Quantifying the Variability of Internode Allometry within and between Trees for Pinus tabulaeformis Carr. Using a Multilevel Nonlinear Mixed-Effect Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Data
| Tree No. | Tree Age (Year) | Age Group | Diameter at Breast Height (cm) | Tree Height (m) | Site Location | Density Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | A1 | 1.8 * | 0.93 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 5 | A1 | 1.7 * | 0.82 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 8 | A2 | 2.5 | 2.06 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 8 | A2 | 2.2 | 2.19 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 47 | A3 | 20.2 | 13.80 | 2 | 4 |
| 6 | 47 | A3 | 17.3 | 13.02 | 2 | 4 |
| 7 | 47 | A3 | 14.4 | 12.95 | 2 | 4 |
| 8 | 47 | A3 | 20.4 | 16.25 | 2 | 3 |
| 9 | 47 | A3 | 15.7 | 13.80 | 2 | 3 |
| 10 | 47 | A3 | 20.4 | 15.85 | 2 | 3 |
| 11 | 21 | A4 | 13.8 | 7.47 | 3 | 2 |
| 12 | 21 | A4 | 12.4 | 7.29 | 3 | 2 |
| 13 | 21 | A4 | 13.4 | 7.10 | 3 | 2 |
| 14 | 11 | A5 | 5.3 | 4.02 | 4 | 1 |
| 15 | 11 | A5 | 3.1 | 2.85 | 4 | 1 |
| 16 | 11 | A5 | 3.4 | 3.24 | 4 | 1 |
| Branch Order | Internode Size | Maximum | Minimum | Mean | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (CV) | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | length (cm) | 37.60 | 0.32 | 13.33 | 9.60 | 0.72 | 211 |
| fresh biomass (g) | 24.98 | 0.03 | 3.96 | 4.88 | 1.23 | ||
| 2 | length (cm) | 18.70 | 0.10 | 3.14 | 2.14 | 0.68 | 969 |
| fresh biomass (g) | 3.44 | 0.01 | 0.45 | 0.76 | 1.69 | ||
| 3 | length (cm) | 3.01 | 0.20 | 1.14 | 0.60 | 0.53 | 431 |
| fresh biomass (g) | 0.60 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.83 |
2.2. Base Allometry Model

2.3. Multi-Level Nonlinear Mixed Model
| Model No. | Mixed-Effect Parameters | AIC | BIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | β1, β2 | 891.6 | 911.2 |
| 2 | β1 | 910.3 | 923.3 |
| 3 | β2 | 1100.2 | 1113.2 |
| Base model | 1220.2 | 1223.0 |
| Model No. | Mixed-Effect Parameters | AIC | BIC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tree Level | First-Order Branch Level | |||
| 1 | β1, β2 | β1, β2 | 2098.2 | 2141.7 |
| 2 | β1, β2 | β1 | 2140.7 | 2174.6 |
| 3 | β1, β2 | β2 | 2165.4 | 2199.3 |
| 4 | β1 | β1, β2 | 2117.0 | 2150.9 |
| 5 | β1 | β1 | 2255.5 | 2279.7 |
| 6 | β1 | β2 | 2192.4 | 2216.6 |
| 7 | β2 | β1, β2 | misconvergence | |
| 8 | β2 | β1 | 2355.0 | 2379.3 |
| 9 | β2 | β2 | 3154.1 | 3178.3 |
| Base model | 3376.0 | 3390.5 | ||
| Model No. | Mixed-Effect Parameters | AIC | BIC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tree Level | First-Order Branch Level | Second-Order Branch Level | |||
| 1 | β1, β2 | β1, β2 | β1, β2 | misconvergence | |
| 2 | β1, β2 | β1, β2 | β1 | misconvergence | |
| 3 | β1, β2 | β1, β2 | β2 | 572.4 | 613.5 |
| 4 | β1, β2 | β1 | β1, β2 | misconvergence | |
| 5 | β1, β2 | β1 | β1 | 585.6 | 618.5 |
| 6 | β1, β2 | β1 | β2 | 616.4 | 649.4 |
| 7 | β1, β2 | β2 | β1, β2 | misconvergence | |
| 8 | β1, β2 | β2 | β1 | 558.0 | 590.9 |
| 9 | β1, β2 | β2 | β2 | 622.9 | 655.8 |
| 10 | β1 | β1, β2 | β1, β2 | misconvergence | |
| 11 | β1 | β1, β2 | β1 | 555.7 | 588.6 |
| 12 | β1 | β1, β2 | β2 | 572.1 | 605.1 |
| 13 | β1 | β1 | β1, β2 | misconvergence | |
| 14 | β1 | β1 | β1 | 604.8 | 629.5 |
| 15 | β1 | β1 | β2 | 637.3 | 662.0 |
| 16 | β1 | β2 | β1, β2 | misconvergence | |
| 17 | β1 | β2 | β1 | 564.6 | 589.3 |
| 18 | β1 | β2 | β2 | 633.6 | 658.3 |
| 19 | β2 | β1, β2 | β1, β2 | misconvergence | |
| 20 | β2 | β1, β2 | β1 | 554.0 | 587.0 |
| 21 | β2 | β1, β2 | β2 | 570.2 | 603.1 |
| 22 | β2 | β1 | β1, β2 | misconvergence | |
| 23 | β2 | β1 | β1 | 586.5 | 611.2 |
| 24 | β2 | β1 | β2 | 621.6 | 646.3 |
| 25 | β2 | β2 | β1, β2 | misconvergence | |
| 26 | β2 | β2 | β1 | 569.0 | 593.7 |
| 27 | β2 | β2 | β2 | 696.5 | 721.2 |
| Base model | 763.8 | 776.2 | |||
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
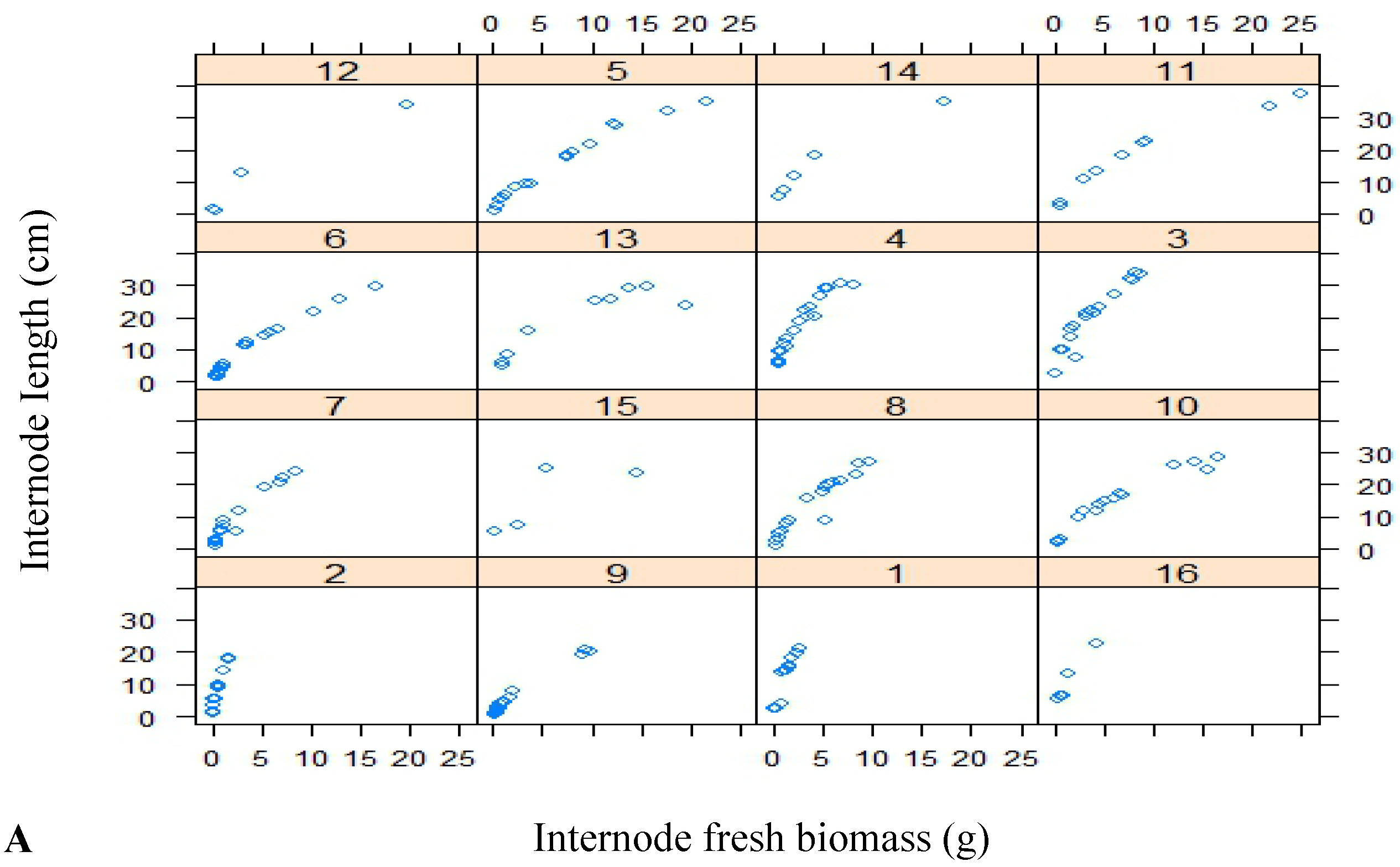
3.1. Variability in Internode Size and Biomass within and among Trees
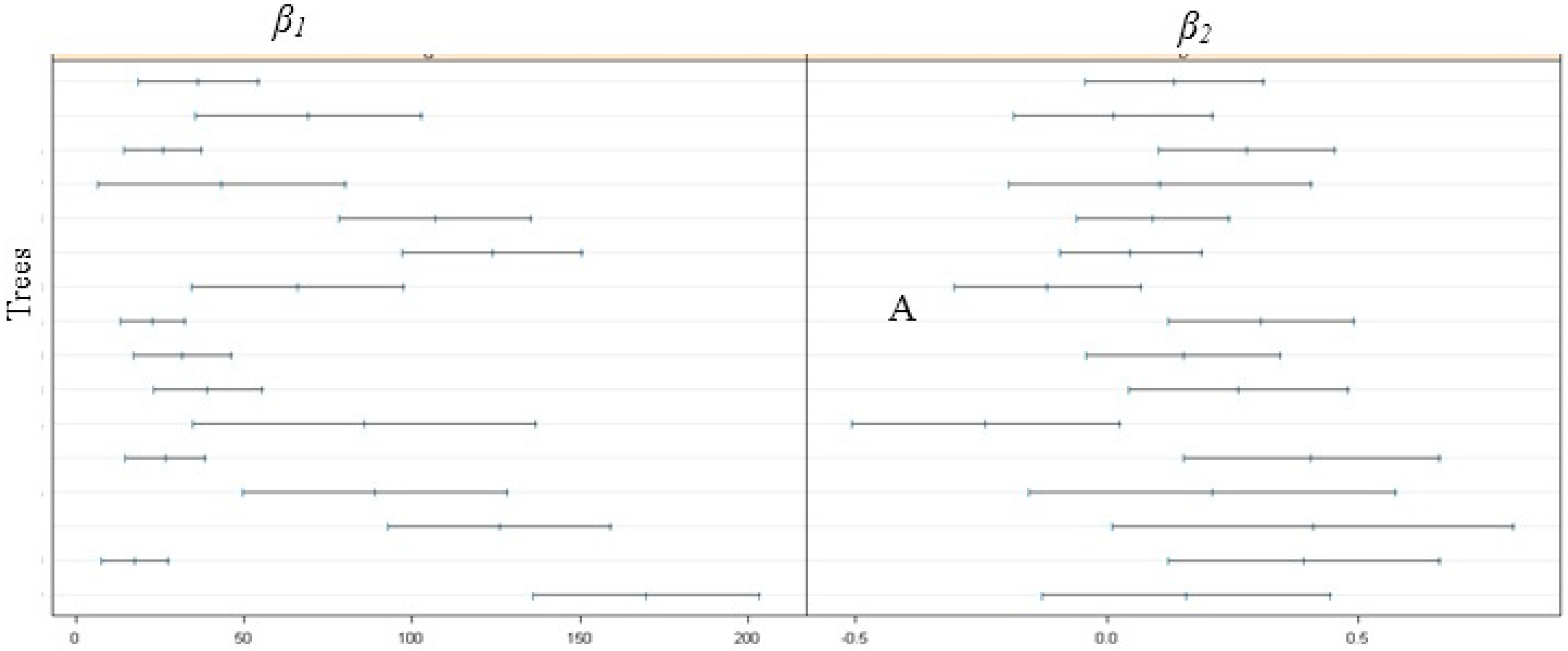
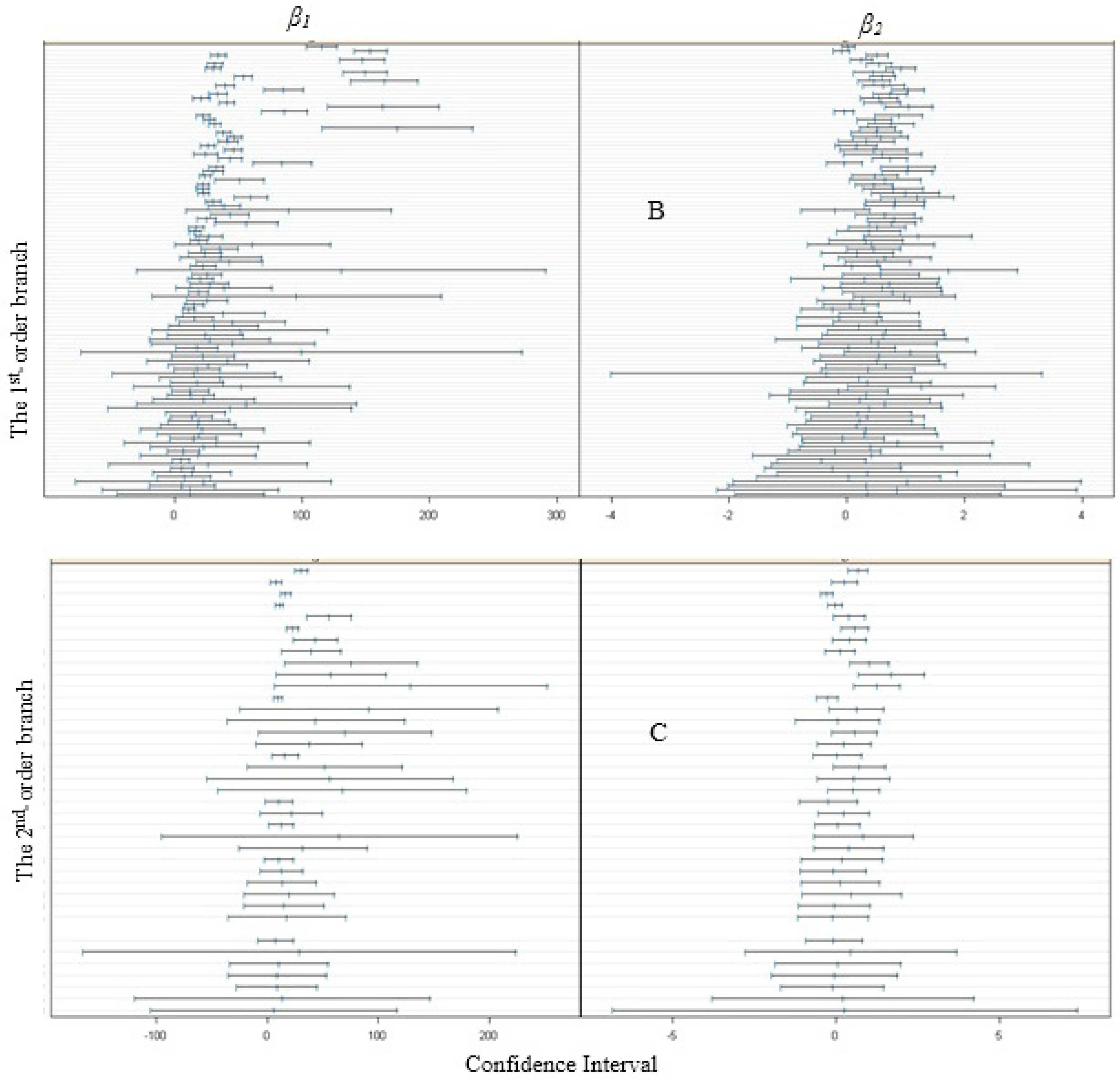
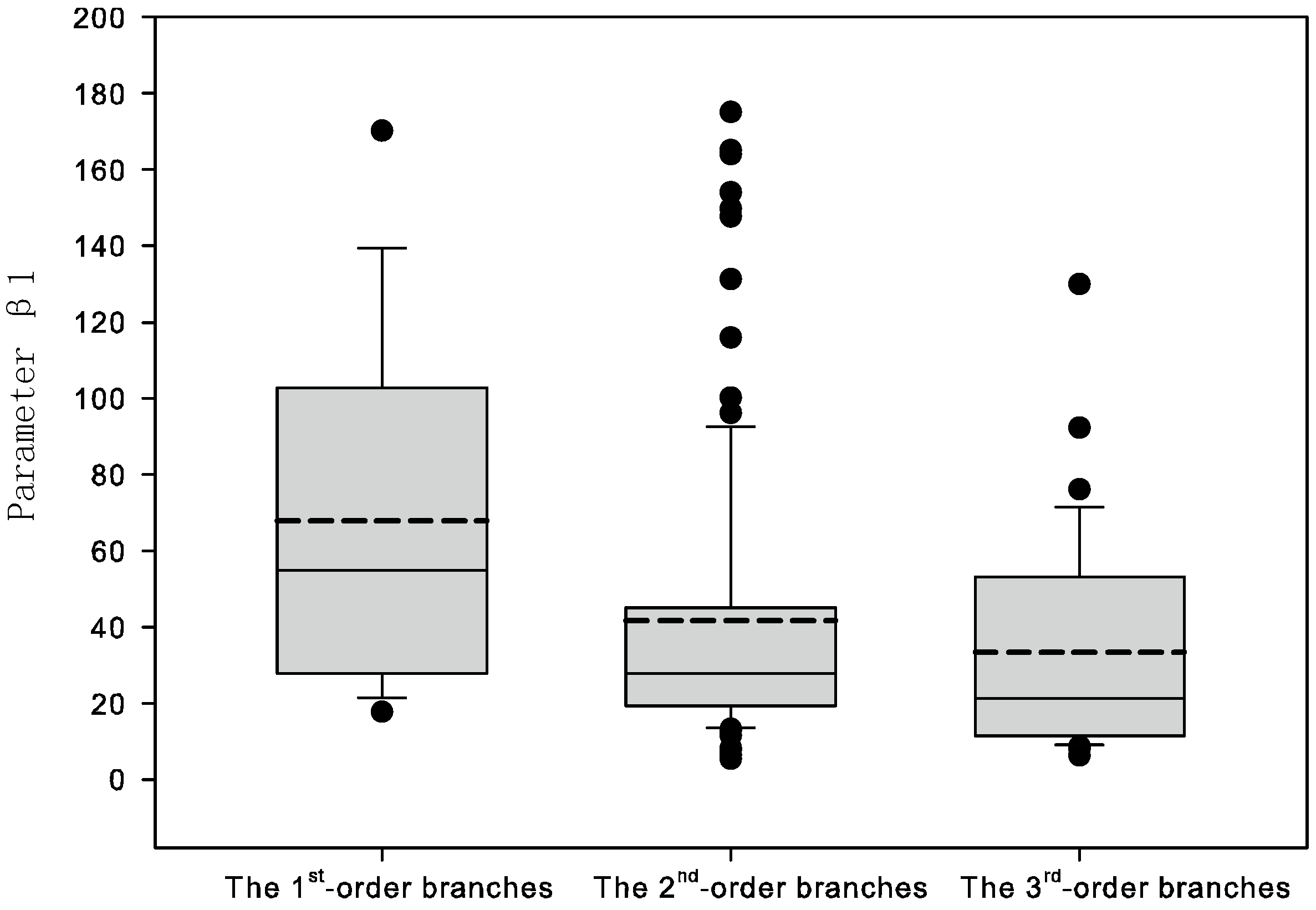
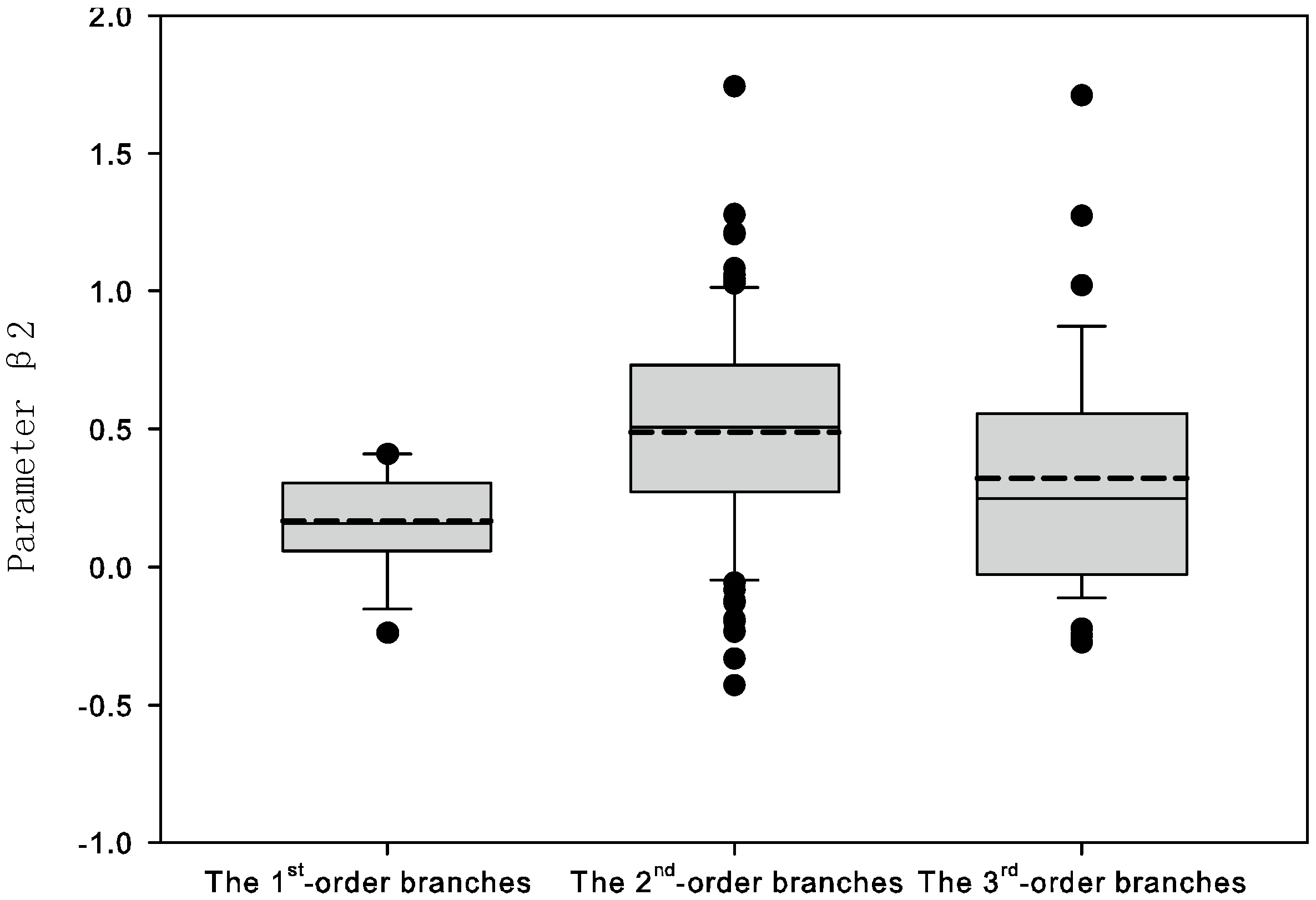
3.2. Model Fitting and Validation
| Fixed Part | Parameter | First-Order Branches | Second-Order Branches | Third-Order Branches | |||||
| β1 | 94.792 (20.954) | 59.992(13.234) | 4.043(0.286) | ||||||
| β2 | 0.122(0.042) | 0.361(0.068) | 0.513(0.036) | ||||||
| Random Part | Tree Level | Tree Level | First-Order Branch Level | Tree Level | First-Order Branch Level | Second-Order Branch Level | |||
| 5.478×103 | 2.153×103 | 93.700 | - | 2.651 | 0.248 | ||||
| 1.646 × 10−2 | 4.836 × 10−2 | 3.323 × 10−2 | 1.676 × 10−2 | 3.562 × 10−3 | - | ||||
| −0.525 | −0.592 | 0.709 | - | 0.879 | - | ||||
| 3.514 | 0.378 | 0.116 | |||||||
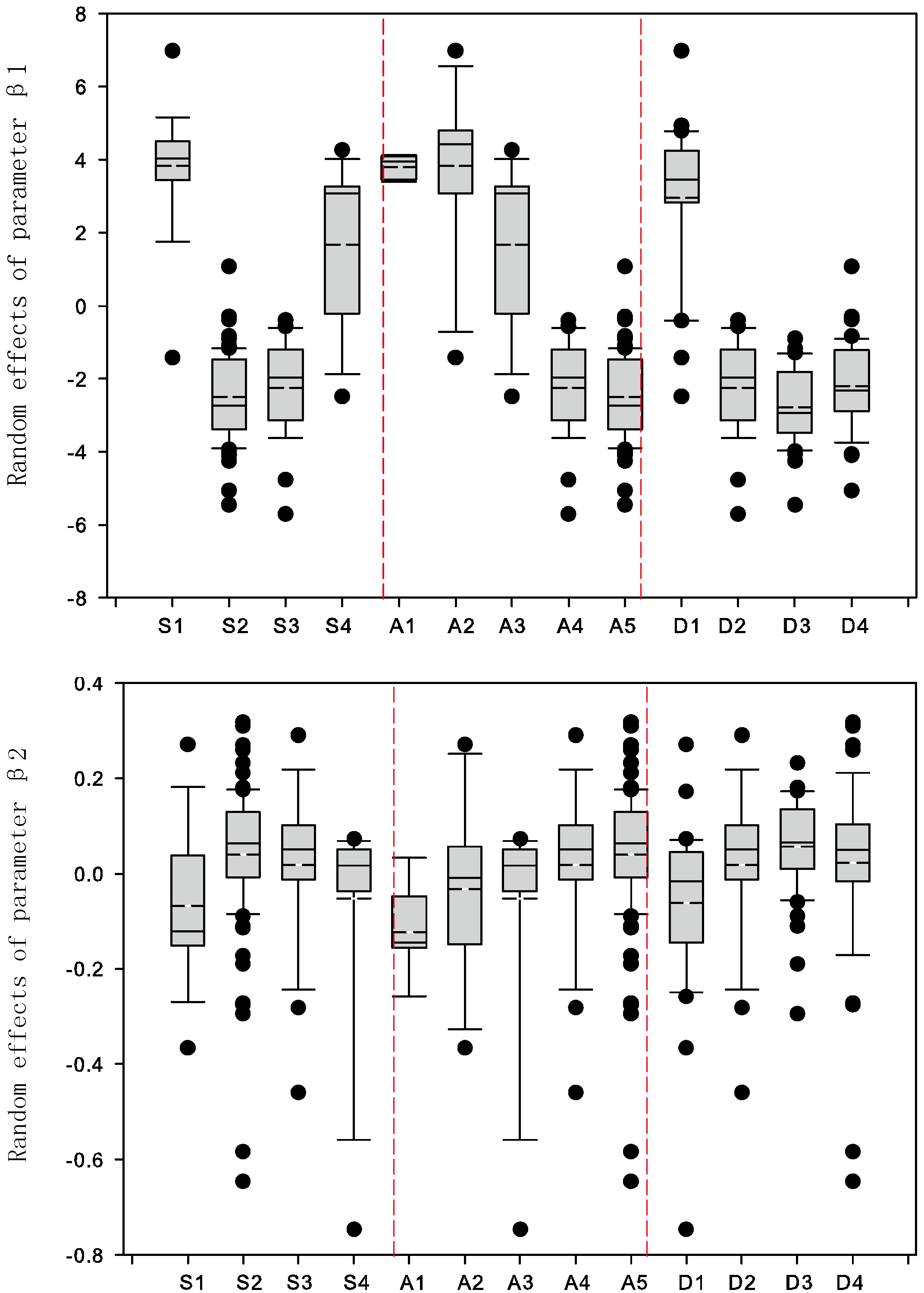
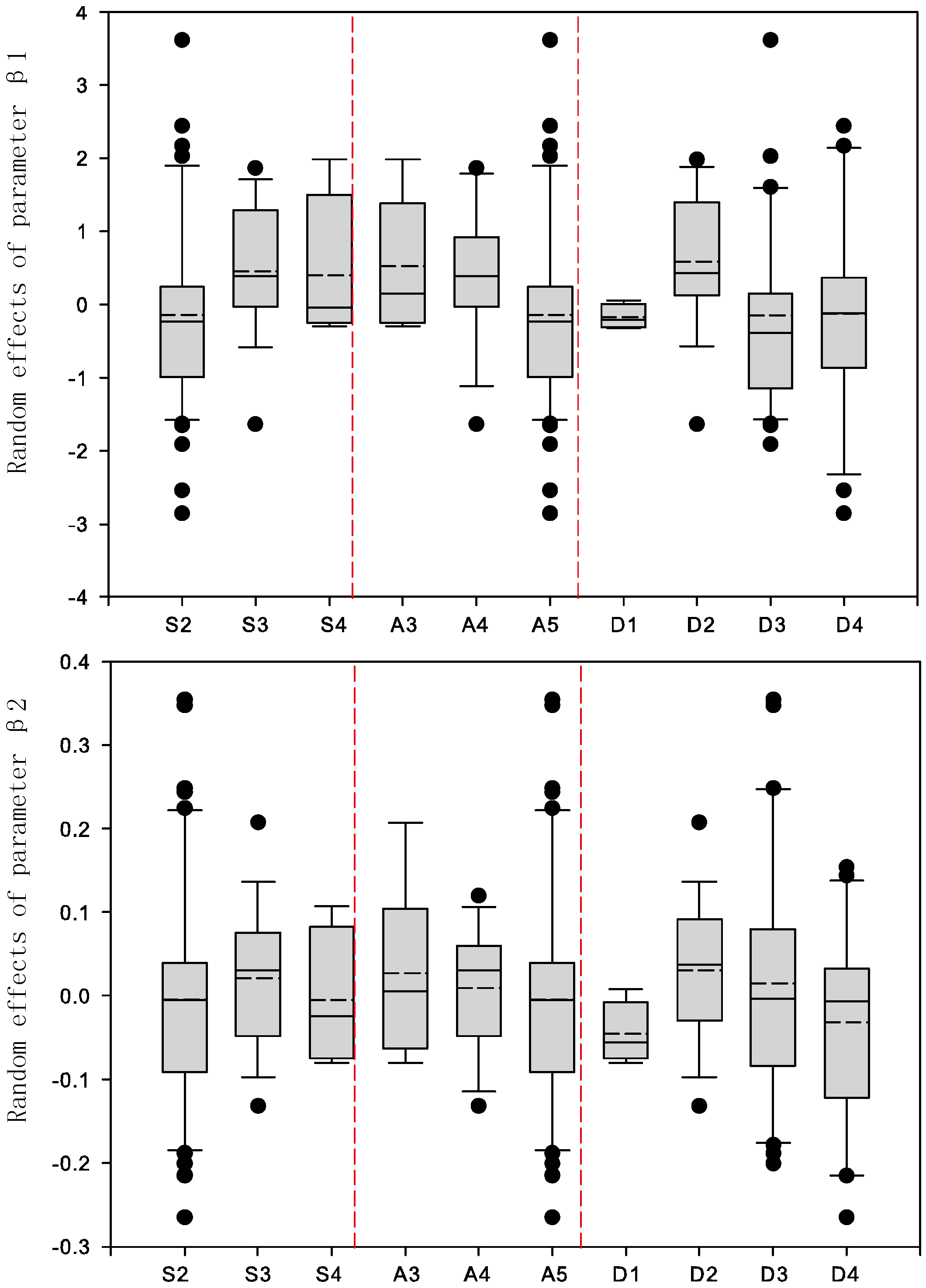
| Branch Order | Models | ARE | ARE Reduction (%) | RMSE | RMSE Reduction (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Base model | 0.071 | −25.35 | 5.745 | −69.14 | ||
| Mixed model | 0.053 | 1.773 | |||||
| 2 | Base model | 0.027 | −40.74 | 1.460 | −60.82 | ||
| Mixed model | 0.016 | 0.572 | |||||
| 3 | Base model | 0.047 | −55.32 | 0.560 | −46.43 | ||
| Mixed model | 0.021 | 0.300 | |||||
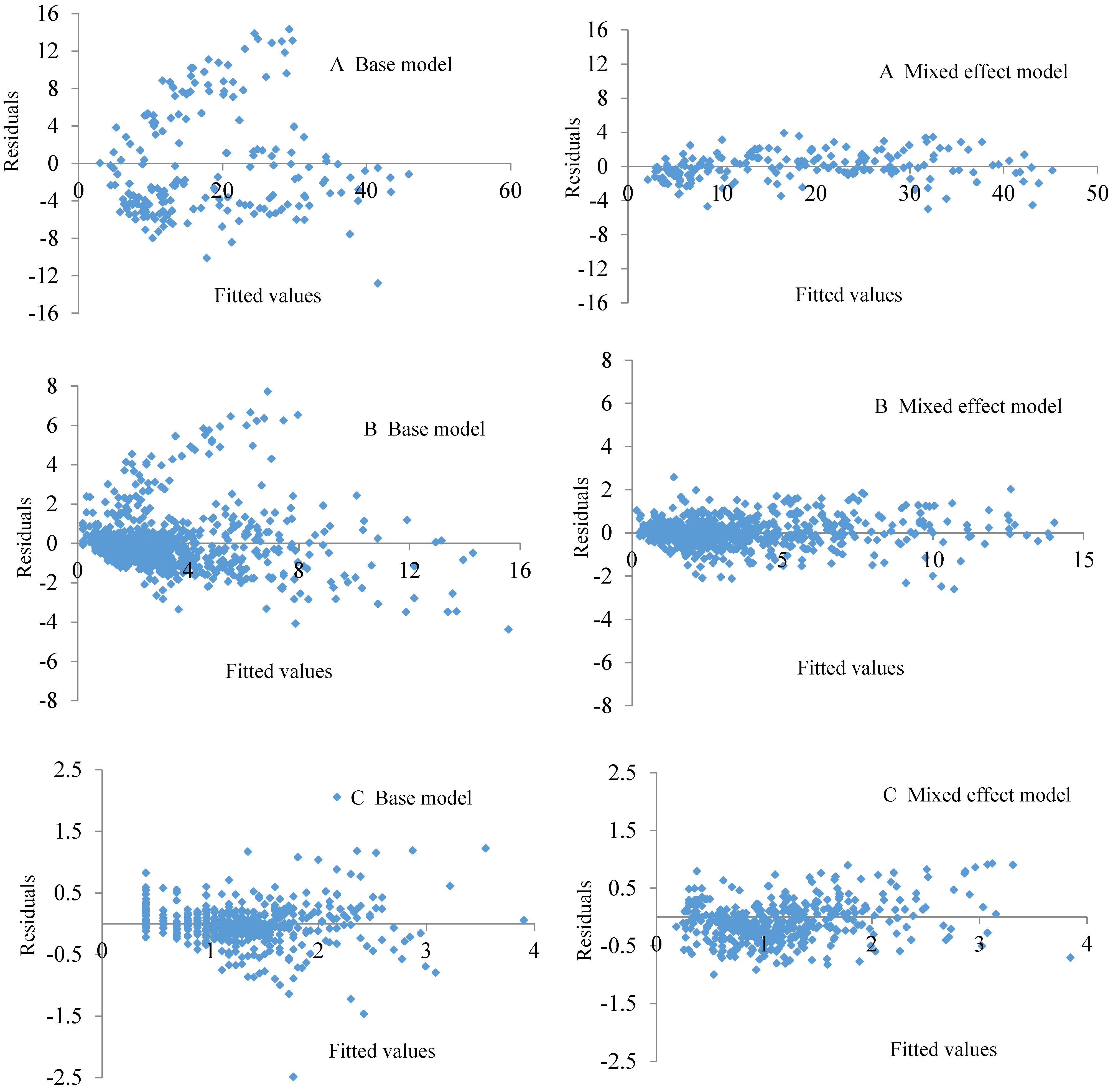
| Branch Order | Models | ARE | ARE Reduction (%) | RMSE | RMSEReduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Base model | 0.087 | −13.97 | 4.616 | −13.63 |
| Mixed model | 0.075 | 3.594 | |||
| 2 | Base model | 0.036 | −41.67 | 1.226 | −85.16 |
| Mixed model | 0.021 | 0.182 | |||
| 3 | Base model | 0.069 | −37.68 | 0.503 | −56.06 |
| Mixed model | 0.043 | 0.221 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peters, R.H. The Ecological Implications of Body Size; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 197–198. [Google Scholar]
- Niklas, K.J. Plant Allometry: The Scaling of Form and Process; University Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Sievanen, R.; Nikinmaa, E.; Nygren, P.; Ozier-Lafontaine, H.; Perttunen, J.; Hakula, H. Components of functional-structural tree models. Ann. For. Sci. 2000, 57, 399–412. [Google Scholar]
- Vos, J.; Evers, J.B.; Buck-Sorlin, G.H.; Andrieu, B.; Chelle, M.; de Visser, P.H.B. Functional-structural plant modelling: A new versatile tool in crop science. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 2101–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.P.; Kang, M.Z.; de Reffye, P.; Dingkuhn, M. A dynamic, architectural plant model simulating resource-dependent growth. Ann. Bot. 2004, 93, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cournède, P.H.; Mathieu, A.; Houllier, F.; Barthélémy, D.; de Reffye, P. Computing competition for light in the GREENLAB model of plant growth: A contribution to the study of the effects of density on resource acquisition and architectural development. Ann. Bot. 2008, 101, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, R.; Turkington, R. Maintenance of morphological variation in a biotically patchy environment. New Phytol. 1988, 109, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnsworth, K.D.; van Gardingen, P.R. Allometric analysis of Sitka spruce branches: Mechanical versus hydraulic design principles. Trees Struct. Funct. 1995, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reffye, P.; Houllier, F.; Blaise, F.; Barthélémy, D.; Dauzat, J.; Auclair, D. A model simulating above- and below-ground tree architecture with agroforestry applications. Agrofor. Syst. 1995, 30, 175–197. [Google Scholar]
- Welham, C.V.J.; Turkington, R.; Sayre, C. Morphological plasticity of white clover (Trifolium repens L.) in response to spatial and temporal resource heterogeneity. Oecologia 2002, 130, 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Salminen, H.; Jalkanen, R. Modelling variation of needle density of Scots pine at high latitudes. Silva Fenn. 2006, 40, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, V.; Denancé, C.; Durel, C.E.; Costes, E. Wide range QTL analysis for complex architectural traits in a 1-year-old apple progeny. Genome 2007, 50, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, D.C.; Graham, J.H.; Emlen, J.M. Developmental stability in plants: Symmetries, stress and epigenesis. Genetica 1993, 89, 97–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.A.; Ogle, K.; White, E.P.; Weitz, J.S. Evaluating scaling models in biology using hierarchical Bayesian approaches. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duursma, R.A.; Mäkelä, A.; Reid, D.E.B.; Jokela, E.J.; Porté, A.J.; Roberts, S.D. Self-shading effects allometric scaling in trees. Funct. Ecol. 2010, 24, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolokotrones, T.; van, S.; Deeds, E.J.; Fontana, W. Curvature in metabolic scaling. Nature 2010, 464, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretzsch, H.; Dieler, J. Evidence of variant intra- and interspecific scaling of tree crown structure and relevance for allometric theory. Oecologia 2012, 169, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Huber, H.; de Kroon, H.; Peeters, A.J.M.; Poorter, H.; Voesenek, L.A.C.J.; Visser, E.J.W. Intraspecific variation in the magnitude and pattern of flooding-induced shoot elongation in Rumex palustris. Ann. Bot. 2009, 104, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, C.H.; Thuiller, W.; Yoccoz, N.G.; Soudant, A.; Boucher, F.; Saccone, P.; Lavorel, S. Intraspecific functional variability: Extent, structure and sources of variation. J. Ecol. 2010, 98, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, C.H.; de Bello, F.; Boulangeat, I.; Pellet, G.; Lavorel, S.; Thuillet, W. On the importance of intraspecific variability for the quantification of functional diversity. Oikos 2012, 121, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolnick, D.I.; Amarasekare, P.; Araújo, M.S.; Bürger, R.; Levine, J.; Novak, M.; Rudolf, V.H.; Schreiber, S.; Urban, M.; Vasseur, D.; et al. Why intraspecific trait variation matters in community ecology. Trends. Ecol. Evol. 2011, 26, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, C.R.; Cassey, P.; Blackburn, T.M. Allometric exponents do not support a universal metabolic allometry. Ecology 2007, 88, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niklas, K.J. Size-dependent allometry of tree height, diameter and trunk taper. Ann. Bot. 1995, 75, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaitaniemi, P.; Lintunen, A. Precision of allometric scaling equations for trees can be improved by including the effect of ecological interactions. Trees Struct. Funct. 2008, 22, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldpausch, T.R.; Banin, L.; Phillips, O.L.; Baker, T.R.; Lewis, S.L.; Quesada, C.A.; Affum-Baffoe, K.; Arets, E.J.M.M.; Berry, N.J.; Bird, M.; Brondizio, E.S.; de Camargo, P. Height-diameter allometry of tropical forest trees. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 1081–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ducey, M.J. Evergreenness and wood density predict height-iameter scaling in trees of the northeastern United States. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 279, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.F.; Wang, J.; Le, X.; Shen, W.J.; Ren, H. Influences of biotic and abiotic factors on the relationship between tree productivity and biomass in China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 264, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretzsch, H. Species-specific allometric scaling under self-thinning: Evidence from long-term 28 plots in forest stands. Oecologia 2006, 146, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretzsch, H. Re-evaluation of allometry: State-of-the-art and perspective regarding individuals and stands of woody plants. Prog. Bot. 2010, 71, 339–369. [Google Scholar]
- Dahle, G.A.; Grabosky, J.C. Allometric patterns in Acer platanoides (Aceraceae) branches. Trees Struct. Funct. 2009, 24, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, A.; Valentine, A.; Valentine, H. Crown ratio influences allometric scaling in trees. Ecology 2006, 87, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letort, V.; Cournède, P.H.; Mathieu, A.; de Reffye, P.; Constant, T. Parametric identification of a functional structural tree growth model and application to beech trees (Fagus Sylvatica.). Funct. Plant Biol. 2008, 35, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Lei, X.D.; Letort, V.; Lu, Y.C.; de Reffye, P. A functional-structural model GreenLab for Pinus tabulaeformis. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2009, 33, 950–957. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Lei, X.D.; Letort, V.; Lu, Y.C. A functional-structural model for adults of Pinus tabulaeformis based on GreenLab. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2011, 35, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Kang, M.Z.; Lu, Q.; Han, H.; Letort, V.; Guo, Y.; de Reffye, P.H.; Li, B.G. Calibration of topological development in the procedure of parametric identification: Application of the stochastic GreenLab model for Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica. In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Plant Growth Modeling, Simulation, Visualization and Applications—PMA’09. IEEE Computer Society, Beijing, China, 9–13 November 2010; pp. 26–33.
- Wang, F.; Kang, M.Z.; Lu, Q.; Letort, V.; Han, H.; Guo, Y.; de Reffye, P.; Li, B.G. A stochastic model of tree architecture and biomass partitioning: Application to Mongolian Scots pines. Ann. Bot. 2011, 107, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura, V.; Cilas, C.; Laurens, F.; Costes, E. Dissecting apple tree architecture into genetic, ontogenetic and environmental effects: Mixed linear modelling of repeated spatial and temporal measures. New Phytol. 2008, 178, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, J.P.; Glas, C.A.W. Bayesian estimation of a multilevel IRT model using Gibbs sampling. Psychometrika 2001, 66, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cam, E.; Link, W.; Cooch, E.; Monnat, J.; Danchin, E. Individual covariation in life-history traits: Seeing the trees despite the forest. Am. Nat. 2002, 159, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.S.; LaDeau, S.; Ibanez, I. Fecundity of trees and the colonizationcompetition hypothesis. Ecol. Monogr. 2004, 74, 415–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.K.; Law, R.; Illian, J.B. Quantification of neighborhood-dependent plant growth by Bayesian hierarchical modelling. J. Ecol. 2006, 94, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstrom, M.J.; Bates, D.M. Nonlinear mixed effects models for repeated measures data. Biometrics 1990, 4, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.B.; Bailey, R.L. Modeling and prediction of forest growth variables based on multilevel nonlinear mixed models. For. Sci. 2001, 47, 311–321. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Lei, X.D.; Cournede, P.; Letort, V. Characterization of the effects of inter-tree competition on source-sink balance in Chinese pine trees with the GreenLab model. Trees Struct. Funct. 2012, 26, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reffye, P.; Blaise, F.; Chemouny, S.; Jaffuel, S.; Fourcaud, T.; Houllier, F. Calibration of a hydraulic architecture-based growth model of cotton plants. Agronomie 1999, 19, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.H.; Guo, Y.; de Reffye, P.H. Plant morphological constructing based on organ biomass accumulation. Acta Entomol. 2003, 23, 2579–2586. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Z.G. Study on a structure-function model of plant growth and its calibration. Ph.D. Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, 2001; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, J.C.; Bates, D.M. Mixed-Effects Models in s and s-Plus; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nothdurft, A.; Kublin, E.; Lappi, J. A non-linear hierarchical mixed model to describe tree height growth. Eur. J. For. Res. 2006, 125, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorado, F.C.; Ulises, D.A.; Diéguez-Aranda, U.; Marcos, B.A.; Anta, M.B.; Rodríguez, M.S.; von Gadow, K. A generalized height-diameter model including random components for radiata pine plantations in northwestern Spain. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 229, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. ISBN 3-900051-07-0. Available online: http://www.r-project.org (accessed on 13 October 2013).
- Chambers, J.Q.; Dos Santos, J.; Ribeiro, R.J.; Higuchi, N. Tree damage, allometric relationships, and aboveground net primary production in central Amazon forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2001, 152, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, G.B.; Brown, J.H.; Enquist, B.J. A general model for the origin of allometric scaling laws in biology. Science 1997, 276, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooijman, S.A.L.M. Dynamic Energy and Mass Budgets in Biological Systems, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: England, Cambridge, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski, J.; Konarzewski, M. Is West, Brown and Enquist’s model of allometric scaling mathematically correct and biologically relevant? Funct. Ecol. 2004, 18, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, J.; Konarzewski, M. West, Brown and Enquist’s model of allometric scaling again: The same questions remain. Funct. Ecol. 2005, 19, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; West, G.; Enquist, B. Yes, West, Brown and Enquist’s model of allometric scaling is both mathematically correct and biologically relevant. Funct. Ecol. 2005, 19, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller-Landau, H.C.; Condit, R.S.; Chave, J.; Thomas, S.C.; Bohlman, S.A.; Bunyavejchewin, S.; Davies, S.; Foster, R.; Gunatilleke, S.; Gunatilleke, N.; Harms, K.E.; et al. Testing metabolic ecology theory for allometric scaling of tree size, growth and mortality in tropical forests. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C.A.; Gilooly, J.F.; Allen, A.P.; Weitz, J.S.; Niklas, K.J. The metabolic theory of ecology: Prospects and challenges for plant biology. New Phytol. 2010, 188, 696–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C.A.; Weitz, J.S.; Savage, V.M.; Stegen, J.; Clarke, A.; Coomes, D.A.; Dodds, P.S.; Etienne, R.S.; Kerkhoff, A.J.; McCulloh, K.; Niklas, K.J.; Olff, H.; Swenson, N.G. Testing the metabolic theory of ecology. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Fang, J.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, B. Climatic control of primary forest structure and DBH-height allometry in Northeast China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 234, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, S.; Spiecker, H. Crown and tree allometry of open-grown ash (Fraxinus excelsior L.) and sycamore (Acer pseudoplatanus L.). Agrofor. Syst. 2008, 73, 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- Puntieri, J.G.; Ghirardi, S. Growth-unit structure in trees: Effects of branch category and position in Nothofagus nervosa, N. obliqua and their hybrids (Nothofagaceae). Trees Struct. Funct. 2010, 24, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, H.A.L.; Aarssen, L.W. The interpretation of stem diameter-height allometry in trees: Biomechanical constraints, neighbour effects, or biased regressions? Ecol. Lett. 1999, 2, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieilledent, G.; Courbaud, B.; Kunstler, G.; Dhôte, J.F.; Clark, J.S. Individual variability in tree allometries determines light resource allocation in forest ecosystems: A hierarchical Bayesian approach. Oecologia 2010, 163, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, M.Z.; Cournède, P.H.; de Reffye, P.; Hu, B.G. Analytic study of a stochastic plant growth model: Application to the GreenLab model. Math. Comput. Simul. 2008, 78, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, A.; Cournède, P.H.; Letort, V.; Barthélémy, D.; de Reffye, P. A dynamic model of plant growth with interactions between development and functional mechanisms to study plant structural plasticity related to trophic competition. Ann. Bot. 2009, 103, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Reffye, P.; Kang, M.Z.; Hua, J.; Auclair, D. Stochastic modelling of tree annual shoot dynamics. Ann. For. Sci. 2012, 69, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.T.; Li, B.G.; Zhan, Z.G.; Guo, Y.; Luquet, D.; de Reffye, P.; Dingkuhn, M. Parameter stability of the functional-structural plant model GREENLAB as affected by variation within populations, among seasons and among growth stages. Ann. Bot. 2007, 99, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, J.; de Reffye, P.; Lei, X.D.; Guo, H.; Letort, V. Simulation of the topological development of young eucalyptus using a stochastic model and sampling measurement strategy. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2012, 80, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diao, J.; Lei, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Guo, H.; Fu, L.; Shen, C.; Ma, W.; Shen, J. Quantifying the Variability of Internode Allometry within and between Trees for Pinus tabulaeformis Carr. Using a Multilevel Nonlinear Mixed-Effect Model. Forests 2014, 5, 2825-2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/f5112825
Diao J, Lei X, Wang J, Lu J, Guo H, Fu L, Shen C, Ma W, Shen J. Quantifying the Variability of Internode Allometry within and between Trees for Pinus tabulaeformis Carr. Using a Multilevel Nonlinear Mixed-Effect Model. Forests. 2014; 5(11):2825-2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/f5112825
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiao, Jun, Xiangdong Lei, Jingcai Wang, Jun Lu, Hong Guo, Liyong Fu, Chenchen Shen, Wu Ma, and Jianbo Shen. 2014. "Quantifying the Variability of Internode Allometry within and between Trees for Pinus tabulaeformis Carr. Using a Multilevel Nonlinear Mixed-Effect Model" Forests 5, no. 11: 2825-2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/f5112825





