PDGFR and IGF-1R Inhibitors Induce a G2/M Arrest and Subsequent Cell Death in Human Glioblastoma Cell Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Ethical Statement
2.4. Cell Proliferation Assays
2.5. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Cell Cycle Phase Distribution
2.6. p-Histone H3 Staining
2.7. Annexin-V Staining
2.8. Chromatin Fragmentation
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Immunoprecipitation
2.11. Apoptosis Array
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
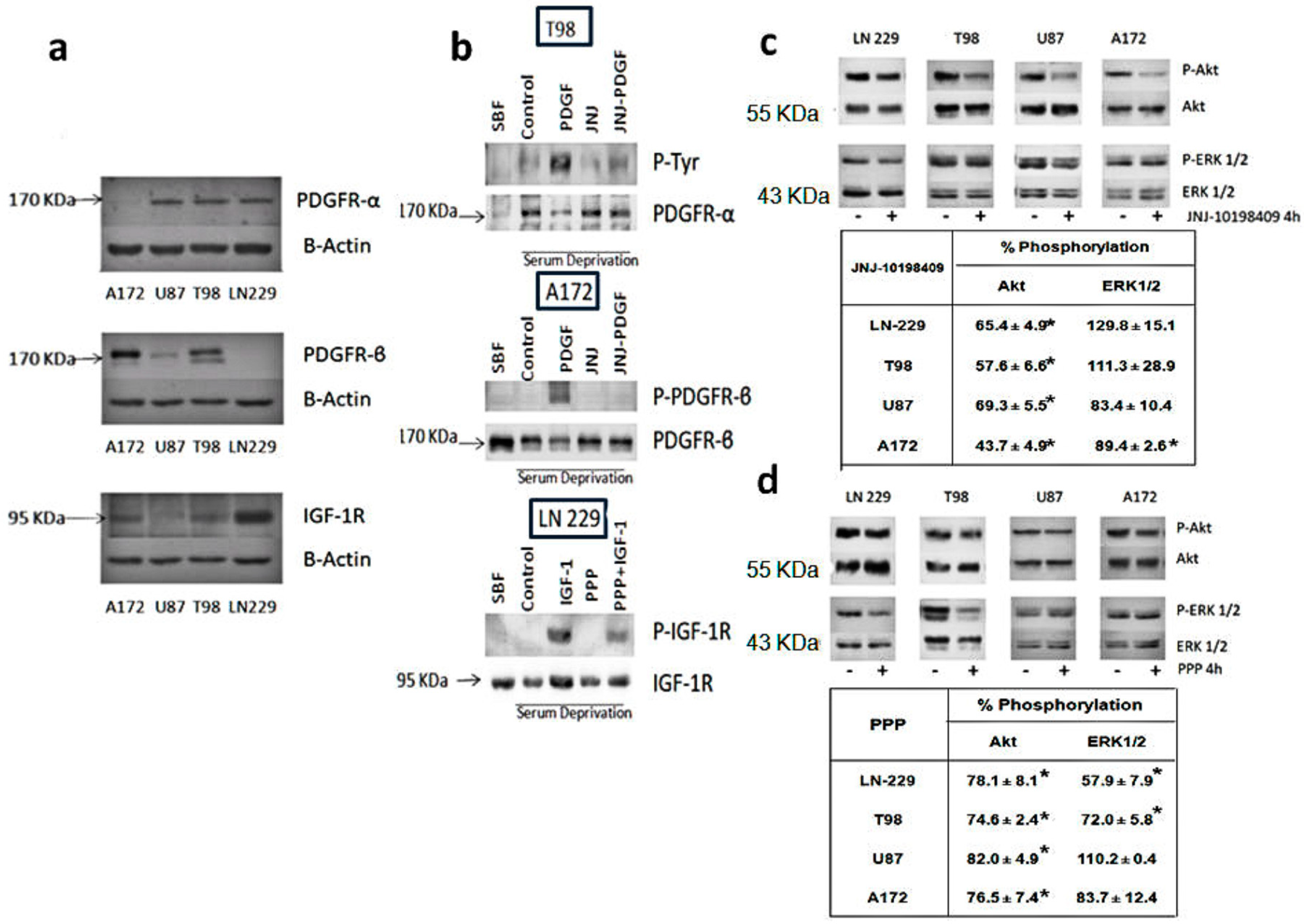
3.1. Expression Levels of PDGFR and IGF-1R in Glioblastoma Cell Lines
3.2. Inhibition of Phosphorylation of PDGFR, IGFR-1R and Downstream Pathways
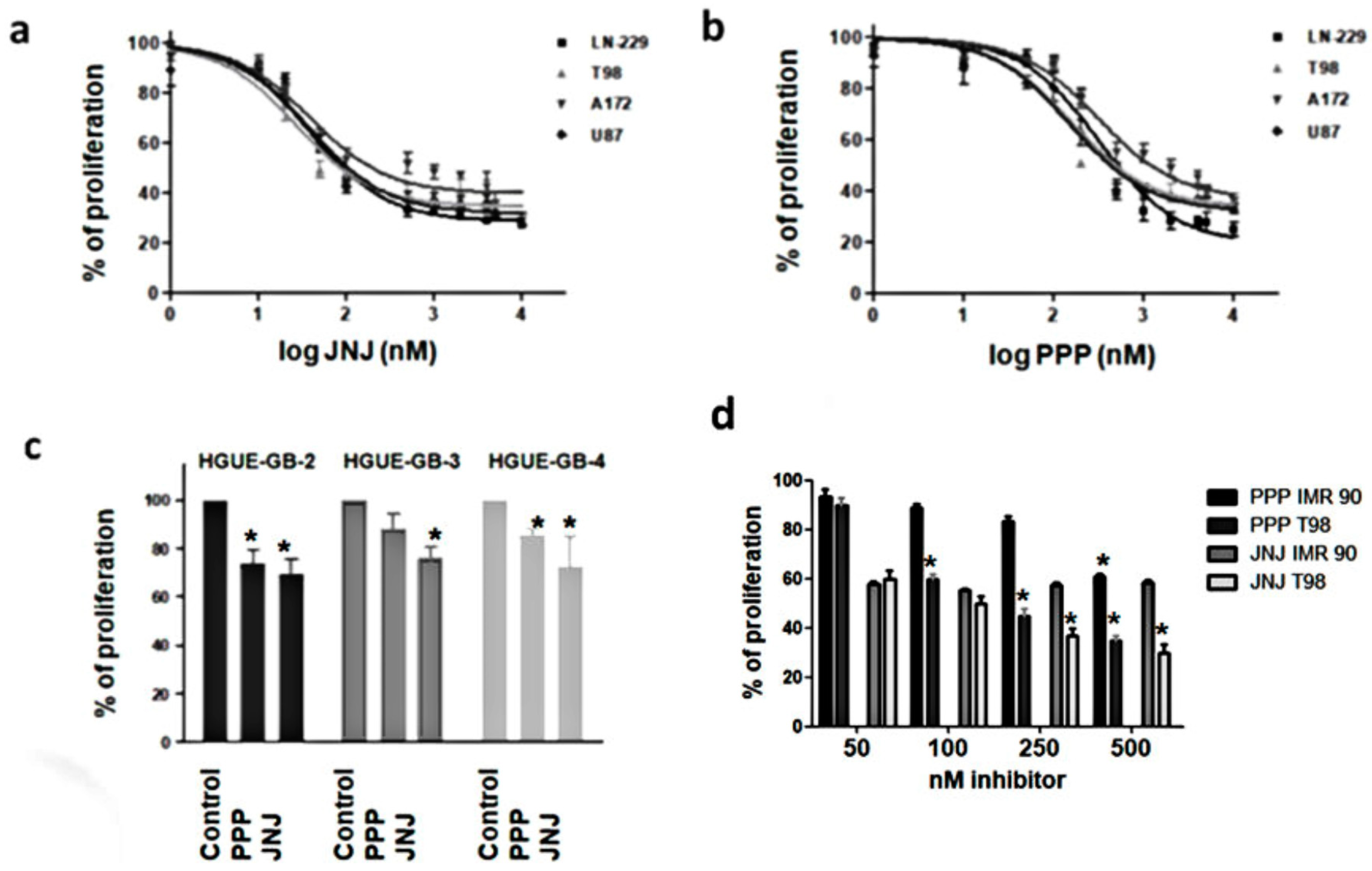
3.3. JNJ and PPP Inhibit Proliferation of Glioblastoma Cell Lines and Primary Cultures
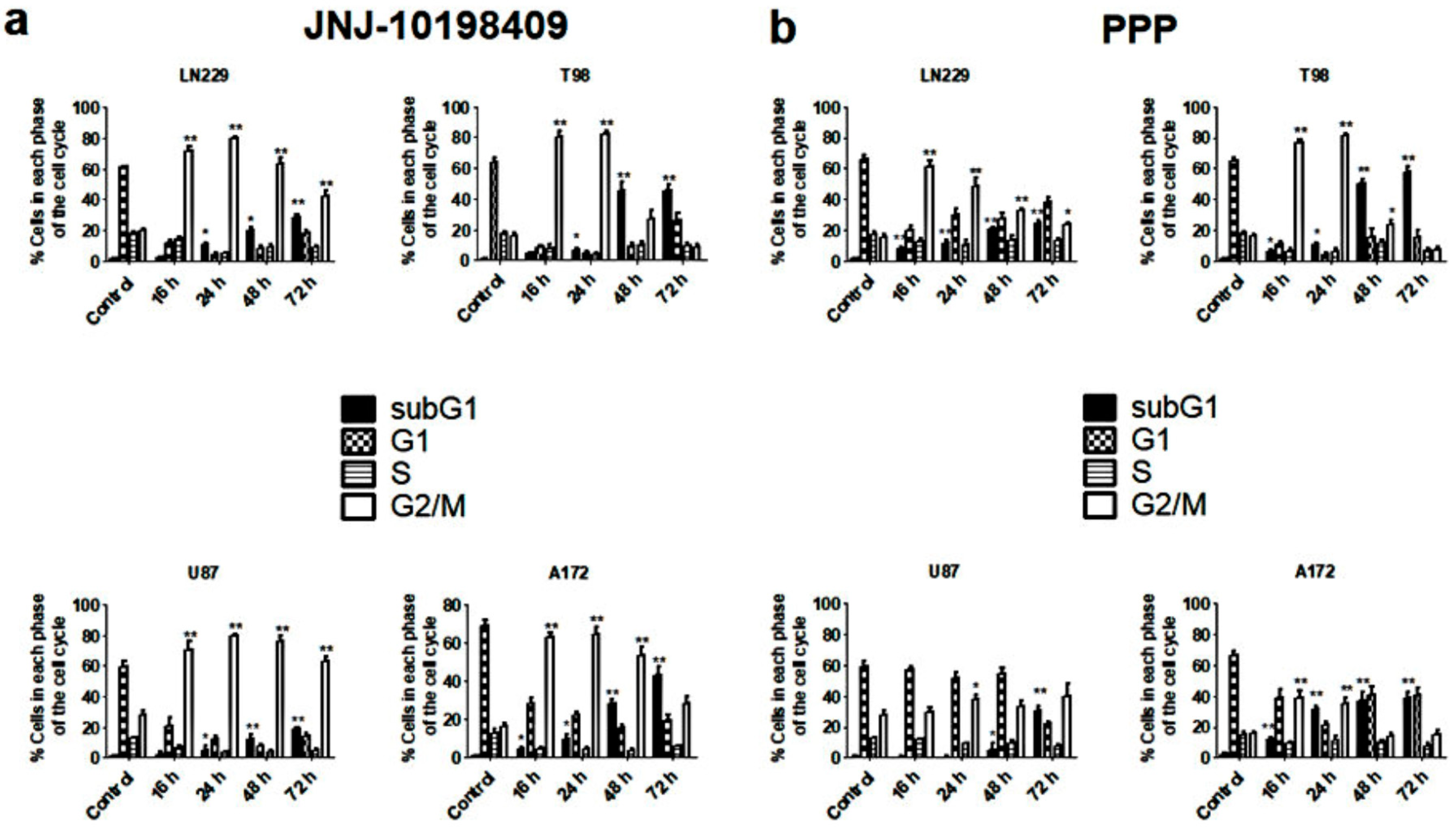
3.4. Effects of JNJ and PPP on Glioblastoma Cell Cycle
3.5. G2/M Arrest Induced by JNJ and PPP
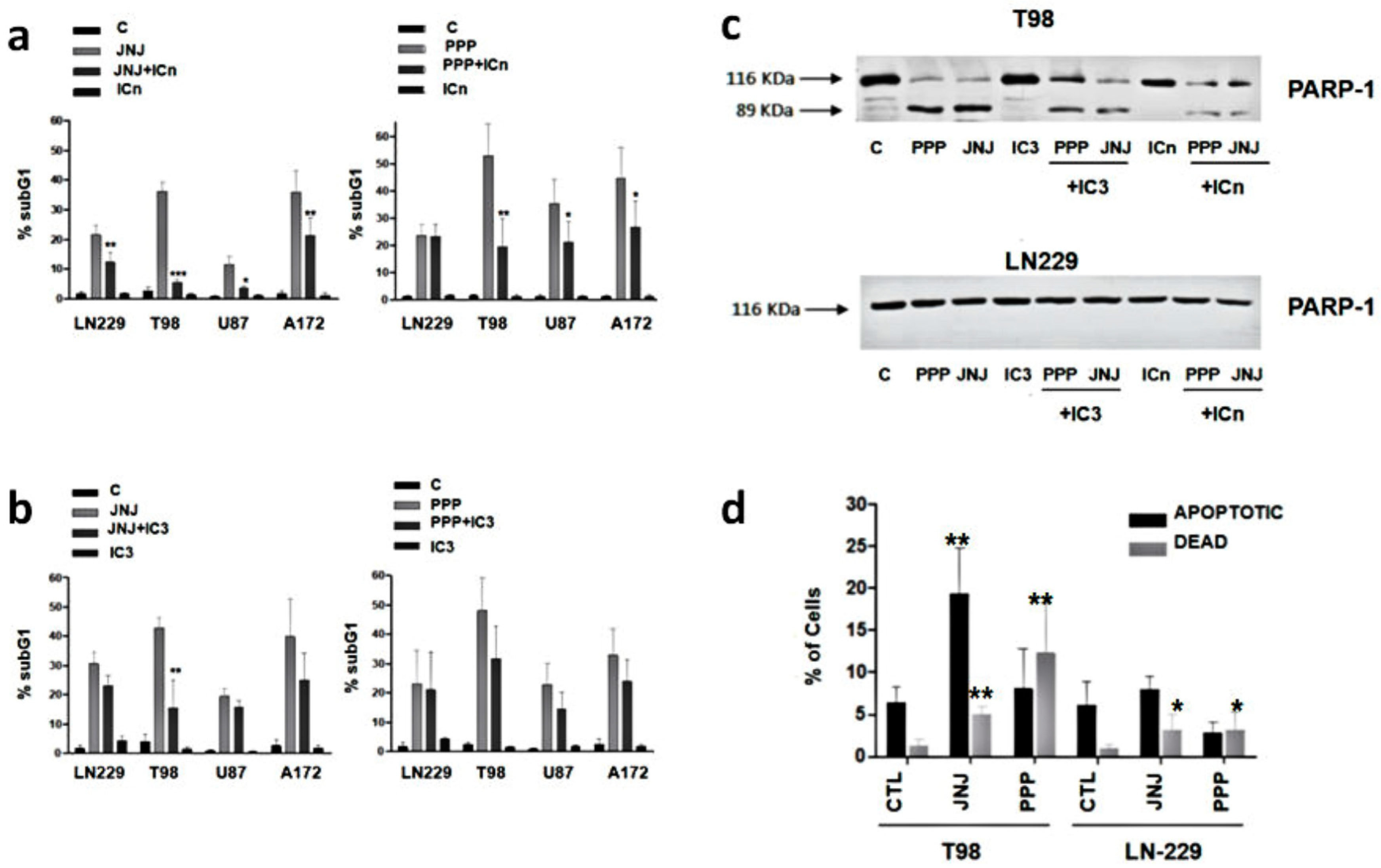
3.6. Are Caspases Involved in JNJ- or PPP-Induced Programmed Cell Death?
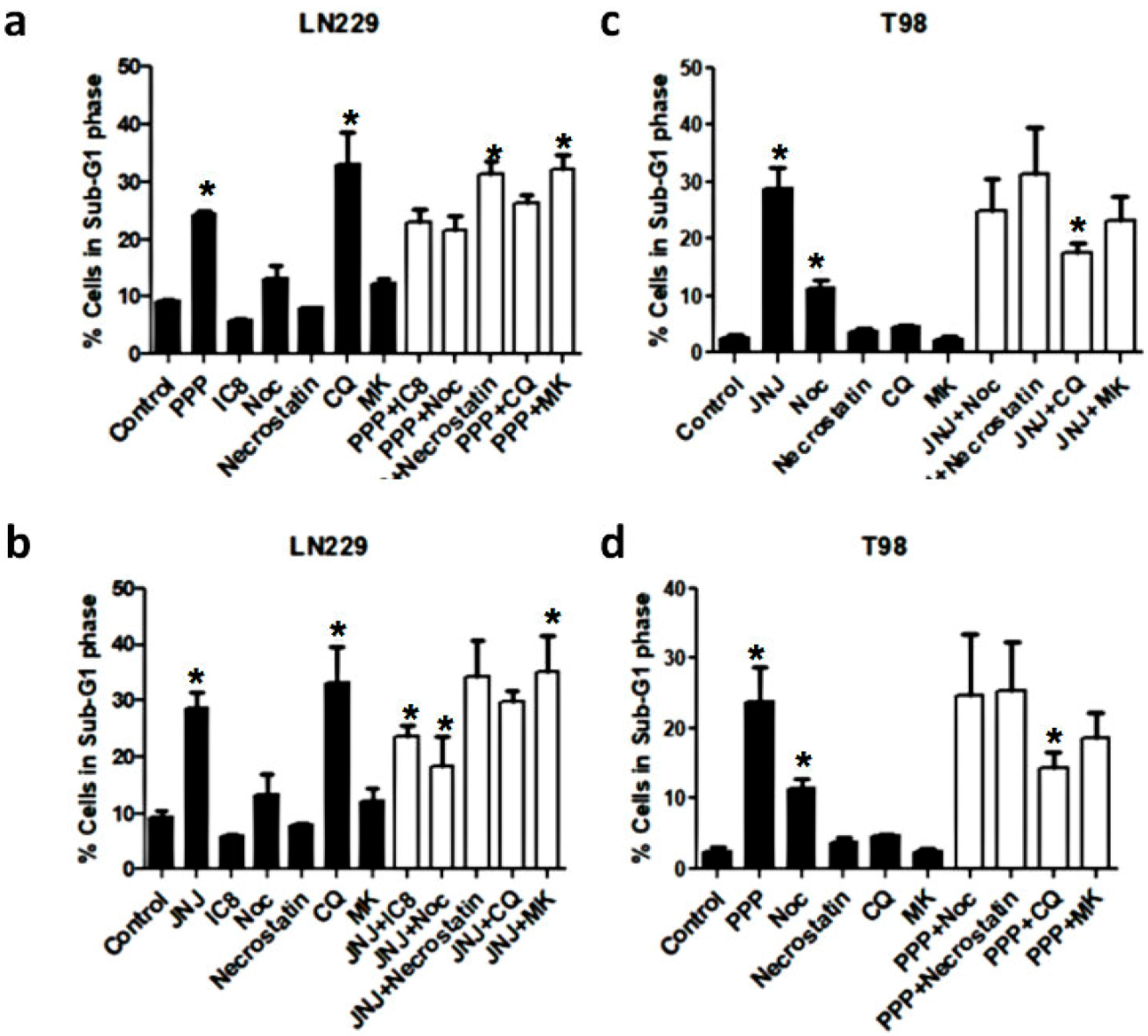
3.7. Is Apoptotic Cell Death Induced by JNJ or PPP?
3.8. Alternative Mechanisms of Programmed Cell Death
3.9. Molecular Characterization of JNJ- and PPP-Induced Cell Death
3.10. Combination of PDGFR and IGF-1R Inhibition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gurney, J.G.; Kadan-Lottick, N. Brain and other central nervous system tumors: Rates, trends, and epidemiology. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2001, 13, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Van Den Bent, M.J.; Mason, W.P.; Weller, M.; Mirimanoff, R.O.; Cairncross, J.G. Changing paradigms—An update on the multidisciplinary management of malignant glioma. Oncologist 2006, 11, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villano, J.L.; Seery, T.E.; Bressler, L.R. Temozolomide in malignant gliomas: Current use and future targets. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2009, 64, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanson, M.; Funa, K.; Koopmann, J.; Maintz, D.; Waha, A.; Westermark, B.; Heldin, C.H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Louis, D.N.; Von Deimling, A.; et al. Association of loss of heterozygosity on chromosome 17p with high platelet-derived growth factor α receptor expression in human malignant gliomas. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maher, E.A.; Furnari, F.B.; Bachoo, R.M.; Rowitch, D.H.; Louis, D.N.; Cavenee, W.K.; DePinho, R.A. Malignant glioma: Genetics and biology of a grave matter. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 1311–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco-Garcia, E.; Saceda, M.; Martinez-Lacaci, I. Role of receptor tyrosine kinases and their ligands in glioblastoma. Cells 2014, 3, 199–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. Clinical.Trial.gov. Available online: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=PDGFR%2C+glioma&Search=Search.
- Ho, C.Y.; Ludovici, D.W.; Maharoof, U.S.; Mei, J.; Sechler, J.L.; Tuman, R.W.; Strobel, E.D.; Andraka, L.; Yen, H.K.; Leo, G.; et al. (6,7-Dimethoxy-2,4-dihydroindeno[1,2-c]pyrazol-3-yl)phenylamines: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors with broad antiproliferative activity against tumor cells. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 8163–8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Andrea, M.R.; Mei, J.M.; Tuman, R.W.; Galemmo, R.A.; Johnson, D.L. Validation of in vivo pharmacodynamic activity of a novel PDGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor using immunohistochemistry and quantitative image analysis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnicoff, M.; Sell, C.; Rubini, M.; Coppola, D.; Ambrose, D.; Baserga, R.; Rubin, R. Rat glioblastoma cells expressing an antisense RNA to the insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) receptor are nontumorigenic and induce regression of wild-type tumors. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 2218–2222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Resnicoff, M.; Li, W.; Basak, S.; Herlyn, D.; Baserga, R.; Rubin, R. Inhibition of rat C6 glioblastoma tumor growth by expression of insulin-like growth factor I receptor antisense mRNA. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 1996, 42, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rininsland, F.; Johnson, T.R.; Chernicky, C.L.; Schulze, E.; Burfeind, P.; Ilan, J. Suppression of insulin-like growth factor type I receptor by a triple-helix strategy inhibits IGF-I transcription and tumorigenic potential of rat C6 glioblastoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5854–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girnita, A.; Girnita, L.; Del Prete, F.; Bartolazzi, A.; Larsson, O.; Axelson, M. Cyclolignans as inhibitors of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and malignant cell growth. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich, A.; Gray, A.; Tam, A.W.; Yang-Feng, T.; Tsubokawa, M.; Collins, C.; Henzel, W.; Le Bon, T.; Kathuria, S.; Chen, E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: Comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 2503–2512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Girnita, A.; Strömberg, T.; Khan, Z.; Andersson, S.; Zheng, H.; Ericsson, C.; Axelson, M.; Nistér, M.; Larsson, O.; et al. Targeting the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor by picropodophyllin as a treatment option for glioblastoma. Neuro. Oncol. 2009, 12, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollak, M. The insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor family as a therapeutic target in oncology. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. Clinical.Trial.gov. Available online: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=IGF1R%2C+glioma&Search=Search.
- Petronczki, M.; Lenart, P.; Peters, J.M. Polo on the Rise—From Mitotic Entry to Cytokinesis with Plk1. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Mizzen, C.A.; Cook, R.G.; Gorovsky, M.A.; Allis, C.D. Phosphorylation of histone H3 at serine 10 is correlated with chromosome condensation during mitosis and meiosis in Tetrahymena. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7480–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prigent, C.; Dimitrov, S. Phosphorylation of serine 10 in histone H3, what for? J. Cell. Sci. 2003, 116, 3677–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendzel, M.J.; Wei, Y.; Mancini, M.A.; Van Hooser, A.; Ranalli, T.; Brinkley, B.R.; Bazett-Jones, D.P.; Allis, C.D. Mitosis-specific phosphorylation of histone H3 initiates primarily within pericentromeric heterochromatin during G2 and spreads in an ordered fashion coincident with mitotic chromosome condensation. Chromosoma 1997, 106, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavrik, I.; Golks, A.; Krammer, P.H. Death receptor signaling. J. Cell. Sci. 2005, 118, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, H.; Arai, T.; Okada, M.; Nishibata, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Sakai, N.; Imagaki, K.; Ohtani, J.; Sakai, T.; Yoshizumi, T.; et al. MK-1775, a small molecule Wee1 inhibitor, enhances anti-tumor efficacy of various DNA-damaging agents, including 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 9, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degterev, A.; Huang, Z.; Boyce, M.; Li, Y.; Jagtap, P.; Mizushima, N.; Cuny, G.D.; Mitchison, T.J.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Yuan, J. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintani, T.; Klionsky, D.J. Autophagy in health and disease: A double-edged sword. Science 2004, 306, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blink, E.; Maianski, N.A.; Alnemri, E.S.; Zervos, A.S.; Roos, D.; Kuijpers, T.W. Intramitochondrial serine protease activity of Omi/HtrA2 is required for caspase-independent cell death of human neutrophils. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, 937–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilenti, L.; Lee, Y.; Hess, S.; Srinivasula, S.; Park, K.M.; Junqueira, D.; Davis, H.; Bonventre, J.V.; Alnemri, E.S.; Zervos, A.S. Characterization of a novel and specific inhibitor for the pro-apoptotic protease Omi/HtrA2. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11489–11494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.Y.; Song, M.G.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.W.; Jin, J.O.; Park, J.I.; Chang, Y.C.; Kwak, J.Y. Apoptosis of human neutrophils induced by protein phosphatase 1/2A inhibition is caspase-independent and serine protease-dependent. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 212, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Morales, P.; Gómez-Martínez, A.; Carrato, A.; Martínez-Lacaci, I.; Barberá, V.M.; Soto, J.L.; Carrasco-García, E.; Menéndez-Gutierrez, M.P.; Castro-Galache, M.D.; Ferragut, J.A.; et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors induced caspase-independent apoptosis in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell lines. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Tiffany-Castiglioni, E.; Koh, H.C.; Son, I.H. Paraquat activates the IRE1/ASK1/JNK cascade associated with apoptosis in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 191, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, D.H.; Noh, Y.H.; Yu, K.; Jung, H.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Youn, Y.C.; Jeong, Y.; et al. Activation of PERK signaling attenuates Aβ-mediated ER stress. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanson, M.; Funa, K.; Hartman, M.; Claesson-Welsh, L.; Heldin, C.H.; Westermark, B.; Nistér, M. Platelet-derived growth factor and its receptors in human glioma tissue: Expression of messenger RNA and protein suggests the presence of autocrine and paracrine loops. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 3213–3219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kiess, W.; Lee, L.; Graham, D.E.; Greenstein, L.; Tseng, L.Y.; Rechler, M.M.; Nissley, S.P. Rat C6 glial cells synthesize insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and express IGF-I receptors and IGF-II/mannose 6-phosphate receptors. Endocrinology 1989, 124, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trojan, J.; Blossey, B.K.; Johnson, T.R.; Rudin, S.D.; Tykocinski, M.; Ilan, J. Loss of tumorigenicity of rat glioblastoma directed by episome-based antisense cDNA transcription of insulin-like growth factor I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 4874–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strömberg, T.; Ekman, S.; Girnita, L.; Dimberg, L.Y.; Larsson, O.; Axelson, M.; Lennartsson, J.; Hellman, U.; Carlson, K.; Österborg, A.; et al. IGF-1 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition by the cyclolignan PPP induces G2/M-phase accumulation and apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells. Blood 2006, 107, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Z.; Choy, E.; Harmon, D.; Yang, C.; Ryu, K.; Schwab, J.; Mankin, H.; Hornicek, F.J. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor cyclolignan picropodophyllin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in multidrug resistant osteosarcoma cell lines. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 2122–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasic, T.B.; Hei, T.K.; Ivanov, V.N. Disruption of IGF-1R signaling increases TRAIL-induced apoptosis: A new potential therapy for the treatment of melanoma. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 1994–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima-Hosoyama, S.; Hosoyama, T.; Nelon, L.D.; Keller, C. IGF-1 receptor inhibition by picropodophyllin in medulloblastoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 399, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomizawa, M.; Shinozaki, F.; Sugiyama, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Sueishi, M.; Yoshida, T. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in proliferation and motility of pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1854–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doghman, M.; Axelson, M.; Lalli, E. Potent inhibitory effect of the cyclolignan picropodophyllin (PPP) on human adrenocortical carcinoma cells proliferation. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2011, 1, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- E, C.; Li, J.; Shao, D.; Zhang, D.; Pan, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X. The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor inhibitor picropodophyllin-induced selective apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell through a caspase-dependent mitochondrial pathway. Oncol. Res. 2013, 21, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Yao, M.; Wang, L.; Yan, X.; Gu, X.; Shi, Y.; Yao, N.; Qiu, L.; Wu, W.; Yao, D. Abnormal expression of insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in hepatoma tissue and its inhibition to promote apoptosis of tumor cells. Tumour. Biol. 2013, 34, 3397–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, I.; Galluzzi, L.; Castedo, M.; Kroemer, G. Mitotic catastrophe: A mechanism for avoiding genomic instability. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 12, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niikura, Y.; Dixit, A.; Scott, R.; Perkins, G.; Kitagawa, K. BUB1 mediation of caspase-independent mitotic death determines cell fate. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 178, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosengren, L.; Vasilcanu, D.; Vasilcanu, R.; Fickenscher, S.; Sehat, B.; Natalishvili, N.; Naughton, S.; Yin, S.; Girnita, A.; Girnita, L.; et al. IGF-1R tyrosine kinase expression and dependency in clones of IGF-1R knockout cells (R–). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 347, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Diepstra, A.; Xu, C.; van Imhoff, G.; Plattel, W.; Van Den Berg, A.; Visser, L. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor is a prognostic factor in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waraky, A.; Akopyan, K.; Parrow, V.; Strömberg, T.; Axelson, M.; Abrahmsén, L.; Lindqvist, A.; Larsson, O.; Aleem, E. Picropodophyllin causes mitotic arrest and catastrophe by depolymerizing microtubules via Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor-independent mechanism. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8379–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanida, I. Autophagosome formation and molecular mechanism of autophagy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 2201–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carew, J.S.; Nawrocki, S.T.; Kahue, C.N.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Chung, L.; Houghton, J.A.; Huang, P.; Giles, F.J.; Cleveland, J.L. Targeting autophagy augments the anticancer activity of the histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA to overcome Bcr-Abl-mediated drug resistance. Blood 2007, 110, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel, A.; Herr, I.; Schwarz, H.; Rodemann, H.P.; Mayer, A. Blocked autophagy sensitizes resistant carcinoma cells to radiation therapy. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Karantza-Wadsworth, V. Role and regulation of autophagy in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 1516–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, A.; Yamada, H.; Moriya, S.; Miyazawa, K. The beta-carboline alkaloid harmol induces cell death via autophagy but not apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Alva, A.; Su, H.; Dutt, P.; Freundt, E.; Welsh, S.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Lenardo, M.J. Regulation of an ATG7-beclin 1 program of autophagic cell death by caspase-8. Science 2004, 304, 1500–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degterev, A.; Hitomi, J.; Germscheid, M.; Ch’en, I.L.; Korkina, O.; Teng, X.; Abbott, D.; Cuny, G.D.; Yuan, C.; Wagner, G.; et al. Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of necrostatins. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, E. Does cancer therapy trigger cell suicide? Science 1999, 286, 2256–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carapancea, M.; Cosaceanu, D.; Budiu, R.; Kwiecinska, A.; Tataranu, L.; Ciubotaru, V.; Alexandru, O.; Banita, M.; Pisoschi, C.; Bäcklund, M.L.; et al. Dual targeting of IGF-1R and PDGFR inhibits proliferation in high-grade gliomas cells and induces radiosensitivity in JNK-1 expressing cells. J. Neurooncol. 2007, 85, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielen, A.; Perryman, L.; Box, G.M.; Valenti, M.; De Haven Brandon, A.; Martins, V.; Jury, A.; Popov, S.; Gowan, S.; Jeay, S.; et al. Enhanced efficacy of IGF1R inhibition in paediatric glioblastoma by combinatorial targeting of PDGFRα/β. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1407–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carrasco-Garcia, E.; Martinez-Lacaci, I.; Mayor-López, L.; Tristante, E.; Carballo-Santana, M.; García-Morales, P.; Ventero Martin, M.P.; Fuentes-Baile, M.; Rodriguez-Lescure, Á.; Saceda, M. PDGFR and IGF-1R Inhibitors Induce a G2/M Arrest and Subsequent Cell Death in Human Glioblastoma Cell Lines. Cells 2018, 7, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7090131
Carrasco-Garcia E, Martinez-Lacaci I, Mayor-López L, Tristante E, Carballo-Santana M, García-Morales P, Ventero Martin MP, Fuentes-Baile M, Rodriguez-Lescure Á, Saceda M. PDGFR and IGF-1R Inhibitors Induce a G2/M Arrest and Subsequent Cell Death in Human Glioblastoma Cell Lines. Cells. 2018; 7(9):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7090131
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarrasco-Garcia, Estefania, Isabel Martinez-Lacaci, Leticia Mayor-López, Elena Tristante, Mar Carballo-Santana, Pilar García-Morales, Maria Paz Ventero Martin, Maria Fuentes-Baile, Álvaro Rodriguez-Lescure, and Miguel Saceda. 2018. "PDGFR and IGF-1R Inhibitors Induce a G2/M Arrest and Subsequent Cell Death in Human Glioblastoma Cell Lines" Cells 7, no. 9: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7090131
APA StyleCarrasco-Garcia, E., Martinez-Lacaci, I., Mayor-López, L., Tristante, E., Carballo-Santana, M., García-Morales, P., Ventero Martin, M. P., Fuentes-Baile, M., Rodriguez-Lescure, Á., & Saceda, M. (2018). PDGFR and IGF-1R Inhibitors Induce a G2/M Arrest and Subsequent Cell Death in Human Glioblastoma Cell Lines. Cells, 7(9), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7090131




