A New Mn–Salen Micellar Nanoreactor for Enantioselective Epoxidation of Alkenes in Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
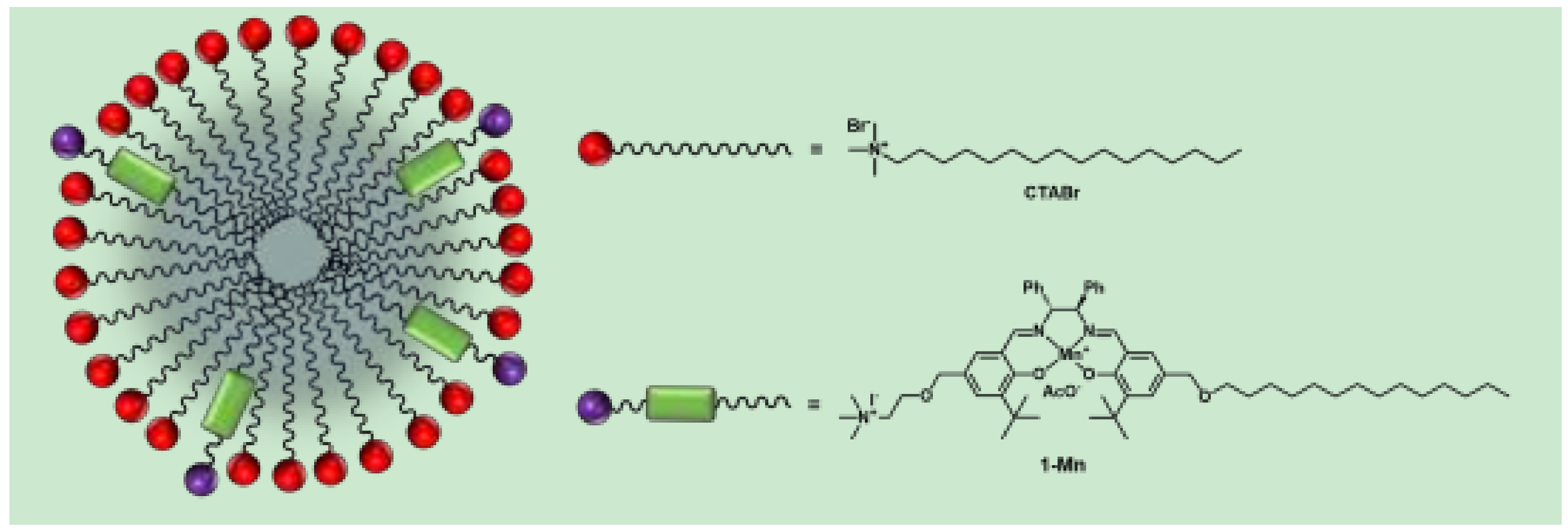
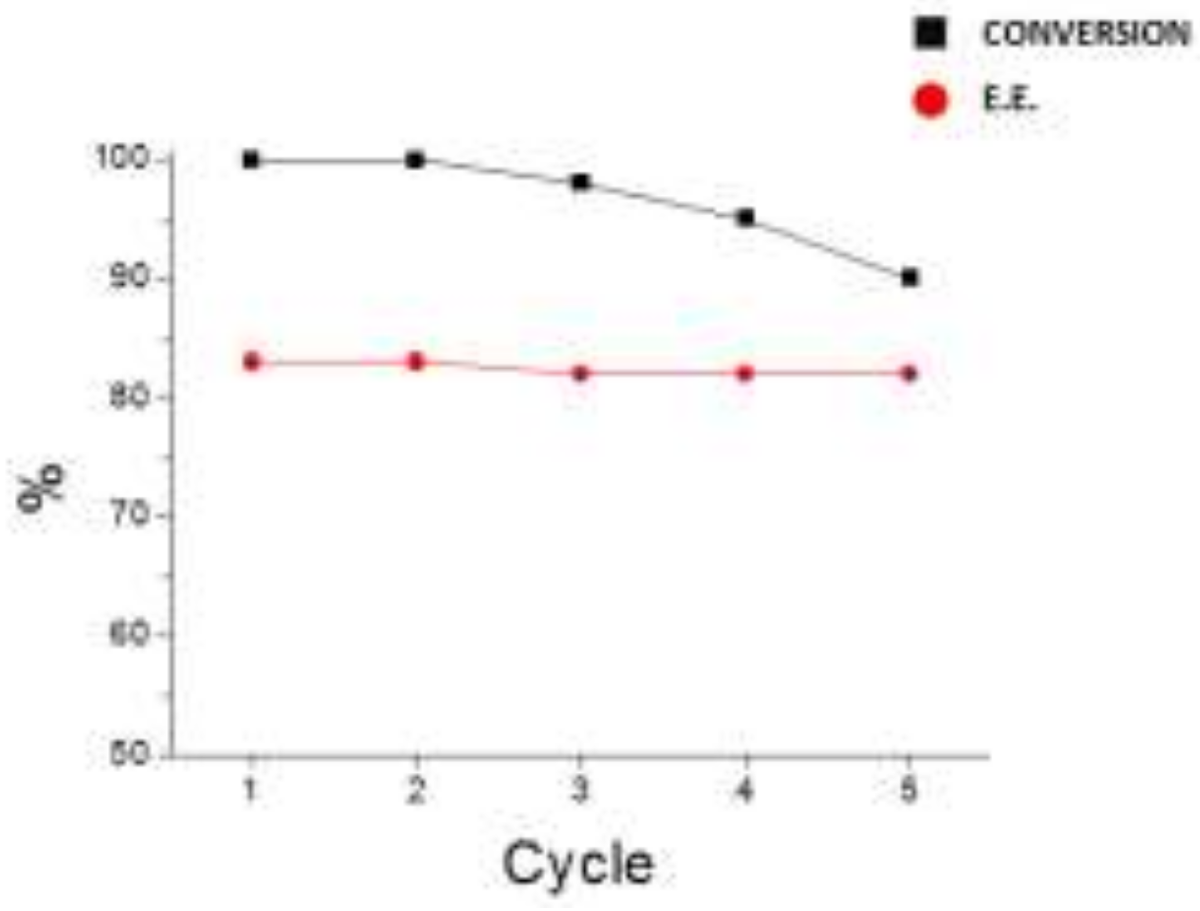
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. DOSY Measurements
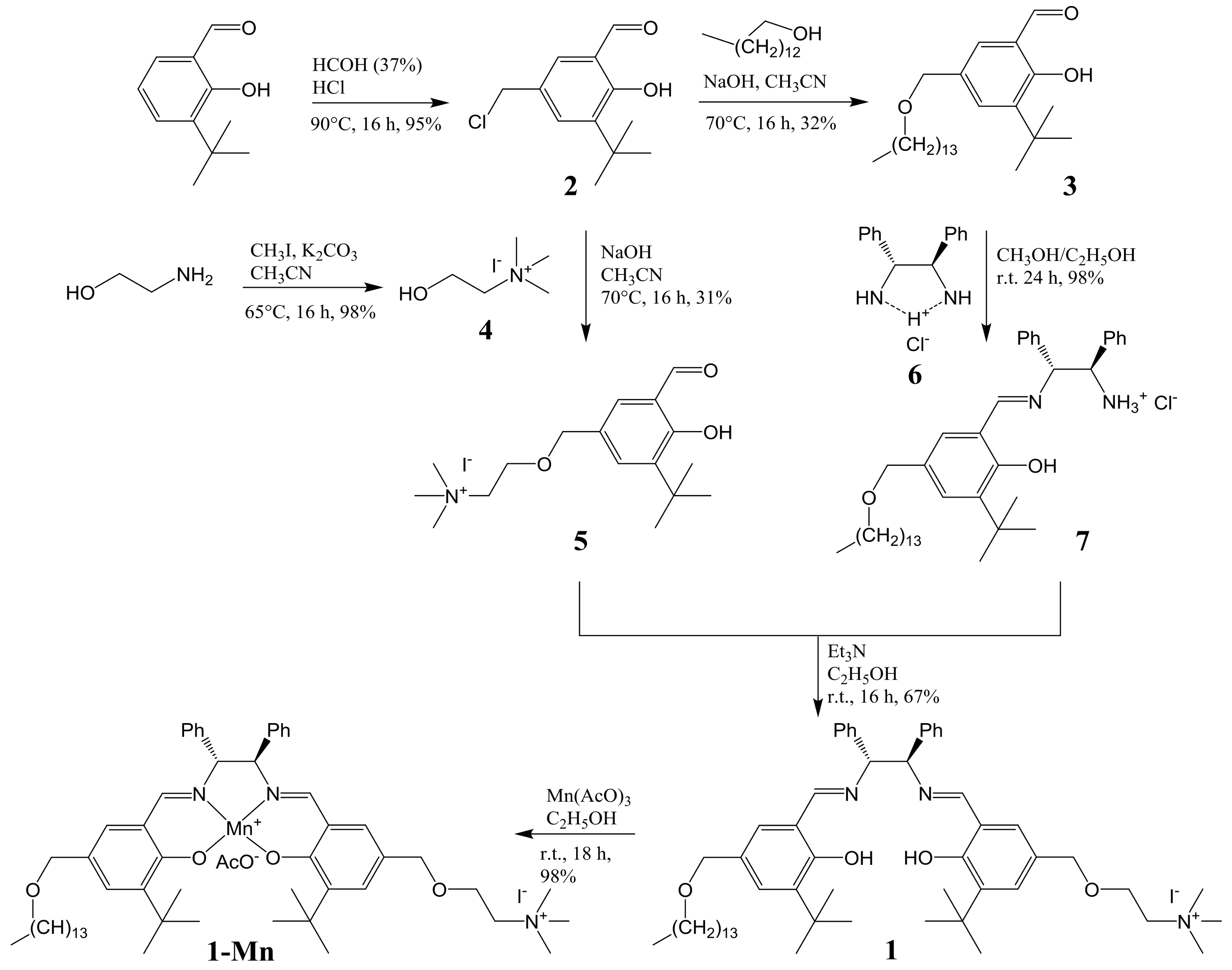
3.3. Synthesis and Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Welton, T. Solvents and sustainable chemistry. Proc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2015, 471, 20150502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangemi, C.M.A.; Pappalardo, A.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. Applications of supramolecular capsules derived from resorcin[4]arenes, calix[n]arenes and metalloligands: From biology to catalysis. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 51919–51933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitanosono, T.; Masuda, K.; Xu, P.; Kobayashi, S. Catalytic Organic Reactions in Water toward Sustainable Society. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 679–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotanda, P.; Lu, A.; Patterson, J.P.; Petzetakis, N.; O’Reilly, R.K. Functionalized Organocatalytic Nanoreactors: Hydrophobic Pockets for Acylation Reactions in Water. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarso, A. Micellar Nanoreactor. In Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2016; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Xie, C.; Yu, F.; Yuan, B.; Yu, S. Selective hydrogenation of α-pinene to cis-pinane over Ru nanocatalysts in aqueous micellar nanoreactors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 54806–54811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.-C.; Lu, J.; Weck, M.; Jones, C.W. Acid−Base Bifunctional Shell Cross-Linked Micelle Nanoreactor for One-Pot Tandem Reaction. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vriezema, D.M.; Aragones, M.C.; Elemans, J.A.A.W.; Cornelissen, J.J.L.M.; Rowan, A.E.; Nolte, R.J.M. Self-Assembled Nanoreactors. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1445–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baleizão, C.; Garcia, H. Chiral Salen Complexes: An Overview to Recoverable and Reusable Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 3987–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, E.N. Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis; Ojima, I., Ed.; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1993; Chapter 4.2; pp. 159–202. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, T.P.; Jacobsen, E.N. Privileged Chiral Catalysts. Science 2003, 299, 1691–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arends, I.W.E.E. Metal-Catalyzed Asymmetric Epoxidations of Terminal Olefins Using Hydrogen Peroxide as the Oxidant. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 6250–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMorn, P.; Hutchings, G.J. Heterogeneous enantioselective catalysts: Strategies for the immobilisation of homogeneous catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.-H.; Li, N.-G.; Shi, Q.-P.; Tang, Y.-P.; Tang, H.; Shen, M.-Z.; Duan, J.-A. Immobilization of Chiral Manganese(III)-salen Complexes for Enantioselective Epoxidation of Unfunctionalised Olefins. Curr. Org. Synth. 2014, 11, 204–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Paglia Fragola, V.; Lupo, F.; Pappalardo, A.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G.; Toscano, R.M.; Ballistreri, F.P.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Gulino, A. A surface-confined O=MnV(salen) oxene catalyst and high turnover values in asymmetric epoxidation of unfunctionalized olefins. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 20561–20565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusso Sfrazzetto, G.; Millesi, S.; Pappalardo, A.; Toscano, R.M.; Ballistreri, F.P.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Gulino, A. Olefin epoxidation by a (salen)Mn(III) catalyst covalently grafted on glass beads. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballistreri, F.P.; Brinchi, L.; Germani, R.; Savelli, G.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Toscano, R.M. Enantioselective epoxidations of alkenes catalyzed by (salen)Mn(III) in aqueous surfactant systems. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 10239–10243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballistreri, F.P.; Gangemi, C.M.A.; Pappalardo, A.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Toscano, R.M.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. (Salen)Mn(III) Catalyzed Asymmetric Epoxidation Reactions by Hydrogen Peroxide in Water: A Green Protocol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1112–11121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bérubé, C.; Barbeau, X.; Lagüe, P.; Voyer, N. Revisiting the Juliá-Colonna Enantioselective Epoxidation: Supramolecular Catalysis in Water. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 5099–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malkov, A.V.; Czemerys, L.; Malyshev, D.A. Vanadium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Epoxidation of Allylic Alcohols in Water. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 3350–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colladon, M.; Scarso, A.; Strukul, G. Towards a Greener Epoxidation Method: Use of Water-Surfactant Media and Catalyst Recycling in the Platinum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Epoxidation of Terminal Alkenes with Hydrogen Peroxide. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, F.; Xie, X.-K.; Liu, F.; Huang, Z.-Z. Synthesis of new functionalized chiral ionic liquid and its organocatalytic asymmetric epoxidation in water. Catal. Commun. 2009, 11, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Achazi, K.; Bottcher, C.; Haag, R.; Sharma, S.K. Fabrication of nanostructures through self-assembly of non-ionic amphiphiles for biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 22121–22132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morotti, T.; Calabrese, V.; Cavazzini, M.; Pedron, D.; Cozzuol, M.; Licciardello, A.; Tuccitto, N.; Quici, S. Zirconium phosphate/phosphonate multilayered films based on push–pull stilbazolium salt: Synthesis, characterization and second harmonic generation. Dalton Trans. 2008, 2974–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuccitto, N.; Giamblanco, N.; Licciardello, A.; Marletta, G. Patterning of lactoferrin using functional SAMs of iron complexes. Chem. Commun. 2007, 2621–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulino, A.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G.; Millesi, S.; Pappalardo, A.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Ballistreri, F.P.; Toscano, R.M.; Fragalà, L. Nerve Gas Simulant Sensing by an Uranyl–Salen Monolayer Covalently Anchored on Quartz Substrates. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 1576–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballistreri, F.P.; Condorelli, G.G.; Fragalà, I.; Motta, A.; Pappalardo, A.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Tudisco, C.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. Covalent functionalization of silicon surfaces with cavitand-modified salen. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 2124–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.E.; Ballistreri, F.P.; D’Agata, S.; Pappalardo, A.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Toscano, R.M.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. Enantioselective Molecular Recognition of Chiral Organic Ammonium Ions and Amino Acids Using Cavitand–Salen Based Receptors. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 5674–5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleij, A.W. Nonsymmetrical Salen Ligands and Their Complexes: Synthesis and Applications. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, A.; Amato, M.E.; Ballistreri, F.P.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Toscano, R.M.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. Pair of Diastereomeric Uranyl Salen Cavitands Displaying Opposite Enantiodiscrimination of α-Amino Acid Ammonium Salts. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 7684–7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Urso, A.; Tudisco, C.; Ballistreri, F.P.; Condorelli, G.G.; Randazzo, R.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Toscano, R.M.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G.; Pappalardo, A. Enantioselective extraction mediated by a chiral cavitand–salen covalently assembled on a porous silicon surface. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 4993–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballistreri, F.P.; Pappalardo, A.; Toscano, R.M.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. A New Heteroditopic Chiral Uranyl–Salen Receptor for Molecular Recognition of Amino Acid Ammonium Salts. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 20, 3806–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, A.; Ballistreri, F.P.; Li Destri, G.; Mineo, P.G.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Toscano, R.M.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. Supramolecular Polymer Networks Based on Calix[5]arene Tethered Poly(p-phenyleneethynylene). Macromolecules 2012, 45, 7549–7556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrida, M.L.; Rizzarelli, E.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Satriano, C.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. A novel fully water-soluble Cu(I) probe for fluorescence live cell imaging. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 9835–9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuccitto, N.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G.; Gangemi, C.M.A.; Ballistreri, F.P.; Toscano, R.M.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Pappalardo, A.; Marletta, G. Memory-Driven Order-Disorder Transition of 3D-Supramolecular Architecture Based on Calix[5]arene and Porphyrin Derivatives. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11681–11684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puglisi, R.; Ballistreri, F.P.; Gangemi, C.M.A.; Toscano, R.M.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Pappalardo, A.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. Chiral Zn–salen complexes: A new class of fluorescent receptors for enantiodiscrimination of chiral amines. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurti, L.; Blewett, M.M.; Corey, E.J. Origin of Enantioselectivity in the Jacobsen Epoxidation of Olefins. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 4592–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulman Page, P.C.; Chan, Y.; Armylisas, A.H.N.; Alahmdi, M. Asymmetric epoxidation of chromenes mediated by iminium salts: Synthesis of mollugin and (3S,4R)-trans-3,4-dihydroxy-3,4-dihydromollugin. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 8406–8416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epoxidation reactions with 6-CN-2,2-dimethylchromene, 1,2-dihydronaphthalene and cis-β-ethylstyrene were carried out also without phosphate buffer (in the same condition of entry 4, 9 and 17 reported in Table 1), obtaining the same results of conversion and enantiomeric excess measured in the presence of phosphate buffer.
- We performed epoxidation of 6-CN-2,2-dimethylchromene without 1-Mn, with CTABr = [0.06], [alkene] = [NaClO] = 1.17 × 10−2 M, 0.05 M Na2HPO4 at pH 11.2, obtaining a conversion of 52% after 1 h, and 100% after 6 h; with 1,2-dihydronaphthalene, with the same conditions, conversion value was 38% after 1 h and 100% after 12 h while with cis-β-ethylstyrene we observed 47% of conversion after 1 h and 100 after 8 h.
- Van Aken, K.; Strekowski, L.; Patiny, L. EcoScale, a semi-quantitative tool to select an organic preparation based on economical and ecological parameters. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gałuszka, A.; Konieczka, P.; Migaszewski, Z.M.; Namiesnik, J. Analytical Eco-Scale for assessing the greenness of analytical procedures. Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, A.; Mosset, P.; Spiegel, M.; Saalfrank, R.W. Reverse asymmetric catalytic epoxidation of unfunctionalized alkenes. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Alkene | Entry | [CTABr] (M) | 1-Mn (%) b | Time (h) | e.e. (%) c | Conv. (%) c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
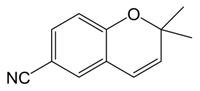 | 1 | 0.03 | 5 | 1 | 83 e | 85 |
| 2 | 0.03 | 5 | 3 | 82 e | 100 | |
| 3 | 0.06 | 5 | 1 | 83 e | 87 | |
| 4 | 0.06 | 5 | 3 | 83 e | 100 | |
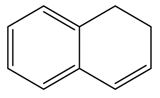 | 5 | 0.03 | 5 | 1 | 83 f | 17 |
| 6 | 0.03 | 5 | 8 | 82 f | 46 | |
| 7 | 0.03 | 10 | 8 | 84 f | 64 | |
| 8 | 0.06 | 10 | 1 | 80 f | 76 | |
| 9 | 0.06 | 10 | 3 | 83 f | 100 | |
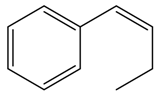 | 10 | 0.03 | 5 | 1 | 50 g | 73 |
| 11 | 0.03 | 5 | 2 | 51g | 100 | |
| 12 d | 0.015 | 10 | 1 | 56 g | 88 | |
| 13 d | 0.015 | 10 | 4 | 57 g | 100 | |
| 14 d | 0.03 | 10 | 1 | 56 g | 86 | |
| 15 d | 0.03 | 10 | 4 | 58 g | 100 | |
| 16 d | 0.06 | 10 | 1 | 58 g | 85 | |
| 17 d | 0.06 | 10 | 4 | 57 g | 100 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ballistreri, F.P.; Toscano, R.M.; Amato, M.E.; Pappalardo, A.; Gangemi, C.M.A.; Spidalieri, S.; Puglisi, R.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. A New Mn–Salen Micellar Nanoreactor for Enantioselective Epoxidation of Alkenes in Water. Catalysts 2018, 8, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040129
Ballistreri FP, Toscano RM, Amato ME, Pappalardo A, Gangemi CMA, Spidalieri S, Puglisi R, Trusso Sfrazzetto G. A New Mn–Salen Micellar Nanoreactor for Enantioselective Epoxidation of Alkenes in Water. Catalysts. 2018; 8(4):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040129
Chicago/Turabian StyleBallistreri, Francesco P., Rosa Maria Toscano, Maria Emanuela Amato, Andrea Pappalardo, Chiara M. A. Gangemi, Sofia Spidalieri, Roberta Puglisi, and Giuseppe Trusso Sfrazzetto. 2018. "A New Mn–Salen Micellar Nanoreactor for Enantioselective Epoxidation of Alkenes in Water" Catalysts 8, no. 4: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040129
APA StyleBallistreri, F. P., Toscano, R. M., Amato, M. E., Pappalardo, A., Gangemi, C. M. A., Spidalieri, S., Puglisi, R., & Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. (2018). A New Mn–Salen Micellar Nanoreactor for Enantioselective Epoxidation of Alkenes in Water. Catalysts, 8(4), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040129