3.2. Sulfur Balance
Microaeration had a significant and rapid effect on the sulfur distribution in reactor, as did RSI supplementation. All sulfur species (i.e., H
2S, S
2−, HS
−, S
0, S
2O
32−, SO
42−) exist in three states: solid, liquid and gas. The mass of all relevant species were measured and are summarized in
Table 4, while
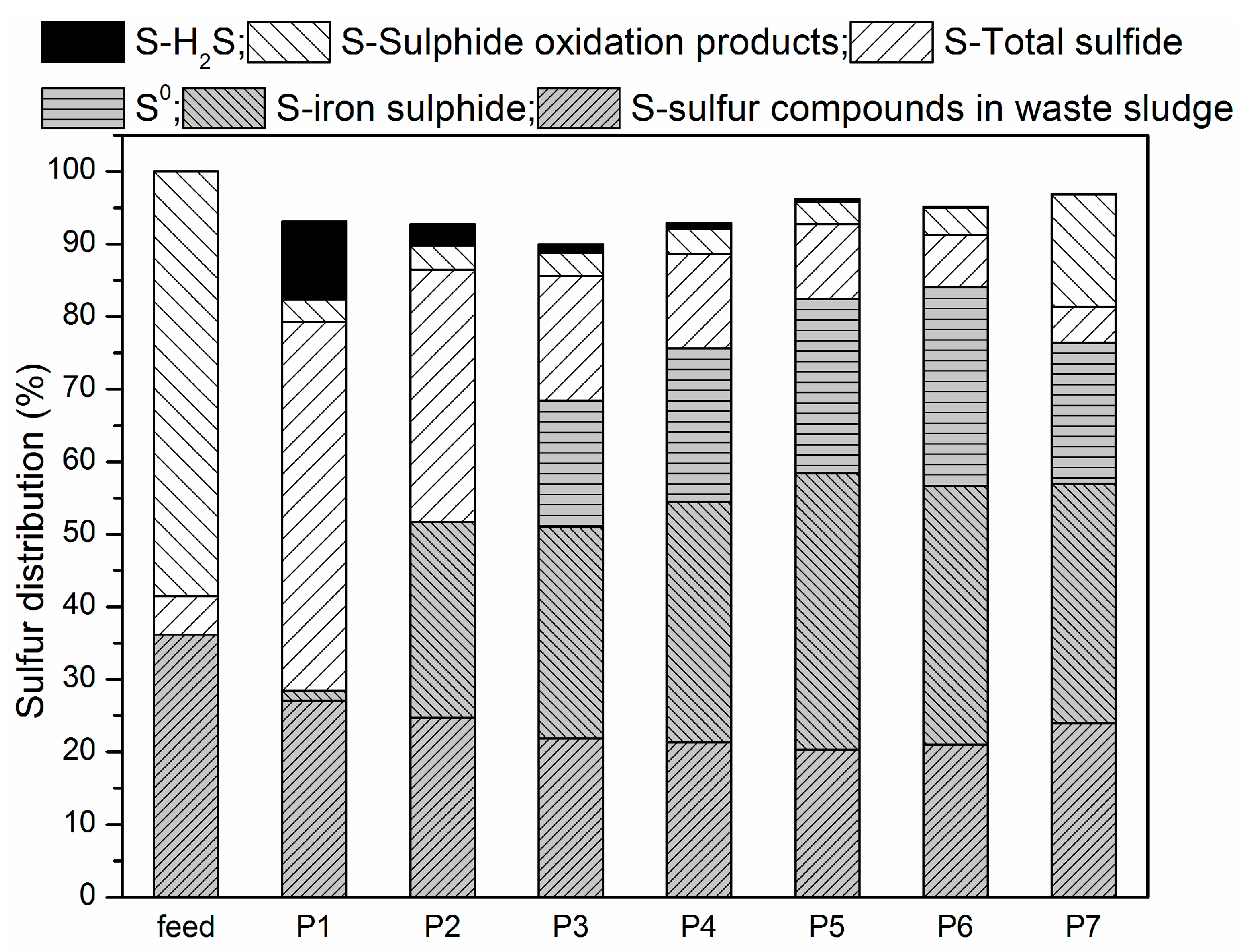
Figure 5 shows species distribution before and after the experiment.
Before anaerobic and microaerobic digestion, the sulfur species in the digester included organic sulfur-containing compounds in the waste sludge and added sulfate. The dissolved sulfur compounds obtained from the waste sludge were mainly sulfate and sulfide, while the thiosulfate were negligible. After anaerobic/microaerobic digestion, six major streams of sulfur species in the digester were identified: (1) sulfur compounds in waste sludge; (2) iron sulphide precipitation; (3) elemental sulfur S0 (deposition in the headspace of the reactors); (4) sulfide in liquid phase; (5) sulphide oxidation products (S2O32−, SO42−); and (6) sulfur in biogas (as hydrogen sulfide).
The solid form of sulphur in this system mainly consisted of sulfur compounds in waste sludge, precipitated iron sulphide and elemental sulfur S
0 (deposition in the headspace of the reactors). It can be seen that after anaerobic and microaerobic digestion, the amount of sulfur compounds in sludge decreased across all the periods, which resulted from the biological reduction of both sulfate and organic sulfur compounds by SRB. In P1, sulfur compounds in sludge decreased by 25.29%, while percent reduction of more than 40% was achieved in the later periods. Combining RSI with O
2 can enhance cell lysis, which released more organic sulfur compounds which can be reduced to sulfide by SRB [
43,
44,
45]. Only 1.44% of the sulfur dosed was present in the solid phase of the iron sulphide precipitation in P1, while over 26% was in P2 due to the addition of RSI. Starting from P3, supply of micro-oxygen promoted the generation of Fe(II) and Fe(III), which further increased the mass of iron sulphide precipitate, which ranged from 45 to 60 mg. In addition, oxygen can also directly to react with sulphide as an electron acceptor. Furthermore, sulfide was transformed into elemental sulfur through SOB activity as an electron donor. In P3 through P6, 26.94%, 32.70%, 37.24% and 42.39% of the sulfur dosed was transformed into elemental sulfur, respectively, while in P7 a 30.07% reduction was achieved. The possible reason could be that excess oxygen was supplied, leading to part of sulphide being oxidized to thiosulfate or sulphate [
46].
The dissolved forms of sulphur in this system are mainly sulfide (S
2−, HS
−, H
2S) and sulphide oxidation products (S
2O
32−, SO
42−). The sulfide detected in the liquid from P1 to P7 accounted for 50.82%, 34.81%, 17.18%, 13.02%, 10.30%, 7.25% and 4.89% of the sulfur dosed, respectively. Thus, the addition of RSI into the reactor decreased not only the concentration of hydrogen sulfide in biogas, but also the concentration of sulfide in the liquid, and combining limited amounts of O
2 with RSI achieved this more effectively. During the first six periods, only negligible amounts (stabilized at around 5 mg) of sulphide oxidation products (S
2O
32−, SO
42−), were found in the liquid. Díaz et al. [
47] discovered that sulphate was found to be easily accessible for sulphate-reducing microorganisms, while organic sulphur in the form of proteins, or cell constituents, was only partly reduced, and a large portion left the bioreactor unchanged. However in P7, the amounts of sulphide oxidation products significantly improved to 23.97 mg. Indeed, the optimum ORP for methane reducing bacteria is below −230 mV while an ORP value above −280 mV is inhibitory to sulphate reducing bacteria [
48,
49]. In P7, the reactor ORP already exceeded the value (
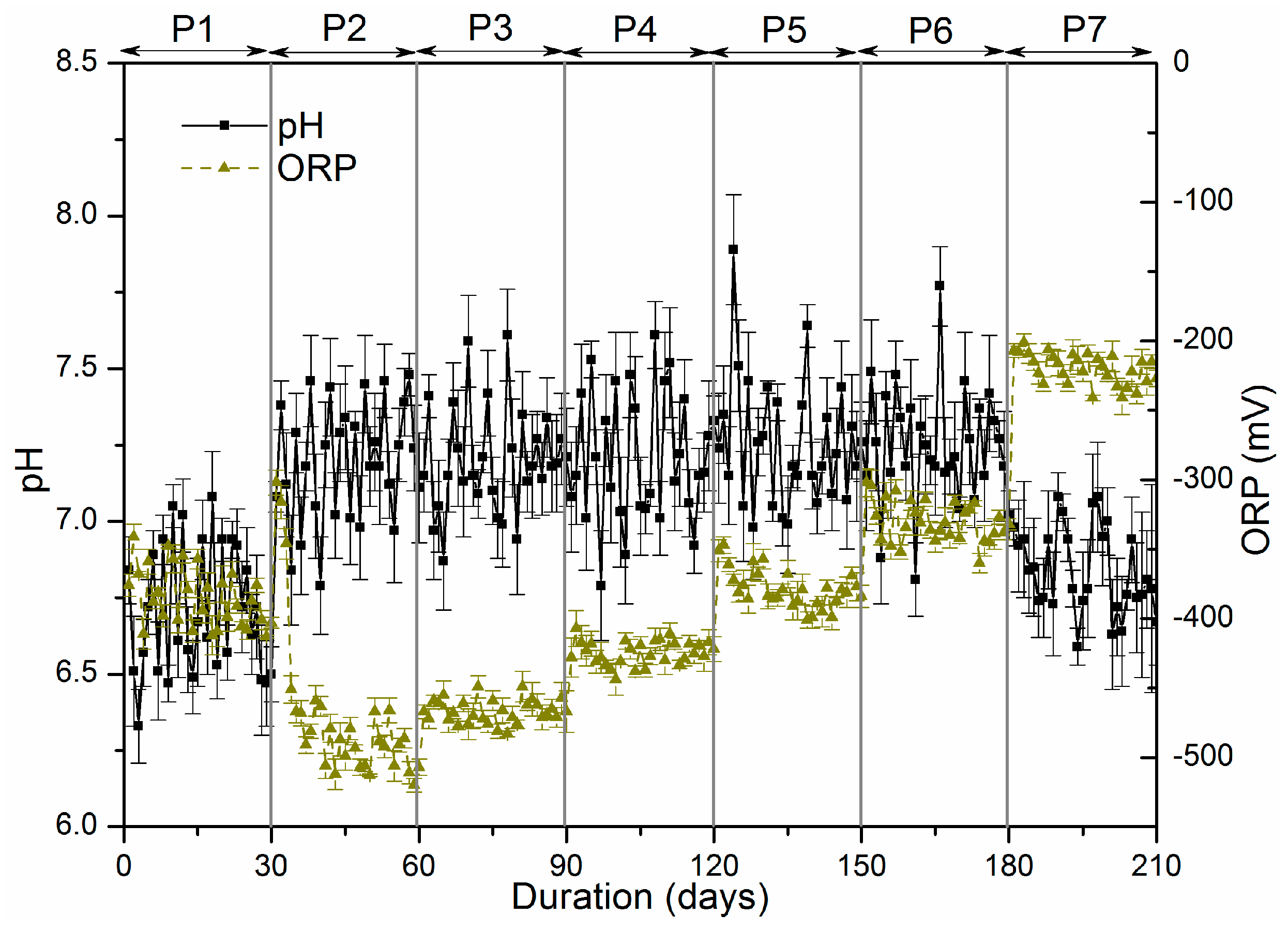
Figure 2).
The gaseous form of sulphur in this system was mainly H2S. The digester was fed with 154.69 mg/day of sulphur, 10.82% was found in biogas during P1, while only 2.99% of sulfur was detected in biogas during P2 resulting from addition of RSI (Fe2+ + S2− → FeS). Starting from P3, O2 was added into the reactor to enhance the biogas desulphurization. A fraction of O2 acting electron acceptor directly reacting with sulphides, and another fraction of O2 corroded iron producing Fe(II) and Fe(III), which then also reacted with sulphide. Of all sulphur dosed into reactor, 2.99%, 1.18%, 0.71%, 0.36%, 0.21% and 0.11% was found in biogas respectively for P3, P4, P5, P6 and P7.
The outputs of sulphur accounted for 93.12%, 92.76%, 89.95%, 92.84%, 96.21%, 95.19% and 96.93% of inputs, respectively. This ‘lost’ sulphur, comparing inputs and outputs, was not analysed in this research. There are several possible explanations for this lack of sulphur in the balance. Firstly, sulphur emission in the biogas may not be limited to H
2S but other possible S-containing gaseous forms emitted in the biogas but were not taken into account in our balance. These include dimethyl sulphide, carbon disulphide, mercaptans, etc. Secondly, total sulphur determination may have been biased by the high total dissolved sulphide content, which could have volatilized during the drying procedure before elemental analysis [
50].
3.4. DGGE Analysis of the Microbial Communities
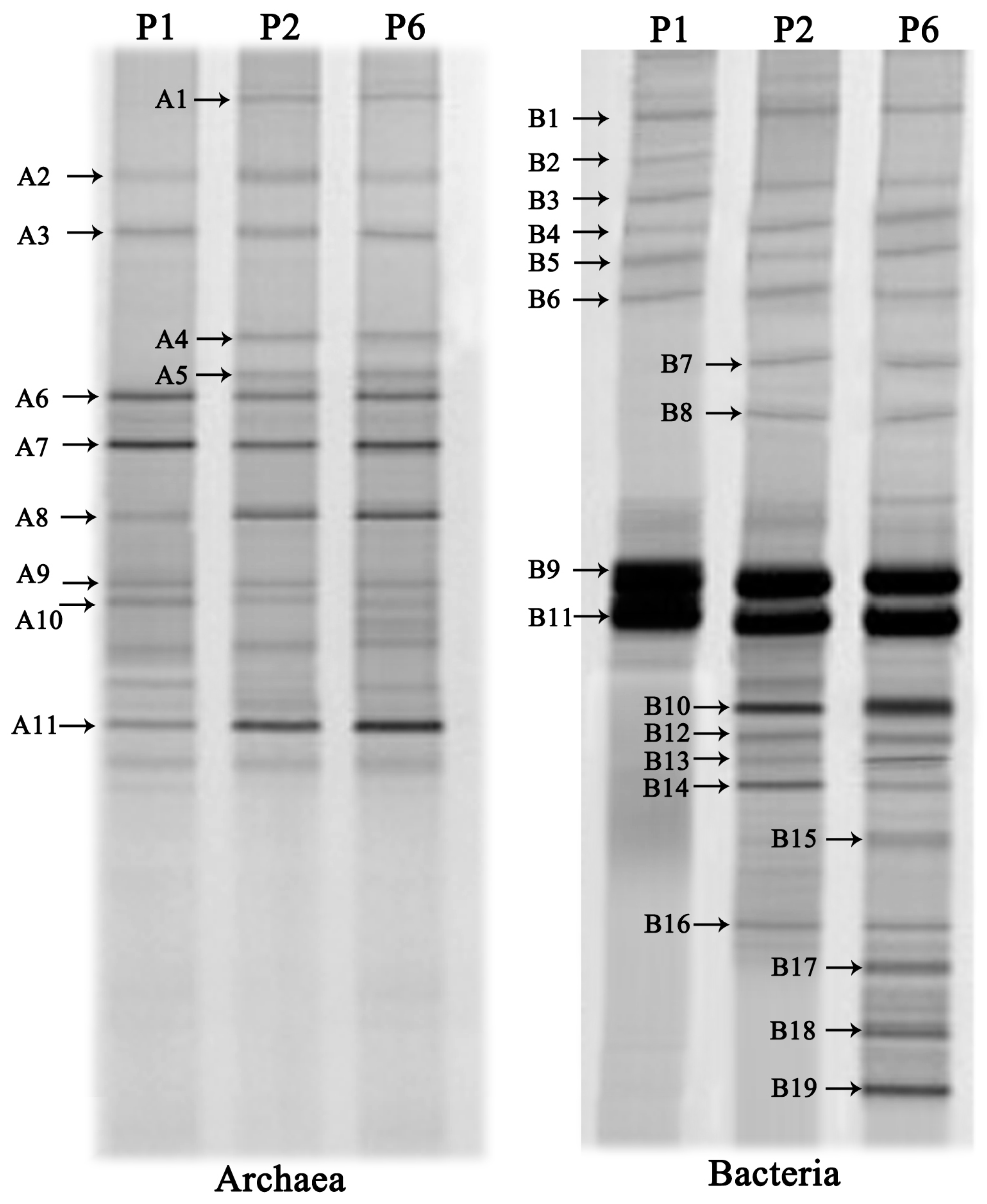
Archaea and bacterial community structure after the anaerobic digestion was studied by the DGGE analysis of PCR amplified 16S rRNA gene fragments (
Figure 7). Representative bands were selected from the DGGE gel for sequencing in order to identify the species presented in the digester and the results are shown in
Table 5. A total of 11 and 19 discernible DGGE bands were respectively observed in the two DGGE profiles for archaea and bacteria.
In this study, the archaea species could be divided into two different classes: Methanomicrobia (band A1–A10), and Methanococci (band A11). This result revealed that Methanomicrobia species were the prevalent methanogens in the archaeal community. Most species were highly coupled with aceticlastic methanogens (band A8–A11) and hydrogenotrophic methanogens (band A1–A7). With RIS addition, the diversity of methanogens was enhanced, particularly hydrogenotrophic methanogens. Band A1, A4 and A5 detected in P2 and P6 only, were closely related to
Methanoculleus palmolei,
Methanolinea tarda and
Methanosarcina mazei, hydrogenotrophic. [
51]. Given the band intensity, the aceticlastic methanogens populations corresponding to band A8–A11 likely formed the dominant methanogen group in all periods. The band intensity of A8 and A11 were enhanced obviously (
Figure 7). In P6, the diversity of methanogens didn’t decreased in the reactor. Therefore, micro-oxygenation did not seem to cause a harmful impact on the archaeal diversity.
Bands B1 and B2 were most closely related to
Methylovirgula ligni and
Methylocella silvestris, respectively. These two species were known as facultative methanotrophs that could attenuate methane emissions [
52]. Both microorganisms were found in P1, while only
Methylovirgula ligni was found in P2 and P6, which indicated that addition of RSI could remove
Methylocella silvestris to weak the consumption of methane biologically [
5]. Some detected microorganisms are capable of degrading complex organic matters to form organic acid, i.e., bands B3 (Uncultured bacterium), B4 (
Sphingopyxis witflariensis), B5 (
Novosphingobium indicum), B6 (
Clostridium orbiscindens), B7 (
Clostridium populeti) and B8 (
Caloramator proteoclasticus). Band B7 was an anaerobic cellulolytic microorganism and band B8 had strong ability to degrade proteins and amino acids [
53]. These two microorganisms have been found in P2 and P6 indicating that iron can enhance the ability of cellulose and protein hydrolysis.
Hydrogen-producing bacteria and acetobacteria may play important roles in anaerobic fermentation since hydrogen and acetate can be directly utilized by methanogenesis [
54]. Band 9 was closest to
Clostridium species belonging to the H
2-producing bacteria, which had been found in the three periods.
Syntrophobacter fumaroxidans (band 10) was enriched in the digester with the RSI (P2 and P6) which was capable of producing both hydrogen and formate by propionate oxidation. Band B11, B12 and B13 showed high sequence similarity to acetobacteria, belonging to
Acetobacter tropicalis,
Roseomonas lacus and
Sporomusa silvacetica, respectively.
Acetobacter tropicalis had been found in the three periods but the other two microorganisms were only generated in P2 and P6 indicating that the iron enhanced the diversity of acetobacteria in the digesters so as to increase acetate production.
Band B14, only found in P6, showed high sequence similarity to
Geobacter bemidjiensis Bem which had the ability to reduce Fe(III) and oxidize acetate and other multi-carbon organic substrates to carbon dioxide [
55]. IRB was only found in the digester with RSI (P2 and P6), which further proved that RSI could enrich IRB to enhance degradation of complex substrates, which contributed higher sludge reduction. Band B15 and B16 showed high sequence similarity to
Acidimicrobium ferrooxidans and
Ferrimicrobium acidiphilum, respectively, which had the ability to oxidize Fe(II) [
56]. Both of them were found in P6, while only band B16 was found in P2. It could be because O
2 supplementation improved the Fe(II) releasing rate and enhanced the diversity of Iron-Oxidizing Bacteria.
In this study, SOB microoganisms were only found in P6. The bands B17, B18 and B19 affiliated to the Epsilonproteobacteria class, Epsilonproteobacteria class and Gammaproteobacteria class were assigned to the Uncultured
Arcobacter species, Uncultured
Epsilonproteobacterium and Uncultured
Acinetobacter species (
Table 5), which are capable of oxidizing sulphide. Band B17 was found in the headspace of microaerobic digesters treating sewage sludge [
57]. Band B18 was described by Kodama and Watanabe [
58] as a chemolithoautotrophic SOB capable of oxidizing H
2S, S
0 and S
2O
32− under microaerobic conditions. And band B19 was partially responsible for H
2S removal in the bioscrubber system developed by Potivichayanon et al. [
59].