Semiconducting Properties of the Hybrid Film of Elastic Poly(styrene-b-butadiene-b-styrene) Block Copolymer and Semiconducting Poly(3-hexylthiophene) Nanofibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
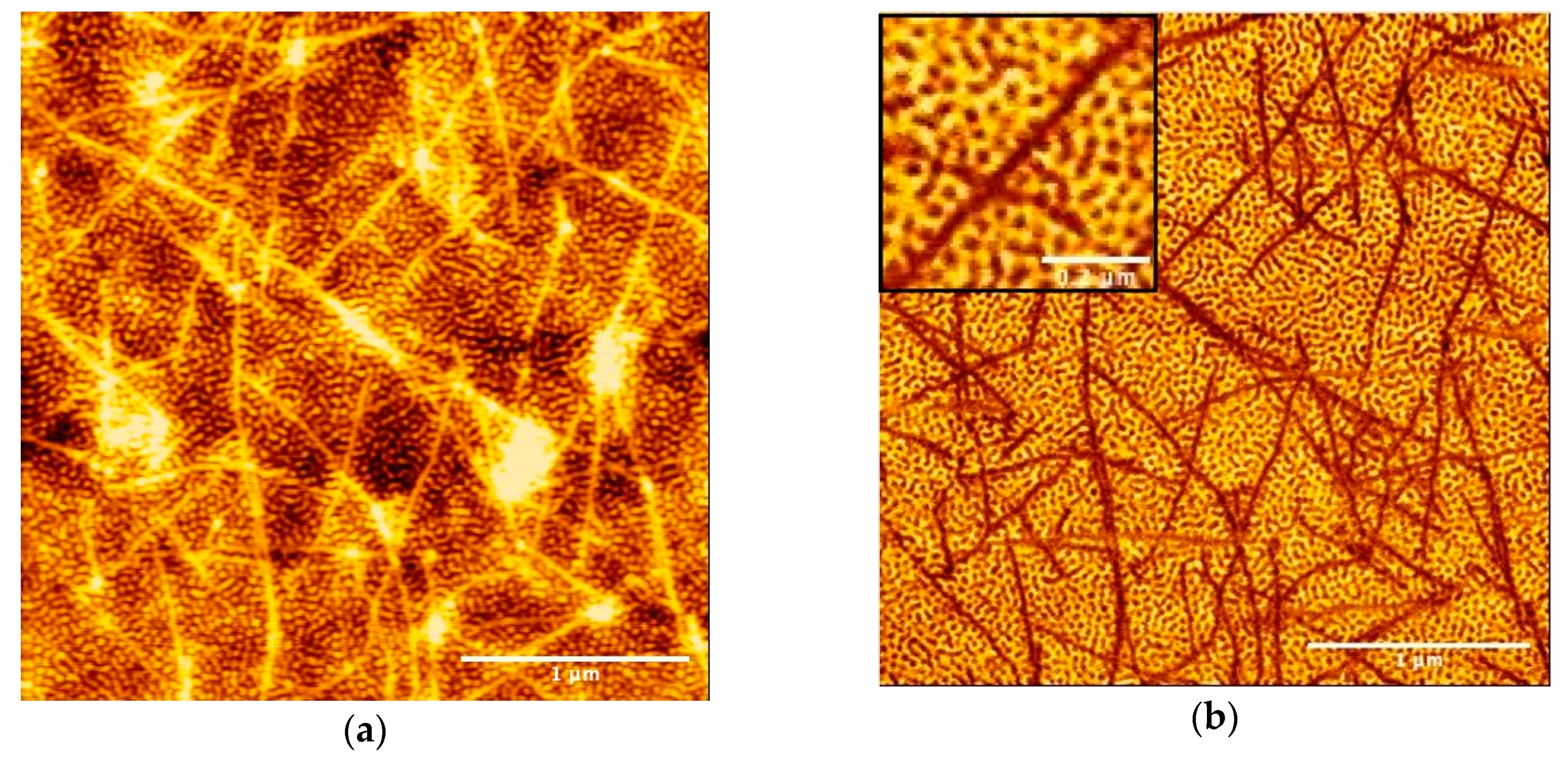
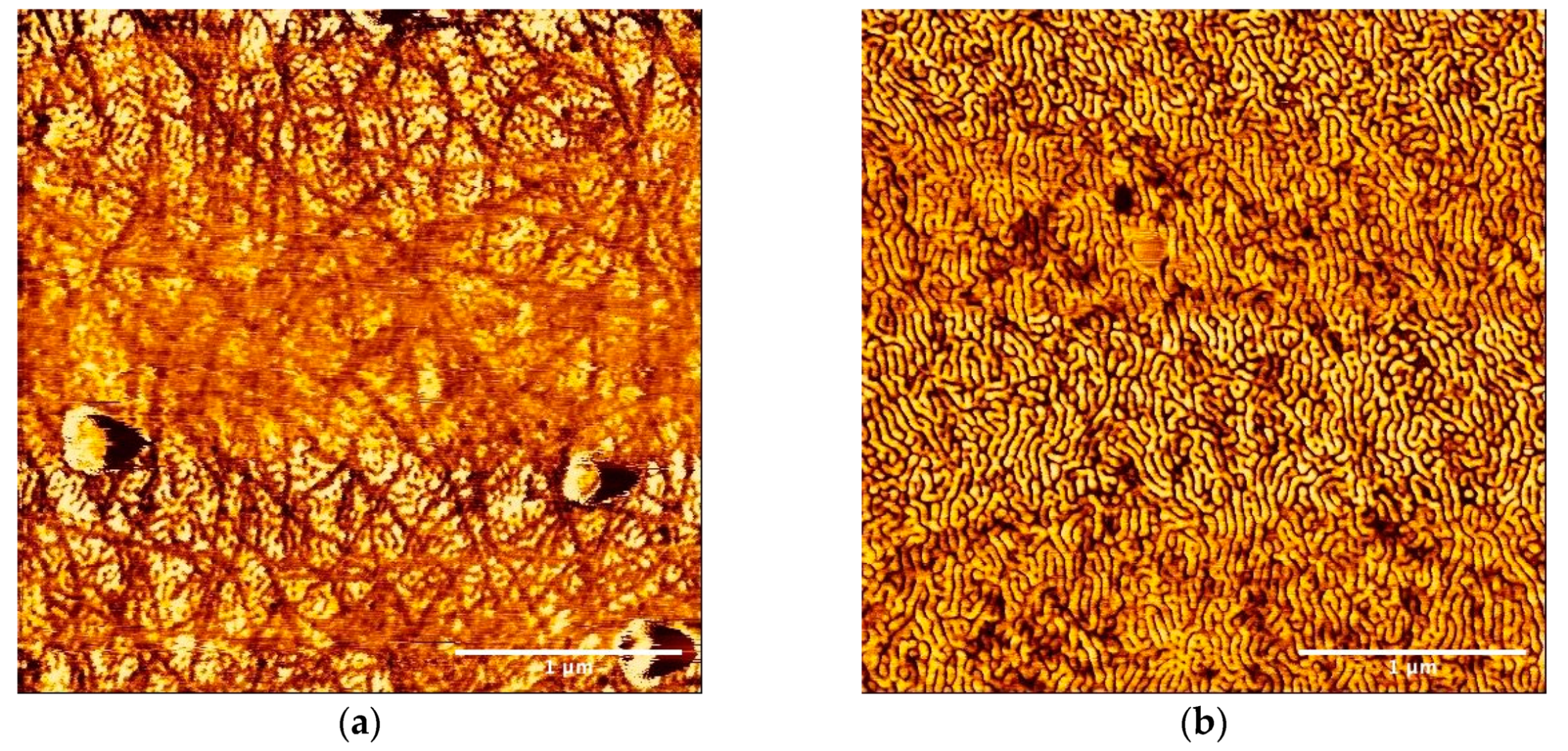
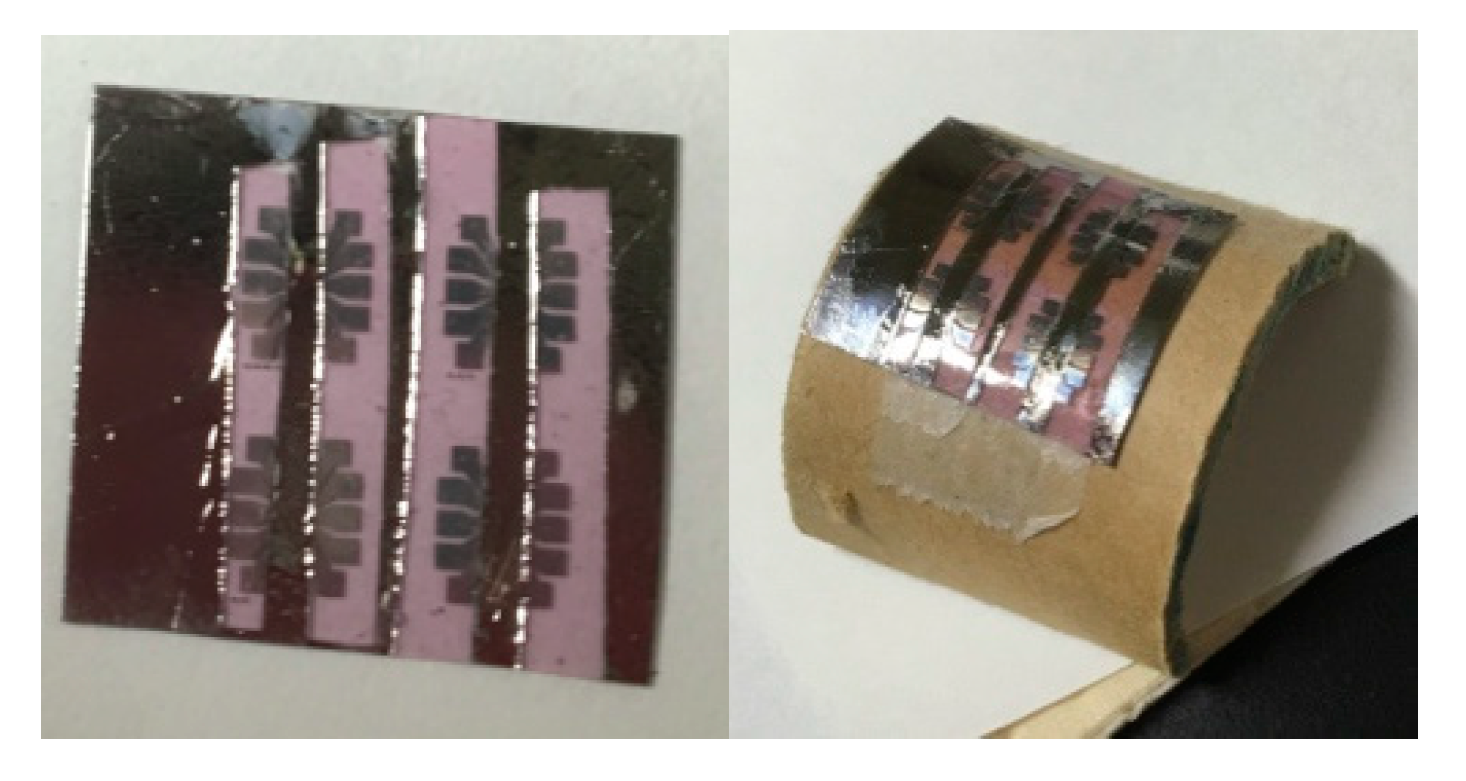
3.1. Microscopic Structure of the SBS Film Loaded with a P3HT Nanofiber
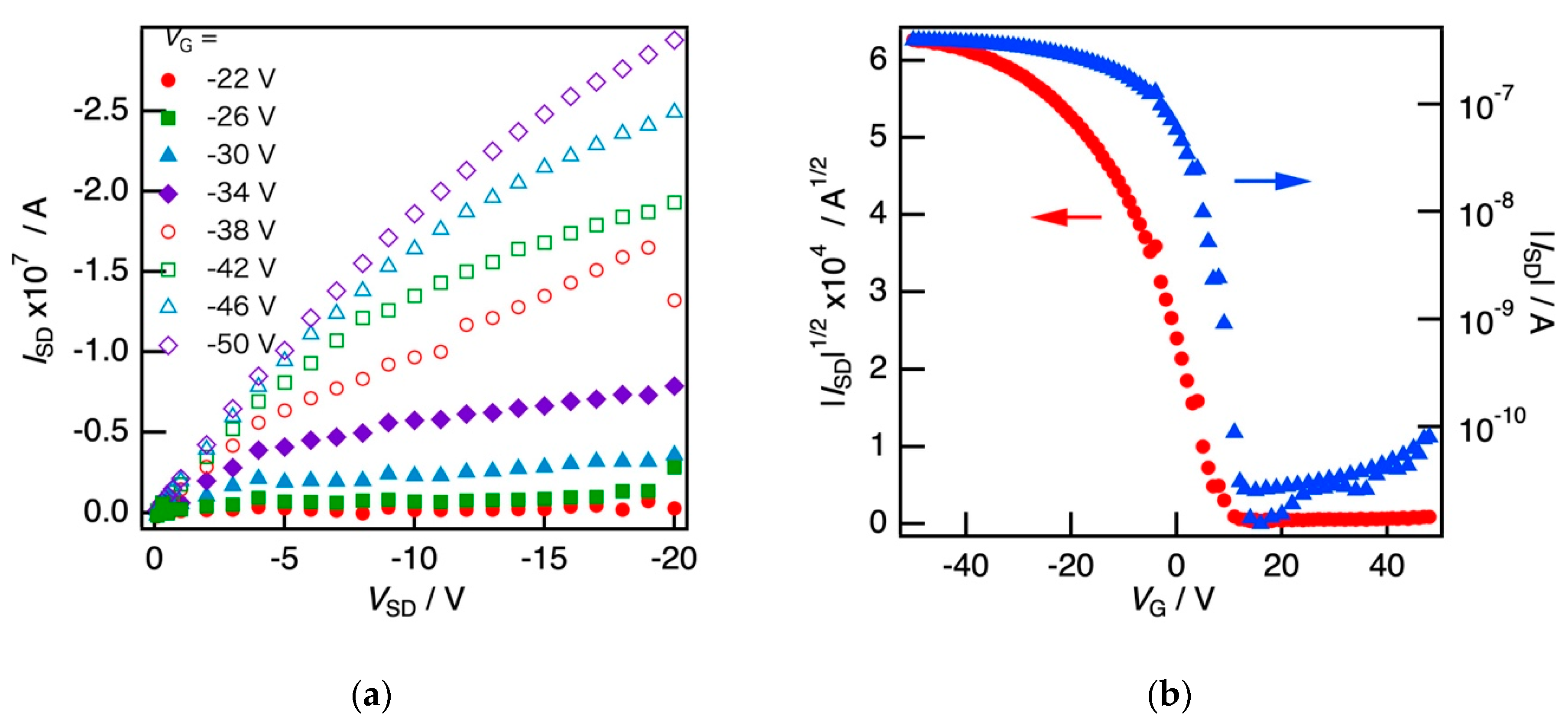
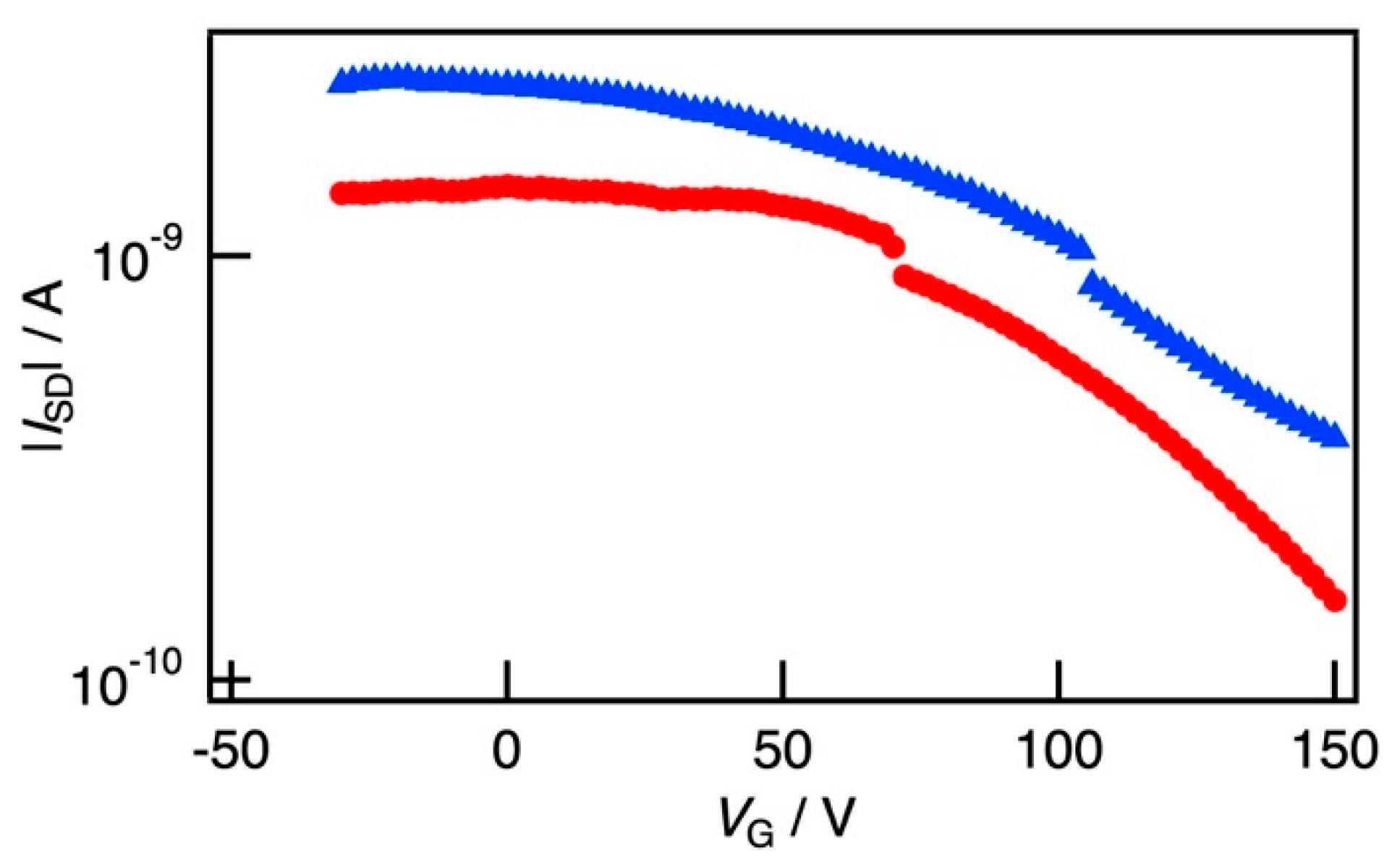
3.2. FET Properties of SBS Film Loaded with a P3HT Nanofiber
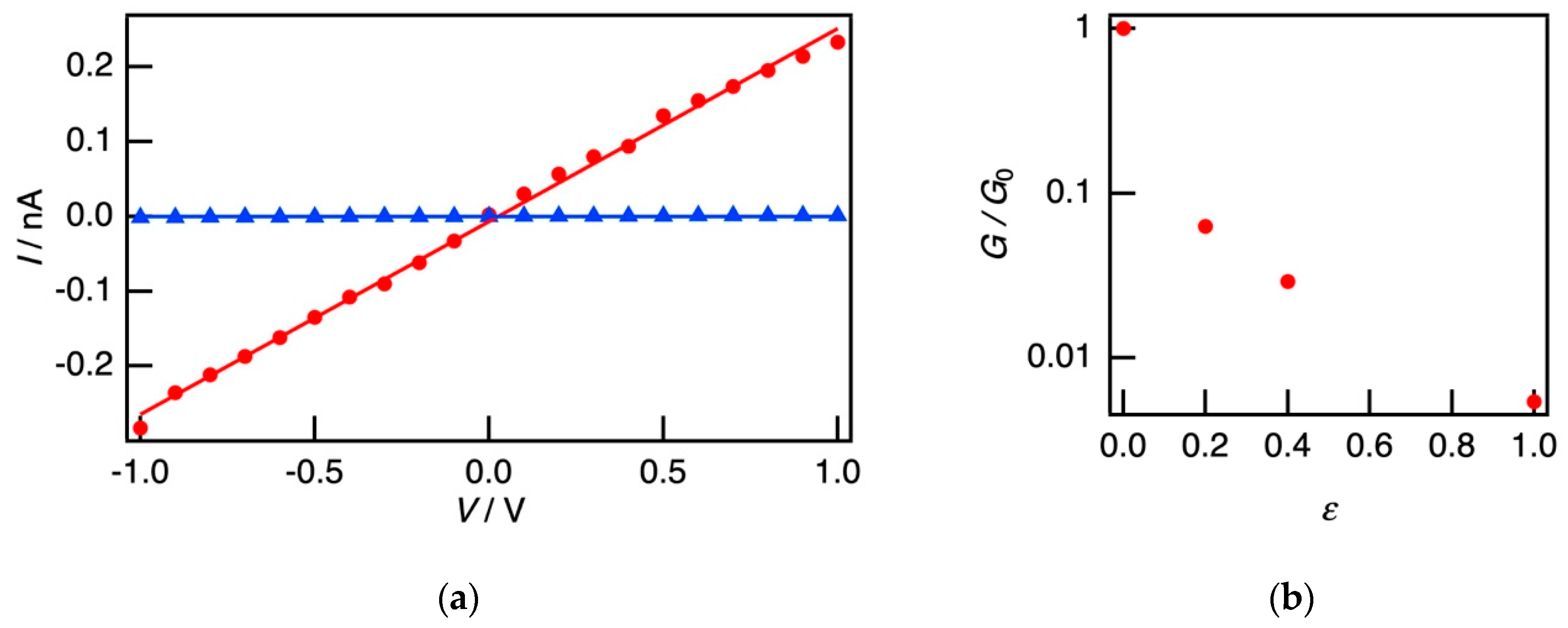
3.3. Electrical Properties of SBS Film Loaded with P3HT Nanofibers under Elongation and Bending Deformation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schenning, A.P.; Meijer, E.W. Supramolecular electronics; nanowires from self-assembled π-conjugated systems. Chem. Commun. 2005, 3245–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleshin, A. Polymer nanofibers and nanotubes: Charge transport and device applications. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briseno, A.L.; Mannsfeld, S.C.; Jenekhe, S.A.; Bao, Z.; Xia, Y. Introducing organic nanowire transistors. Mater. Today 2008, 11, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.D.; Li, D.; Kaner, R.B. One-dimensional conducting polymer nanostructures: Bulk synthesis and applications. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.A.; Liu, F.; Ferdous, S.; Muthukumar, M.; Briseno, A.L. Polymer semiconductor crystals. Mater. Today 2010, 13, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, I.D.; Shaker, M.M.; Ko, F.K.; MacDiarmid, A.G. Electrostatic fabrication of ultrafine conducting fibers: Polyaniline/polyethylene oxide blends. Synth. Met. 2000, 114, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDiarmid, A.; Jones, W.; Norris, I.; Gao, J.; Johnson, A.; Pinto, N.; Hone, J.; Han, B.; Ko, F.; Okuzaki, H.; et al. Electrostatically-generated nanofibers of electronic polymers. Synth. Met. 2001, 119, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, N.J.; Johnson, A.T.; MacDiarmid, A.G.; Mueller, C.; Theofylaktos, N.; Robinson, D.C.; Miranda, F.A. Electrospun polyaniline/polyethylene oxide nanofiber field-effect transistor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Freitag, M.; Hone, J.; Staii, C.; Johnson, A.T.; Pinto, N.J.; MacDiarmid, A.G. Fabrication and electrical characterization of polyaniline-based nanofibers with diameter below 30 nm. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Babel, A.; Jenekhe, S.A.; Xia, Y. Nanofibers of conjugated polymers prepared by electrospinning with a two-capillary spinneret. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 2062–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Reccius, C.H.; Craighead, H.G. Single electrospun regioregular poly (3-hexylthiophene) nanofiber field-effect transistor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 253106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronakis, I.S.; Grapenson, S.; Jakob, A. Conductive polypyrrole nanofibers via electrospinning: Electrical and morphological properties. Polymers 2006, 47, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuzaki, H.; Takahashi, T.; Miyajima, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Kuwabara, T. Spontaneous formation of poly(p-phenylenevinylene) nanofiber yarns through electrospinning of a precursor. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 4276–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, O.; Bravo, A.G.; Pinto, N.J. Fabrication of poly (vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene)/poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-polystyrene sulfonate composite nanofibers via electrospinning. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 7924–7929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Lee, J.; Choi, J.; Jung, D.; Shim, S.E. Electrospun PEDOT: PSS/PVP nanofibers as the chemiresistor in chemical vapour sensing. Synth. Met. 2010, 160, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihn, K.J.; Moulton, J.; Smith, P. Whiskers of poly (3-alkylthiophene)s. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1993, 31, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, J.A.; Frisbie, C.D. Field effect conductance of conducting polymer nanofibers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2003, 41, 2674–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, J.A.; Frisbie, C.D. Field effect transport and trapping in regioregular polythiophene nanofibers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 19169–19179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-F.; Sun, B.; Breiby, D.W.; Nielsen, M.M.; Solling, T.; Giles, M.; McCulloch, I.; Sirringhaus, H. Enhanced mobility of poly (3-hexylthiophene) transistors by spin-coating from high-boiling-point solvents. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 4772–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shin, T.J.; Yang, L.; Cho, K.; Ryu, C.Y.; Bao, Z. Effect of mesoscale crystalline structure on the field-effect mobility of regioregular poly (3-hexyl thiophene) in thin-film transistors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Jang, Y.; Park, Y.D.; Cho, K. Controlled one-dimensional nanostructures in poly (3-hexylthiophene) thin film for high-performance organic field-effect transistors. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 15763–15768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Li, B.; Iovu, M.C.; Jeffries-El, M.; Sauve, G.; Cooper, J.; Jia, S.; Tristram-Nagle, S.; Smilgies, D.; Lambeth, D.N.; et al. Nanostructure dependence of field-effect mobility in regioregular poly (3-hexylthiophene) thin film field effect transistors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3480–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samitsu, S.; Shimomura, T.; Heike, S.; Hashizume, T.; Ito, K. Effective production of poly (3-alkylthiophene) nanofibers by means of whisker method using anisole solvent: Structural, optical, and electrical properties. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 8000–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Arif, M.; Zou, J.; Khondaker, S.I.; Zhai, L. Controlling poly (3-hexylthiophene) crystal dimension: Nanowhiskers and nanoribbons. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 9390–9393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinhenz, N.; Persson, N.; Xue, Z.; Chu, P.H.; Wang, G.; Yuan, Z.; McBride, M.; Choi, D.; Grover, M.A.; Reichmanis, E. Ordering of poly (3-hexylthiophene) in solutions and films: Effects of fiber length and grain boundaries on anisotropy and mobility. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 3905–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Torrent, M.; Boer, D.D.; Durkut, M.; Hadley, P.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. Field effect transistors based on poly(3-hexylthiophene) at different length scales. Nanotechnology 2004, 15, S265–S269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Liu, J.; Zhai, L.; Khondaker, S.I. Poly (3-hexylthiophene) crystalline nanoribbon network for organic field effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 243304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samitsu, S.; Shimomura, T.; Heike, S.; Hashizume, T.; Ito, K. Field-effect carrier transport in poly (3-alkylthiophene) nanofiber networks and isolated nanofibers. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 7891–7894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, T.; Takahashi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; Noguchi, K.; Heike, S.; Hashizume, T. Relationship between structural coherence and intrinsic carrier transport in an isolated poly (3-hexylthiophene) nanofiber. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 115314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Lim, J.A.; Wang, X.; Lee, W.H.; Hwang, M.; Cho, K. Versatile use of vertical-phase-separation-induced bilayer structures in organic thin-film transistors. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Lee, W.H.; Wang, X.; Kim, J.S.; Lim, J.A.; Kwak, D.; Lee, S.; Cho, K. Organic thin-film transistors based on polythiophene nanowires embedded in insulating polymer. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1349–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.A.; Qiu, L.; Lee, W.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kwak, D.; Cho, K.; Kim, J.-H. Inkjet-printed single-droplet organic transistors based on semiconductor nanowires embedded in insulating polymers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 3292–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.-I.; Kawasaki, M.; Toda, Y.; Yamashita, S.; Shimomura, T. Microscopic conduction pathways of poly (3-hexylthiophene) nanofibers embedded in polymer film. Polym. J. 2012, 44, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Tang, H.; Huan, Y.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X. Enhanced charge transportation in semiconducting polymer/insulating polymer composites: The role of an interpenetrating bulk interface. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 1714–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronggaowa, B.; Toda, Y.; Ito, N.; Shikinaka, K.; Shimomura, T. Transparent conductive films fabricated from polythiophene nanofibers composited with conventional polymers. Polymers 2013, 5, 1325–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yagi, M.; Ito, N.; Kawasaki, M.; Shimomura, T. Semiconducting properties of p- and n-type organic nanofiber/poly (methyl methacrylate) composite films for film rectifier. Synth. Met. 2016, 213, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Park, J.; Hyun, W.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.B.; Song, C.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Hyeon, T.; et al. Stretchable heater using ligand-exchanged silver nanowire nanocomposite for wearable articular thermotherapy. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6626–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Shin, S.; Lee, S.; Seo, J.; Lee, J.; Son, S.; Cho, H.J.; Algadi, H.; Al-Sayari, S.; Kim, D.E.; et al. Ag nanowire reinforced highly stretchable conductive fibers for wearable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3114–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingford, C.; Smith, H.; Yan, X.; Bowen, C.; Figiel, Ł.; McNally, T.; Wan, C. Electrical dual-percolation in MWCNTs/SBS/PVDF based thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) composites and the effect of mechanical stretching. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 112, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroni, L.; Rosolen, J.; Felisberti, M.I.; Nogueira, A.F.; Soto-Oviedo, M.A. Conductivity and mechanical properties of composites based on MWCNTs and styrene-butadiene-styrene block™ copolymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 3241–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Silva, J.; Ansón-Casaos, A.; Martinez, M.T.; Abad, M.-J.; Viana, J.C.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Effect of carbon nanotube type and functionalization on the electrical, thermal, mechanical and electromechanical properties of carbon nanotube/styrene–butadiene–styrene composites for large strain sensor applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 61, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staudinger, U.; Satapathy, B.K.; Jehnichen, D. Nanofiller dispersion, morphology, mechanical behavior, and electrical properties of nanostructured styrene-butadiene-based triblock copolymer/CNT composites. Polymers 2019, 11, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, M.; Oh, J.Y.; Byun, K.-E.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, B.; Baik, H.-K.; Park, J.-J.; Jeong, U. Polythiophene nanofibril bundles surface-embedded in elastomer: A route to a highly stretchable active channel layer. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, G.-J.N.; Zhu, C.; Luo, S.; Jin, L.; Gu, X.; Chen, S.; Feig, V.R.; To, J.W.F.; et al. Highly stretchable polymer semiconductor films through the nanoconfinement effect. Science 2017, 355, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, H.-C.; Zhu, C.; Ehrlich, A.; Shaw, L.; Nikolka, M.; Wang, S.; Molina-Lopez, F.; Gu, X.; Luo, S.; et al. Multi-scale ordering in highly stretchable polymer semiconducting films. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.; Kang, B.; Choi, H.H.; Sin, D.H.; Lee, H.; Lee, W.H.; Cho, K. Stretchable and transparent organic semiconducting thin film with conjugated polymer nanowires embedded in an elastomeric matrix. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 2, 1500250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Galuska, L.; Roy, A.; Lorenz, M.; Chen, B.; Luo, S.; Li, Y.; Hung, C.; Qian, Z.; et al. Tacky elastomers to enable tear-resistant and autonomous self-healing semiconductor composites. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Thukral, A.; Sharma, S.; Yu, C. Biaxially stretchable fully elastic transistors based on rubbery semiconductor nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1800043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauhofer, W.; Kovacs, J.Z. A review and analysis of electrical percolation in carbon nanotube polymer composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, A.W.; Silva, G.G.; Liu, J.-W.; Martens, W.N.; Waclawik, E.R. Structure and conductivity of multi-walled carbon nanotube/poly (3-hexylthiophene) composite films. Polymers 2007, 48, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goto, T.; Morita, J.; Maekawa, Y.; Kanehashi, S.; Shimomura, T. Semiconducting Properties of the Hybrid Film of Elastic Poly(styrene-b-butadiene-b-styrene) Block Copolymer and Semiconducting Poly(3-hexylthiophene) Nanofibers. Polymers 2020, 12, 2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092118
Goto T, Morita J, Maekawa Y, Kanehashi S, Shimomura T. Semiconducting Properties of the Hybrid Film of Elastic Poly(styrene-b-butadiene-b-styrene) Block Copolymer and Semiconducting Poly(3-hexylthiophene) Nanofibers. Polymers. 2020; 12(9):2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092118
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoto, Takanori, Jun Morita, Yuya Maekawa, Shinji Kanehashi, and Takeshi Shimomura. 2020. "Semiconducting Properties of the Hybrid Film of Elastic Poly(styrene-b-butadiene-b-styrene) Block Copolymer and Semiconducting Poly(3-hexylthiophene) Nanofibers" Polymers 12, no. 9: 2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092118
APA StyleGoto, T., Morita, J., Maekawa, Y., Kanehashi, S., & Shimomura, T. (2020). Semiconducting Properties of the Hybrid Film of Elastic Poly(styrene-b-butadiene-b-styrene) Block Copolymer and Semiconducting Poly(3-hexylthiophene) Nanofibers. Polymers, 12(9), 2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12092118




