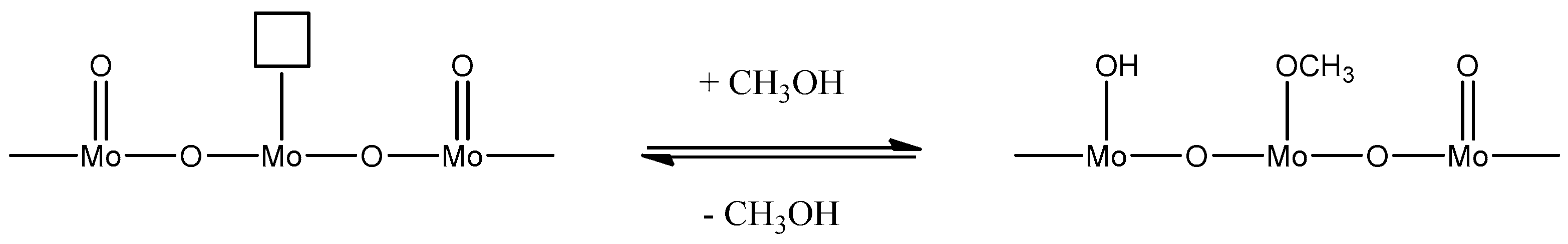1. Introduction
The selective oxidation of methanol to formaldehyde is a fundamental industrial reaction, reflected by its global demand in excess of 30 million tonnes
per annum [
1]. Formaldehyde stands as the most profitable aldehyde, heavily relied upon due to its diverse and widespread applications including as a building block to the production of dyes, resins, and adhesives.
Since 1931 [
2], the most commonly adopted catalyst employed industrially is an iron molybdate based catalyst, Fe
2(MoO
4)
3, to which an excess of MoO
3 is added to the chemical composition. This mixed oxide catalyst is considered by many to be a more economical means of effecting partial oxidation of methanol, compared to other oxides and Ag catalysts. Under this approach, formaldehyde yields of 95% are reported, however in order to exploit this process further it is crucial that scientist’s gain an understanding of the working catalyst, and the active site/s which dictate the chemistry.
The addition of excess MoO
3 to the catalyst is considered essential. Although the process is operated at relatively low temperatures to discourage over-oxidation of methanol, at these temperatures MoO
3 is shown to sublime from the catalyst as a white residue [
3]. This consequently leaves a catalyst Fe rich in nature, which is detrimental to catalyst performance, directing selectivity towards carbon oxide products [
4,
5]. With excess MoO
3 in the chemical make-up, catalyst lifetimes are prolonged to last between 6 and 12 months.
With both an excess of MoO
3 and stoichiometric Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 deemed necessary in the chemical composition, debate has arisen between authors regarding which of these phases dominates as the active species [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10], or whether indeed there is a synergy between the two [
11,
12]. MoO
3 is highly regarded for its excellent selectivity to formaldehyde, due to its high capacity to increase oxygen availablity at the catalyst surface. However, whilst MoO
3 may be a highly selective system, the conversion of methanol feedstock is poor. This is a consequence of its low surface area and anisotropic structure [
13], which reduces the availability of active sites for the reaction. Conversely, Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 is isotropic in nature with an increased surface area, therefore making it a more suitable catalyst choice in terms of activity. Nonetheless, Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 does not present an analogous performance to MoO
3 in terms of its’ selectivity, unable to compete with the almost 100% selectivity to formaldehyde reported for the single phase oxide [
14]. A recent study by Söderhjelm et al. [
11] has highlighted that both phases are required for optimized performance, emphasising that the MoO
3 is not simply there to replenish lost Mo. Here they proposed a synergistic effect between MoO
3 and Fe
2(MoO
4)
3; implying that the active phase may be Mo-rich, existing as an amorphous layer in octahedral co-ordination at the surface. Each oxide plays its own specific role. Specifically, MoO
3 is believed to enable dissociation of molecular O
2 to atomic oxygen, whilst Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 utilises this atomic oxygen to oxidise methanol to formaldehyde. The theory postulated arises from initial studies involving MoS
2/Co
9S
8. Here it was suggested that the promotion of one phase occurs at the junction of the two phases, modifying the electronic density of the catalytic active phase. This is in line with the remote control theory [
15], which is applied to catalysts with two oxide phases. One acts as an acceptor phase (in this instance Fe
2(MoO
4)
3), whilst the other is the donor (MoO
3). Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 enables HC activation, acting independently with limited activity. MoO
3 as the donor phase has a role in providing oxygen activation at a high rate, to spill over and accelerate the overall catalytic cycle. Routray et al. more recently propose a further hypothesis [
12]. Work also highlighted a possible synergy between the two oxides. The addition of excess crystalline MoO
3 to the crystalline Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 phase significantly increased the overall steady-state catalytic performance toward HCHO formation. The enhanced catalytic performance of the bulk catalyst in the presence of excess MoO
3 was attributed to the formation of third species, a segregated surface MoO
x monolayer. The role of the excess crystalline MoO
3 was identified to replenish the surface MoO
x lost by volatilization during methanol oxidation. Work herein exploits this theory, with the challenging aim to unravel the nature of the active site in commercial Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 catalysts, through use of model MoO
x/Fe
2O
3 catalysts. Also questioned is the role of Fe in the catalyst.
2. Mo Segregation
Although the exact nature of the active species in iron molybdate based systems remains unknown, it is now frequently reported [
7,
10,
12,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20] that Mo surface-segregation readily occurs in iron molybdate systems. XPS studies of bulk iron molybdate have revealed that annealing at 400 °C facilitates the migration of molybdenum to the catalyst surface [
21], even when present at low bulk levels. The majority of surface investigations however have exploited electron microscopy studies. Work by Bowker et al. has used aberration corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy (acSTEM) [
22], to show that the surface of these catalysts are enriched with Mo. EDX line scans showed a clear dominance of the surface region by Mo, to the detriment of Fe. In support of this, Holmberg et al. [
11] have focused on the surface of FeMo catalysts, specifically the origin of the improved catalytic performance of bulk iron molybdate catalysts with extra crystalline MoO
3. Low-energy ion scattering (LEIS) analysis of the outermost surface layer revealed that the molybdate catalysts possessed a monolayer of surface MoO
x species, onto which surface CH
3OH and CH
3O were shown to be present by IR spectroscopy. The enhanced catalytic performance of bulk Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 catalysts in the presence of excess MoO
3 was attributed to this surface MoO
x monolayer. HRTEM imaging proved an amorphous surface structure on the edges of the crystals. A similar structure was observed by Gai and Labun [
23], when focussing on bulk structures and their reduction. The EDS data showed that the amorphous structure on the fresh catalyst was rich in Mo, whereas for the post reaction sample there was a lower Mo content. The link between ageing and composition implied that the active material was the amorphous structure at the surface.
In addition to characterization, reactivity data has proved a key tool in providing evidence of Mo segregation [
14]. Fe
2O
3 itself is a highly unselective catalyst for methanol oxidation, producing a formate intermediate leading to CO
2 through complete combustion. However, with low loadings of Mo (just 0.25 monolayers present), iron oxide exhibits a significantly different selectivity, apparent by the identification of CO and H
2CO in the reaction profile. The change in selectivity is reflective of the dominance of Mo at the surface. This has also been seen through TPD (Temperature Programmed Desorption) analysis. TPD of Methanol on MoO
3 and Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 are remarkably similar (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2), albeit a slight difference in the ratio of formaldehyde production due to the difference in activity of these two materials. This infers a similar terminating layer in these bulk materials, a surface rich in Mo. Mo has been concluded to be dominant at the surface of iron molybdate based catalysts, existing in its active and selective form, Mo (VI). Mo under this oxidation state is deemed crucial to optimal catalyst performance. Confirmation derives from experiments carried out to determine the activity profile of the other main oxidation state of Mo, which is Mo (IV) [
22,
24]. During reaction, the active Mo (VI) briefly exists as reduced Mo (IV), which can readily use gas phase oxygen to re-oxidise back to Mo (VI). The identification of the specific conformation of the active site, however, remains elusive.
4. Making XAFS Surface Sensitive
Characterisation of bulk FeMo catalysts has been possible through a number of techniques, most commonly through Raman, FT-IR, DRIFTS, XRD and XPS [
14,
22,
26,
27,
28,
29]. The structures of MoO
3 and Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 are reasonably well understood, however there still remains some doubt in how they react with methanol, and which phase is predominantly involved in the reaction. There is a requirement to turn to more surface sensitive techniques to probe the uppermost layers in these catalysts. The use of X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) has been the primary focus of our group.
The use of XAS to probe bulk Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 has so far been limited in the literature. Due to the significance of the surface layer, XAS as a bulk technique has not been highly considered. There are however a few examples of surface Mo studies [
30]. Sarti et al. [
31] have investigated the structural and morphological characterization of Mo coatings for high gradient accelerating structures on Al
2O
3. XAS experiments were performed at the Mo K-edge, to determine the chemical status of the Mo atoms. Mo was discovered to exist as a slightly disordered structure at the surface. Hu et al. [
32] have also studied the surface structures of supported MoO
3 catalysts by Raman and Mo
l-edge XANES. Supported MoO
3 catalysts on TiO
2, Al
2O
3, ZrO
2, and SiO
2, were prepared through incipient-wetness impregnation. At high surface coverages of MoO
3, for TiO
2, the Mo species was shown to form in octahedral coordination, whereas for Al
2O
3 there was a mixture of tetrahedral and octahedral co-ordinated species. On SiO
2 the Mo oxide showed an isolated structure, which resembles a mixed coordination between tetrahedral and octahedral formation.
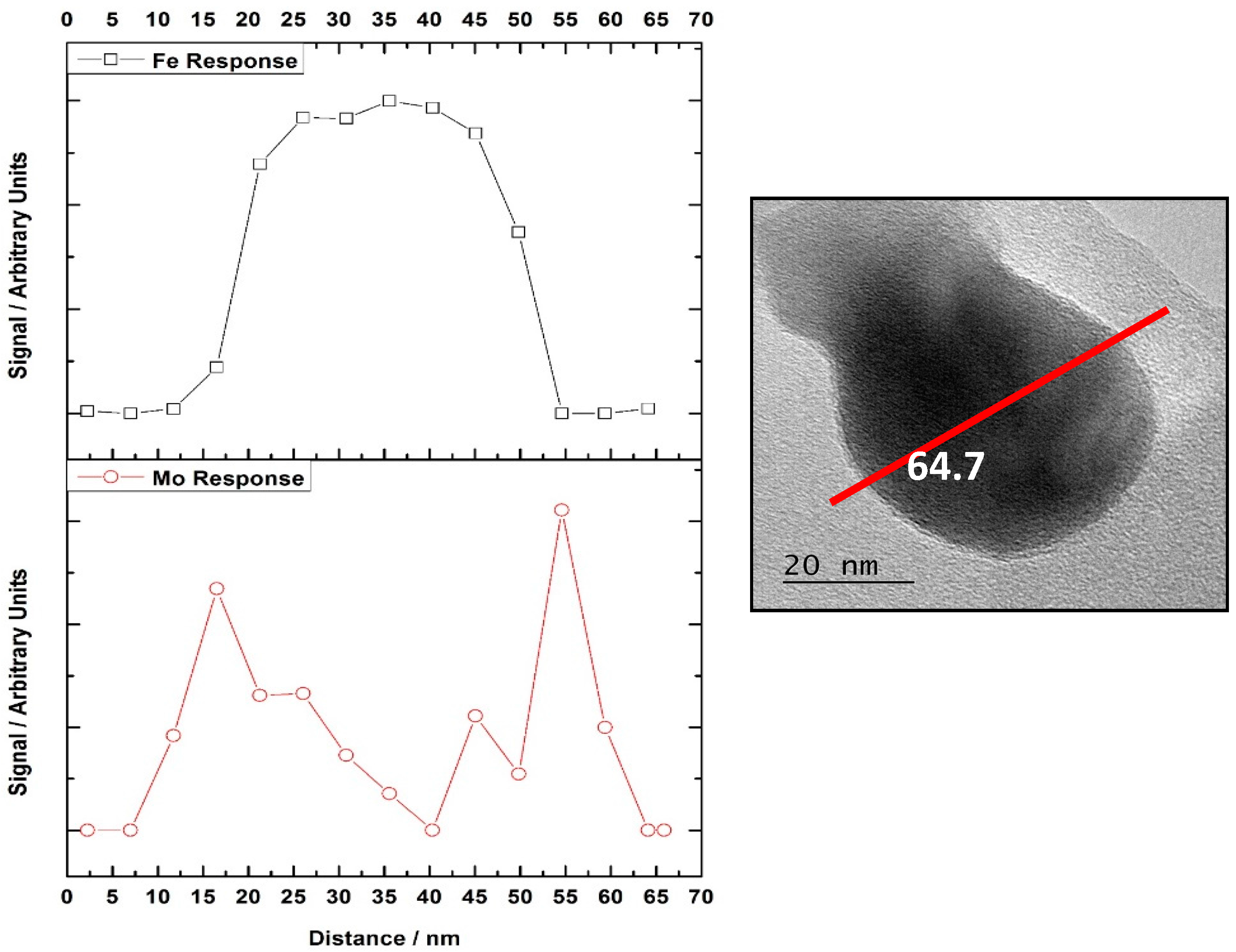
Most recent work of the author group has turned to studying model materials of the type MoO
x/Fe
2O
3 [
7,
16,
27], in order to gain knowledge into the active surface Mo species. Brookes et al. [
16] have confirmed Mo segregation in these core-shell structures, through exploitation of TEM-EDX studies. Inspecting EDX line profiles, Mo was demonstrated to be populated at the surface to the detriment of Fe (
Figure 3). Reactivity data supported this, with a stark difference in methanol reactivity between in the absence of Mo (CO
2 and H
2O dominant products) and with Mo present (H
2CO and CO dominant products), inferring the Mo to play a key role in adsorbing the incoming MeOH at surface. Since Mo is present only at the surface, this enables the use of XAFS, which is normally a bulk averaging technique, to be exploited in a surface sensitive approach when tuned to the Mo K-edge.
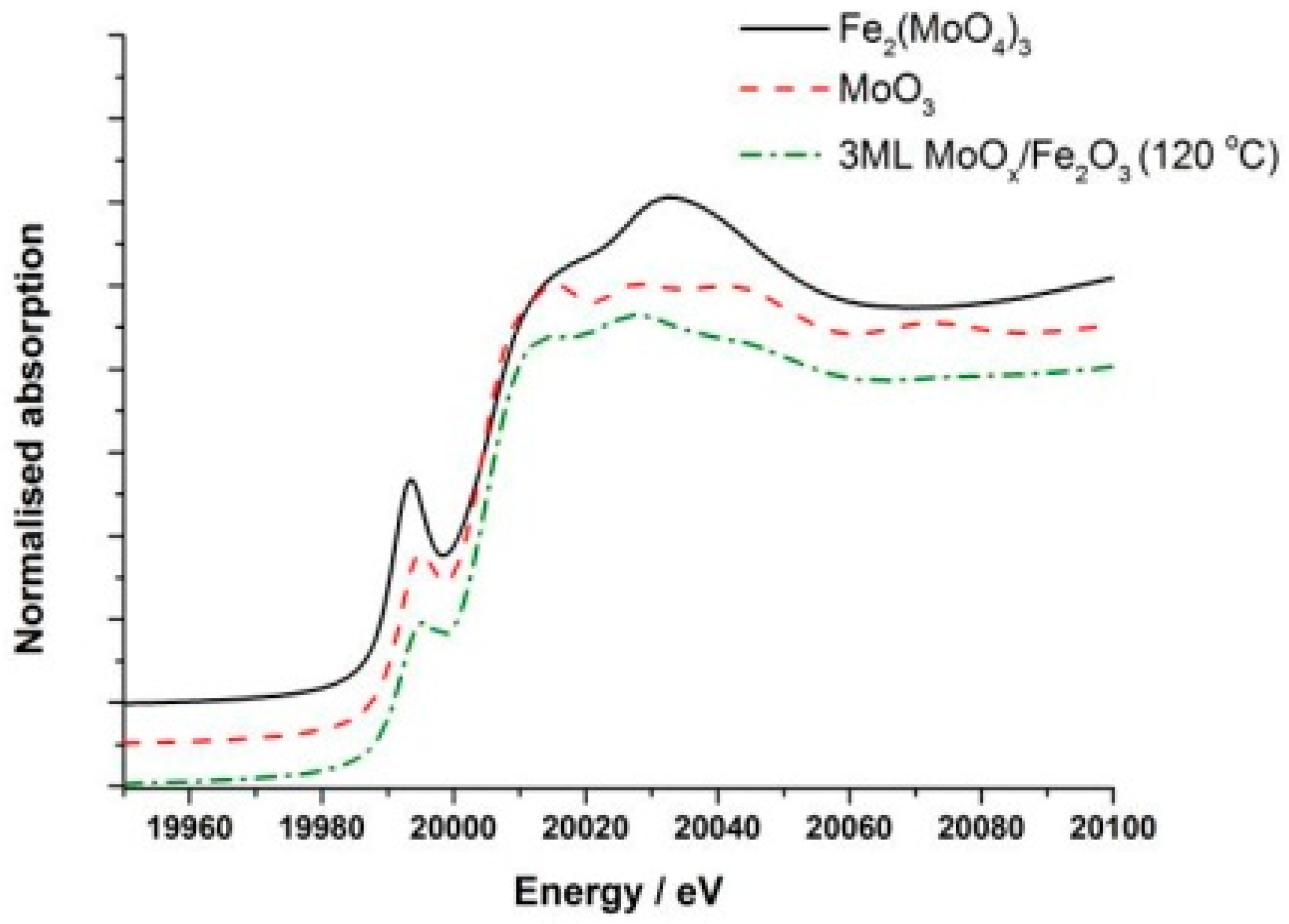
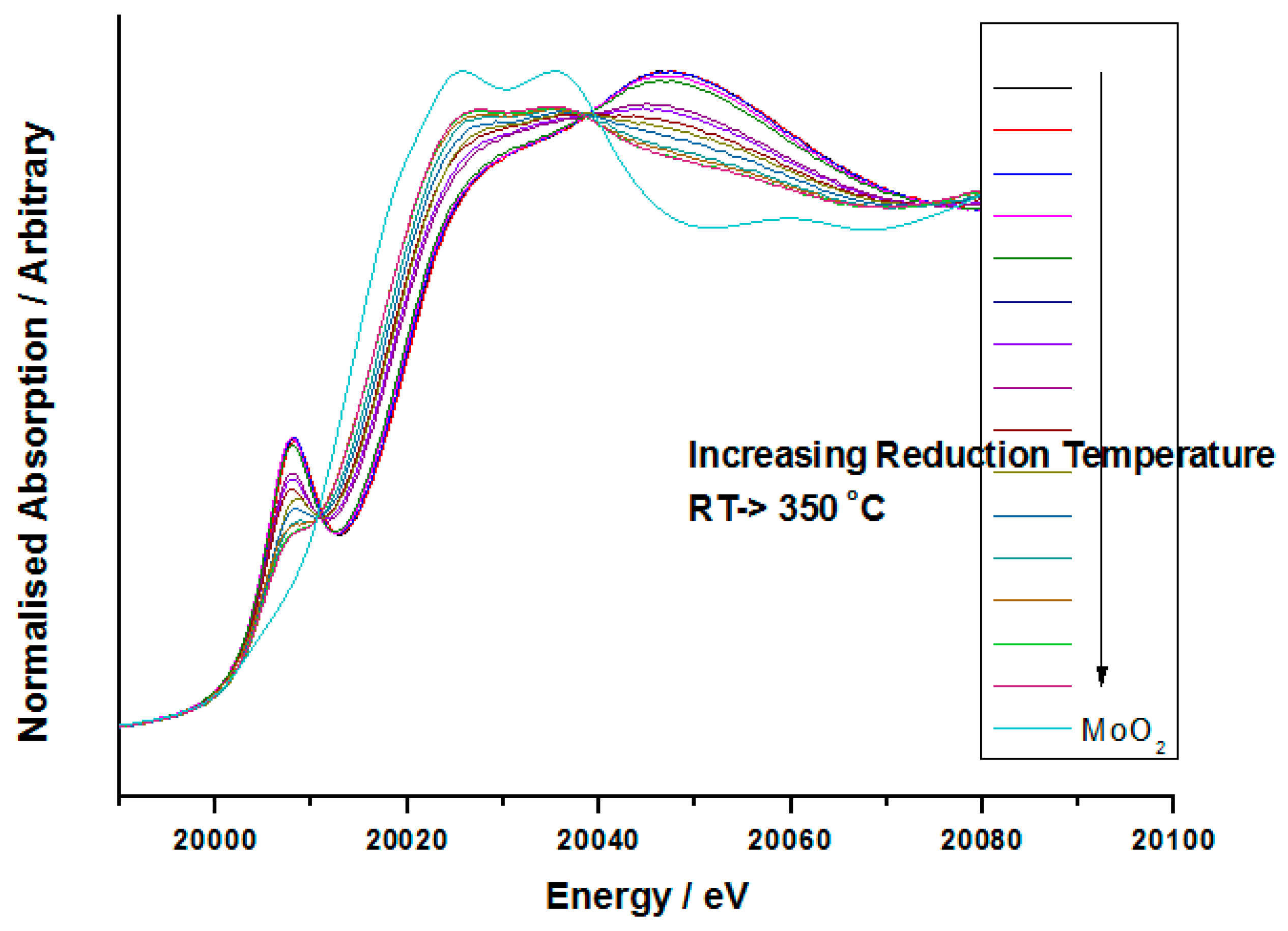
Initial work involved dosing three monolayers (3ML) of Mo onto the surface of Fe
2O
3, since this gave good sensitivity for spectroscopy techniques, most importantly for XANES. The interpretation of the Mo XANES spectra included the assignment of the pre-edge peak at ca. 19,995 eV, and the peak at 20,010 eV. The first is attributed to the dipole-forbidden/quadrupole-allowed 1s–4d transition [
33], associated primarily with tetrahedral geometry, but it is also present, albeit weaker, in structures with distorted octahedral geometry. The peak at 20,010 eV is assigned to the dipole-allowed 1s–5p transition and is a characteristic feature of Mo species with octahedral/distorted octahedral geometry. The XANES spectrum of the dried 3ML MoO
x/Fe
2O
3 sample (120 °C) is shown in
Figure 4. Comparing this with bulk MoO
3 (
Figure 4 also), it was found that the dried phase showed a much weaker pre-edge feature at 19,995 eV, associated with the distorted octahedral structure of this initial phase. Differences were also evident in the intensity of the peak at 20,010 eV.
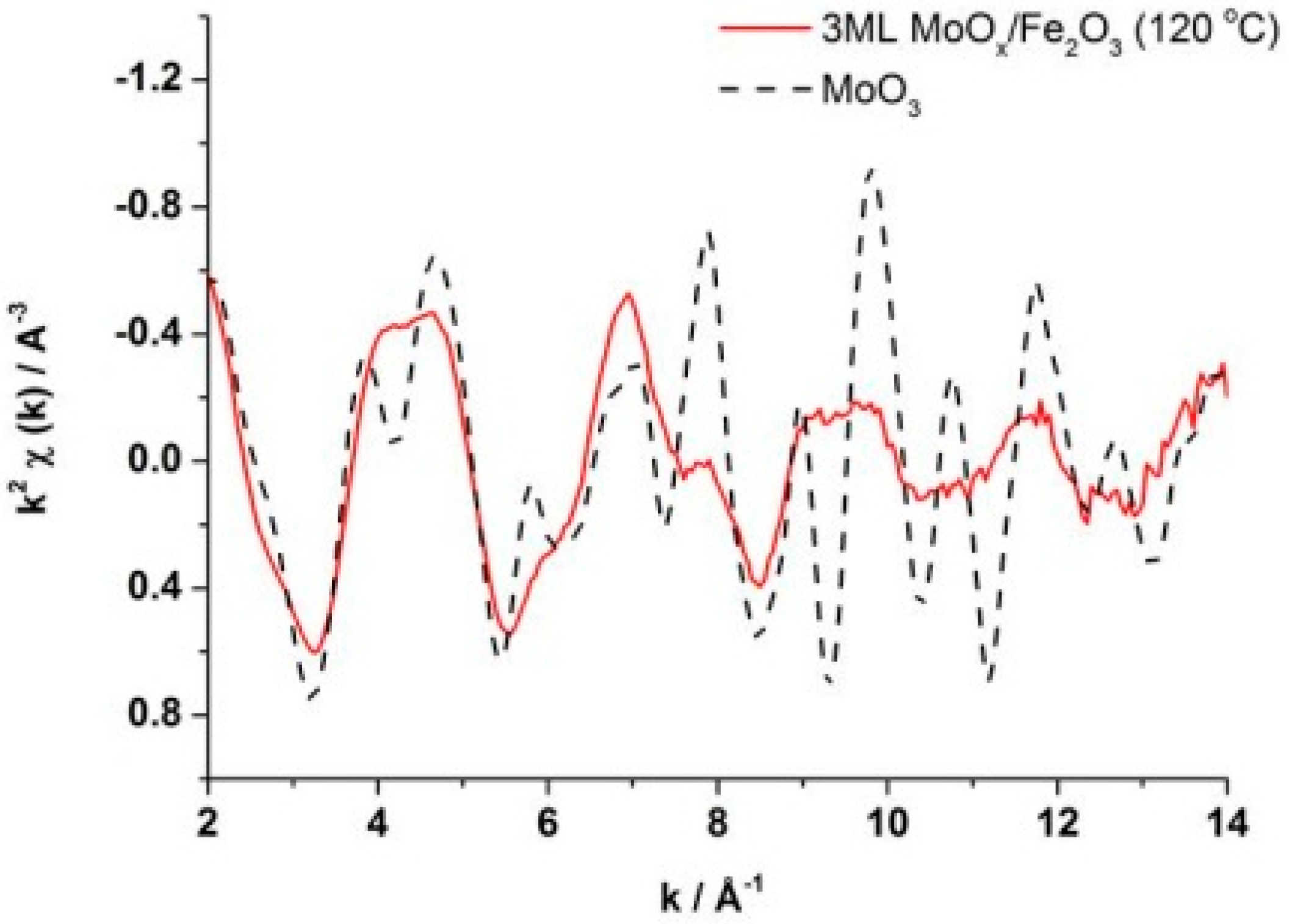
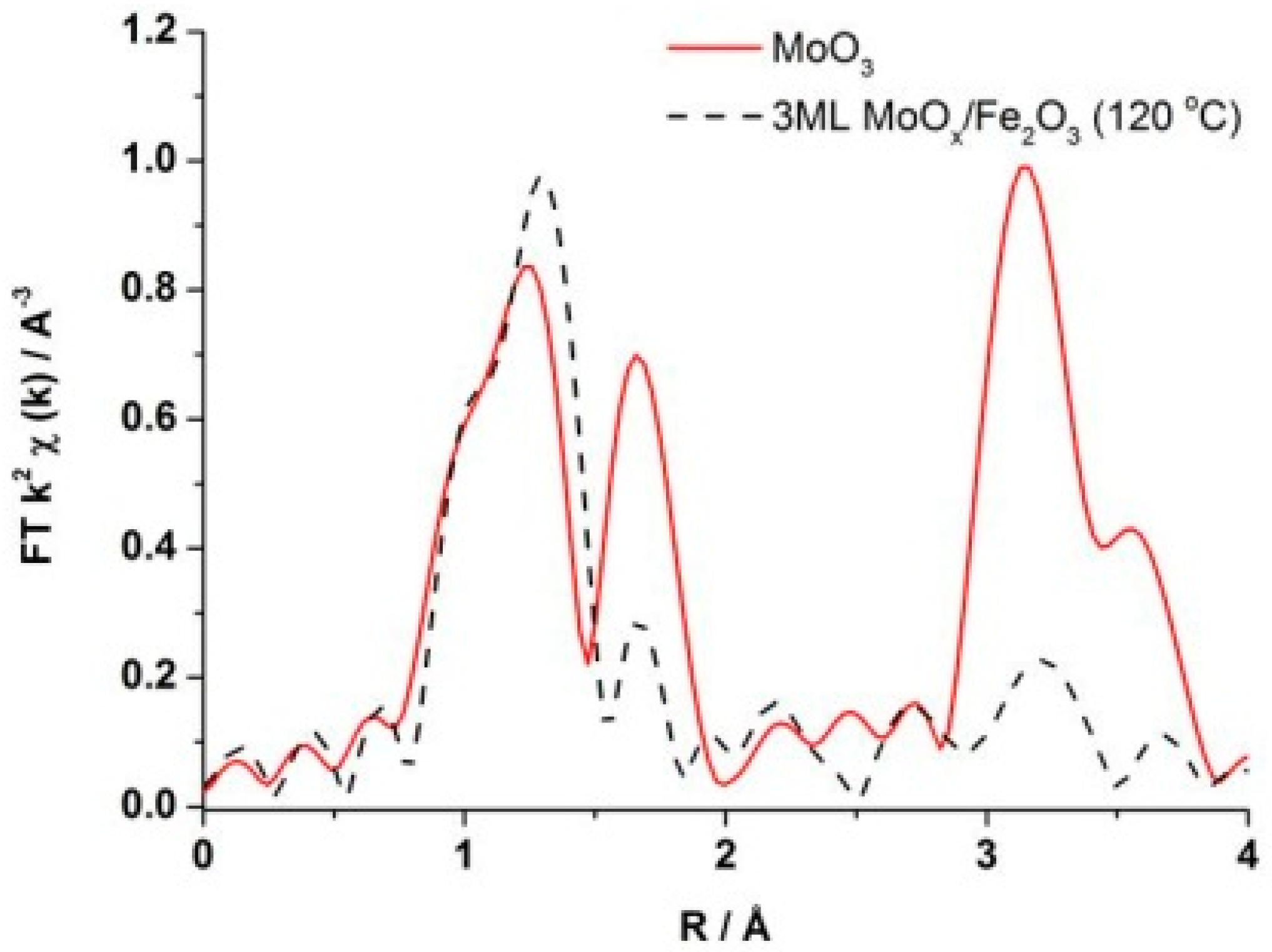
EXAFS interpretation (
Figure 5 and
Figure 6) was also assessed to clarify differences between the dried phase and commercial MoO
3. The
k2-weighted χ data showed a similar phasing and amplitude for the two samples at values of low k. However, the discrepancy at higher k inferred a lack of long range order for the dried sample, also supported by the radial distribution plot which showed an absence of a secondary coordination shell (Mo–Mo) as seen for MoO
3 (
Figure 6). This was indicative of the fewer high Z neighbours associated with the dried phase, and its overall lack of dimensionality. For this reason the dried phase was referred to as MoO
x, since it could not be indexed to any known phase of Mo.
The effect of annealing temperature on the nature of the Mo within these samples was also investigated. Assessing through XANES (
Figure 7), analysis showed there were no changes observed between the dried material and that calcined to 300 °C. The
k2-weighted χ spectrum of the 400 °C annealed sample however, indicated that the sample began to show features associated with MoO
3 phase formation. With further annealing to 500 °C, large amounts of Mo began to be incorporated into a tetrahedral Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 phase, depicted through a distinctive rise in the pre-edge feature at 19,995 keV (
Figure 7).
Table 1 details the phase compositions calculated through linear combination fittings (LCF’s) for various anneal temperatures between 120 and 600 °C. LCF’s were performed using the initial dried at 120 °C phase (MoO
x), MoO
3 and Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 as references. For a theoretical understanding,
Figure 8 displays a simplified schematic with the associated summary of these initial findings. It is shown that at temperatures above 400 °C, most of the Mo converted to Fe
2(MoO
4)
3, with Mo from the surface reacting with the Fe
2O
3 core to form a tetrahedral structure. Below this temperature, nanocrystalline MoO
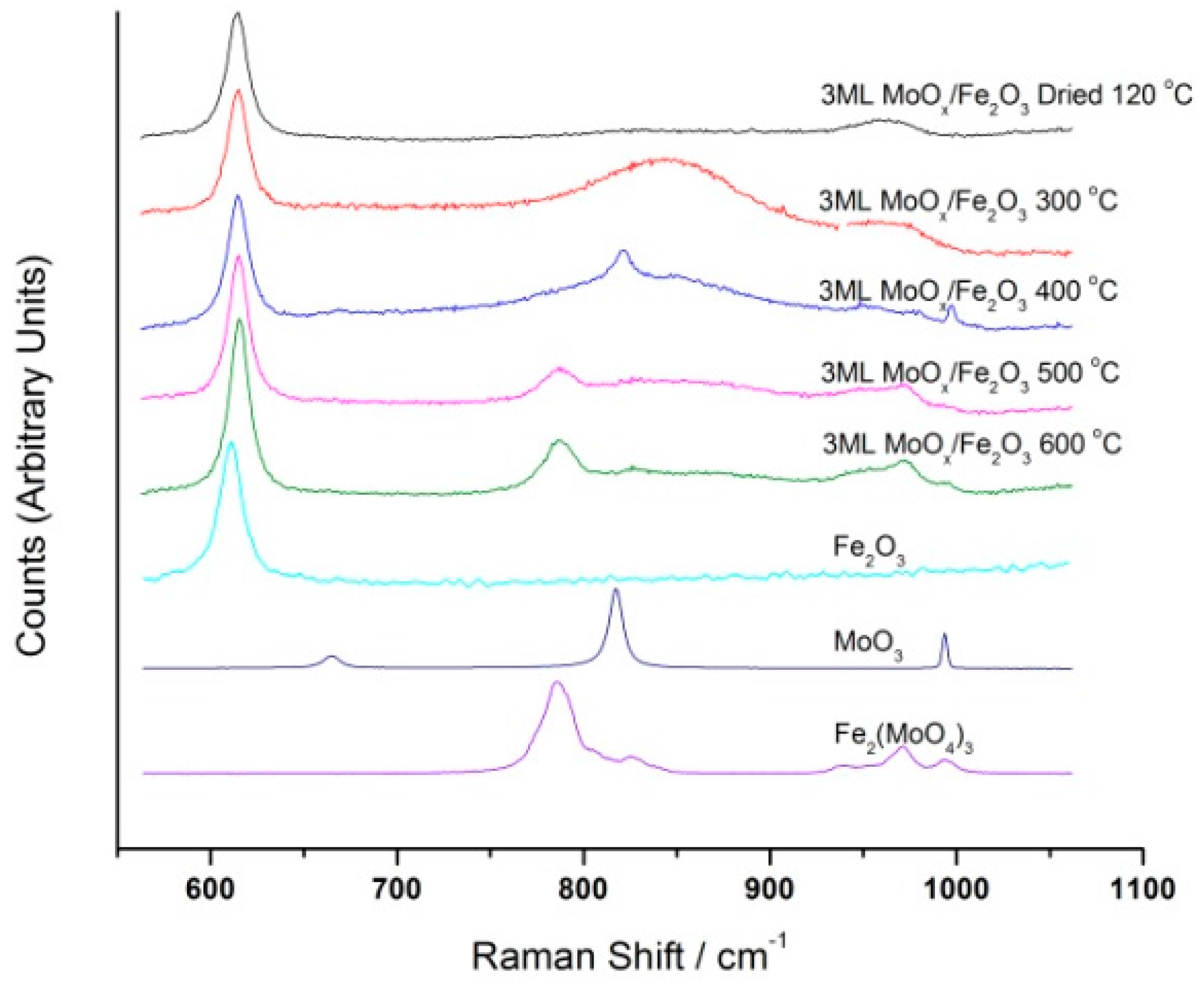
3 was present in the sample, forming at 400 °C. Crucially, Raman was only able to prove the existence of these two Mo oxide phases (
Figure 9), being MoO
3 and Fe
2(MoO
4)
3, whereas XAFS revealed a third component, MoO
x, present under all heat treatments employed. This is much in line with the opinions of Routray et al. [
12]. Interestingly, despite the differing Mo oxide phases between the samples dried at 120 °C, 400 and 500 °C, all of these catalysts showed a similar activity (
Figure 10, reactivity dominated by H
2CO and CO formation for all catalysts) [
16]. For this reason, the octahedral MoO
x surface layer present for all temperatures between 120 and 600 °C, was deemed the active and selective overlayer for formaldehyde synthesis. The material was both activated and improved in selectivity due to the dominance of the methoxy species on this Mo-doped material, in contrast to the stable formate which is seen to form on Fe
2O
3 [
4].
To extend from this study, further monolayer coverages were investigated by Brookes et al. [
7]. It was discovered that just one monolayer of Mo on iron oxide alone was successful in producing formaldehyde, albeit with a slight increase in CO production due to the inability to form a complete monolayer coverage over the Fe
2O
3 core. This lack of coverage subsequently leaves a surface with exposed Fe sites, which are detailed by Bowker et al. to be responsible for CO production through direct methanol dehydrogenation [
8,
27]. Fe
2O
3 coverage is considered crucial in dictating the selectivity of the reaction. Work by Huang et al. [
34] has investigated the influence of thermal spreading of MoO
3 on the surface of Fe
2O
3, and the solid-state reaction that produces Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 during heat treatment. XPS, SEM and Mössbauer spectroscopy were used to characterize the evolution of the surface. It was found that a small amount of MoO
3 can be dispersed onto the surface of Fe
2O
3 relatively easily by simple grinding of the two oxides. In addition, the thermal spreading of MoO
3 is facilitated at around 400 °C. Further thermal spreading and the solid-state reaction yield a shell of Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 encapsulating the remaining Fe
2O
3 grains, but a small amount of MoO
3 remains on the external surface of the resulting Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 shell.
In support of this, Brookes et al. [
16] have demonstrated the benefits of calcination time, comparing the effects of both a 2 and 24 h treatment on various monolayer catalysts of MoO
x/Fe
2O
3 calcined at 500 °C. Catalysts across the monolayer range all demonstrated a significantly improved selectivity towards formaldehyde with a longer calcination time, with the 1ML catalyst showing the most significant improvement. For 1ML dosed, a clear production of CO
2 was observed though TPD analysis after a two hour calcination. This is in stark contrast to the performance after a 24 h heat treatment, which only disclosed CO and H
2CO to desorb from the surface. This is reflective of the improved spread of the Mo at the surface, although no characterization has been performed to support this. The work highlighted the importance of investigating the evolution of the surface state during the preparation of a catalyst.
With an ongoing interest in this active amorphous overlayer of Mo, focus turned to studying the 1ML MoO
x/Fe
2O
3 catalyst more thoroughly through spectroscopy techniques [
7]. Both Raman and XANES data revealed a uniform absorption spectrum across the calcination range for 1ML MoO
x/Fe
2O
3 treated between 120 C and 600 °C (
Figure 11), also analogous to the dried 3ML MoO
x/Fe
2O
3 phase previously discussed. It was therefore recognized that for a monolayer (or sub-monolayer) amount of a species (labelled MoO
x), the molybdenum remains segregated at the surface of the Fe
2O
3, with complete O
h geometry under all calcination conditions (
Figure 11).
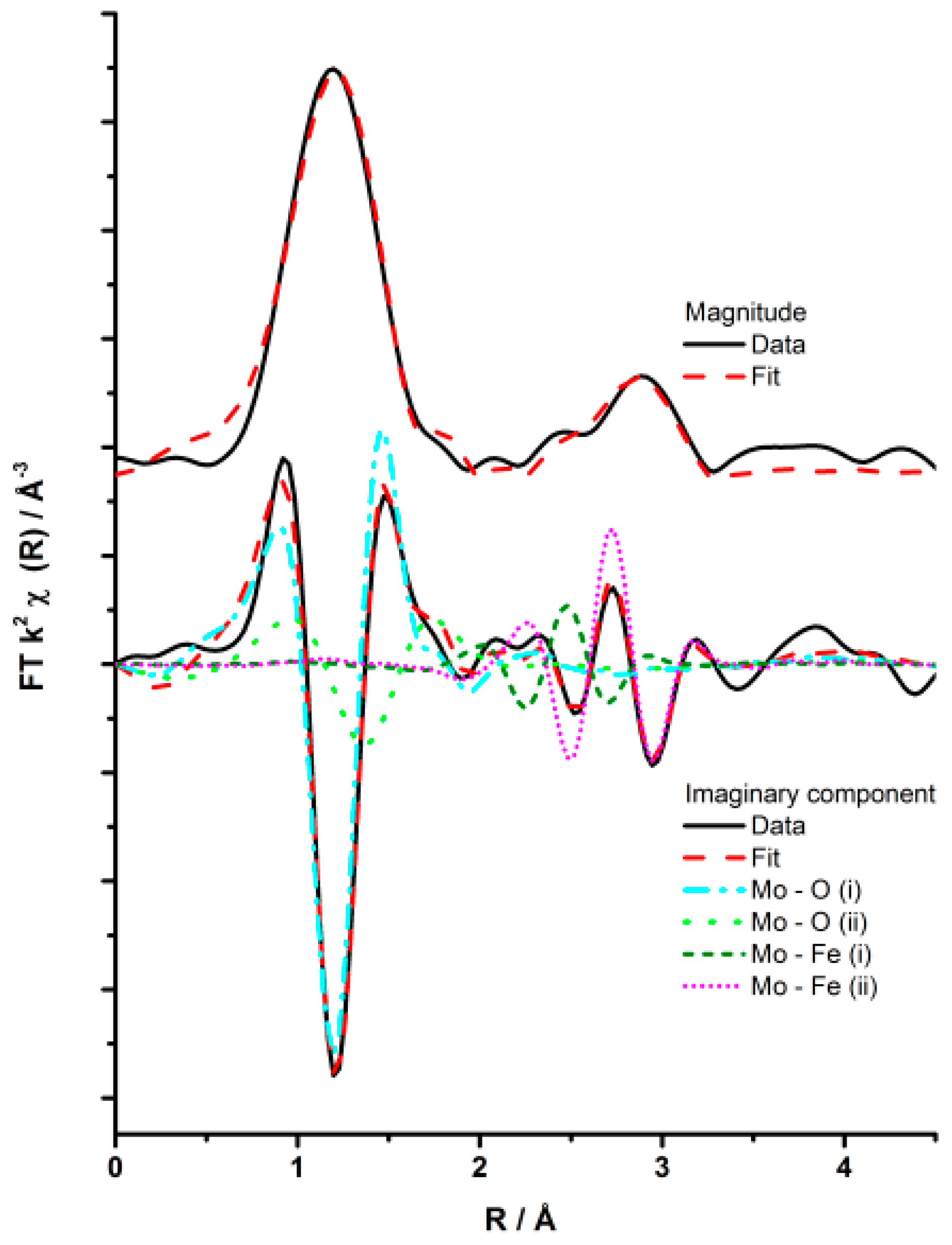
A detailed EXAFS analysis was able to assess the local structure of this amorphous O
h overlayer in more detail. The non-phase-corrected Fourier transform of the
k2-weighted EXAFS data for the 1ML MoO
x/Fe
2O
3 sample annealed at 500 °C for 24 h is detailed in
Figure 12, with obtained EXAFS parameters in
Table 2. EXAFS data exposed that the O
h Mo units are bound to the Fe
2O
3 surface with through a Mo–Fe interaction. The primary Mo O
h environment was dominated by oxygen neighbors, with the major contribution at low values of R in the Fourier transform. This was ascribed to a short Mo–O (distance = 1.74 Å) scattering path (
Table 2). Also present was a longer Mo–O scattering path (distance = 1.95 Å), but with less impact on the EXAFS data as a consequence of the large disorder associated with it. Further out in R space (after 2 Å), Mo–Fe scattering paths dominated, albeit weak in intensity due to their out of phase nature (See imaginary part,
Figure 12). Computational studies performed later in collaboration with David Mora Fonz of UCL, were in agreement with the results obtained through EXAFS [
7]. Modelling was undertaken to determine the nature of the preferred adsorption site on the most stable surface (0001) of α-Fe
2O
3. The favoured adsorption site was indicated to be where the Mo would have three Fe neighbors at approximately 3 Å, in addition to one shorter distance Fe neighbor.
Figure 13 represents these findings [
7].
In conclusion so far, the data have indicated a stable amorphous O
h overlayer of Mo at the surface of Fe
2O
3, present for a range of monolayer coverages and calcination temperatures. Catalyst screening studies revealed a comparable performance for all levels of Mo dosed onto Fe
2O
3. Most significantly, catalysts with just one monolayer coverage of molybdenum on Fe
2O
3 resulted in a very selective catalyst for methanol oxidation to formaldehyde. It was proposed by Brookes et al. [
16] that this common surface overlayer present for all such catalysts, is also the active overlayer in bulk ferric molybdate catalysts of the type used industrially.
5. Initial Investigations into the Mechanism and Reaction Site of Methanol on FeMo Based Catalysts
In highlighting the use of model MoO
x/Fe
2O
3 catalysts to gain knowledge into the possible surface terminations in bulk FeMo systems, the work of Brookes et al. [
35] next exploited in situ characterization, specifically to address the reaction mechanisms occurring with methanol. Although widely valued for its efficacy in the reaction, there is a surprising lack of knowledge regarding the catalyst surface layer in Fe
2(MoO
4)
3, and more importantly how it reacts with the incoming methanol reactant under high pressure conditions. This has been a topic of great interest, with many authors able to identify the phases which are formed through reduction and regeneration of the catalyst [
3,
36,
37,
38], but unable to designate these intermediate phases to a defined reaction mechanism.
The mechanism of methanol adsorption and reaction on the surface of FeMo based catalysts has been extensively researched, with the majority of authors recognizing that the Mars-Van Krevelen mechanism applies [
12,
39]. Under this mechanism, methanol oxidation employs surface lattice oxygen [
40], inducing a temporary partial reduction of the surface to Mo (IV).
The reduction mechanism has been reported to occur as follows, resulting in a mixed phase catalyst [
38]:
This is then counteracted by a quick regeneration through gas phase oxygen to Mo (VI).
House et al. [
22,
41] have exploited TPD and pulsed flow studies to investigate this reduction phenomenon in more detail. The reaction and reduction of iron molybdate (Mo:Fe = 2.2:1) with methanol feedstock under anaerobic conditions was adopted. The first pulse of methanol demonstrated comparable conversion and selectivity to formaldehyde, as would be seen under aerobic conditions. This indicated that gas phase oxygen is not directly required in the reaction, but is merely there to re-oxidise the surface for continued use, again supporting the MVK mechanism. With further reduction at low temperatures, the catalyst performance diminished, reflecting the significant loss of oxygen from the catalyst surface. However, contrary to this, as the temperature is elevated above 250 °C, the catalyst was able to reinstate its previous activity, as bulk oxygen migrates to the surface at a higher rate to enable the production of formaldehyde. With loss of bulk oxygen, further oxide phases inevitably formed, with XRD evidencing α-FeMoO
4, MoO
2, and Mo
4O
11. The study was informative not only in providing information regarding these reduced phases, but also in preliminary investigating the mechanisms occurring at the surface.
TPR studies performed by Zhang et al. [
42] on Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 with excess MoO
3 highlighted the transformation of Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 to β-FeMoO
4 and Mo
4O
11, MoO
3 to MoO
2 and β-FeMoO
4 to Fe
2Mo
3O
8 and Fe
3O
4. Beale et al. also describe their related work [
38], specifically studying Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 using in situ WAXS, XANES and UV- Vis. Under reducing conditions, they observed the reduction to produce β-FeMoO
4 and MoO
3, which can further reduce to MoO
2. It is thought from previous literature studies of methanol oxidation over bulk Fe
2(MoO
4)
3, that the formation of reduced α-FeMoO
4 occurs at lower temperatures, whilst β-FeMoO
4 dominates at higher temperatures above 310 °C [
43].
Due to its dominance of the surface layer of highly selective ferric molybdate catalysts, focus has turned to studying methanol reaction on Mo surfaces, specifically MoO
3. The crystallographic planes in MoO
3 have been resolved by electron diffraction as the apical (001 + 101), side (100) and basal (010) planes. The basal (010) plane was found to possess the lowest free energy, lying parallel to the double layer. Ab initio quantum mechanical calculations performed by Allison et al. [
44] supported a multistep mechanism involving reaction of methanol with dual-dioxo catalytic sites. Since these dual sites were shown to exist on the (010) face of MoO
3 (
Figure 14), this face was deemed as the reactive site [
45]. However, this is not unanimously agreed, with several authors revealing that the (010) plane exhibits especially low saturation, and any methanol adsorption occurring does not contribute to formaldehyde production. The role of this face is still under investigation for selective methanol oxidation [
14,
45].
It has since been proposed that methanol adsorption occurs at the edge and defect sites of α-MoO
3, since the uptake of methanol correlates accordingly with the number of active centres on these sites. Edge planes are formed by the bond cleavage perpendicular to the MoO
3 double-layers [
46], exposing co-ordinatively unsaturated molybdenum onto which adsorption can occur [
47]. Non (010) faces possess the required dual acid-base sites, as outlined in
Figure 15. Pre-treatment of the surface with pyridine has shown to inhibit methanol oxidation due to poisoning of the MoO
3 surface. This implies Lewis acid sites, as proposed by Tatibouet et al. [
47]. The Lewis acid character revealed by these adsorption studies [
48], facilitates substrate interactions.
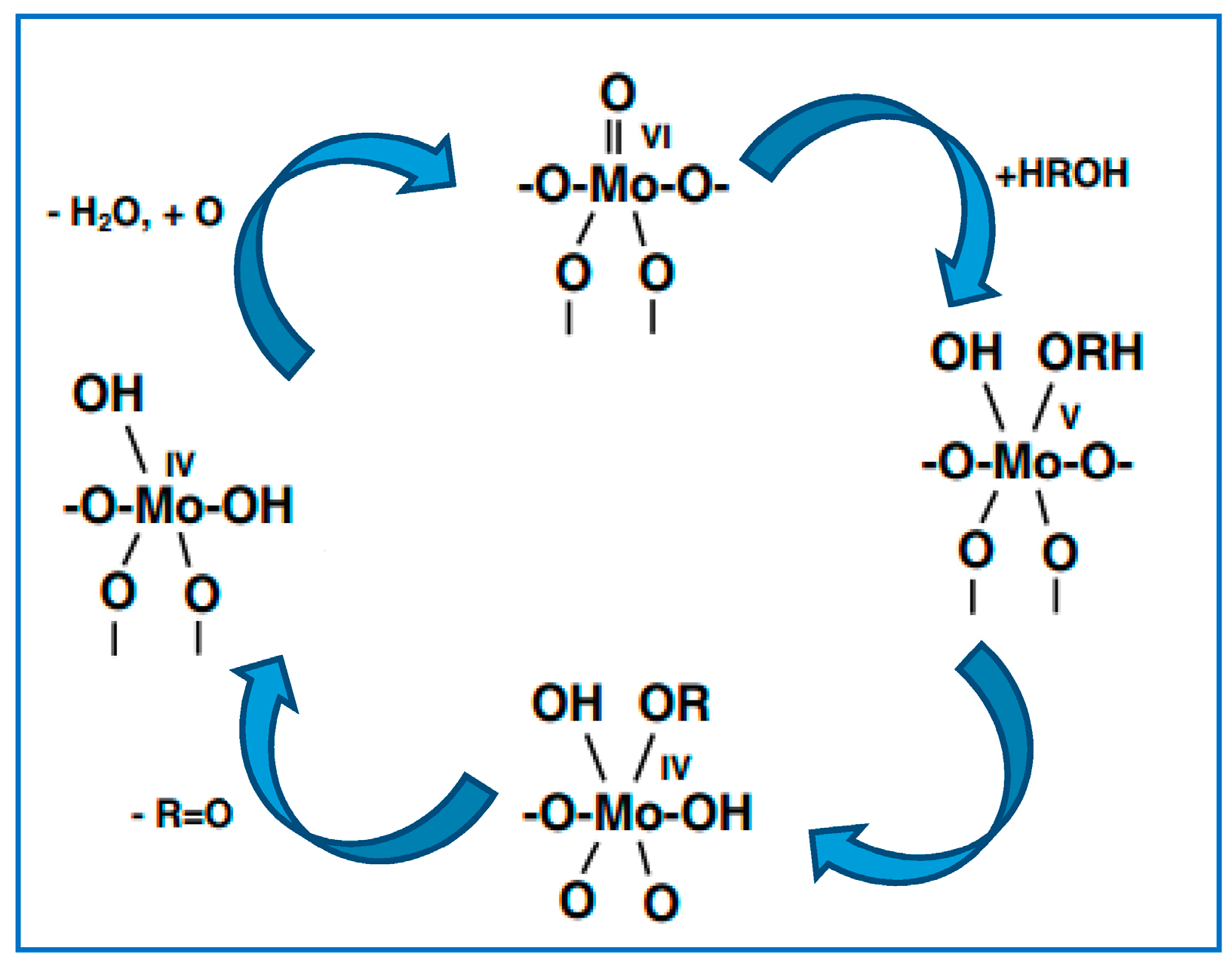
The steps which follow the methoxy adsorption, are dependent on the oxidation state of the Mo active centre. If Mo exists as active and selective Mo (VI), the reaction proceeds via scission of the C-H bond, considered to be the rate-determining step. The process yields formaldehyde and a proton, which reacts with lattice oxygen to form a second hydroxide, which proceeds to be lost as water under oxidative conditions [
52]. If the oxygen level is insufficient, the produced hydrogen will be introduced into the surface, creating a surface bronze denoted H
xMoO
3. With even further reduction, loss of H occurs with subsequent MoO
2 formation, a known reduced state of MoO
3. The reactivity of iron molybdate is comparable to that of the pure α-MoO
3 in terms of selectivity [
22], however, the activity of this mixed phase oxide supersedes that of MoO
3, due to the greater number of exposed catalytic active sites present for isotropic Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 than for anisotropic MoO
3. Only the edge sites for MoO
3 can carry out the catalysis, whereas all the exposed planes in Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 can dissociatively chemisorb CH
3OH as well as oxidise methanol to formaldehyde.
It is agreed that during the reaction, partial surface reduction occurs, followed by a very rapid regeneration using gas phase oxygen. It could be that Mo (IV) exists temporarily, agreeing with the initial mechanisms of Bowker et al., however, it has not been possible to isolate this species under normal oxidative reaction conditions.
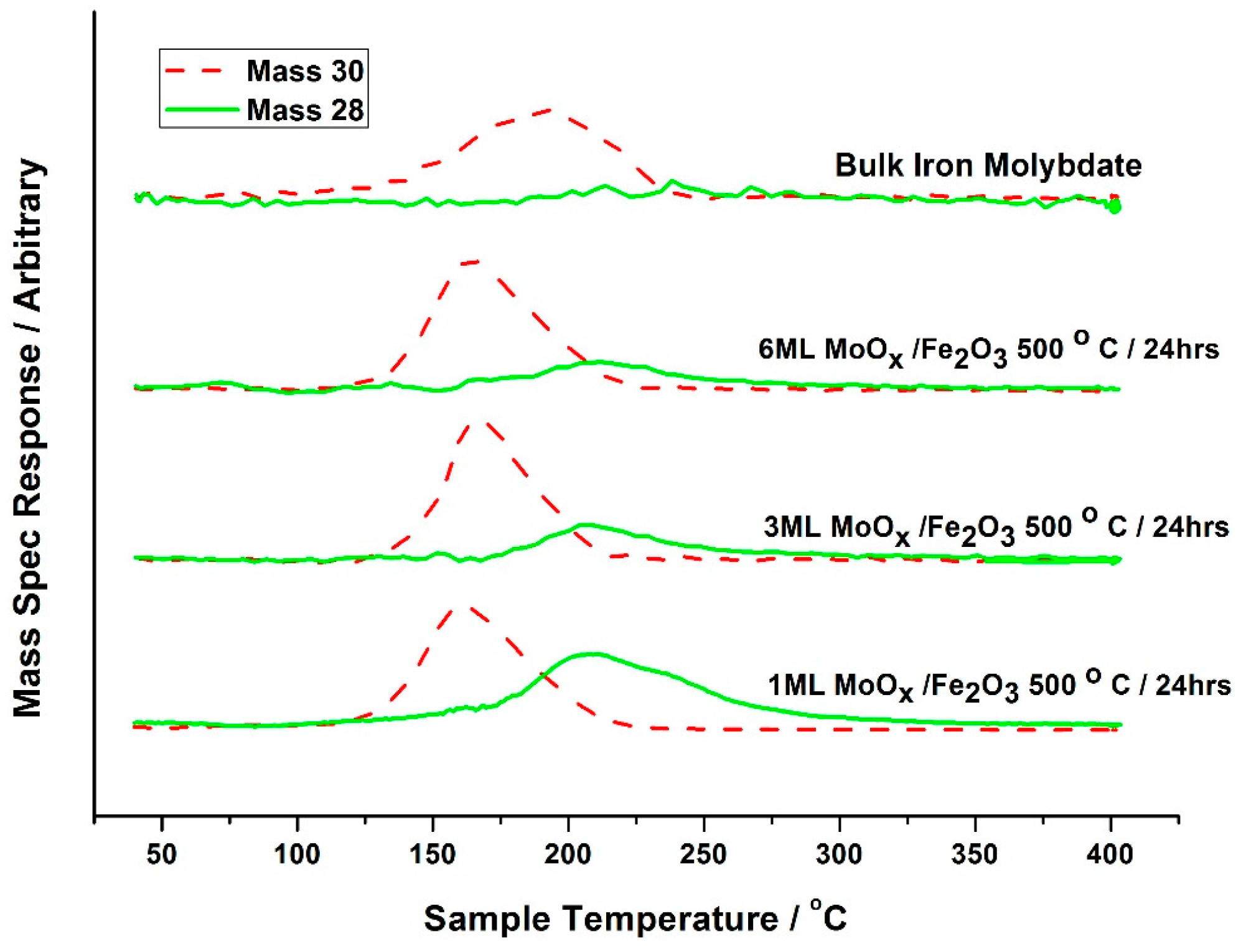
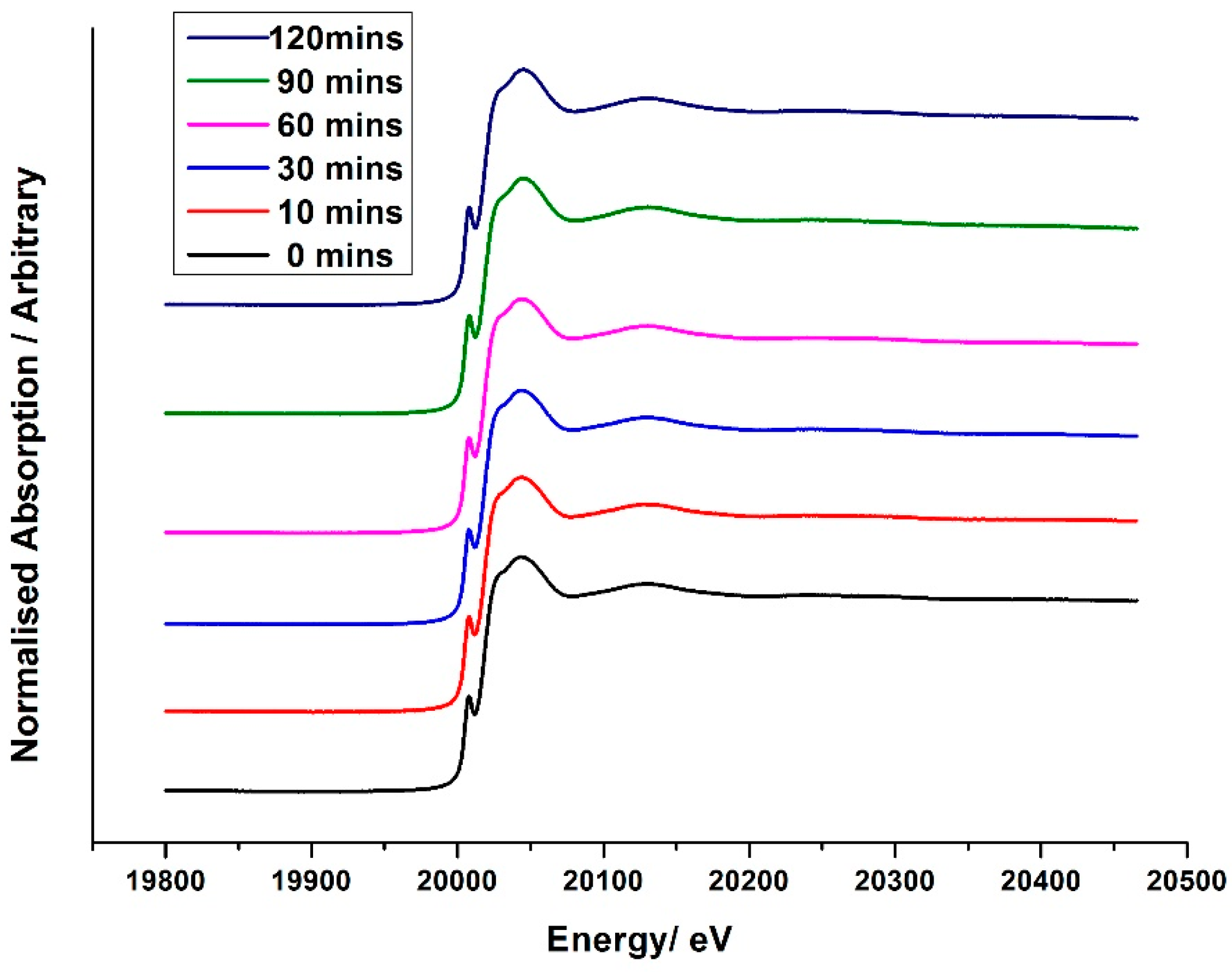
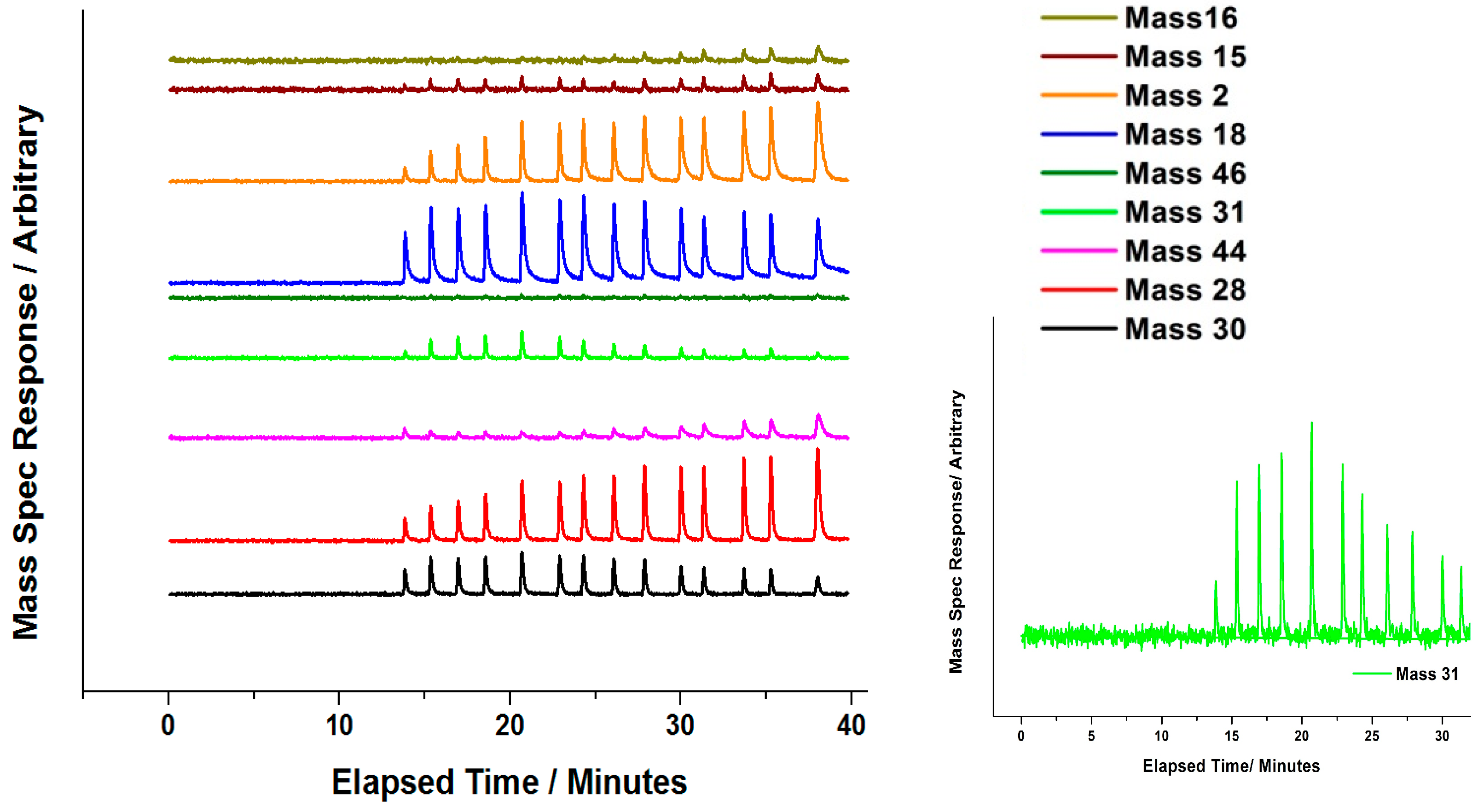
Attempts have been made by our group to explore the nature of Mo during the
oxidative reaction with methanol [
35]. In situ isothermal reaction studies were performed under transmission mode XAFS coupled with mass spectrometry analysis, whilst maintaining the temperature at 250 °C. During formaldehyde production (Mass 30,
Figure 16 and
Figure 17), no obvious changes were observed in the Mo speciation, inferred by the constant pre-edge position, and maintained T
d co-ordination throughout. With a sustained Mo environment, this allowed for continued production of formaldehyde, as revealed by the mass spectrometer data collected online during the experiment (
Figure 17). Previous studies have identified that surface oxygen is consumed in the reaction [
7,
16]. It is therefore shown from these oxidative studies that any removal of surface oxygen and temporary Mo reduction is difficult to probe, due to the rapid re-oxidation by gas phase oxygen to maintain the catalyst in its desired Mo (VI) state. It could be that Mo (IV) exists momentarily under reactive conditions, but is unable to be seen due to the time scale of these studies. This has proved a challenge for many researchers [
24,
45].
Other authors have exploited alternative approaches to investigating the mechanisms on Mo dominated catalysts.
Bowker et al. [
22] have focussed the role of Mo in the selective oxidation of methanol, proposing the terminating Mo = O as an initial single adsorption site for methanol oxidation (
Figure 18) [
22]. The majority of authors also identify this Mo = O site as a possible dehydrogenation centre for the mild oxidation [
7,
22,
37,
47,
49]. Trifiro et al. [
53] have long maintained the opinion that Mo = O double bonds are essential in oxidation catalysts, with dioxo centres at the core of the reactivity due to their ability to extract both hydrogens from methanol. During the reaction proposed by Bowker et al., the active Mo (VI) reduces to Mo (IV), which can readily use lattice or gas phase oxygen to re-oxidise back to Mo
6+ Confirmation of this derives from experiments carried out to determine the activity profile of the other main oxidation state of Mo, which is Mo (IV). From experimental observations the scheme was proposed as:
An acid-base type reaction occurs at the terminal Mo = O site, resulting in methoxy and OH formation (g = gas phase, a = adsorbed species). The terminal oxygen is deemed the most stable site for hydrogen adsorption.
Attack of the bridging oxygen on the adsorbed methoxy yields adsorbed formaldehyde and a hydroxyl. This C-H abstraction on methoxy occurs at much higher temperature, and is deemed as the rate-determining step in formaldehyde formation. It is presumed that the step involves bridging oxygen, since when Fe is present at the surface, high selectivity to CO occurs due to the changed bonding energy of the Mo-O-Fe bridging oxygen which dehydrogenates the methoxy intermediate.
OH recombination occurs to yield H
2O from the catalyst [
52]. The anion vacancy is re-oxidised from the bulk (anaerobic) or gas phase (aerobic) oxygen.
Once formed, formaldehyde can be further oxidised to CO or CO2. However, the high selectivity of α-MoO3 is derived from the presence of undissociated methanol and water blocking the adsorption sites, which retards this further oxidation.
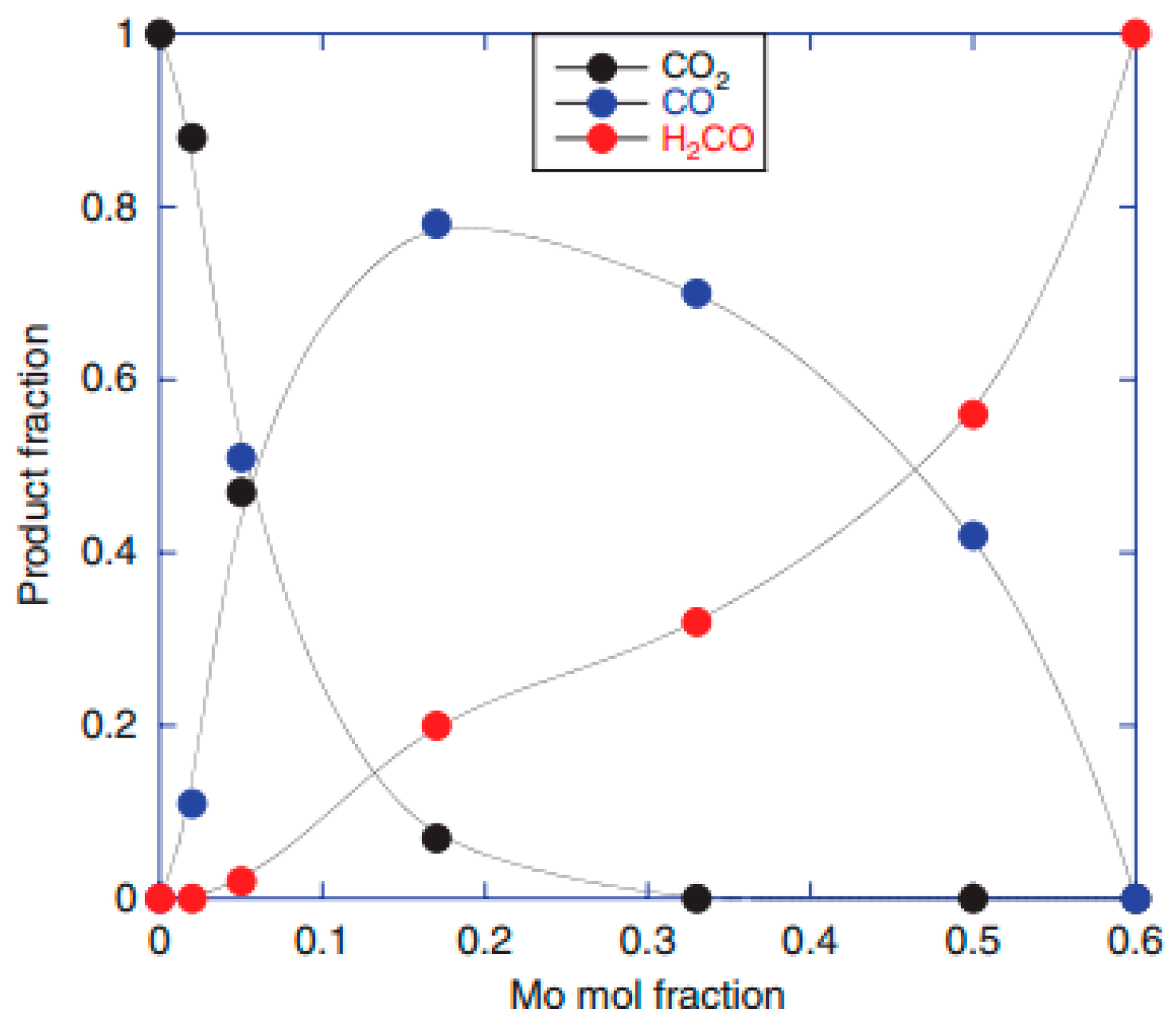
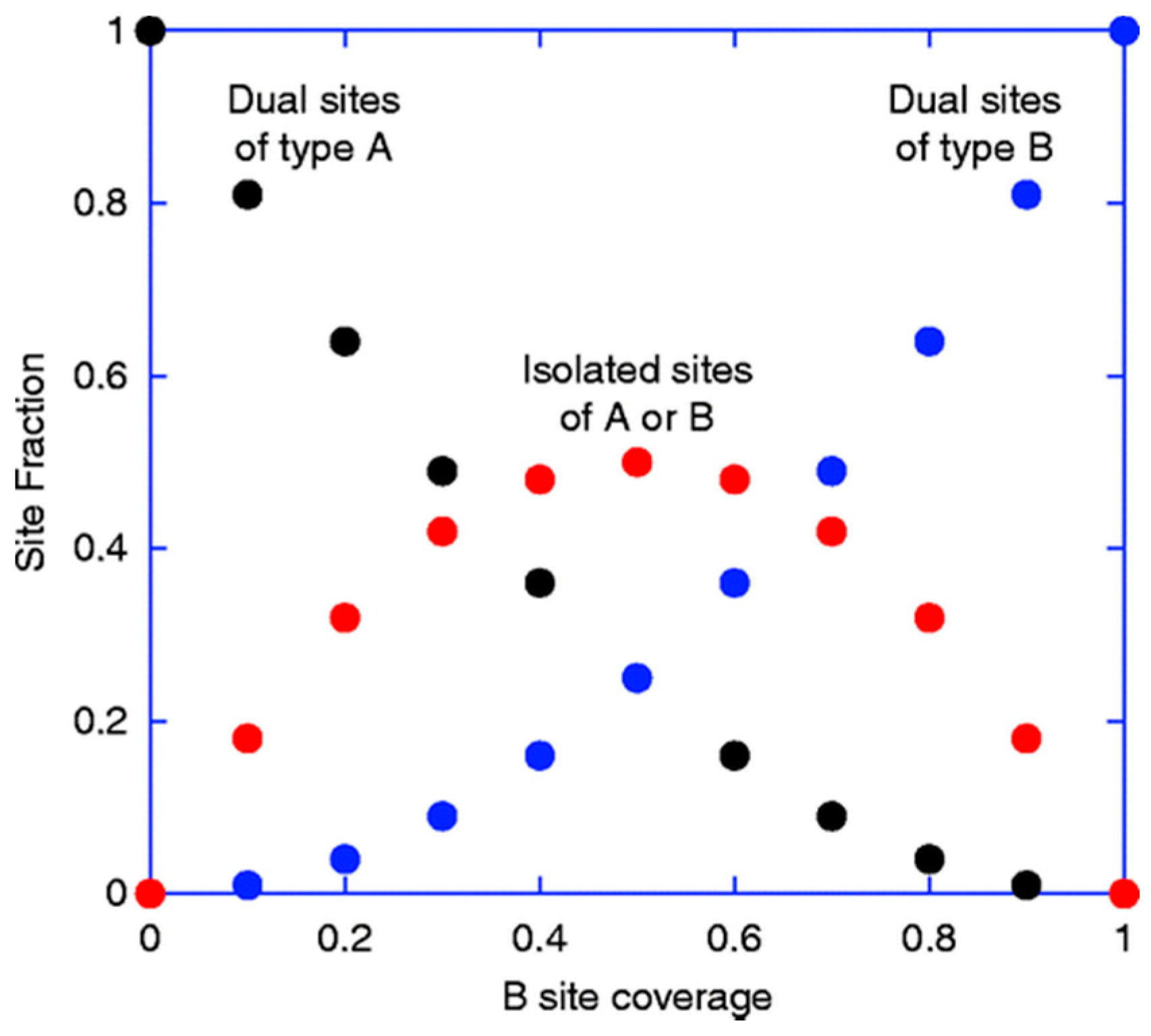
A recent paper from our research team reports a simple quantative model to describe the behavior of bi-cationic systems [
36], comparing selectivity as a function of Mo loading on Fe
2O
3 (
Figure 19 and
Figure 20). Surface doped materials are commended for their use in learning about the active configuration and its relationship to high selectivity. It was found that product distribution was highly dominated by the distribution of dual and single sites of the two species (Mo and Fe) at the surface. Mo is highly selectivity on its own to formaldehyde, and is proposed to be present in commercial catalysts as an active Mo monolayer on top of ferric molybdate. Product yield was measured from iron oxide, through to the stoichiometric catalyst, Fe
2(MoO
4)
3, considering various Mo doping levels. CO
2 was shown to be dominant at high Fe levels, while H
2CO prevailed for low Fe content. However, over a wide range of the intermediate concentrations, CO was the primary product (
Figure 19). It was postulated that double sites are important for the selective reaction. For formaldehyde production, it was concluded that two Mo sites are required, whilst double Fe sites promote combustion on iron oxide via formate adsorption. Where CO was the dominant product, a different active site was proposed, requiring only one cation to be involved in the rate determining step. This appeared to show the general trend of behaviour observed.
DRIFTS studies on 6ML (monolayers) MoO
x/Fe
2O
3 calcined at 600 °C, have been carried out by the authors of this review, in support of this theory (
Figure 21). Studying model catalysts produced in this way paves the way for a surface analysis approach, whilst also producing catalysts with higher surface areas for maximised infrared signal. Upon dosing with MeOH at room temperature, the formation of two methanol related surface species. The first species exists as a non-dissociatively adsorbed O-H group of methanol, appearing at 3100–3500 cm
−1 with a second species is observed as pair of bands at ~2955 and 2847 cm
−1 which can be indexed to the stretch and the first overtone of the symmetric bend of methanol CH
3, respectively [
54]. By 100 °C, the DRIFTS spectrum (
Figure 21) could also distinguish the bands of methoxy on moderately Lewis-acidic oxides (2933 & 2835 cm
−1), differentiating them from the C-H vibrations of undissociated methanol on acidic surfaces at this temperature (2959/2854 cm
−1). It should be noted, whilst molecular methanol remains the dominant surface species at low temperature, methoxy dominates at higher temperatures, shown through the maintained intensity of methoxy compared to the loss of related MeOH bands. This would reflect the stronger surface interactions of the methoxy. All associated bands diminished by 200 °C, as reactants subsequently form products.
6. In Situ Investigations under MeOH/He to Provide Insights into the Reaction Mechanisms under Methanol
Due to the difficulty in probing the active site under oxidative conditions, an alternative approach has been advocated amongst the group of Brookes et al. [
35]
, exploiting their core-shell structures of Mo on Fe
2O
3 under MeOH/He. Reacting anaerobically enforced a reduction of the surface, which could be analogous to the structural changes occurring momentarily under reaction with MeOH under aerobic conditions. Specifically studying core-shell MoO
x/Fe
2O
3 catalysts enabled the use of in situ XAFS as a surface sensitive analysis tool, exclusively probing the active topmost layers, without the added complication of secondary phases such as MoO
2 and β-FeMoO
4, which we are shown to be produced during the reduction of bulk Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 [
42,
55].
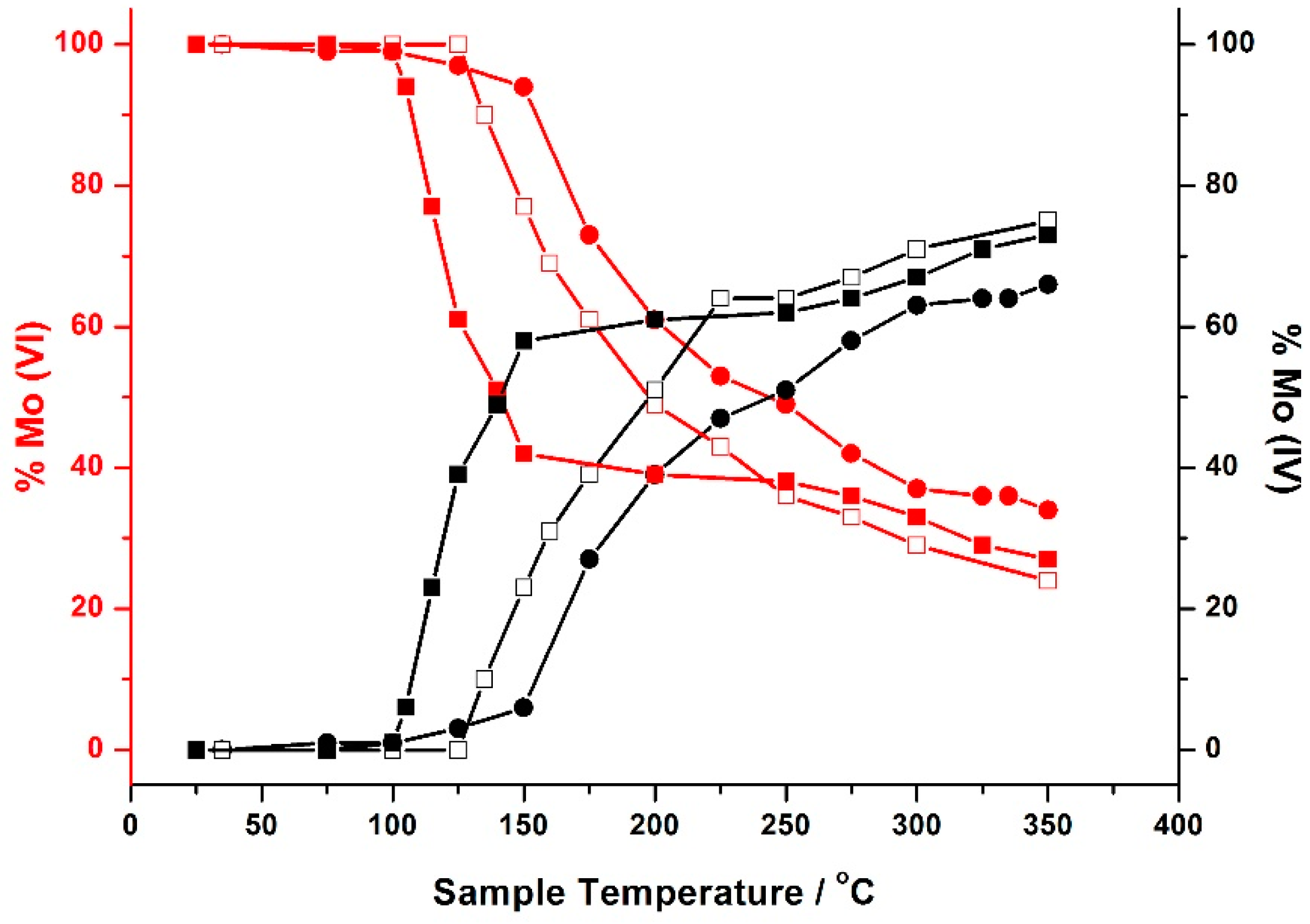
Figure 22 details the extent of reduction as a function of temperature for 1, 3 and 6 monolayer loadings of Mo on Fe
2O
3, acquired through XANES analysis. Since it was not possible to source appropriate references to perform satisfactory LCA, results were ascertained through observing the move in edge position between Mo (
VI) from the original post reduced catalyst, to Mo (
IV) referenced from MoO
2, a known reduced state of Fe
2(MoO
4)
3,. Observed was an edge shift of approximately 70% towards Mo (
IV) for all coverages, implying MoO
2 itself did not form (
Figure 23). Further characterization through Raman and XRD was also unable to establish isolated MoO
2, as is the case for bulk Fe
2(MoO
4)
3.
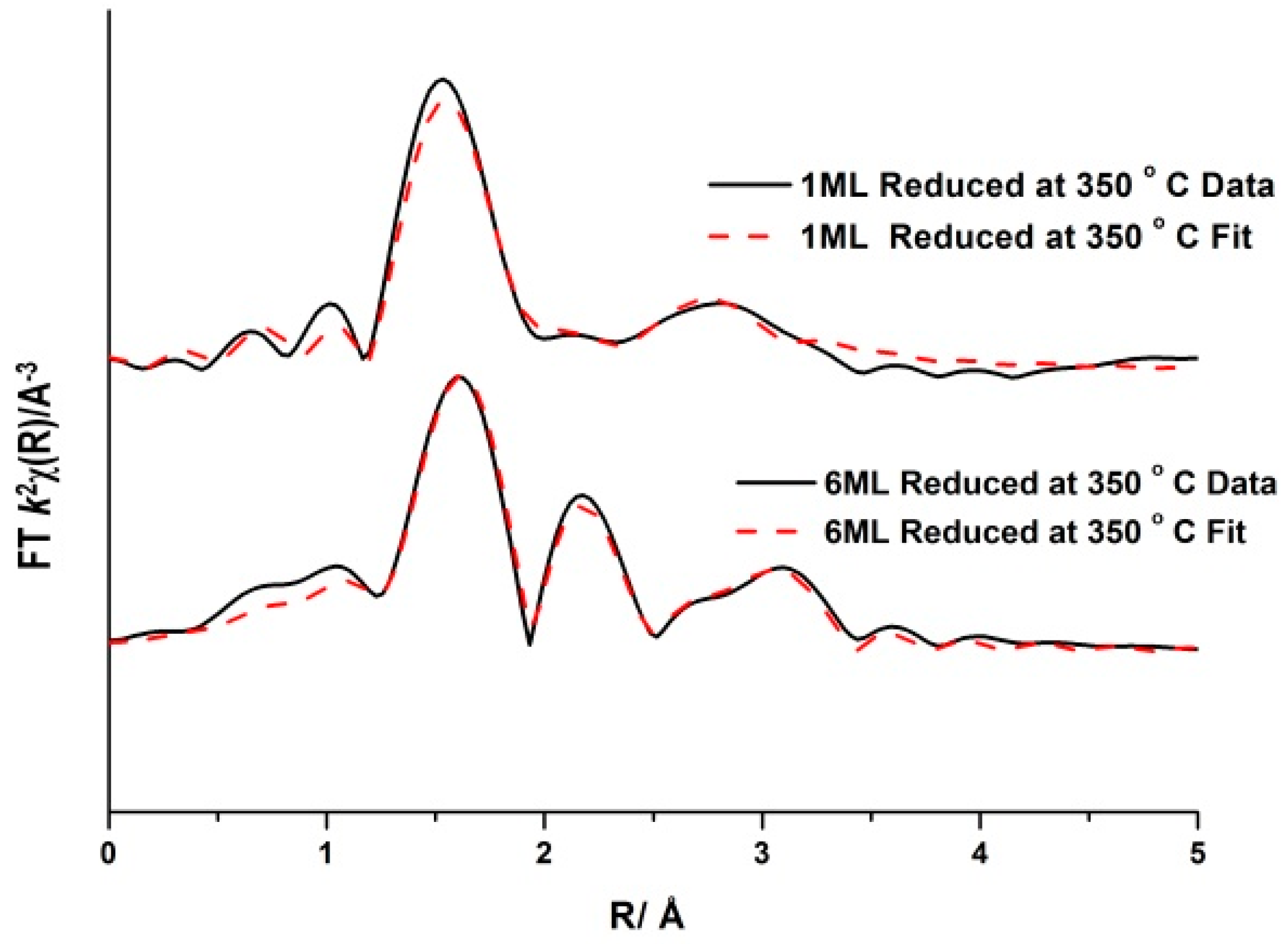
To elucidate this reduction process further, EXAFS analysis was influential. The end state
k2-weighted Fourier transform data for the reduced samples of the 1 and 6ML MoO
x/Fe
2O
3 catalysts are shown in
Figure 24. The obtained fits were comprised of five scattering paths; one Mo–Mo, 2 Mo–O and 2 Mo–M, where M = Fe or Mo. Two oxygen scattering paths featured at 1.78 and 2.02 Å, indicative of reduced forms of Mo, as well as the distorted nature of the Mo octahedra. Significantly, all monolayers displayed a strong contribution from an Mo–Mo distance at 2.6 Å (
Table 3). Literature assigns this to a bonded distance indicating a Mo (V) dimer or Mo (IV) trimer [
44]. This bond distance is different from that in MoO
2, which has a shorter distance of 2.5 Å, and with a reduced average co-ordination number.
This surface specific Mo–Mo bonded distance was an important finding, indicating the presence of a reduced cluster of Mo after reduction under MeOH/He. The significance of these Mo clusters is that the possible dimer unit could suggest a two centred Mo reaction site, which could be the reactive site that temporarily forms on reaction with methanol (the reductant) before its quick and efficient re-oxidation back to the original catalyst. This complements the results of Kikutani et al. [
56] who found that a 2.6 Å Mo–Mo bond in fixed dimer catalysts as the most distinctive feature for unique dimeric active sites. This proposal is now recognized by many, with evidence highly favouring this dual site option. A study by Lopez et al. used density functional theory (DFT) to describe the unique character of the Mo (VI)–Mo (IV) pairs as the most active and selective sites on the surface, to establish the controlling factors of selectivity, and the role of dopants [
57]. It has been suggested that iron reduces the energy requirements of the redox Mo (VI)–Mo (IV) pair by acting as an electron reservoir.
7. Investigating the Role of Fe in Fe2(MoO4)3
The redox ability of molybdenum based catalysts has been discussed [
8,
37,
58,
59], with the oxidation state of the Mo considered a key contribution in catalyst reactivity. With extensive investigations into the role of Mo in the selective oxidation of methanol, the requirement for Fe in the active catalyst is still questioned, considering that it constitutes such a high proportion of the commercially-used catalyst.
There have been many theories postulated for the necessity of the iron containing phase [
6,
10,
60]. Firstly it yields a catalyst with improved surface area, bringing increased overall activity in the oxidative reaction to formaldehyde. MoO
3 alone suffers from a very low surface area, therefore making it inappropriate for commercial use. Secondly, although it cannot compete with MoO
3, Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 demonstrates a satisfactory performance in the reaction to formaldehyde Moreover, Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 is thought to have superior properties such as its bulk lattice oxygen mobility, which allows the catalyst to always ensure sufficient oxygen regeneration to the surface during reaction, maintaining catalyst selectivity. The bulk reduction process of iron molybdate based catalysts has been investigated by Mössbauer [
61] measurements on pure Fe
2(MoO
4)
3. The reduction takes place at temperatures above 230 °C, with the catalyst reducing to β-FeMoO
4. The process is shown to be completely reversible under oxygen at temperatures above 270 °C, with the catalyst efficiently reinstating its former Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 structure.
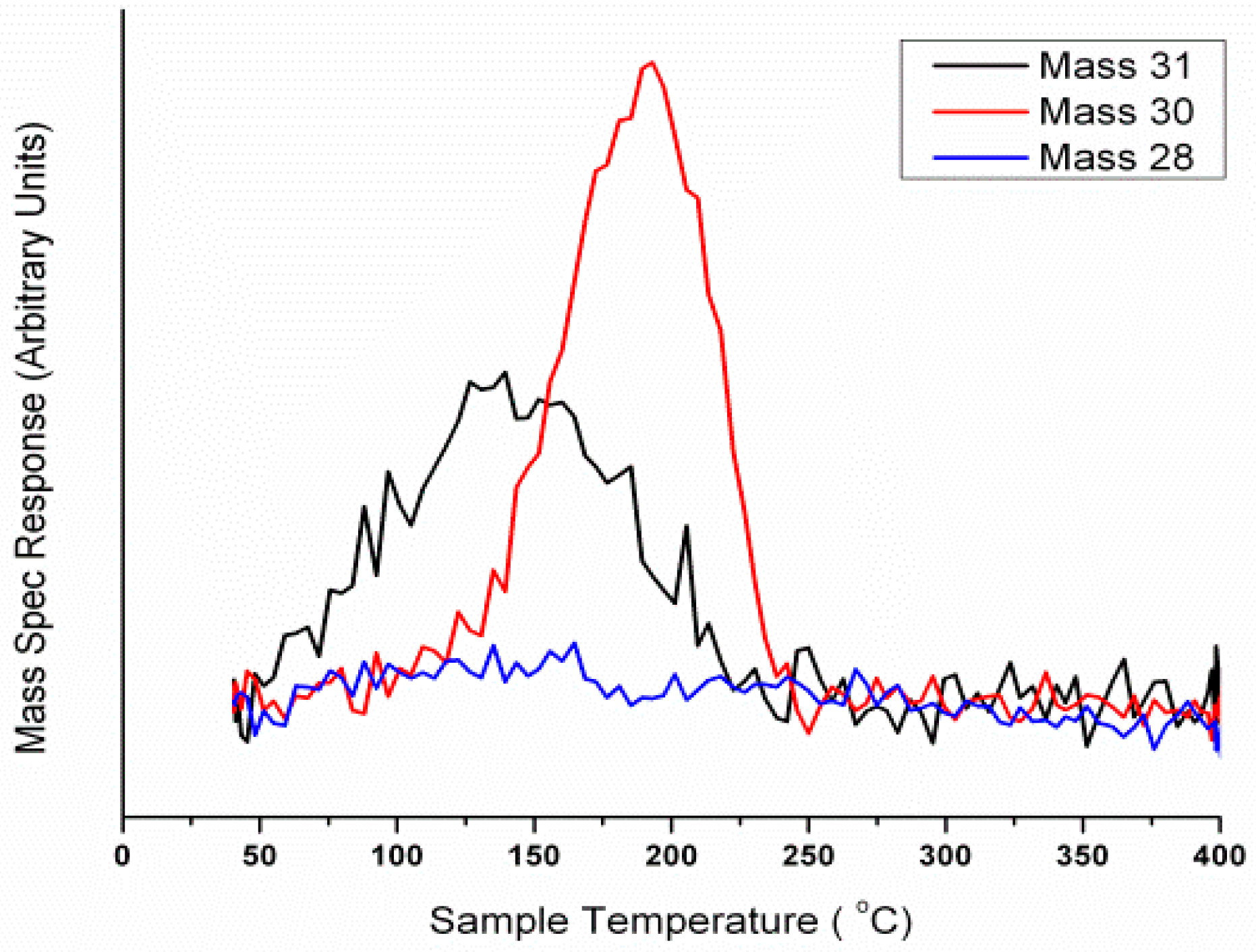
Further investigation into the properties in Fe
2(MoO
4)
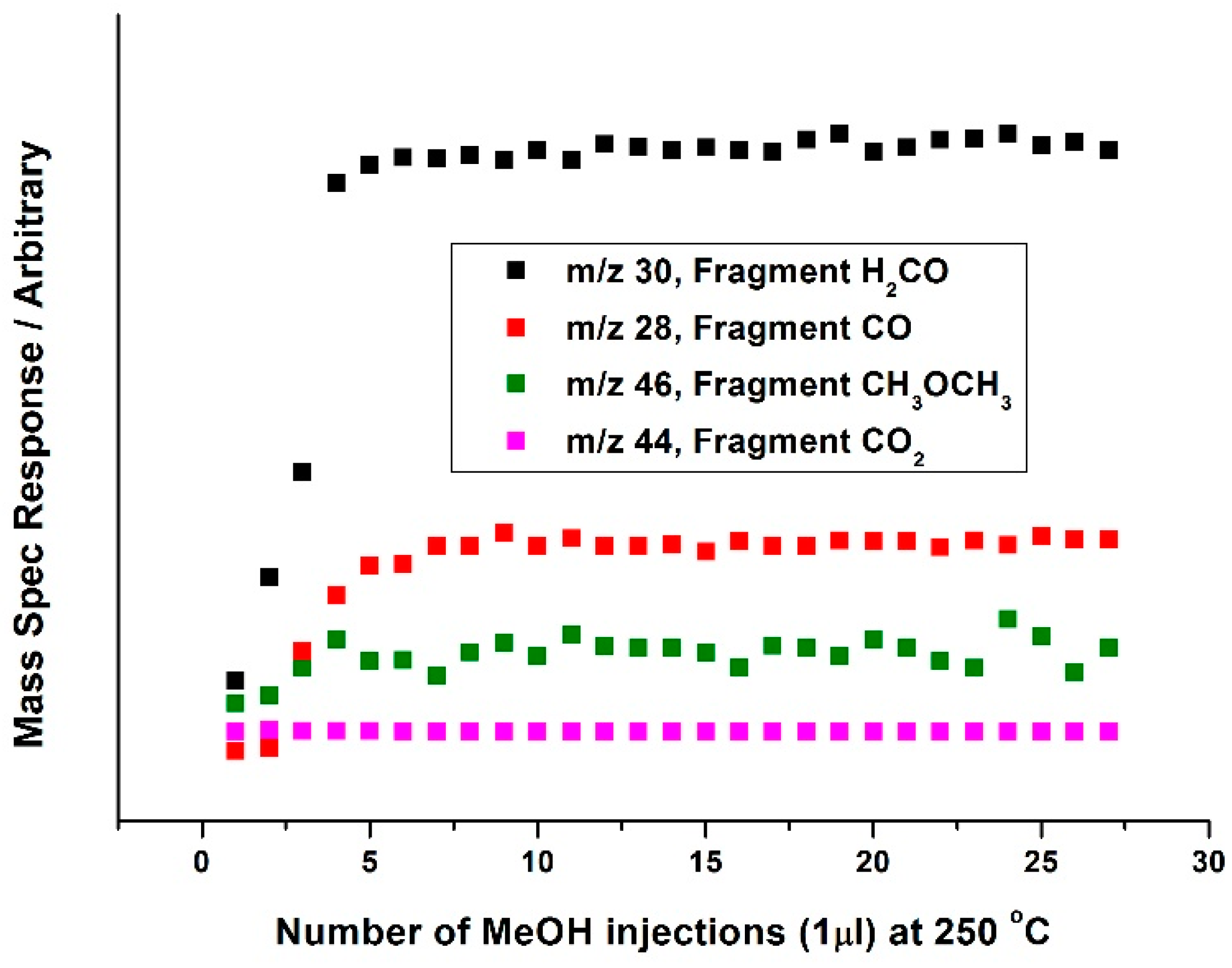
3 have been addressed by the authors of this review, in an attempt to define the role of Fe in the industrially employed catalyst. MeOH pulsing studies have been executed under anaerobic conditions. Catalysts were subjected to continual MeOH pulsing, whilst being held isothermally at 350 °C under He. It was concluded that oxygen mobility at this temperature was enabled in Fe
2(MoO
4)
3, especially since the mixed oxide was able to maintain selectivity to formaldehyde for the duration of the experiment (
Figure 25, Mass 30), though it also produced some CO (see Equation (7)). The presence of H
2CO was indicative of the presence of a methoxy intermediate at the surface. Methoxy has been proven to be present on MoO
3 [
52,
62].
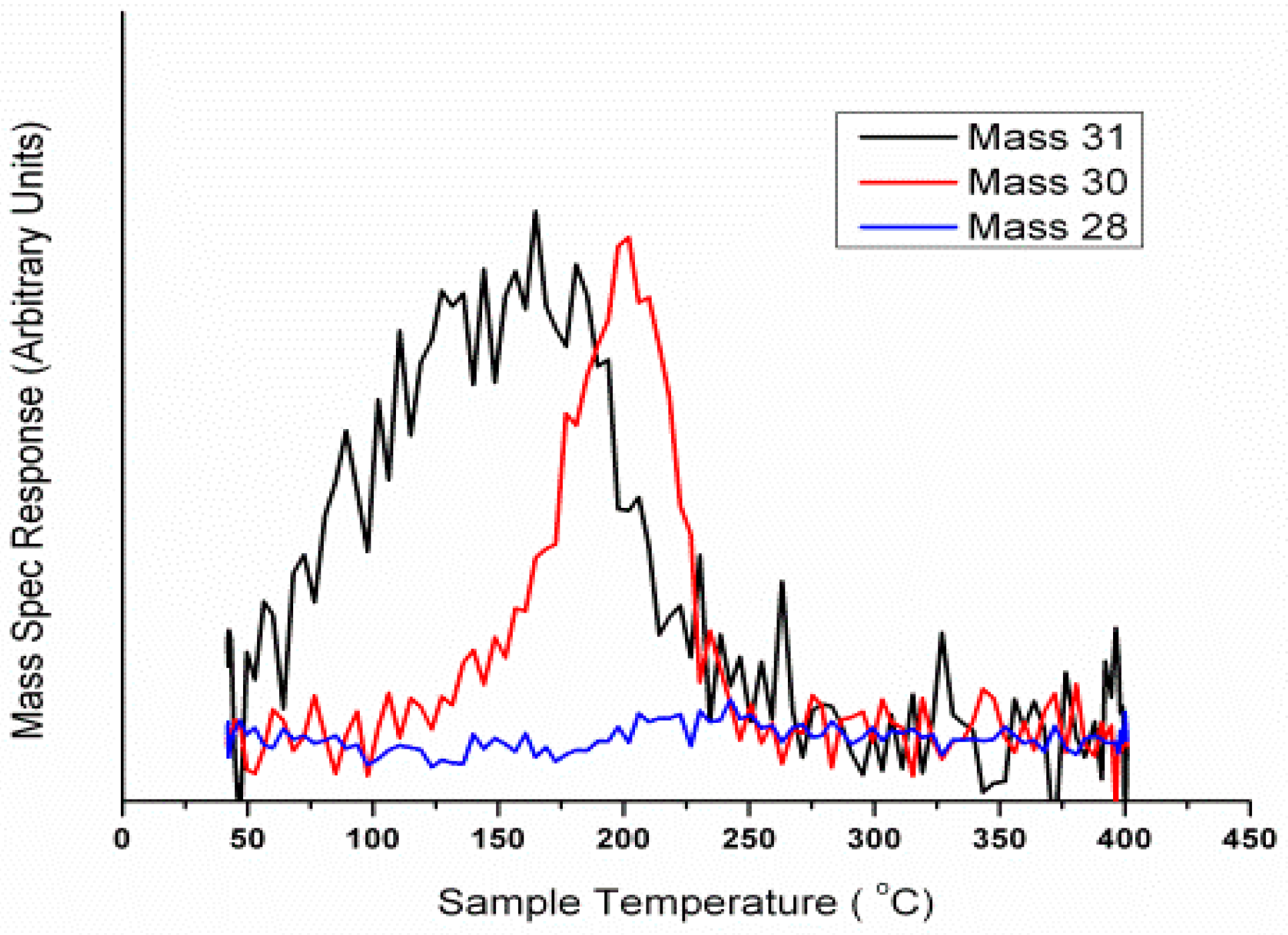
An equivalent pulsing experiment was performed on commercial MoO
3 (
Figure 26). The catalyst was unable to match the performance of Fe
2(MoO
4)
3, with the conversion of methanol (Mass 31) occurring after approximately ten minutes into the pulsing regime, as opposed to the almost instant conversion for Fe
2(MoO
4)
3. The selectivity of formaldehyde was not maintained for the duration, with a significant drop in its production towards the end of the reaction. This is counterbalanced by an increase in CO production and conversion, which is not seen so quickly for Fe
2(MoO
4)
3. This suggests that bulk oxygen diffusion is hindered in MoO
3, causing significant reduction in the surface region (Equation (7)). Data suggests that Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 has properties other than simply providing an improved activity of the catalyst; it can also ameliorate the extent of this surface reduction. This corresponds well with other work in the literature [
12,
58,
63]. A study by Ressler et al. [
64] investigated the reduction of MoO
3 in propene, and the corresponding re-oxidation of MoO
2 by in situ X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). The results revealed crucial information regarding solid-state kinetics of the processes, whilst also elucidating the structural changes occurring. It is believed that at temperatures below ~600 K, the contribution of oxygen from the MoO
3 bulk is negligible, leaving MoO
2 at the catalyst surface. A paper of Bowker et al. contrasts the behaviour of MoO
3 and MoO
2, with the latter showing an overall worse selectivity with a significantly higher proportion of CO produced [
24]. It is not until 700 K that oxygen vacancy diffusion in the bulk is enough to allow for a slow-moving redox mechanism to occur. Above 700 K it is believed that fast oxygen diffusion permits the participation of a considerable amount of the lattice oxygen, and helps maintain the surface oxidation level for a longer period of time.
To elaborate further on this phenomenon, the oxygen lattice mobility has been investigated for Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 and MoO
3. It should be noted here that MoO
3 was produced in-house via precipitation, to produce the oxide with an equivalent surface area to that of Fe
2(MoO
4)
3. Although this area was difficult to maintain after one reaction cycle, it provided a means of fairly comparing the oxygen mobility in these two oxides (
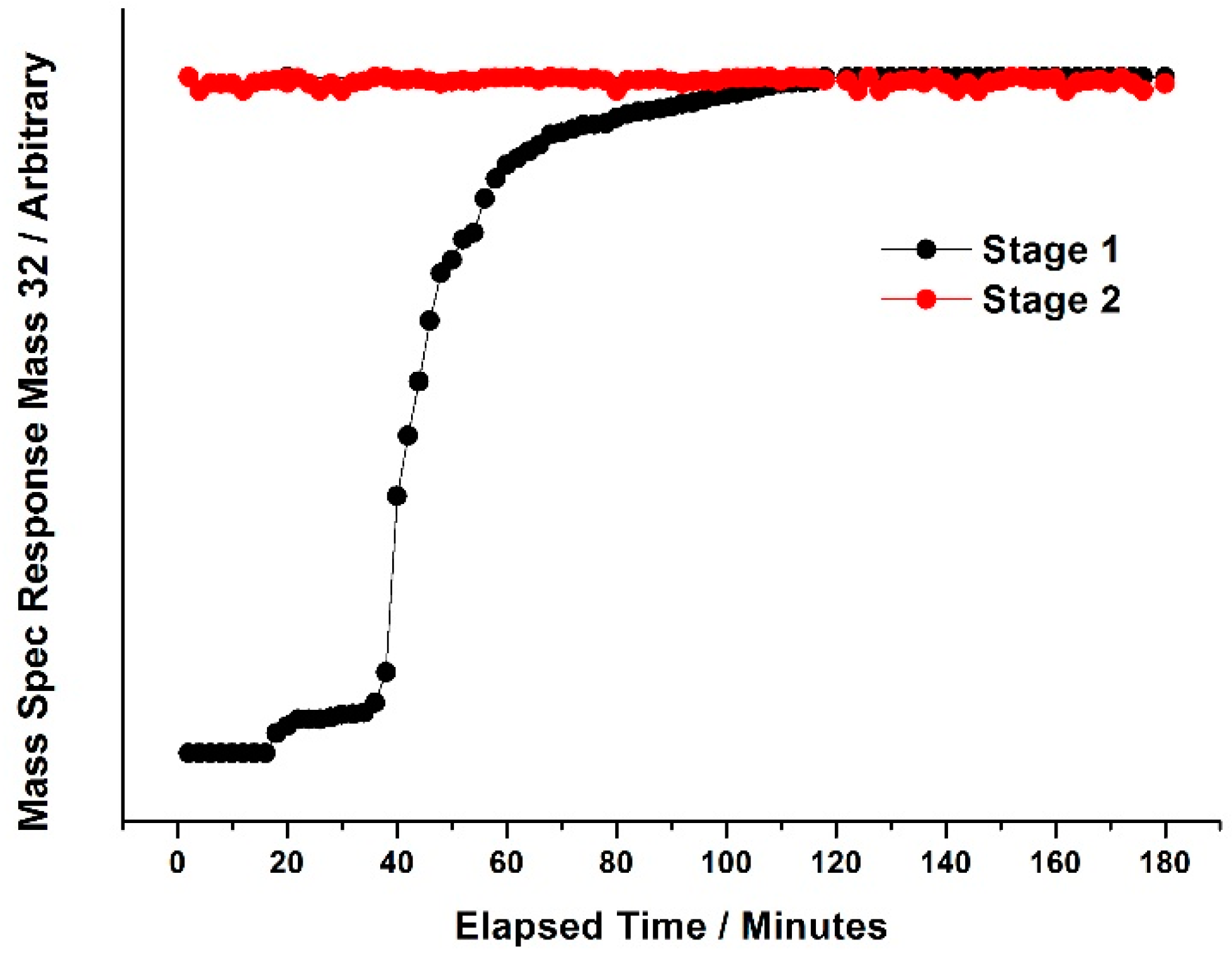
Figure 27 and
Figure 28). Following reduction in MeOH/He, catalysts were subjected to pulses of 10% O
2/He every 2 min at 350 °C. It was shown that for Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 (
Figure 26), it was not until approximately 60 min into stage one of the pulsing regime, that the Mass 32 (oxygen) signal appeared. Oxygen saturation is not accomplished until 180 min, as shown through the consistency in peak area after this elapsed time. In an equivalent study on MoO
3, (
Figure 28), a response for Mass 32 was seen after just 20 min into stage one of the pulsing regime, with a sharp rise from 40 min. The catalyst became fully saturated with oxygen after just 120 min, with no further uptake from this point. From these pulsing studies, it was revealed that Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 has a greater oxygen uptake than MoO
3, implying that the catalyst was more reduced under the same reduction regime. This therefore indicates a better redox activity of the catalyst. The study complements the reactivity data reported for the two catalysts (
Figure 25 and
Figure 26).
TPPFR (Temperature Programmed Pulsed Flow Reaction) with MeOH/O
2 has also been indicative of surface oxygen removal. Bowker et al. [
14,
22] have demonstrated that surface oxygen is more readily removed from Fe
2(MoO
4)
3, established through the lowered temperature of conversion and formaldehyde production for this oxide The ease of reducibility has been shown by others to follow as: Fe
2O
3 > Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 > MoO
3 [
65], suggesting that the mobility of the oxygen anions follows the same order, with the highest mobility in Fe
2O
3 and lowest in MoO
3. Not all agree however. Beale et al. [
38] recently published a study involving a combined multi-technique in situ approach to probe the stability of Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 catalysts during redox cycling. According to these authors, the Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 phase is the primary active phase, and that during standard reaction, a partial reduction of this phase occurs, resulting in the formation of formaldehyde, inactive β-FeMoO
4 and MoO
3. The FeMoO
4 phase is short lived, and is rapidly re-oxidised back to Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 by gas phase oxygen. To probe this mechanism in more detail, the stoichiometric Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 catalyst has been studied in harsher anaerobic conditions, to accelerate the changes occurring. The catalyst was first reduced under MeOH/He, yielding formaldehyde. Post anaerobic treatment the catalyst was re-oxidised under air to monitor the ability of the catalyst to regenerate. In situ combined wide-angle X-ray scattering, X-ray absorption near edge spectroscopy and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy with online mass spectrometry were combined to study the structure-activity relationships under redox cycling. Under redox cycling, it was shown that the initial Fe
2(MoO
4)
3 is partially regenerated, however with subsequent re-oxidation, little regeneration occurs, and can only do after a long period of time.