.; Cremers, A. Cesium and rubidium ion equilibria in illite clay. J. Phys. Chem. 1983, 87, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzinga, E.J.; Sparks, D.L. Nickel sorption mechanisms in a pyrophyllite-montmorillonite mixture. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 213, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, J.D.; Semrau, J.D.; Hayes, K.F. An X-ray absorption spectroscopy study of the structure and reversibility of copper adsorbed to montmorillonite clay. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 2709–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachara, J.M.; Smith, S.C.; Liu, C.X.; McKinley, J.P.; Serne, R.J.; Gassman, P.L. Sorption of Cs+ to micaceous subsurface sediments from the hanford site, USA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, M.H.; Baeyens, B. A mechanistic description of Ni and Zn sorption on Na-montmorillonite 2. Modelling. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1997, 27, 223–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dähn, R.; Baeyens, B.; Bradbury, M.H. Investigation of the different binding edge sites for Zn on montmorillonite using P-EXAFS—The strong/weak site concept in the 2SPNE SC/CE sorption model. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 5154–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, G.N.; Zelazny, L.W. Analysis and implications of the edge structure of dioctahedral phyllosilicates. Clays Clay Miner. 1988, 36, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, P. Crystal Growth: An Introduction; North-Holland Publishing Co./American Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Bickmore, B.R.; Rosso, K.M.; Nagy, K.L.; Cygan, R.T.; Tadanier, C.J. Ab initio determination of edge surface structures for dioctahedral 2:1 phyllosilicates: Implications for acid-base reactivity. Clays Clay Miner. 2003, 51, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churakov, S.V. Ab initio study of sorption on pyrophyllite: Structure and acidity of the edge sites. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 4135–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churakov, S.V. Structure and dynamics of the water films confined between edges of pyrophyllite: A first principle study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 1130–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremleva, A.; Kruger, S. Comparative computational study of Np(V) and U(VI) adsorption on (110) edge surfaces of montmorillonite. Clays Clay Miner. 2016, 64, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremleva, A.; Kruger, S.; Rosch, N. Uranyl adsorption at solvated edge surfaces of 2:1 smectites. A density functional study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 13757–13768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremleva, A.; Krüger, S.; Rösch, N. Toward a reliable energetics of adsorption at solvated mineral surfaces: A computational study of uranyl(VI) on 2:1 clay minerals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, X.; Meijer, E.J.; Wang, R.; Zhou, H. Atomic-scale structures of interfaces between phyllosilicate edges and water. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 81, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, X.; Sprik, M.; Cheng, J.; Meijer, E.J.; Wang, R. Acidity of edge surface sites of montmorillonite and kaolinite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 117, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.D.; Cheng, J.; Sprik, M.; Lu, X.C.; Wang, R.C. Surface acidity of 2:1-type dioctahedral clay minerals from first principles molecular dynamics simulations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 140, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazi, S.; Rotenberg, B.; Salanne, M.; Sprik, M.; Sulpizi, M. Absolute acidity of clay edge sites from ab-initio simulations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 94, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.G.; Sposito, G. Molecular dynamics simulations of pyrophyllite edge surfaces: Structure, surface energies, and solvent accessibility. Clays Clay Miner. 2015, 63, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cygan, R.T.; Liang, J.J.; Kalinichev, A.G. Molecular models of hydroxide, oxyhydroxide, and clay phases and the development of a general force field. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelman, C.H.; Favejee, J.C.L. On the crystal structure of montmorillonite and halloysite. Z. Kristallogr. 1940, 102, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.D.; Newton, A.G. Structure and stability of pyrophyllite edge surfaces: Effect of temperature and water chemical potential. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 190, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.; Kwon, K.; Cheong, D.-K. Edge structure of montmorillonite from atomistic simulations. Minerals 2016, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleam, W.F.; Welhouse, G.J.; Janowiak, M.A. The surface coulomb energy and proton coulomb potentials of pyrophyllite (010), (110), (100), and (130) edges. Clays Clay Miner. 1993, 41, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, J.L.; Kabalan, L.; Khader, M.; Coveney, P.V. Ab initio molecular dynamics study of the interlayer and micropore structure of aqueous montmorillonite clays. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 169, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadars, S.; Guegan, R.; Garaga, M.N.; Bourrat, X.; Le Forestier, L.; Fayon, F.; Huynh, T.V.; Allier, T.; Nour, Z.; Massiot, D. New insights into the molecular structures, compositions, and cation distributions in synthetic and natural montmorillonite clays. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 4376–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz-Diaz, C.I.; Timon, V.; Botella, V.; Artacho, E.; Hernandez-Laguna, A. Quantum mechanical calculations of dioctahedral 2:1 phyllosilicates: Effect of octahedral cation distributions in pyrophyllite, illite, and smectite. Am. Mineral. 2002, 87, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz-Díaz, C.I.; Cuadros, J.; Hernández-Laguna, A. Analysis of cation distribution in the octahedral sheet of dioctahedral 2:1 phyllosilicates by using inverse monte carlo methods. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2001, 28, 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Lantenois, S.; Champallier, R.; Bény, J.M.; Muller, F. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of dioctahedral smectites: A montmorillonites series. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 38, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinholdt, M.; Brendlé, J.; Tuilier, M.-H.; Kaliaguine, S.; Ambroise, E. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of Ni-Al montmorillonite-like phyllosilicates. Nanomaterials 2013, 3, 48–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinholdt, M.; Miehe-Brendle, J.; Delmotte, L.; Le Dred, R.; Tuilier, M.H. Synthesis and characterization of montmorillonite-type phyllosilicates in a fluoride medium. Clay Min. 2005, 40, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinholdt, M.; Miehe-Brendle, J.; Delmotte, L.; Tuilier, M.H.; le Dred, R.; Cortes, R.; Flank, A.M. Fluorine route synthesis of montmorillonites containing Mg or Zn and characterization by XRD, thermal analysis, MAS-NMR, and EXAFS spectroscopy. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 2831–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerich, K.; Wolters, F.; Kahr, G.; Lagaly, G. Clay profiling: The classification of montmorillonites. Clays Clay Miner. 2009, 57, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Grigera, J.R.; Straatsma, T.P. The missing term in effective pair potentials. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 6269–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Lemus, J.; Chapela, G.A.; Alejandre, J. Effect of flexibility on surface tension and coexisting densities of water. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 128, 174703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasawa, N.; Goddard, W.A. Acceleration of convergence for lattice sums. J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 7320–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimpton, S.J. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckaert, J.-P.; Ciccotti, G.; Berendsen, H.J. Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: Molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J. Comput. Phys. 1977, 23, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Schmidt, J.R.; Skinner, J.L. Hydrogen bonding definitions and dynamics in liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 204107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.J.; Segall, M.D.; Pickard, C.J.; Hasnip, P.J.; Probert, M.J.; Refson, K.; Payne, M.C. First principles methods using CASTEP. Z. Kristallogr. 2005, 220, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderbilt, D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1990, 41, 7892–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, M.; Gillan, M.J. The energy and elastic dipole tensor of defects in ionic-crystals calculated by the supercell method. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1985, 18, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J. Aquatic Chemistry: Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural Waters, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mulliken, R.S.; Roothaan, C.C.J. Electronic population analysis on LCAO–MO molecular wave functions. I. J. Chem. Phys. 1955, 23, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleuzen, A.; Pittet, P.A.; Helm, L.; Merbach, A.E. Water exchange on magnesium(II) in aqueous solution: A variable temperature and pressure 17O NMR study. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1997, 35, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, J.; Connick, R. Rate of water exchange from hydrated magnesium ion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1970, 92, 3476–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Lu, X.; Meijer, E.J.; Wang, K.; He, M.; Wang, R. Cadmium(II) complexes adsorbed on clay edge surfaces: Insight from first principles molecular dynamics simulation. Clays Clay Miner. 2016, 64, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churakov, S.V.; Dähn, R. Zinc adsorption on clays inferred from atomistic simulations and EXAFS spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 5713–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dähn, R.; Scheidegger, A.M.; Manceau, A.; Schlegel, M.L.; Baeyens, B.; Bradbury, M.H.; Chateigner, D. Structural evidence for the sorption of Ni(II) atoms on the edges of montmorillonite clay minerals: A polarized X-ray absorption fine structure study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W. Structures of layer silicates. In Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals and Their X-ray Indentification; Brindley, G.W., Brown, G., Eds.; Mineralogical Society: London, UK, 1980; Volume 5, pp. 1–124. [Google Scholar]
| Octahedral Surface Groups | Erel (kJ/mol) | |
|---|---|---|
| x1 = 0.25 | x2 = 0.375 | |
| ≡Al–(OH)(OH2) + ≡Al–(OH)(OH2) * | 0 | 0 |
| ≡Mg–(OH)(OH2) + ≡Al–(OH)(OH2) | −56.9 | 158.1 |
| ≡Mg–(OH2)2 + ≡Al–(OH)2 | −98.4 | 85.8 |
| ≡Mg–(OH)2 + ≡Al–(OH2)2 | 79.1 † | n/r |
| α-β Pair | Interatomic Distance (Å) | |
|---|---|---|
| x1 = 0.25 | x2 = 0.375 | |
| Alsol–O | 1.94 | 1.85 |
| Alsol–Ow | - | 3.74 |
| Alsol–Oh | 1.85 | 1.80 |
| Alpbc–O | 1.92 | 1.91 |
| Mgsol–O | 2.12 | - |
| Mgsol–Ow | 2.32 | - |
| Mgpbc–O | - | 2.07 |
| Albulk–O | 1.93 | 1.92 |
| Mgbulk–O | - | 2.07 |
| α-β Pair | rpeak (Å) | +/− | CN | +/− | ρ (Å) | +/− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alsol–O | 1.87 | 0.011 | 5.72 | 0.037 | 2.81 | 0.067 |
| Alsol–Ow | 2.06 | 0.022 | 0.57 | 0.038 | 2.74 | 0.101 |
| Alsol–Oh | 1.85 | 0.008 | 1.14 | 0.000 | 2.11 | 0.022 |
| Alpbc–O | 1.95 | 0.010 | 6.00 | 0.001 | 2.67 | 0.036 |
| Mgsol–O | 2.12 | 0.017 | 5.99 | 0.005 | 2.52 | 0.030 |
| Mgsol–Ow | 2.20 | 0.019 | 1.99 | 0.004 | 2.52 | 0.028 |
| Mgpbc–O | 2.11 | 0.012 | 6.00 | 0.003 | 2.44 | 0.027 |
| Albulk–O | 1.93 | 0.010 | 6.00 | 0.000 | 2.71 | 0.028 |
| Mgbulk–O | 2.11 | 0.005 | 6.00 | 0.000 | 2.46 | 0.025 |
| Surface Group | H-Bond | N(H-Bonds) | +/− |
|---|---|---|---|
| ≡Mg–(OH2)2 | Total | 1.54 | 0.287 |
| - | D | 1.53 | 0.281 |
| - | A | 0.01 | 0.050 |
| ≡Al–(OH)2 | Total | 1.46 | 0.329 |
| - | D | 0.47 | 0.244 |
| - | A | 0.99 | 0.186 |
| ≡Al(OH2)–(OH) | Total | 1.75 | 0.198 |
| - | D | 0.65 | 0.132 |
| - | A | 1.10 | 0.140 |
| ≡Al(OH)–(OH2) | Total | 1.24 | 0.233 |
| - | D | 1.24 | 0.231 |
| - | A | 0.01 | 0.043 |
| ≡Si–OH | Total | 1.31 | 0.132 |
| - | D | 0.78 | 0.081 |
| - | A | 0.53 | 0.106 |
| ≡SiAl–OH | Total | 1.18 | 0.308 |
| - | D | 0.79 | 0.200 |
| - | A | 0.39 | 0.230 |
| ≡SiMg–OH | Total | 1.50 | 0.375 |
| - | D | 0.86 | 0.173 |
| - | A | 0.64 | 0.297 |
| α-β Pair | rpeak, Å | CN | ρ, Å |
|---|---|---|---|
| a/b | a/b | a/b | |
| Na–O | 2.34/2.36 | 6.17/5.89 | 3.02/3.01 |
| Na–Ow | 2.37/2.37 | 1.98/3.99 | 2.83/3.12 |
| Na–Oh | 2.28/2.32 | 2.01/2.27 | 2.62/3.26 |
| Na–Ob | 2.49/5.26 | 1.97/14.37 | 3.18/6.23 |
| Na–Al | 3.27/3.53 | 2.99/1.01 | 3.91/3.99 |
| Na–Mg | 7.94/6.54 | 0.99/1.00 | 8.34/7.20 |
| Na–Si | 3.46/3.47 | 1.96/1.12 | 4.10/3.97 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Newton, A.G.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kwon, K.D. Na-Montmorillonite Edge Structure and Surface Complexes: An Atomistic Perspective. Minerals 2017, 7, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7050078
Newton AG, Lee J-Y, Kwon KD. Na-Montmorillonite Edge Structure and Surface Complexes: An Atomistic Perspective. Minerals. 2017; 7(5):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7050078
Chicago/Turabian StyleNewton, Aric G., Jin-Yong Lee, and Kideok D. Kwon. 2017. "Na-Montmorillonite Edge Structure and Surface Complexes: An Atomistic Perspective" Minerals 7, no. 5: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7050078