Sustainability Study on Heavy Metal Uptake in Neem Biodiesel Using Selective Catalytic Preparation and Hyphenated Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Treatment
2.2. High-Resolution ICP-MS
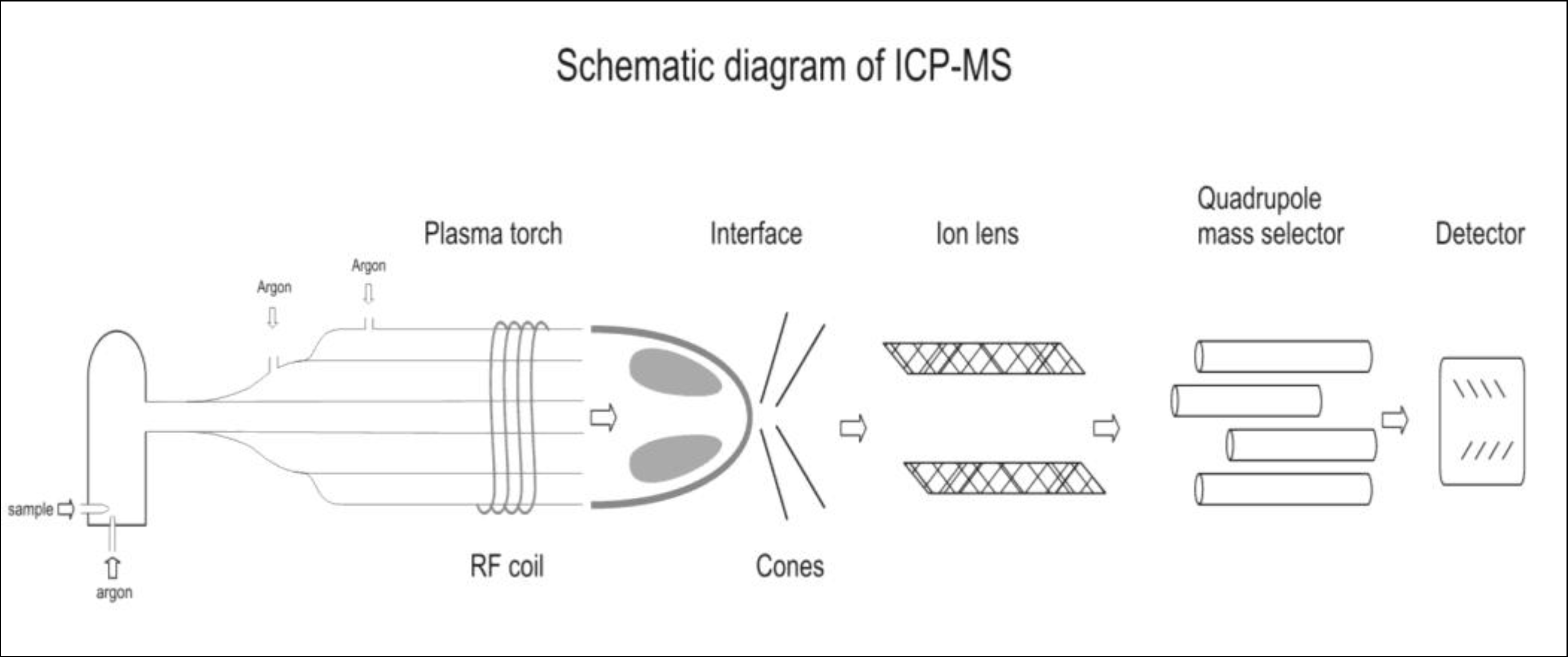
2.3. Instrumental Performance
| Measurement | Be | Mg | Co | Ni | In | Ce | Bi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.5 | 10.3 | 9.9 | 9.9 | 9.6 | 9.8 | 9.1 |
| 2 | 10.7 | 10.6 | 10.6 | 10.1 | 9.5 | 9.1 | 9.6 |
| 3 | 10.6 | 10.6 | 9.9 | 10 | 9.6 | 9.2 | 9.1 |
| Mean ± RSD | 10.6 ± 0.94% | 10.5 ± 1.7% | 10.1 ± 4.0% | 10.0 ± 1.0% | 9.6 ± 0.6% | 9.4 ± 4.0% | 9.3 ± 3.1% |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Base Catalysts
3.1.1. Homogeneous Catalysts
3.1.2. Heterogeneous Catalyst
3.2. Selectivity of Metal Uptake
3.2.1. Light Elements (Z ≤ 20)

3.2.2. First-Row Transition Metals

3.2.3. Heavy Elements (Z > 30)
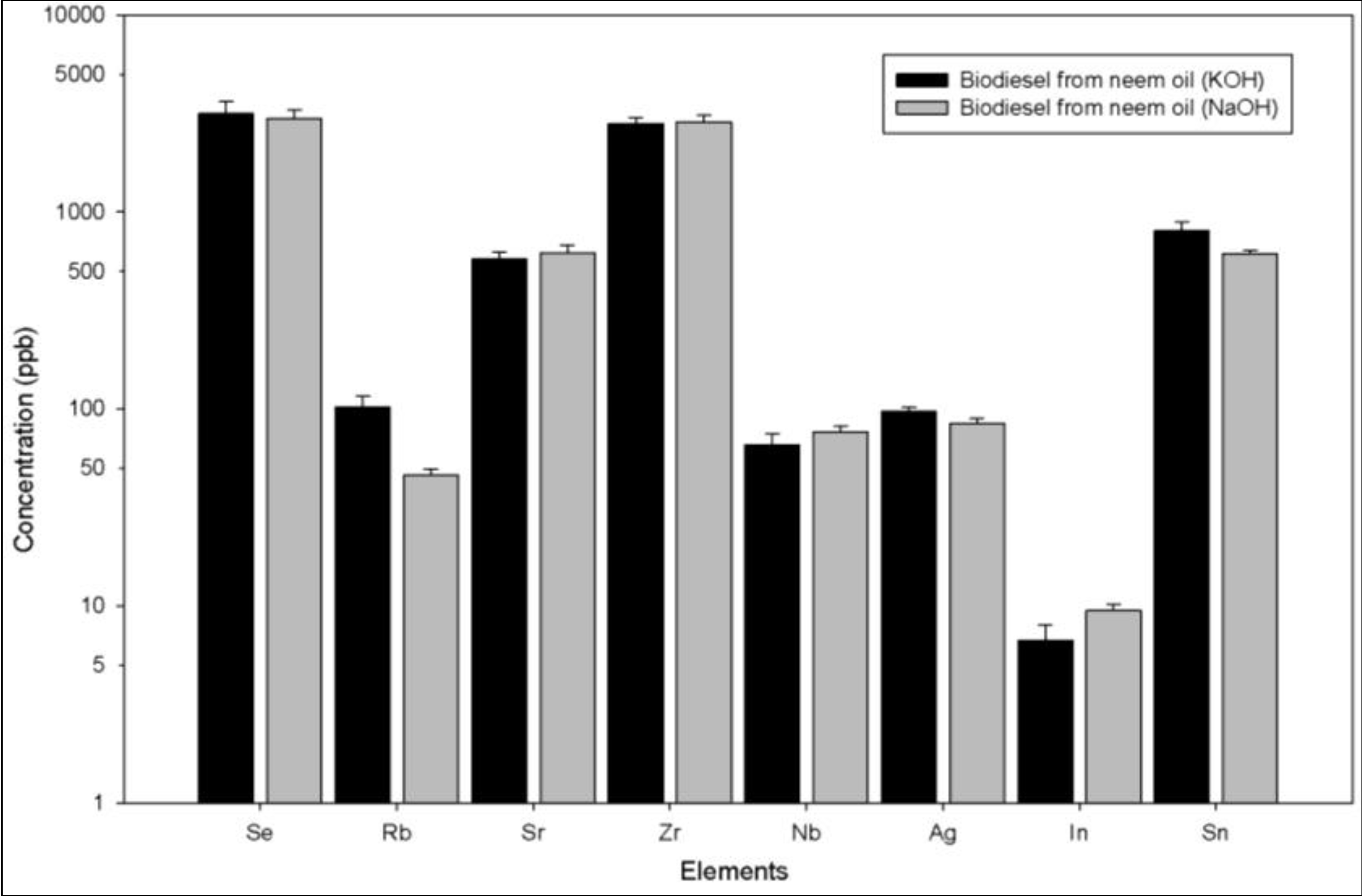
3.3. Sustainability/Environmental Implications

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, F.; Hanna, M.A. Biodiesel production: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 70, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achten, W.M.J.; Mathijs, E.; Verchot, L.; Singh, V.P.; Aerts, R.; Muys, B. Jatropha biodiesel fueling sustainability a perspective. Biofuels. Bioprod. Biorefin. 2007, 1, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Makkar, H.P.S. Jatropha curcas: A potential source for tomorrow’s oil and biodiesel. Lipid Technol. 2008, 20, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, H.P.S.; Becker, K. Jatropha curcas: A promising crop for the generation of biodiesel and value-added coproducts. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2009, 111, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helwani, Z.; Othman, M.R.; Aziz, N.; Kim, J.; Fernando, W.J.N. Solid catalysis for transesterification of triglycerides with methanol. Appl. Catal. A 2009, 363, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, D.Y.C.; Wu, X.; Leung, M.K.H. A review on biodiesel production using catalyzed transesterification. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, K.Y. Heterogeneous base catalysts for transesterification in biodiesel synthesis. Catal. Surv. Asia 2009, 13, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotero, E.; Liu, Y.; Lopez, D.E.; Suwannakarn, K.; Bruce, D.A.; Goodwin, J.G. Synthesis of biodiesel via acid catalysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 5353–5363. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, H.; Kondo, A.; Noda, H. Biodiesel fuel production by transesterification of oils. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2001, 92, 405–416. [Google Scholar]
- Berchmans, H.J.; Hirata, S. Biodiesel production from crude Jatropha curcas L. seed oil with a high content of free fatty acids. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1716–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Serio, M.; Cozzolino, M.; Giordano, M.; Tesser, R.; Patrono, P.; Santacesaria, E. From homogeneous to heterogeneous catalysts in biodiesel production. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 6379–6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchardta, U.; Serchelia, R.; Vargas, R.M. Transesterification of vegetable oils: A review. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 1998, 9, 199–210. [Google Scholar]
- Sivasamy, A.; Cheah, K.Y.; Fornasiero, P.; Kemausour, F.; Zinoviev, S.; Miertus, S. Catalytic applications in the production from vegetable oil. Chem. Sus. Chem. 2009, 2, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Chhetri, A.B.; Tango, M.S.; Budge, S.M.; Watts, K.C.; Islam, M.R. Non-edible plant oils as new sources for biodiesel production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Serio, M.; Tesser, R.; Pengmei, L.; Santacesaria, E. Heterogeneous catalysts for biodiesel production. Energ. Fuel. 2008, 22, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Comparison of transesterification methods for production of biodiesel from vegetable oils and fats. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsezen, A.N.; Canakci, M. Determination of performance and combustion characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with canola and waste palm oil methyl esters. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukkaya, E. Effects of biodiesel on a DI diesel engine performance, emission and combustion characteristics. Fuel 2010, 89, 3099–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, H.; Bayindir, H. Performance and emission analysis of cottonseed oil methyl ester in a diesel engine. Renew. Energ. 2010, 35, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celikten, I.; Koca, A.; Arslan, M.A. Comparison of performance and emissions of diesel fuel, rapeseed and soybean oil methyl esters injected at different pressures. Renew. Energ. 2010, 35, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Shuai, S. A study on the emission performance of a diesel engine fueled with five typical methyl ester biodiesels. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1481–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Li, R.J. Engine performance and emission characteristics of marine fish-oil biodiesel produced from the discarded parts of marine fish. Fuel Process. Tech. 2009, 90, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.H.; Geng, L.M.; Chen, H.; Bian, Y.Z.; Liu, J.; Ren, X.C. Combustion and performance evaluation of a diesel engine fueled with biodiesel produced from soybean crude oil. Renew. Energ. 2009, 34, 2706–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.F.; Huang, J.H.; Huang, D.Y. Experimental study of the effects of vegetable oil methyl ester on DI diesel engine performance characteristics and pollutant emissions. Fuel 2009, 88, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheman, H.; Ghadge, S.V. Performance of compression ignition engine with mahua (Madhuca indica) biodiesel. Fuel 2007, 86, 2568–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakopoulos, C.D.; Antonopoulos, K.A.; Rakopoulos, D.C.; Hountalas, D.T.; Giakoumis, E.G. Comparative performance and emissions study of a direct injection diesel engine using blends of diesel fuel with vegetable oils or bio-diesels of various origins. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2006, 47, 3272–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usta, N. An experimental study on performance and exhaust emissions of a diesel engine fuelled with tobacco seed oil methyl ester. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2005, 46, 2373–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilkilic, C.; Yucesu, H.S. Investigation of the effect of sunflower oil methyl ester on the performance of a diesel engine. Energy Sourc. 2005, 27, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, A.E.; Elkadi, M.; Fok, S.C.; Stephen, S.; Manuel, J.; Khan, M.Z.; Unnithan, S. A comparison of trace metal profiles of neem biodiesel and commercial biofuels using high performance ICP-MS. Fuel 2012, 97, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serio, M.D.; Ledda, M.; Cozzolino, M.; Minutillo, G.; Tesser, R.; Santacesaria, E. Transesterification of soybean oil to biodiesel by using heterogeneous basic catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 3009–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; He, H.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhu, S.L.; Piao, X.L. Transesterification of soybean oil to biodiesel using CaO as a solid base catalyst. Fuel 2008, 87, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Piao, X.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhu, S.L.; He, H.Y. Calcium methoxide as a solid base catalyst for the transesterification of soybean oil to biodiesel with methanol. Fuel 2008, 87, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, M.C.; Mamilla, V.R.; Mallikarjun, M.V.; Reddy, K.V. Production of Biodiesel from Neem Oil. Int. J. Eng. Stud. 2009, 1, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Jenner, G.A.; Longerich, H.P.; Jackson, S.E.; Fryer, B.J. ICP-MS—A powerful tool for high-precision trace-element analysis in Earth sciences: Evidence from analysis of selected U.S.G.S. reference samples. Chem. Geol. 1990, 83, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srokol, Z.W.; Rothenberg, G. Practical issues in catalytic and hydrothermal biomass conversion: Concentration effects on reaction pathways. Top. Catal. 2010, 53, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.G. The limits to caring: sustainable living and the loss to biodiversity. Conserv. Biol. 1993, 7, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Shearman, R. The meaning and ethics of sustainability. Environ. Manag. 1990, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A. Environmental Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Wiley Eastern Limited: New Delhi, India, 1994. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Elkadi, M.; Pillay, A.; Manuel, J.; Khan, M.Z.; Stephen, S.; Molki, A. Sustainability Study on Heavy Metal Uptake in Neem Biodiesel Using Selective Catalytic Preparation and Hyphenated Mass Spectrometry. Sustainability 2014, 6, 2413-2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6052413
Elkadi M, Pillay A, Manuel J, Khan MZ, Stephen S, Molki A. Sustainability Study on Heavy Metal Uptake in Neem Biodiesel Using Selective Catalytic Preparation and Hyphenated Mass Spectrometry. Sustainability. 2014; 6(5):2413-2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6052413
Chicago/Turabian StyleElkadi, Mirella, Avin Pillay, Johnson Manuel, Mohammad Zubair Khan, Sasi Stephen, and Arman Molki. 2014. "Sustainability Study on Heavy Metal Uptake in Neem Biodiesel Using Selective Catalytic Preparation and Hyphenated Mass Spectrometry" Sustainability 6, no. 5: 2413-2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6052413
APA StyleElkadi, M., Pillay, A., Manuel, J., Khan, M. Z., Stephen, S., & Molki, A. (2014). Sustainability Study on Heavy Metal Uptake in Neem Biodiesel Using Selective Catalytic Preparation and Hyphenated Mass Spectrometry. Sustainability, 6(5), 2413-2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6052413




