Efficacy of Bacterial Cellulose as a Carrier of BMP-2 for Bone Regeneration in a Rabbit Frontal Sinus Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
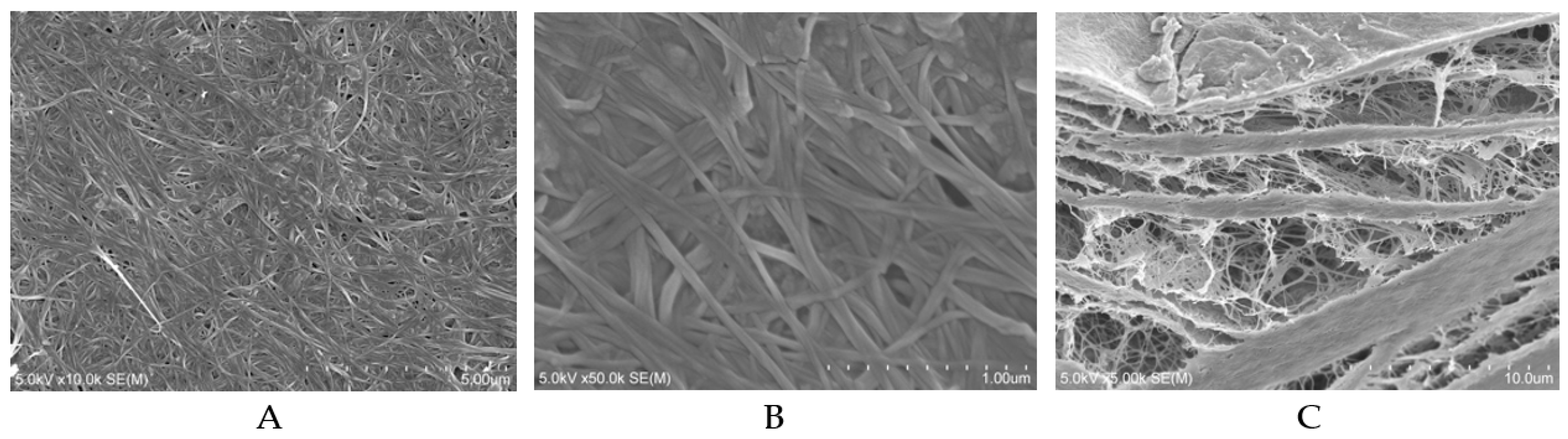
2.1.1. BC Sheets
2.1.2. BMP-2
2.1.3. BC+BMP-2 Composite
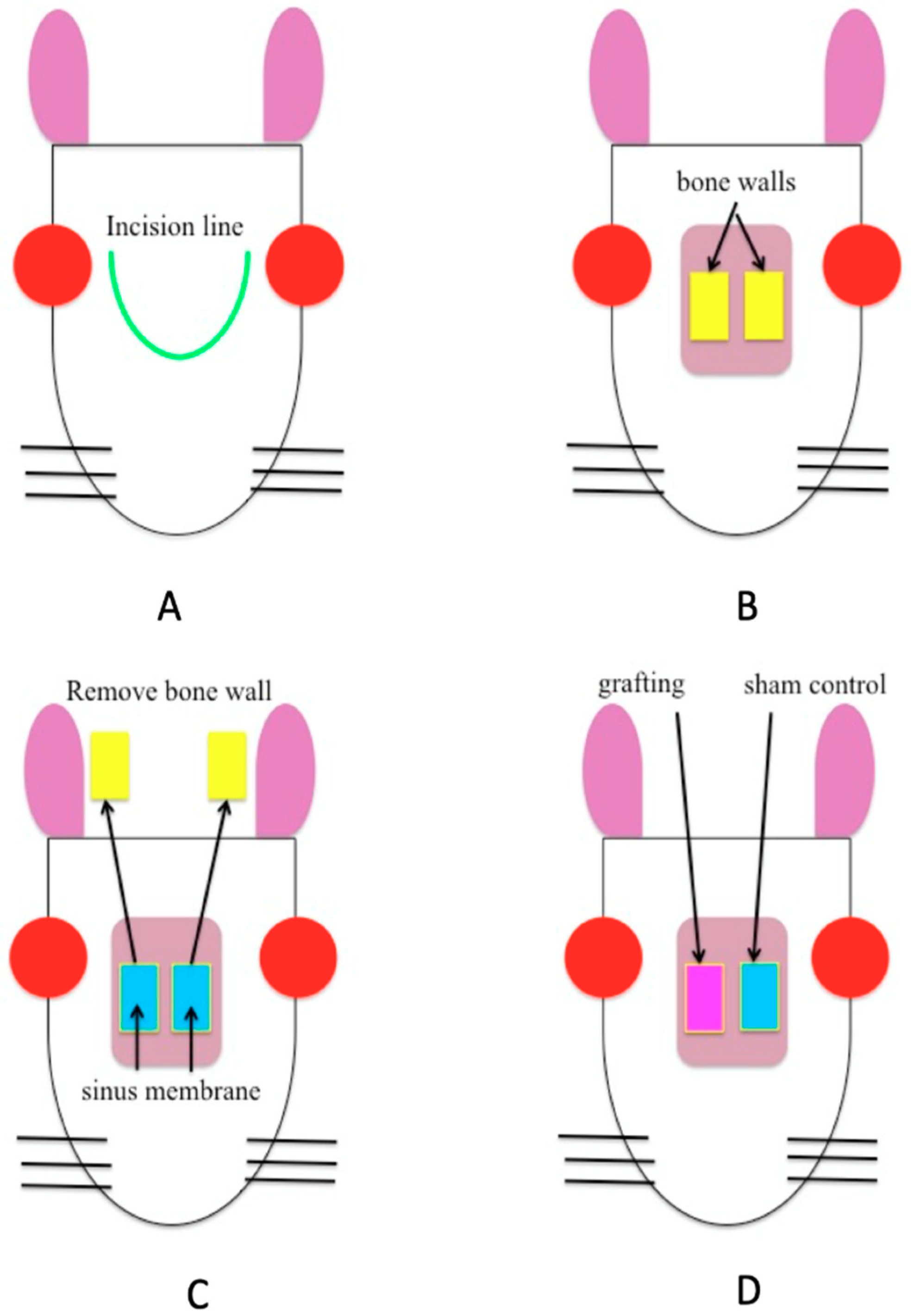
2.2. Experimental Method
2.3. Hematoxylin–Eosin (H and E) Staining
2.4. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.5. Histomorphometric Examination
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. H and E Staining Evaluation
3.1.1. Histomorphology
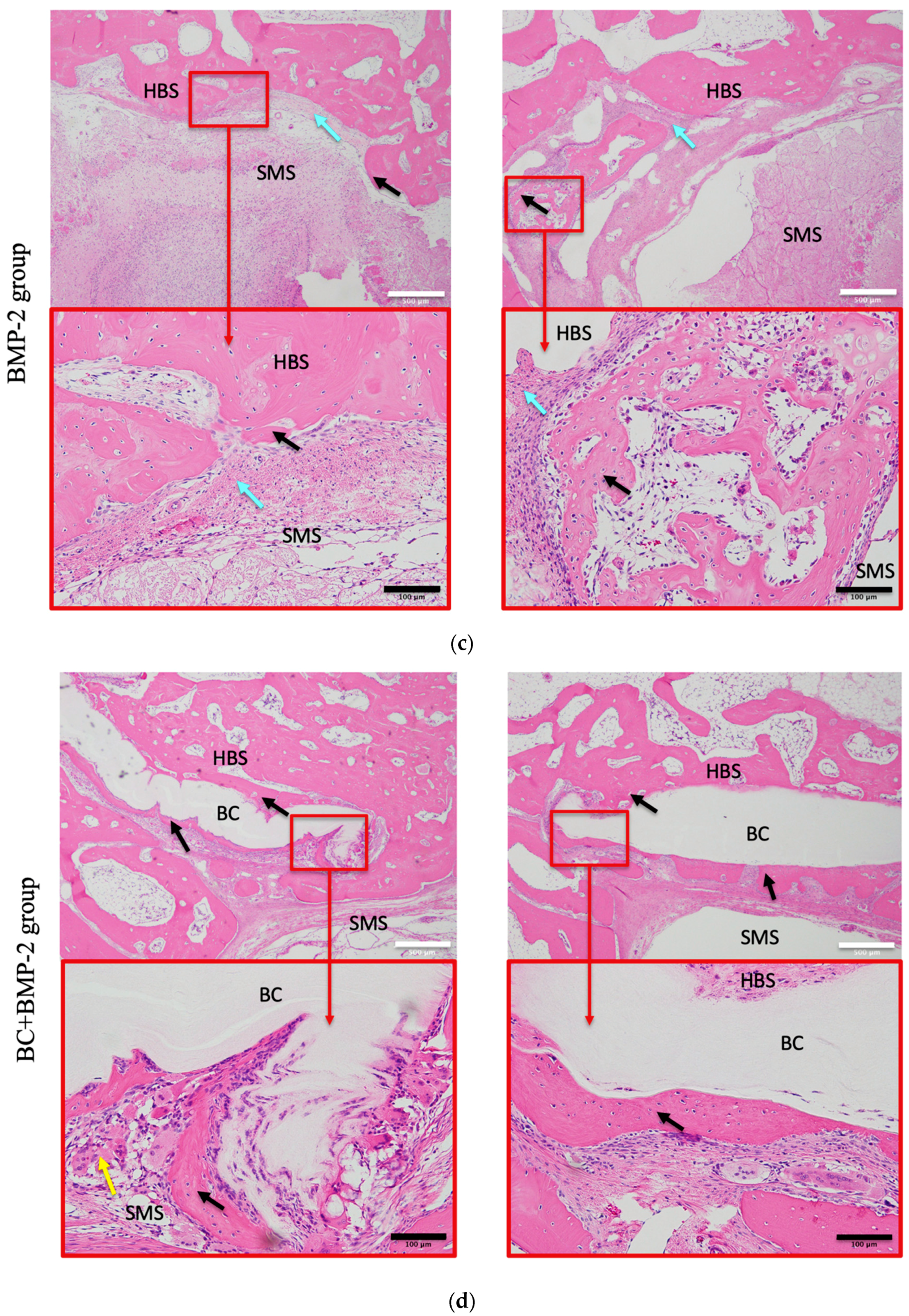
3.1.2. H and E Staining of Newly Formed Bone
3.2. Immunohistochemical Evaluation
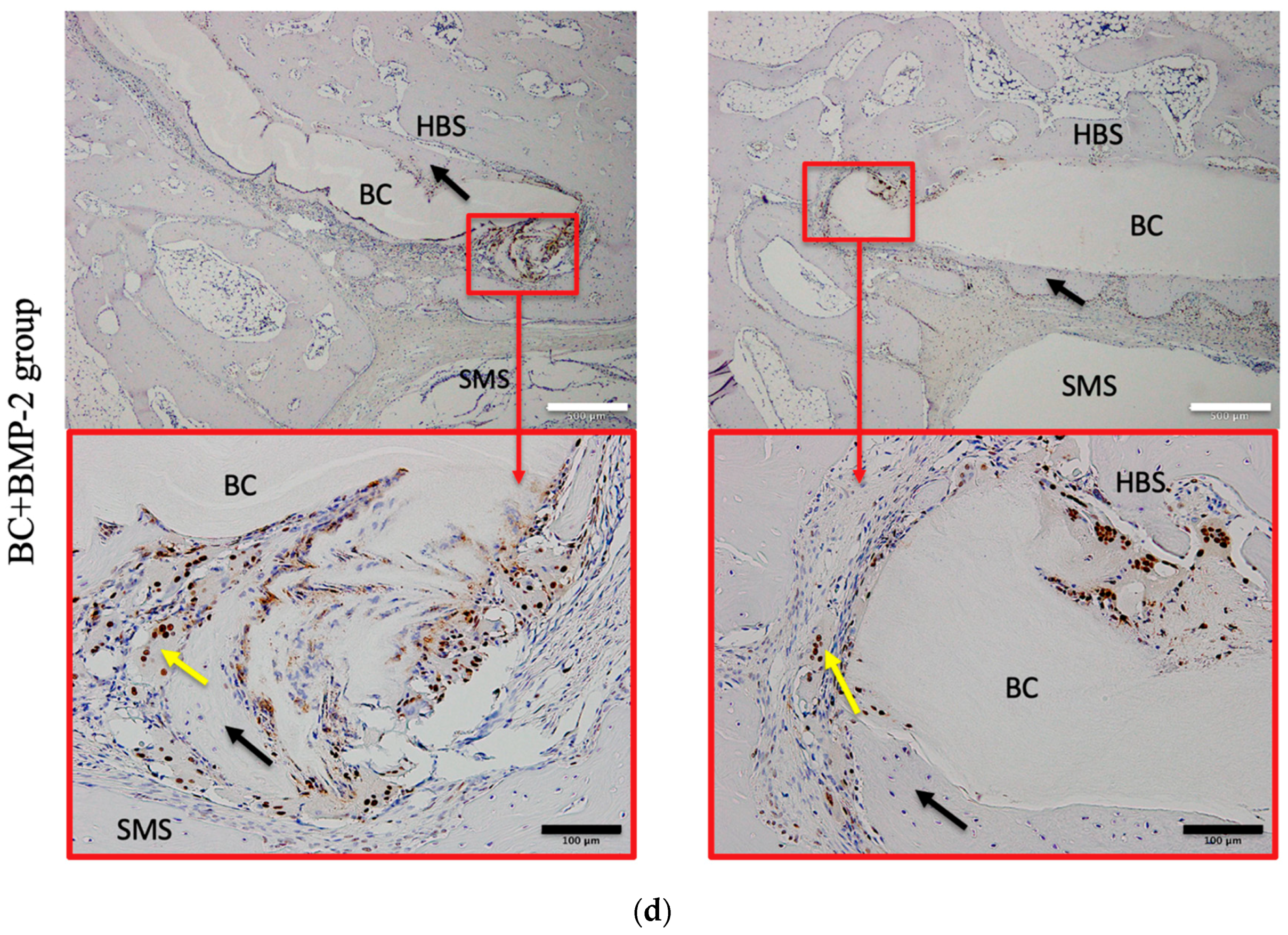
3.2.1. PCNA
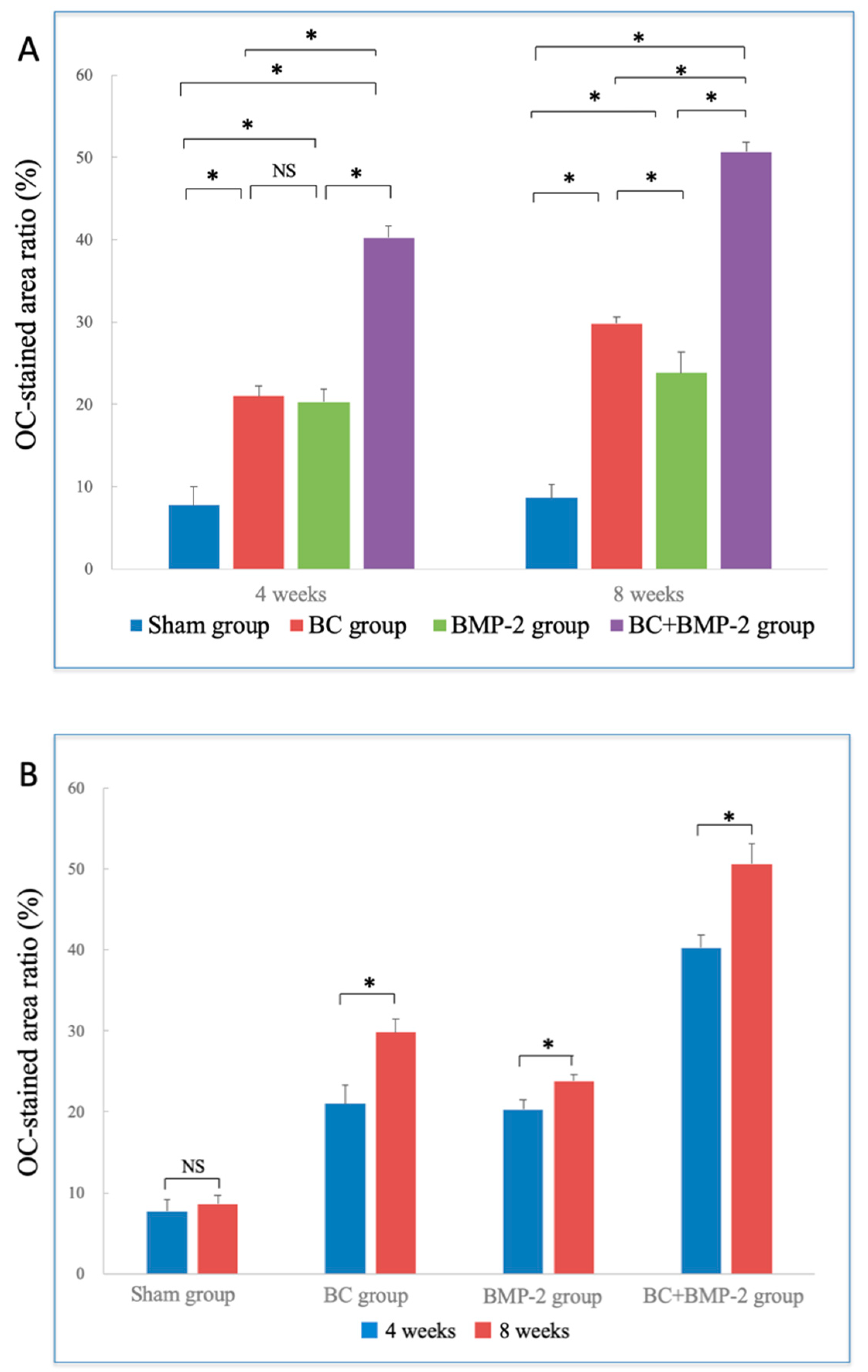
3.2.2. OC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sugai, T. Maxillary sinus floor elevation: lateral approach and alveolar crest approach. Jpn. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 56, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marukawa, K.; Ueki, K.; Okabe, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Yamamoto, E. Use of self-setting α-tricalcium phosphate for maxillary sinus augmentation in rabbit. Clin. Oral. Impl. Res. 2011, 22, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, Y.; Hokugo, A.; Morita, S. Experimental study of sinus augmentation by controlled release of basic fibroblast growth factor. J. Jpn. Asso. Regenerative. Dentistry. 2008, 5, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, F.; Leonard, A.; Drion, P.; Sourice, S.; Layrolle, P.; Rompen, E. Influence of space-filling materials in subantral bone augmentation: blood clot vs. autogenous bone chips vs. bovine hydroxyapatite. Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 2011, 22, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakir, M.; Karaca, I.R.; Firat, A.; Kaymaz, F.; Bozkaya, S. Experimental evaluation of the effects of ankaferd blood stopper and collagenated heterologous bone graft on bone healing in sinus floor augumentation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants. 2015, 30, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, M.D.; Nunes, L.S.; Oliveira, R.V.; Holgado, L.A.; Filho, H.N.; Matsumoto, M.A.; Ribeiro, D.A. Bovine hydroxyapatite (Bio-OssR) induces osteocalcin, RANK-L and osteoprotegerin expression in sinus lift of rabbits. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2012, 40, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.C.; Zhang, M.L.; Lee, J.S.; Jung, U.W.; Choi, S.H. Effect of different hydroxyapatite: β-tricalcium phosphate ratios on the osteoconductivity of biphasic calcium phosphate in the rabbit sinus model. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants. 2015, 30, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitajo, H.; Maida, T.; Murata, M.; Akazawa, T.; Tazaki, J. BMP-2 release characteristics and osteoinduction of calcium phosphate ceramics improved by partial dissolution-precipitation treatment. J. Jpn. Soc. Oral implant 2013, 26, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, Y.; Izumi, N.; Yoshizawa, M.; Saito, C. Histological study of bone formation associated with the implantation of bone marrow cells/porous beta-TCP block composites. Jpn. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 53, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jimi, E.; Hirata, S.; Fukushima, H. Basic approaches for bone regeneration. J. Kyushu. Dent. Soc. 2010, 64, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T.; Sato, J.; Kato, M.; Kanazashi, M. Autologous cultured bone-marrow cell transplantation using an atherocollagen carrier for parietal bone defects in rabbits. Tsurumi. Univ. Dent. J. 2008, 34, 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kawana, H.; Mori, T.; Kimura, A.; Nakagawa, T.; Asanami, S. Histologic and histomorphometric analysis of β-tricalcium phosphate block as a material of paranasal sinus augmentation in rabbits. J. Bio. Integ. 2015, 5, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hashiguchi, H.; Kizu, H.; Suzuki, K.; Asanami, S. Clinical evaluation of the effectiveness of β-TCP in maxillary sinus floor elevation. J. Bio. Integ. 2013, 3, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Shimizu, Y.; Ooya, K. Histomorphometric study of the stability of newly formed bone after elevation of the floor of the maxillary sinus. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 43, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, A.; Tabuchi, M.; Uo, M.; Tatusumi, H.; Hideshima, K.; Kondo, S.; Sekine, J. Applicability of bacterial cellulose as an alternative to paper points in endodontic treatment. Acta. Biomater. 2013, 9, 6116–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Yang, L.; Jie, S.; Hua, Z.; Lei, C.; Bing, C.; Huilin, Y.; Zhaoxu, W. The osteogenesis of bacterial cellulose scaffold loaded with bone morphogenetic protein-2. Biomaterials. 2012, 33, 6644–6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lim, Y.M.; Jeong, S.I.; An, S.J.; Kang, S.S.; Jeong, C.M.; Huh, J.B. The effect of bacterial cellulose membrane compared with collagen membrane on guided bone regeneration. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2015, 7, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saska, S.; Barud, H.S.; Gasper, A.M.M.; Marchetto, R.; Ribeiro, S.J.L.; Messaddeq, Y. Bacterial Cellulose-Hydroxyapatite nanocomposites for bone regeneration. Int. J. Biomater. 2011, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picheth, G.F.; Pirich, C.L.; Sierakowski, M.R.; Woehl, M.A.; Sakakibara, C.N.; de Souza, C.F.; Martin, A.A.; da Silva, R.; de Freitas, R.A. Bacterial cellulose in biomedical applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salata, L.A.; Craig, G.T.; Devlin, A.J.; Hatton, P.V.; Brook, I.M. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of e-PTFE and alkali-cellulose membranes for guided bone regeneration. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2003, 12, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahina, I. Bone regenerative therapy using bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2011, 239, 817–821. [Google Scholar]
- Asahina, I. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins: Their History and Characteristics. J. Hard Tissue Biol. 2014, 23, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nakatani, H. Experimental study of bone regeneration using bone morphogenetic protein (BMP). Dent. J. Iwate Med. Univ. 2003, 28, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, K. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP): from basic studies to clinical approaches. Folia. Pharmacol. Jpn. 2000, 116, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy-Garcia, S.; van Driel, M.; Witte-Buoma, J.; Walles, H.; van Leeuwen, J.P.T.M.; van Osch, G.J.V.; Farrell, E. NELL-1, HMGB1, and CCN2 Enhance Migration and Vasculogenesis, But Not Osteogenic Differentiation Compared to BMP2. Tissue. Eng. Part A. 2017, 24, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Cha, J.K.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, S.H.; Cho, K.S. Increased osteoinductivity and mineralization by minimal concentration of bone morphogenetic protein-2 loaded onto biphasic calcium phosphate in a rabbit sinus. J. Periodontal. Implant. Sci. 2016, 46, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, A.J.; Freire, C.S.; Neto, C.P. Do bacterial cellulose membranes have potential in drug-delivery systems? Expert. Opin. Drug. Deliv. 2014, 11, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, K.; Matsuo, K.; Akasaki, Y.; Kanao, M.; Maeda, T.; Ishikawa, A.; Hosokawa, R. Effects of thymosinβ4 on the bone formation of calvarial defects in rats. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2013, 57, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, T.; Watanabe, T.; Satou, J. An experimental study on maxillary sinus floor elevation and simultaneous implant placement into the frontal sinus of dogs using bone substitutes. Tsurumi. Univ. Dent. J. 2008, 31, 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, F.; Leonard, A.; Drion, P.; Sourice, S.; Pilet, P.; Rompen, E. The effect of collagenated space filling materials in sinus bone augmentation: a study in rabbits. Clin. Oral. Impl. Res. 2013, 24, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T.; Yoshizawa, M.; Saito, C.; Kobayashi, T. Experimental evaluation of three-dimensional bone regeneration with combined use of a thermoplastic bioresorbable plate and beta-tricalcium phosphate grafting substitute. Jpn. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 61, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kasuya, S.; Inui, S.; Kato-Kogoe, N.; Omori, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Inoue, K.; Ito, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Hirata, A.; Ueno, T. Evaluation of guided bone regeneration using the bone substitute Bio-Oss® and a collagen membrane in a rat cranial bone defect model. J. Hard Tissue Biol. 2018, 27, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, S.; Yue, Z.; Tomita, Y.; Kondo, T.; Iwase, H.; Yamaguchi, D.; Hashimoto, T. Bacterium organizes hierarchical amorphous structure in microbial cellulose. Eur. Phys. J. E. 2008, 26, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolpak, F.J.; Weih, M.; Blackwell, J. Mercerization of cellulose: 1. Determination of the structure of Mercerized cotton. Polymer (Guildf) 1978, 19, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soykeabkaew, N.; Sian, C.; Gea, S.; Nishino, T.; Peijs, T. All-cellulose nanocomposites by surface selective dissolution of bacterial cellulose. Cellulose 2009, 16, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, J.D.; De Souza, A.M.; Fontana, C.K.; Torriani, I.L.; Moreschi, J.C.; Gallotti, B.J.; De Souza, S.J.; Narcisco, G.P.; Bichara, J.A.; Farah, L.F.X. Acetobacter cellulose pellicle as a temporary skin substitute. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1990, 24–25, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, W.; Krystynowicz, A.; Bielecki, S.; Brown, R.M. Microbial cellulose—The natural power to heal wounds. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostrom, M.P.G. Expression of bone morphogenetic proteins in fracture healing. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1998, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostrom, M.P.G.; Lane, J.M.; Berberian, W.S.; Missri, A.A.E.; Tomin, E.; Weiland, A.; Doty, S.B.; Glaser, D.; Rosen, V.M. Immunolocalization and expression of bone morphogenetic proteins 2 and 4 in fracture healing. J. Orthop. Res. 1995, 13, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddi, A.H. Role of morphogenetic proteins in skeletal tissue engineering and regeneration. Nat. Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, M.; Reddi, A.H. The application of bone morphogenetic proteins to dental tissue engineering. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, T.; Takahashi, S.-I.; Ito, H.; Inagaki, H.; Noishiki, Y. Tissue biocompatibility of cellulose and its derivatives. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1989, 23, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesundera, K.K.; Izawa, T.; Fujita, D.; Denda, Y.; Seto, E.; Sasai, H.; Kuwamura, M.; Yamate, J. Spontaneous extraskeletal osteosarcoma in arabbit (Olyctolagus cuniculus): Histopathological and Immunohistochemical findings. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 26, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Lim, P.; Yoon, H.J. The influence of cortical perforateon on guided bone regeneration using synthetic bone substitutes: A study of rabbit cranial defects. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants. 2014, 29, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Ogata, A. Expression of the osteoblastic marker in human alveolar bone cells spheroid. J. Jpn. Soc. Periodontol. 2006, 48, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maga, G.; Hubscher, U. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA): A dancer with many partners. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 3051–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovatti, E.; Freire, C.S.R.; Pinto, P.C.; Almeida, I.F.; Costa, P.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Neto, C.P.; Rosado, C. Bacterial cellulose membranes applied in topical and transdermal delivery of lidocaine hydrochloride and ibuprofen: In vitro diffusion studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 435, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.H.C.S.; Drumond, I.; Almeida, I.F.; Costa, P.; Rosado, C.F.; Neto, C.P.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D. Topical caffeine delivery using biocellulose membranes: A potential innovative system for cellulite treatment. Cellulose 2014, 21, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, X.; Nguyen, T.X.; Tang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yang, G. Nano-cellulose 3D-networks as controlled-release drug carriers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2976–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Tabuchi, M.; Morinaga, Y.; Yoshinaga, F. Structural features and properties of bacterial cellulose produced in agitated culture. Cellulose 1998, 5, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Wahid, F.; Santos, H.A.; Khan, T. Advances in biomedical and pharmaceutical applications of functional bacterial cellulose-based nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 150, 330–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, F.C.A.; Pinto, F.C.M.; Neto, C.; da Silva, S.; Leal, M.D.C.; Cesário, J.; Aguiar, J.L.D.A. Treatment of tympanic membrane perforation using bacterial cellulose: A randomized controlled trial. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 82, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biskin, S.; Damar, M.; Oktem, S.N.; Sakalli, E.; Erdem, D.; Pakir, O. A new graft material for myringoplasty: bacterial cellulose. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2016, 273, 3561–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakane, K.; Matsumoto, A.; Kawanami, M. Periodontal regeneration using rhBMP-2 in middle-aged beagles. J. Jpn. Soc. Periodontol. 2003, 45, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Sato, D.; Sasaki, T.; Taira, H.; Arisue, M. Regeneration of periodontal tissue by bone morphogenetic protein-treated DNA/atelocollagen in beagle dogs. Jpn. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2003, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koike, T.; Sha, J.; Bai, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Hideshima, K.; Yamada, T.; Kanno, T. Efficacy of Bacterial Cellulose as a Carrier of BMP-2 for Bone Regeneration in a Rabbit Frontal Sinus Model. Materials 2019, 12, 2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12152489
Koike T, Sha J, Bai Y, Matsuda Y, Hideshima K, Yamada T, Kanno T. Efficacy of Bacterial Cellulose as a Carrier of BMP-2 for Bone Regeneration in a Rabbit Frontal Sinus Model. Materials. 2019; 12(15):2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12152489
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoike, Takashi, Jingjing Sha, Yunpeng Bai, Yuhei Matsuda, Katsumi Hideshima, Takaya Yamada, and Takahiro Kanno. 2019. "Efficacy of Bacterial Cellulose as a Carrier of BMP-2 for Bone Regeneration in a Rabbit Frontal Sinus Model" Materials 12, no. 15: 2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12152489
APA StyleKoike, T., Sha, J., Bai, Y., Matsuda, Y., Hideshima, K., Yamada, T., & Kanno, T. (2019). Efficacy of Bacterial Cellulose as a Carrier of BMP-2 for Bone Regeneration in a Rabbit Frontal Sinus Model. Materials, 12(15), 2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12152489





