Development of Biomimetic NiTi Alloy: Influence of Thermo-Chemical Treatment on the Physical, Mechanical and Biological Behavior
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Experimental Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melton, K.N.; Mercier, O. The mechanical properties of NiTi-based shape memory alloys. Acta Metall. Mater. 1981, 29, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrini, L.; Migliavacca, F. Biomedical Applications of Shape Memory Alloys. J. Metall. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shape Memory Alloys for Biomedical Applications; Yoneyama, T.; Miyazaki, S. (Eds.) Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2009.
- Huang, H.H.; Chiu, H.Y.; Lee, H.T.; Wu, S.C.; Yang, H.W.; Su, K.H.; Hsu, C.C. Ion Release from NiTi Orthodontic Wires in Artificial Saliva with Various Acidities. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3585–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Y.; Bao, X.; Huang, Y.; Qu, Y.H.; Lu, H.Q.; Lu, Z.H. Mechanisms of cytotoxicity of nickel ions based on gene expression profiles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger-Gorbet, M.; Broxup, B.; Rivard, C.; Yahia, L.H. Biocompatibility testing of Ni–Ti screw using immuno histochemistry on sections containing metallic implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1996, 32, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Wu, S.L.; Chan, Y.L.; Chu, P.K.; Chung, C.Y. Surface characteristics, biocompatibility, and mechanical properties of nickel-titanium plasma-implanted with nitrogen at different implantation voltages. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 82A, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, K.W.K.; Poon, R.W.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Ho, J.P.Y. Corrosion resistance, surface mechanical properties, and cytocompatibility of plasma immersion ion implantation–treated nickel-titanium shape memory alloys. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2005, 75A, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uo, M.; Watari, F.; Yokoyama, A. Hironobu Matsuno. Tissue reaction around metal implants observed by X-ray scanning analytical microscopy. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, V.; Khalil-Allafi, J.; Maleki-Ghaleh, H. Characterisation of HA–Si composite coatings on NiTi for biomedical applications. Surf. Eng. 2014, 30, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katic, J.; Metikoš-Hukovic, M.; Babic, R.; Marciuš, M. Sol-gel Derived Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Ceramics on Nitinol for Medical Applications. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 1394–1408. [Google Scholar]
- Surmenev, R.A.; Ryabtseva, M.A.; Shesterikov, E.V.; Pichugin, V.F.; Peitsch, T.; Epple, M. The release of nickel from nickel–titanium (NiTi) is strongly reduced by a sub-micrometer thin layer of calcium phosphate deposited by rf-magnetron sputtering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Heredia, M.A.; Sohier, J.; Gaillard, C.; Quillard, S.; Dorget, M.; Layrolle, P. Rapid prototyped porous titanium coated with calcium phosphate as a scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2608–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweh, S.W.K.; Khor, K.A.; Cheang, P. An in vitro investigation of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite (HA) coatings produced with flame-spheroidized feedstock. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Chu, P.K.; Ding, C.X. Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2004, 47, 49–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediaswanti, K.; Wen, C.; Ivanova, E.P.; Berndt, C.C.; Wang, J. Chapter 2: Sputtered Hydroxyapatite Nanocoatings on Novel Titanium Alloys for Biomedical Applications. In Titanium Alloys-Advances in Properties Control; Sieniawski, J., Ziaja, W., Eds.; InTechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kokubo, T.; Mijyaji, F.; Kim, H.M. Spontaneous formation of bonelike apatite layer on chemically treated titanium metals. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1996, 79, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.W.; Tay, B.Y.; Lim, C.S.; Yong, M.S. Biomimetic deposition of apatite coating on surface-modified NiTi alloy. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6916–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.F.; Yang, X.J.; Hu, R.X.; Cui, Z.D.; Man, H.C. Bioactive NiTi shape memory alloy used as bone bonding implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2004, 24, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiardi, A.; Aparicio, C.; Planell, J.A.; Gil, F.J. New Oxidation Treatment of NiTi Shape Memory Alloys to Obtain Ni-Free Surfaces and to Improve Biocompatibility. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 77, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokubo, T.; Kim, H.-M.; Kawashita, M. Novel bioactive materials with different mechanical properties. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2161–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.W.; Tay, B.Y.; Lim, C.S.; Yong, M.S. Characterization of bioactive surface oxidation layer on NiTi alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 252, 2038–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firstov, G.S.; Vitchev, R.G.; Kumar, H.; Blanpain, B.; van Humbeeck, J. Surface oxidation of NiTi shape memory alloy. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4863–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, J.; Balamurugan, A.; Benhayoune, H.; Torres, P.; Balossier, G.; Ferreira, J.M.F. Morphological and chemical characterisation of biomimetic bone like apatite formation on alkali treated Ti6Al4V titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 29, 1252–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L.; Müller, F.A. Preparation of SBF with different HCO3− content and its influence on the composition of biomimetic apatites. Acta Biomater. 2006, 2, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohl, M.; Glogowski, T.; Kuhn, S.; Hessing, C.; Unterumsberger, F. Formation of titanium oxide coatings on NiTi shape memory alloys by selective oxidation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 481–482, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.L.; Chung, C.Y.; Chu, P.K. Surface oxidation of NiTi shape memory alloy in a boiling aqueous solution containing hydrogen peroxide. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 417, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.M.; Trigwell, S.; Duerig, T. Oxidation of a NiTi alloy. Surf. Interface Anal. 1990, 15, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, D.A.; Grant, D.M. Characterisation of surface-modified nickel titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 349, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigwell, S.; Hayden, R.D.; Nelson, K.F. Effects of surface treatment on the surface chemistry of NiTi alloy for biomedical applications. Surf. Interface Anal. 1998, 26, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.M.; Grant, D.M.; Wood, J.V. XPS characterisation of surface modified Ni-Ti shape memory alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1997, 224, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinós, J.P.; Fernández, A.; González-Elipe, A.R. Oxidation and diffusion process in NiTi oxide systems. Surf. Sci. 1993, 295, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Uchid, M.; Kim, H.M.; Kokubo, T.; Nakamura, T. Apatite-forming ability of CaO-containing titaniam. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T.; Kushitani, H.; Sakka, S.; Kitsugi, T.; Yamamuro, T. Solutions able to reproduce in vivo surface-structure changes in bioactive glass-ceramic A-W. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1990, 24, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiguci, Y. Medical Applications in Shape Memory Alloys; Funakubo, H., Ed.; Gordon and Breach Science Publishers: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1984; pp. 10–23. [Google Scholar]
- Suárez, C.; Vilar, T.; Gil, F.J.; Sevilla, P. In vitro evaluation of surface topographic changes and nickel release of lingual orthodontic archwires. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arciniegas, M.; Gaillard, Y.; Peña, J.; Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J. Thermoelastic phase transformation in TiNi alloys under cyclic instrumented indentation. Intermetallics 2009, 17, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.J.; Cenizo, M.; Espinar, E.; Rodriguez, A.; Rúperez, E.; Manero, J.M. NiTi superelastic orthodontic wires with variable stress obtained by ageing treatments. Mater. Lett. 2013, 104, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederbrant, K.; Anderson, C.; Andersson, T.; Marcusson-Ståhl, M.; Hultman, P. Cytokine Production, Lymphocyte Proliferation and T-Cell Receptor Vβ Expression in Primary Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Cultures from Nickel-Allergic Individuals. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2003, 132, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, F.; Mogi, M.; Ohura, Y.; Hamanaka, H. The super-elastic property of the Japanese NiTi alloy wire for use in orthodontics. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1986, 90, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Cui, L. A transforming metal nanocomposite with large elàstic strain, low modulus and high strength. Science 2013, 339, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
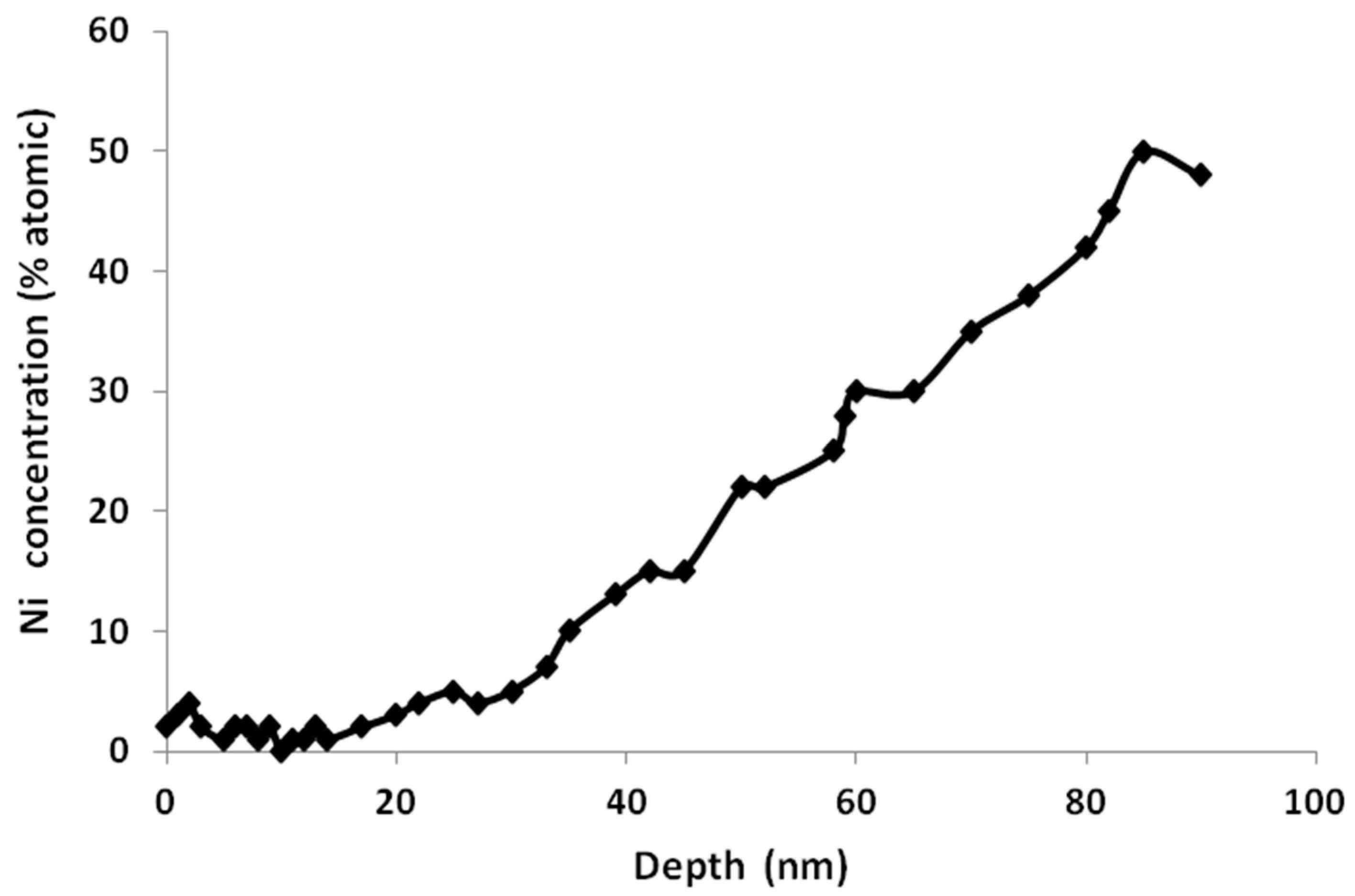
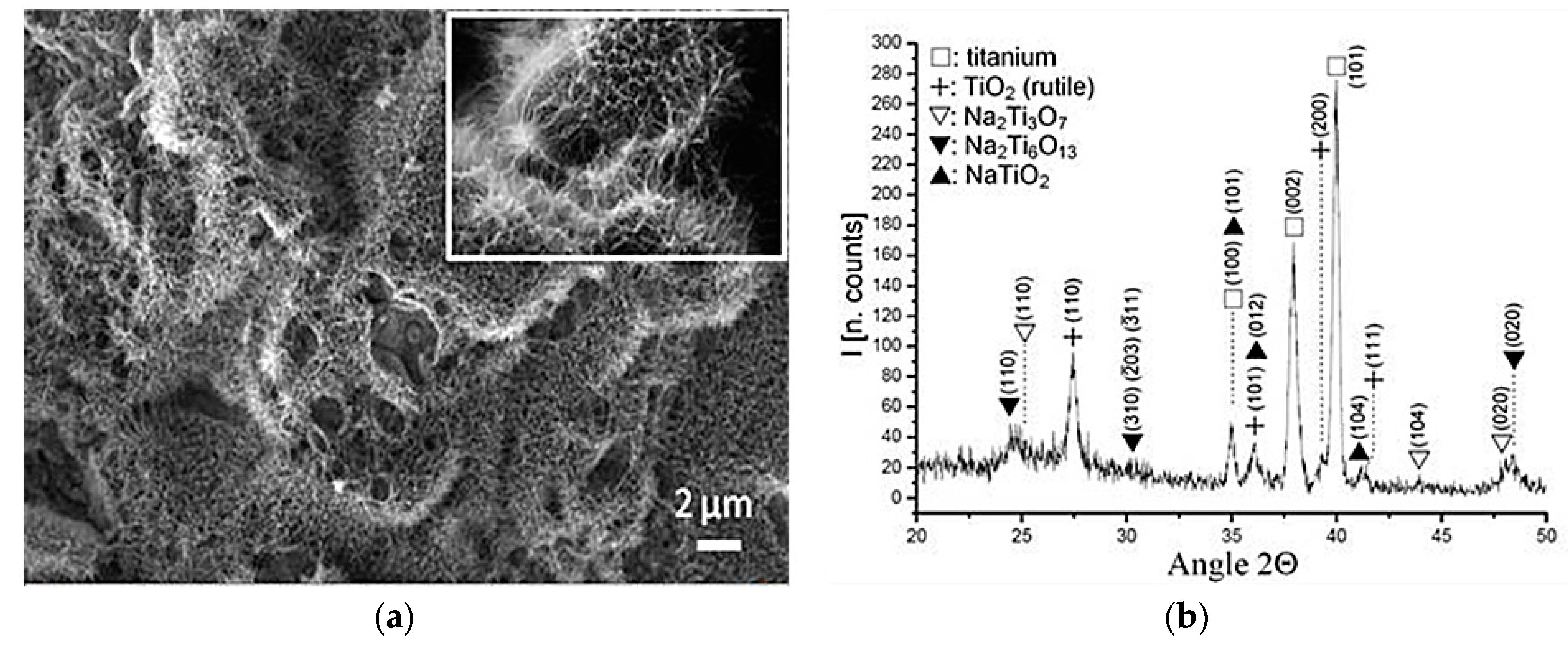
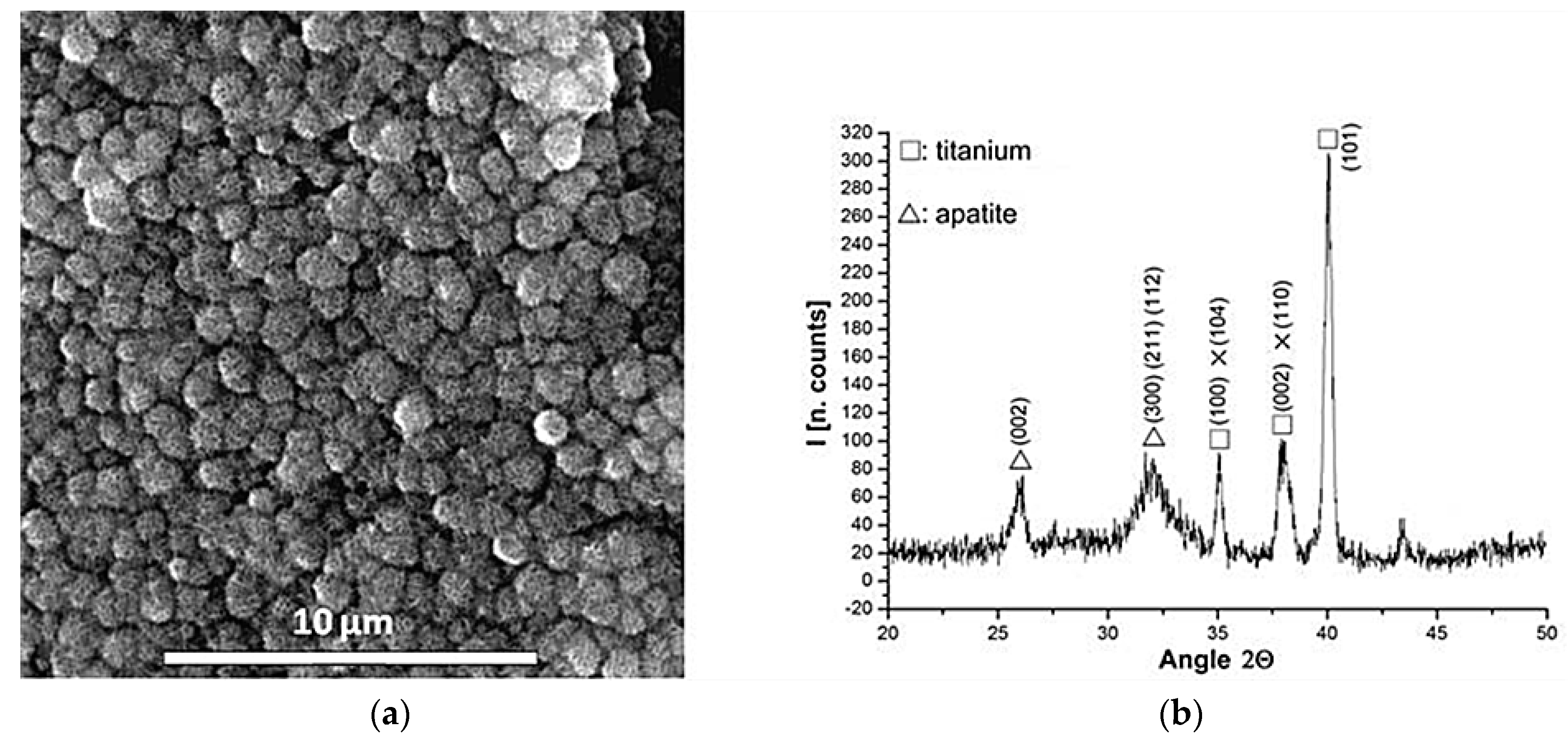

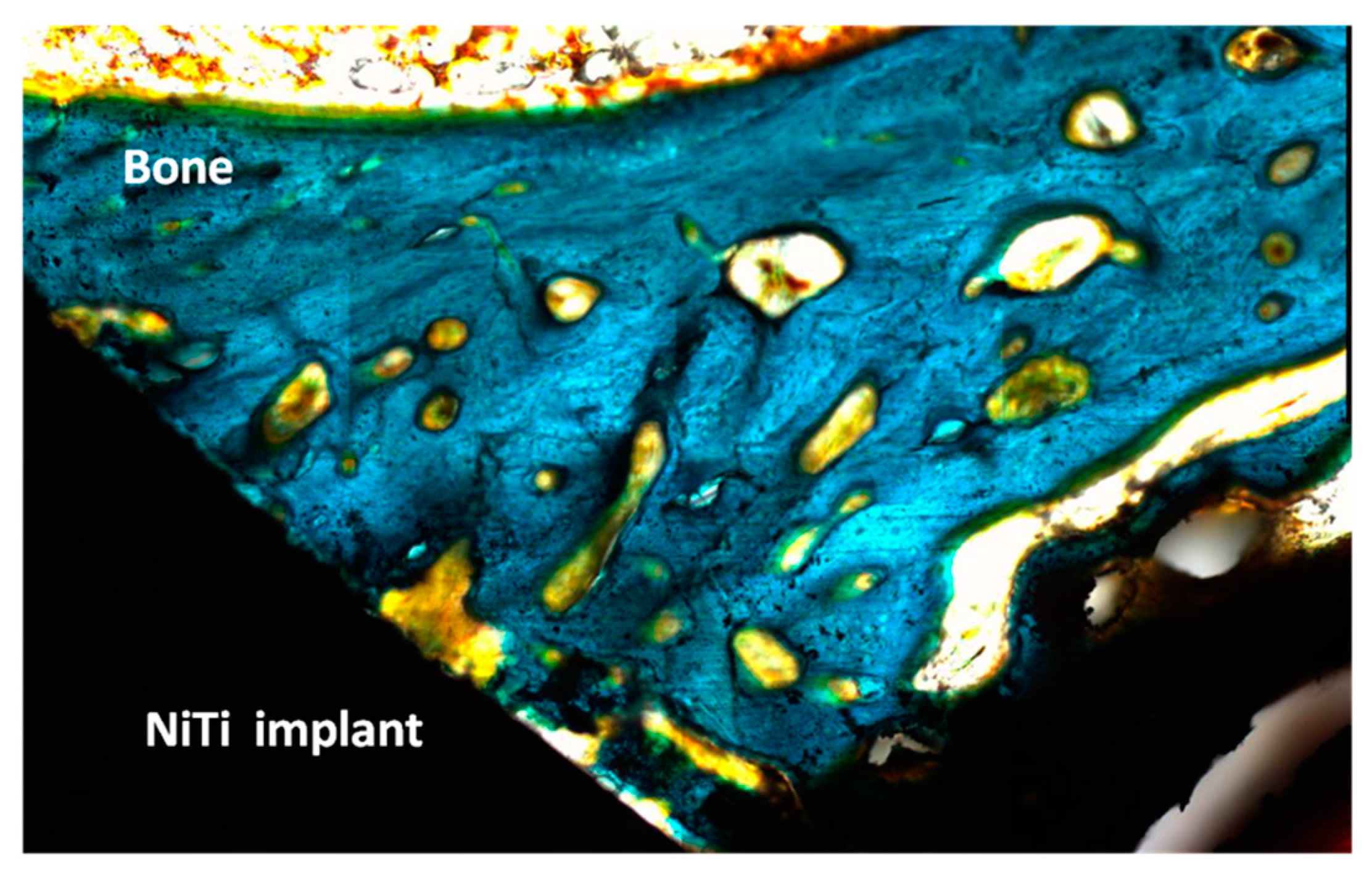
| Treatment | Sputtering Time (min)/Depth (nm) | Chemical Element | % of total Ti 2p Signal |
|---|---|---|---|
| UT | 0/0 | Ti0 Ti+2, Ti+3/Ti+4 | 8/10/82 |
| OT | 0/0 | Ti+4 | 100 |
| OT | 1/6 | Ti3+ Ti4+ | 61/39 |
| Type of Implants | 1 Week | 6 Weeks |
|---|---|---|
| NiTi | 9% (±4%) | 44% (±11%) |
| NiTi bioactive | 27% (±5%) | 68% (±15%) |
| Alloy | Ms | Mf | As | Af |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 74.1 ± 0.3 | 55.7 ± 0.4 | 86.9 ± 0.1 | 129.3 ± 0.7 |
| M-bioactive | 64.2 ± 0.6 | 46.1 ± 0.5 | 71.0 ± 0.1 | 109.3 ± 0.7 |
| A | 9.8 ± 0.2 | 6.2 ± 0.3 | 7.1 ± 0.4 | 20.4 ± 0.5 |
| A-bioactive | 0.5 ± 2.4 | −3.9 ± 1.2 | −0.4 ± 1.7 | 11.2 ± 4.5 |
| Autenitic NiTi Alloy | Critical Stresses | 20 °C | 37 °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiTi original | σβ→SIM (MPa) | 150 ± 17 | 262 ± 24 |
| σSIM→β (MPa) | 55 ± 5 | 211 ± 19 | |
| NiTi bioactive | σβ→SIM (MPa) | 180 ± 15 | 290 ± 22 |
| σSIM→β (MPa) | 65 ± 9 | 183 ± 19 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rupérez, E.; Manero, J.M.; Bravo-González, L.-A.; Espinar, E.; Gil, F.J. Development of Biomimetic NiTi Alloy: Influence of Thermo-Chemical Treatment on the Physical, Mechanical and Biological Behavior. Materials 2016, 9, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9060402
Rupérez E, Manero JM, Bravo-González L-A, Espinar E, Gil FJ. Development of Biomimetic NiTi Alloy: Influence of Thermo-Chemical Treatment on the Physical, Mechanical and Biological Behavior. Materials. 2016; 9(6):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9060402
Chicago/Turabian StyleRupérez, Elisa, José María Manero, Luis-Alberto Bravo-González, Eduardo Espinar, and F.J. Gil. 2016. "Development of Biomimetic NiTi Alloy: Influence of Thermo-Chemical Treatment on the Physical, Mechanical and Biological Behavior" Materials 9, no. 6: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9060402
APA StyleRupérez, E., Manero, J. M., Bravo-González, L.-A., Espinar, E., & Gil, F. J. (2016). Development of Biomimetic NiTi Alloy: Influence of Thermo-Chemical Treatment on the Physical, Mechanical and Biological Behavior. Materials, 9(6), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9060402








