Performance Evaluation of Asphalt Modified with Municipal Wastes for Sustainable Pavement Construction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Viscosity
3.2. Measurement of Elasticity of LDP-, HDP-, and CR-Modified Binders
3.2.1. LDP Modified Binders
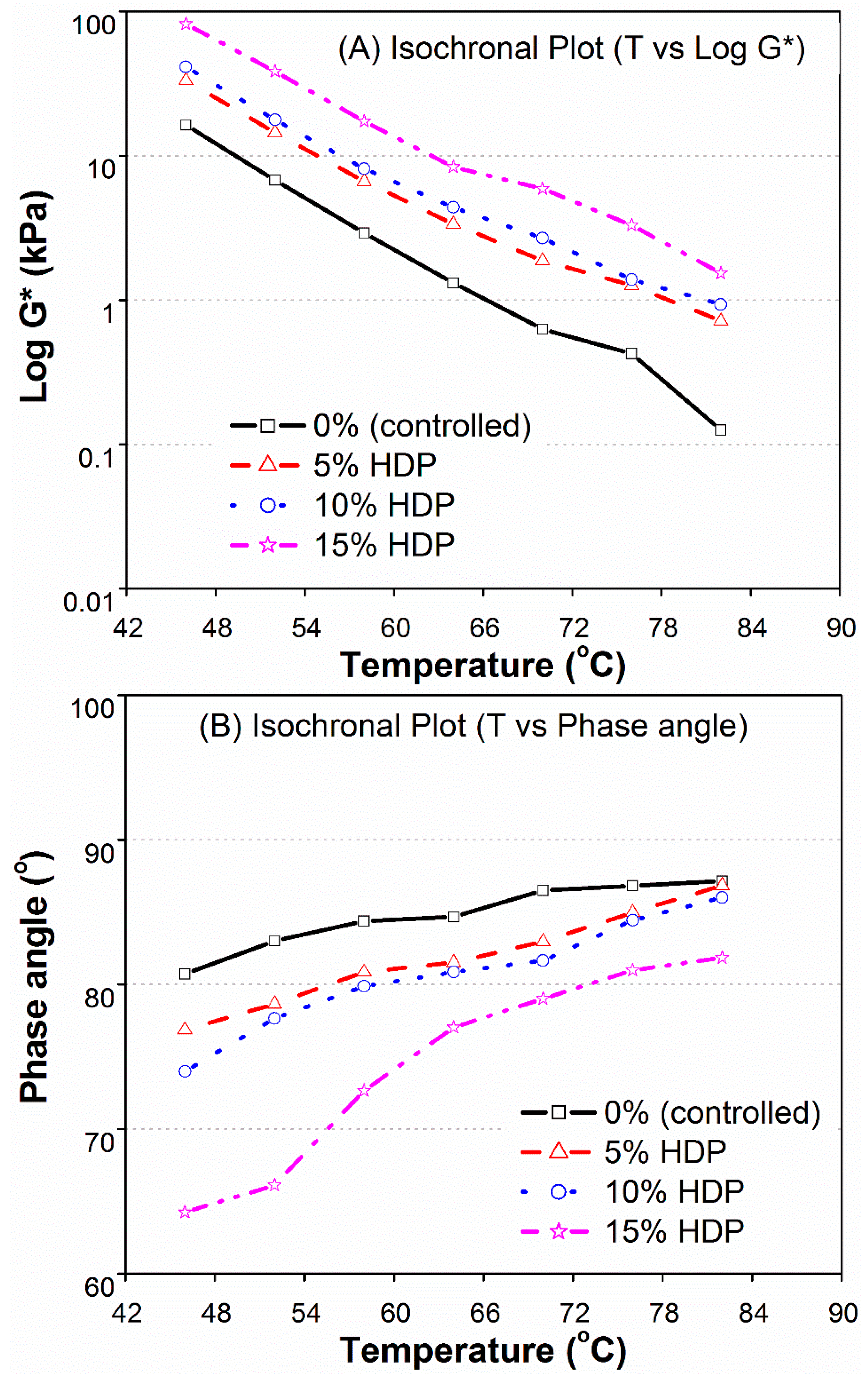
3.2.2. HDP Modified Binders
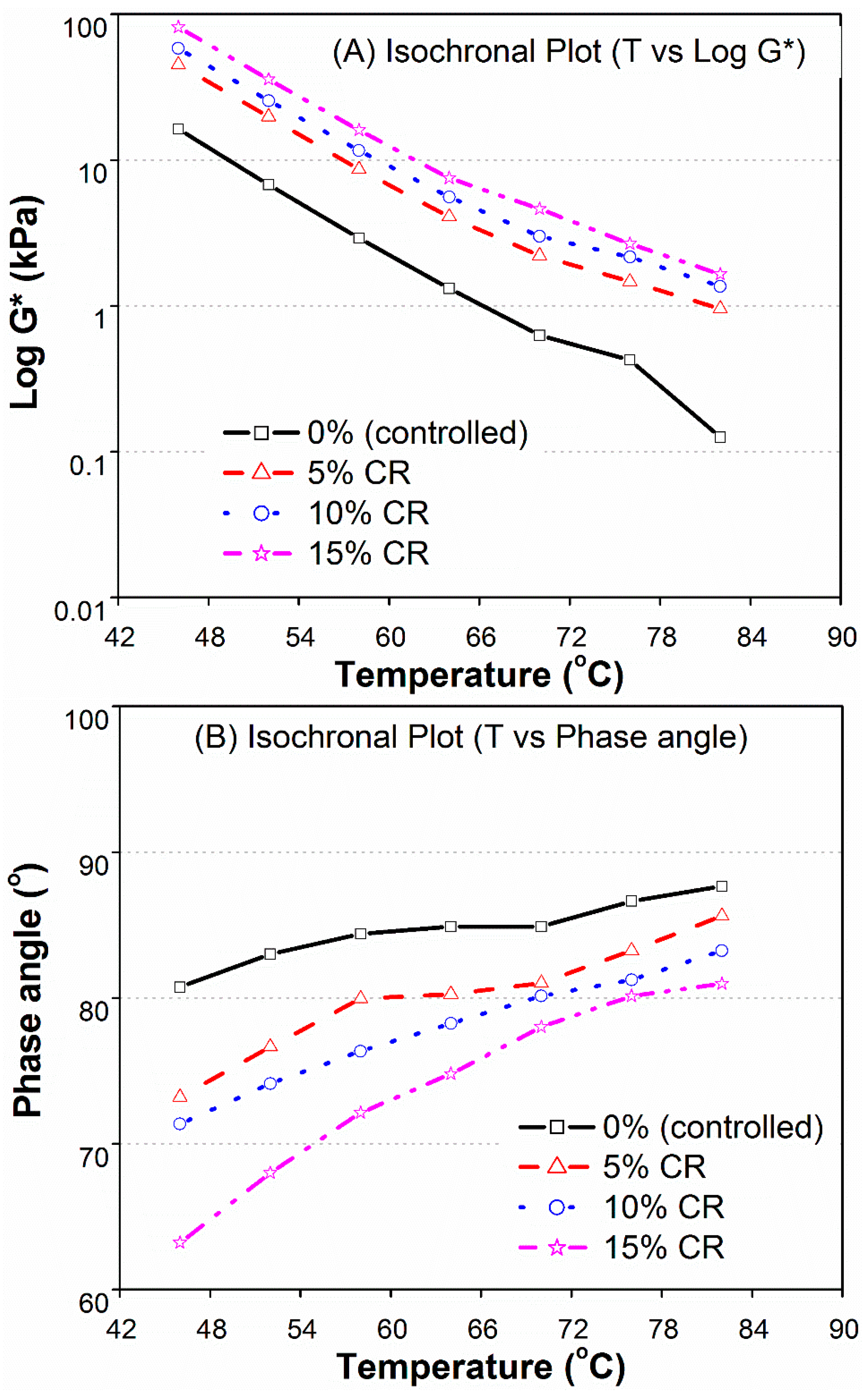
3.2.3. CR Modified Binders
3.3. Rutting Susceptibility of Modified Binders
3.3.1. LDP-MB
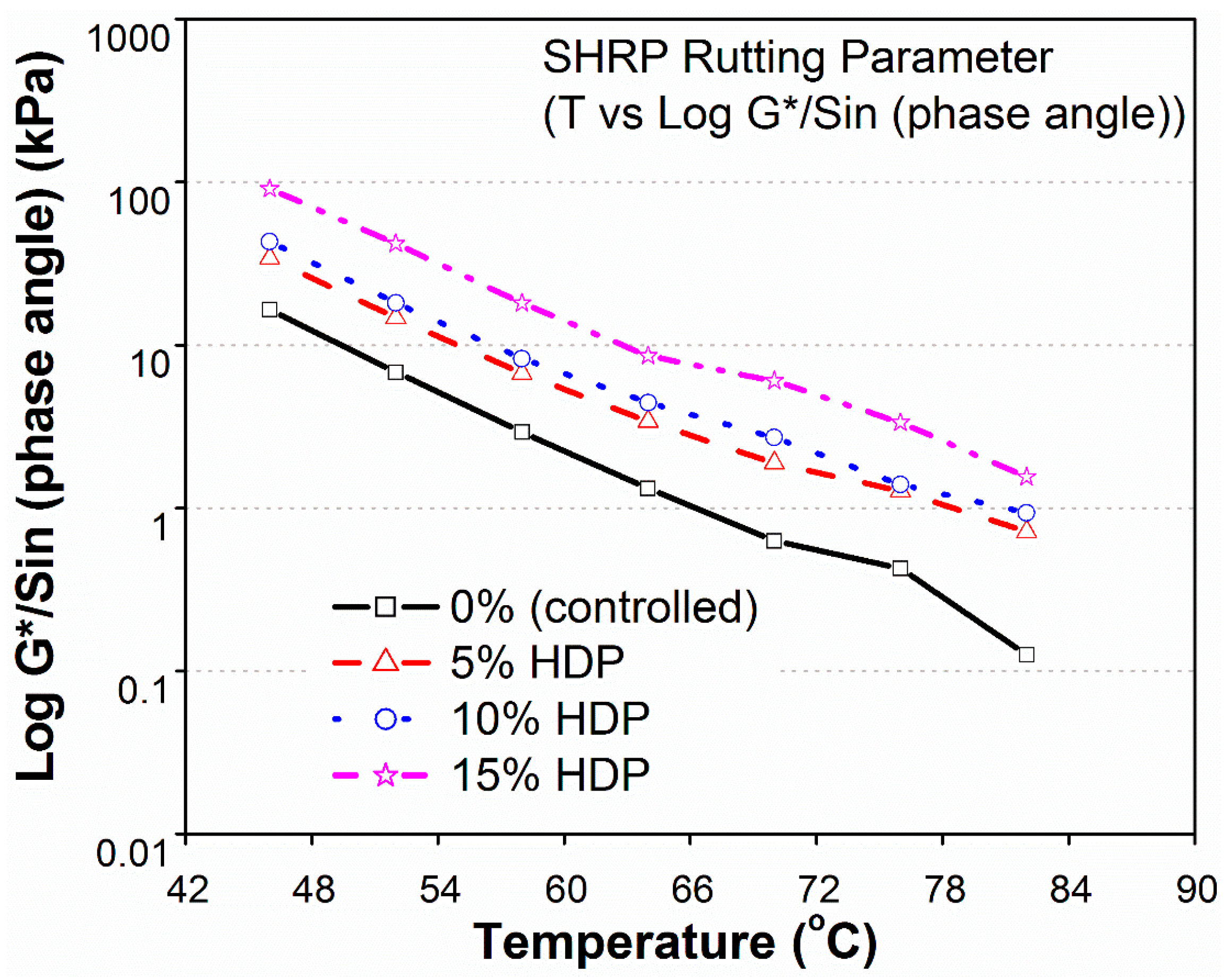
3.3.2. HDP-MB
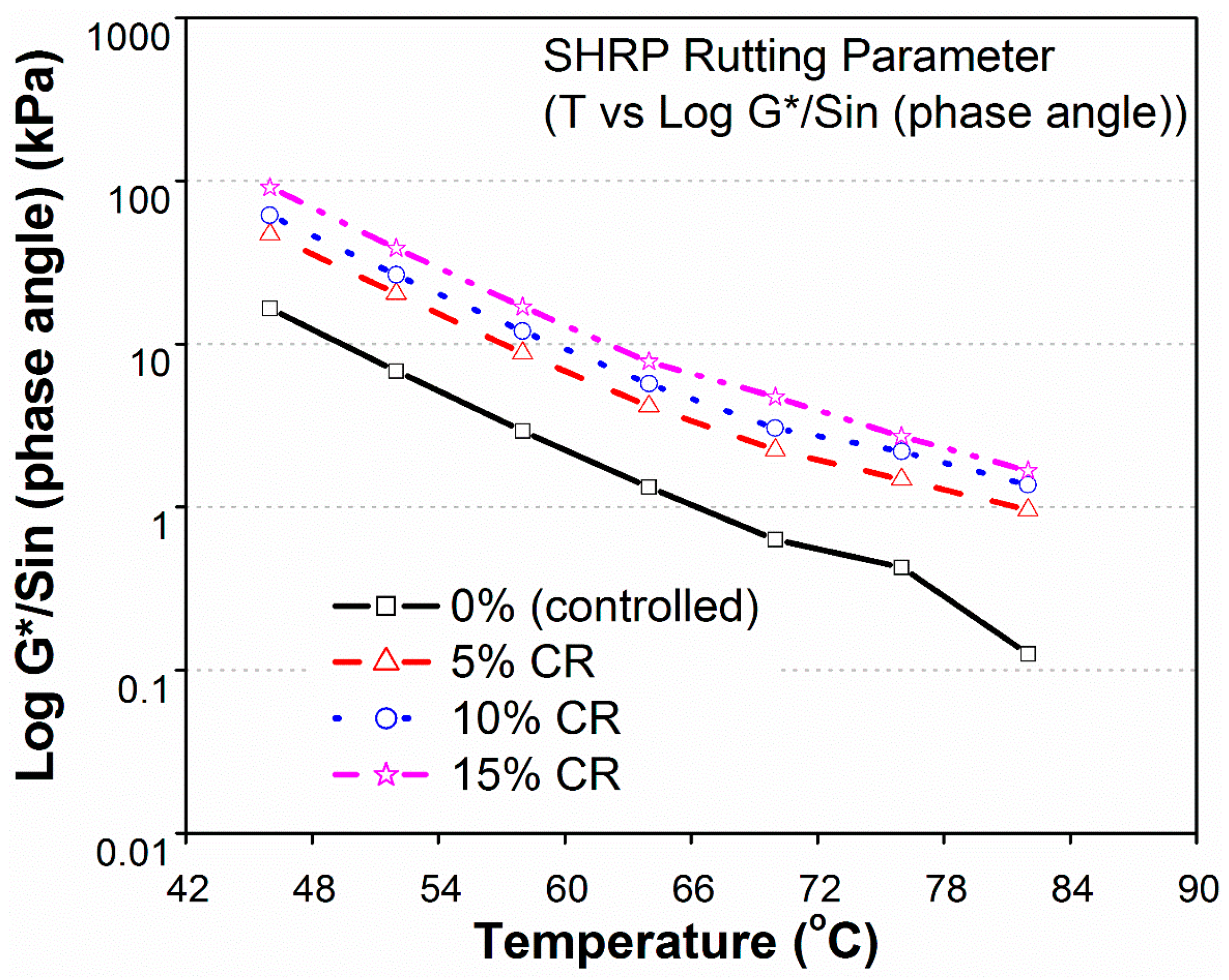
3.3.3. CR-MB
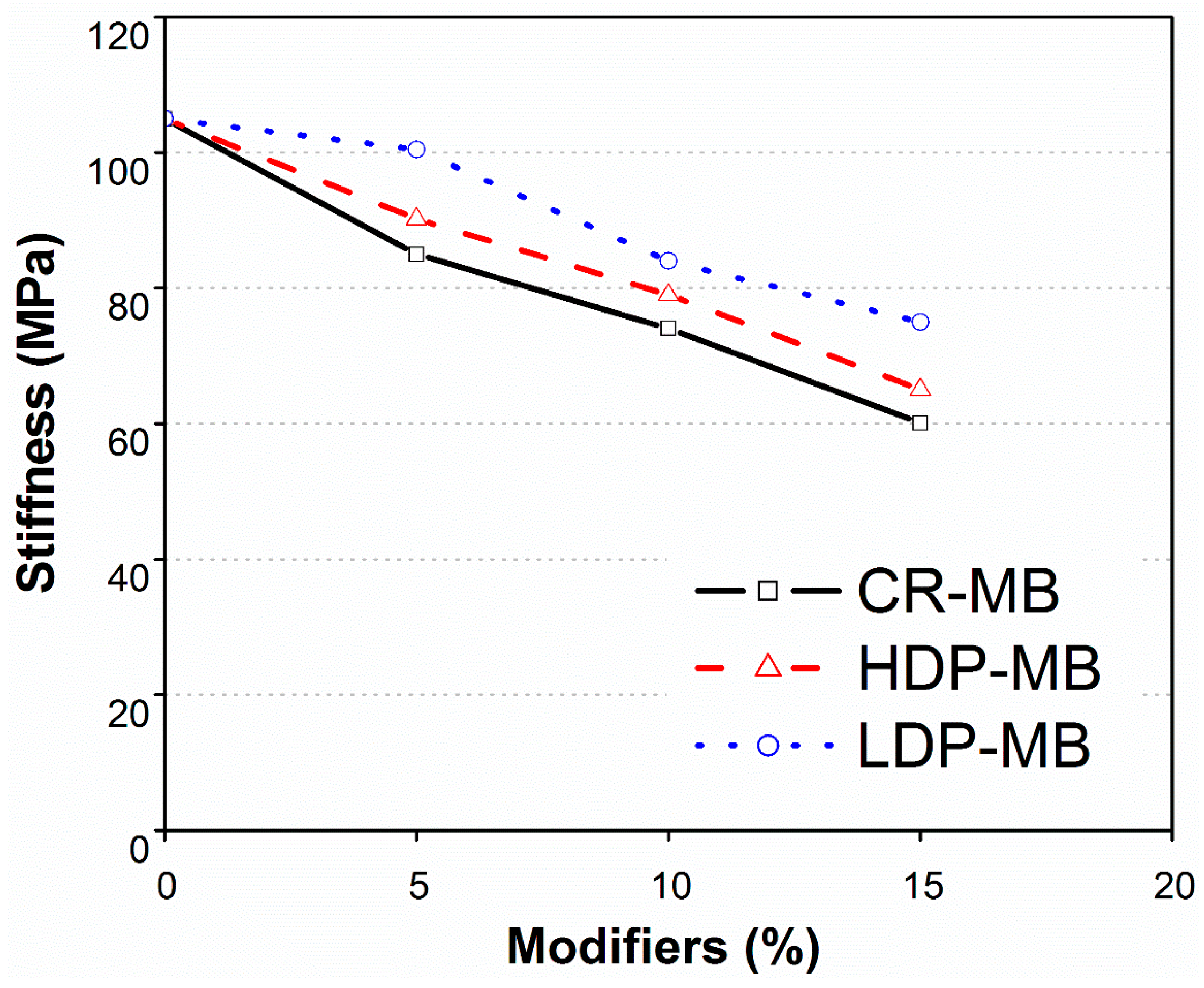
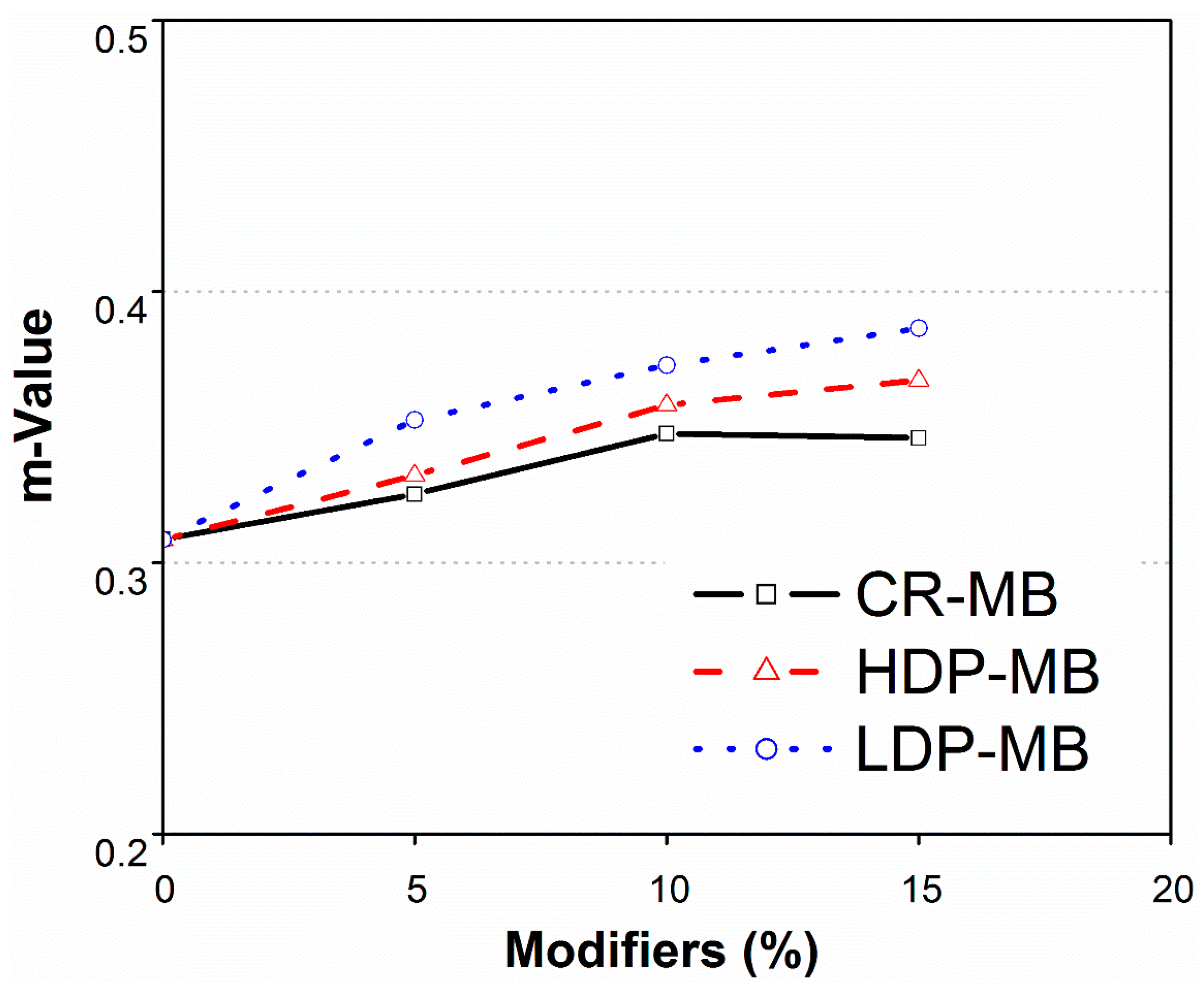
3.4. Creep Stiffness of Modified Binders
4. Conclusions
- Binder modified with CR, HDP, and LDP showed significant improvement of viscosity. However, viscosity of 15% CR-MB exceeded the SuperPave specifications, which could affect the workability of the asphalt mix during its mixing and placing. To overcome this problem, SASOBIT® could be added to CR-MB to reduce this exceeded viscosity.
- Increased percentages of CR, HDP, and LDP had significant effects on the visco-elastic properties of the modified binders. The modified binders showed improved elasticity as compared to base bitumen due to increase in the complex modulus (G*) and the decline in phase angle (δ) values. The increase in G* for LDE, HDP, and CR were 2–7, 4–11,and 4–12 times, respectively, as compared to controlled bitumen for temperatures 46, 52, 58, 64, 70, 76, and 82 °C.
- The base binder (PG 64-10) was found to be more susceptible to rutting at temperatures above 64 °C.
- The SHRP rutting parameter (G*/Sinδ) was improved significantly in modified binders at higher temperatures. Binders modified with 5%–15% of HDP and CR, and 10%–15% of LDP, satisfied the minimum requirements of SuperPave rutting criteria, at temperatures of 70 and 76 °C. Moreover, the performance grade of base binder (PG 64-10) was improved to PG 76-10 for HDP and CR modifications, and up to PG 70-10 for 10%–15% LDP.
- Binder modified with 15% LDP and HDP exceeded the minimum SuperPave rutting criteria at the highest temperature (82 °C) and, hence, the performance grade rose to PG 82-10. Consequently, bitumen modified with 15% LDP, HDP, and CR could satisfactorily be used in road construction throughout KSA.
- An inverse relationship was observed between creep stiffness and the binder resistance against low temperature cracks. Increased dosage of modifiers results in a decrease of the stiffness value and, hence, offered more resistance to low temperature cracks in asphalt pavements.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PG | Performance Grade |
| HDP | High-Density Polyethylene |
| LDP | Low-Density Polyethylene |
| CR | Crumb Rubber |
| RV | Rotational Viscometer |
| DSR | Dynamic Shear Rheometer |
| BBR | Bending Beam Rheometer |
| SBS | Styrene Butadiene Styrene |
| SBR | Styrene Butadiene Rubber |
| EVA | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate |
| G* | Complex Modulus |
| δ | Phase angle |
| cP | Centipoise |
| rpm | Revolution per minute |
| SHRP | Strategic Highway Research Program |
| CR-MB | Crumb Rubber—Modified Bitumen |
| LDP-MB | Low-Density Polyethylene—Modified Bitumen |
| HDP-MB | High-Density Polyethylene—Modified Bitumen |
| kPa | Kilo-Pascal |
| RTFO | Rolling Thin Film Oven |
| PAV | Pressure Aging Vessel |
| MSCR | Multiple Stress Creep Recovery |
| Pa·s | Pascal second |
References
- Masad, E.; Huang, C.; Airey, G.; Muliana, A. Nonlinear viscoelastic analysis of unaged and aged asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 2170–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airey, G. Rheological evaluation of ethylene vinyl acetate polymer modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2002, 16, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Kadi, A.; Brahimi, H.; Bousmina, M. Polymer blends for enhanced asphalt binders. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 1724–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, R.; Rodríguez, R.; García-Garduño, M.; Castaño, V.M. Rheological properties of styrene-butadiene copolymer-reinforced asphalt. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 61, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesp, S.A.; Woodhams, R.T. Asphalt–polyolefin emulsion breakdown. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1991, 269, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.K. Dynamic shear rheological properties of polymer-modified asphalt binders. J. Elast. Plast. 1998, 30, 245–263. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi, A.A. Polyethylene dispersions in bitumen: The effects of the polymer structural parameters. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 3183–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Su, M.; Zhao, S.F.; Zhang, Y.P.; Zhang, Z.P. High and low temperature properties of Nano-particles/polymer modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehab, A.; Salahuddin, N. Nanocomposite materials based on polyurethane intercalated into montmorillonite clay. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 399, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.Y.; Feng, P.C.; Zhang, H.L. Effect of organo-montmorillonite on aging properties of asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2636–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X. Effect of montmorillonite on properties of styrene–butadiene–styrene copolymer modified bitumen. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2007, 47, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Yu, R.; Zhang, Y. Combined modification of asphalt with polyethylene packaging waste and organophilic montmorillonite. Polym. Test. 2012, 31, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, L.A.; Martinez, B.F.; Gallegos, C.; Gonzalez, O.; Munoz, M.; Santamaria, A. Influence of the processing conditions on the rheological behaviour of polymer-modified bitumen. Fuel 2003, 82, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Isacsson, U. Modification of road bitumen with thermoplastic polymers. Polym. Test. 2001, 20, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, O.; Pena, J.; Munoz, M.; Santamaria, A.; Perez, L.A.; Martinez, B.F. Rheological techniques as a tool to analyze polymer-bitumen interactions: Bitumen modified with polyethylene and polyethylene-based blends. Energy Fuel 2002, 16, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacco, G.; Berlincioni, S.; Biondi, D.; Stastna, J.; Zanzotto, L. Asphalt modification with different polyethylene-based polymers. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 2831–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, N.; Kamaruddin, Z.; Napiah, M.; Tan, M. Rheological properties of polyethylene and polypropylene modified bitumen. Int. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2011, 3, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S.M.; Zakariya, K. Biodegradable waste to biogas: Renewable energy option for the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 2013, 4, 101–113. [Google Scholar]
- Kosseva, M.R. Chapter 3 Processing of Food Wastes. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2009, 58, 57–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hakamil, B.A.; El-Sayed, S.A.S. Household Solid Waste Composition and Management in Jeddah City, Saudi Arabia: A planning model. Int. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Saudi Industrial Property Authority. Report on waste tires in KSA. 2013. Available online: http://www.modon.gov.sa/en/pages/default.aspx (accessed on 3 March 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Francesco, M.; Cesare, S.; Valeria, V.; Claudio, L.; Giulio, D. Rheological characterization of bituminous mastics containing waste bleaching clays. In Proceedings of the 8th RILEM International Symposium on Testing and Characterization of Sustainable and Innovative Bituminous Materials, Ancona, Italy, 7–9 October 2015; Volume 11, pp. 595–606.
- Ministry of Transport, Saudi Arabia. Available online: http://www.mot.gov.sa/ (accessed on 20 February 2014).
- Farhat, M.A.; Asi, I.M.; Wahhab, H.A.; Al-Dubabe, I.A. Characterization of Polymer Modified Gulf Asphalts. Pet. Sci. Technol. 1999, 17, 125–145. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D7175-08. Standard Test Method for Determining the Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder Using a Dynamic Shear Rheometer; American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D2872-04. Standard Test Method for Effect of Heat and Air on a Moving Film of Asphalt (Rolling Thin-Film Oven Test); American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D6521-08. Standard Practice for Accelerated Aging of Asphalt Binder Using a Pressurized Aging Vessel (PAV); American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D6648-08. Standard Test Method for Determining the Flexural Creep Stiffness of Asphalt Binder Using the Bending Beam Rheometer (BBR); American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D4402. Standard Test Method for Viscosity Determination of Asphalt at Elevated Temperatures Using a Rotational Viscometer; American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Asphalt Institute. SP-1 Superpave Performance Graded Asphalt Binder Specification and Testing; Asphalt Institute: Lexington, KY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, J.Z.; Ping, G. Workability of Sasobit Warm Mixture Asphalt. Energy Procedia 2012, 16, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, W. Viscoelastic characterization of polymer modified asphalt binders of pavement applications. Appl. Rheol. 2003, 13, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, H.A.; Asi, I.M.; Ibrahim, A.D.; Alit, M.F. Development of performance-based bitumen specifications for the Gulf countries. Constr. Build. Mater. 1997, 11, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Test/ Physical Property | Bitumen | LDP | HDP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specific Gravity | 1.019 | Density = 922 kg/m3 | Density = 961 kg/m3 |
| Penetration @ 25 °C, 0.1 mm | 60–70 | ||
| Softening point (°C) | 49.45 | ||
| Flash point (°C) | 310 | ||
| Ductility (mm) | 126.5 | ||
| Viscosity @ 135 °C (cP) | 460.35 | ||
| Super-Pave Performance Grade (PG) | 64-10 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amin, M.N.; Khan, M.I.; Saleem, M.U. Performance Evaluation of Asphalt Modified with Municipal Wastes for Sustainable Pavement Construction. Sustainability 2016, 8, 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8100949
Amin MN, Khan MI, Saleem MU. Performance Evaluation of Asphalt Modified with Municipal Wastes for Sustainable Pavement Construction. Sustainability. 2016; 8(10):949. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8100949
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmin, Muhammad Nasir, Muhammad Imran Khan, and Muhammad Umair Saleem. 2016. "Performance Evaluation of Asphalt Modified with Municipal Wastes for Sustainable Pavement Construction" Sustainability 8, no. 10: 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8100949






