Demand-Side Energy Management Based on Nonconvex Optimization in Smart Grid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
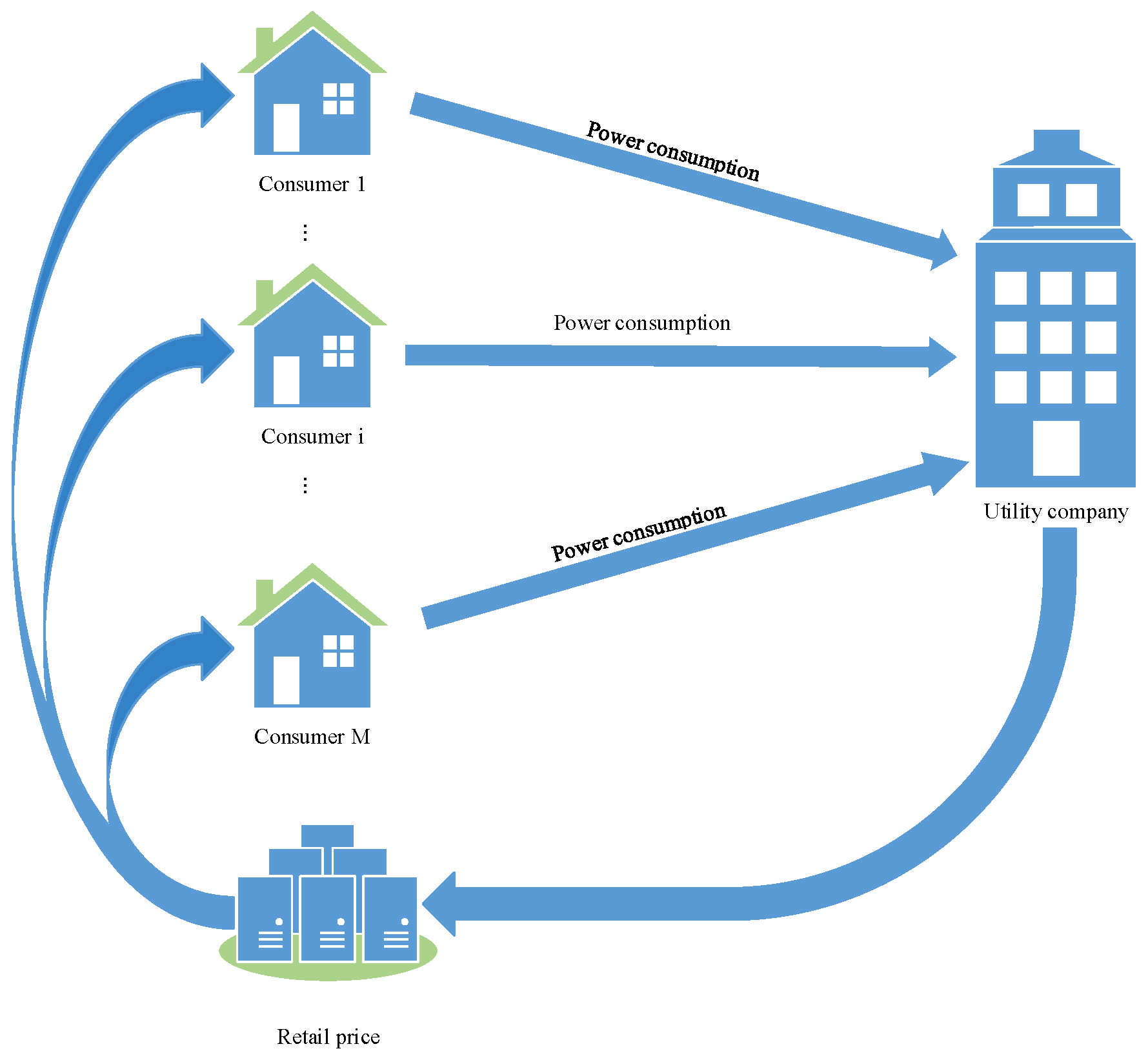
2. Problem Formulation
3. Iterative Algorithms
Part 1: Multiplier Method
| Algorithm 1 The multiplier algorithm. |
| Initialization: |
|
| Iteration: |
|
Part 2: Powell Direction Acceleration Method
| Algorithm 2 The Powell direction acceleration algorithm. |
| Initialization: |
|
| Iteration: |
|
Part 3: Advance and Retreat Method
| Algorithm 3 The advance and retreat algorithm. |
| Initialization: |
|
| Iteration: |
|
Part 4: Golden Section Method
| Algorithm 4 The golden section algorithm. |
| Initialization: |
| The search interval: ; . |
| Iteration: |
|
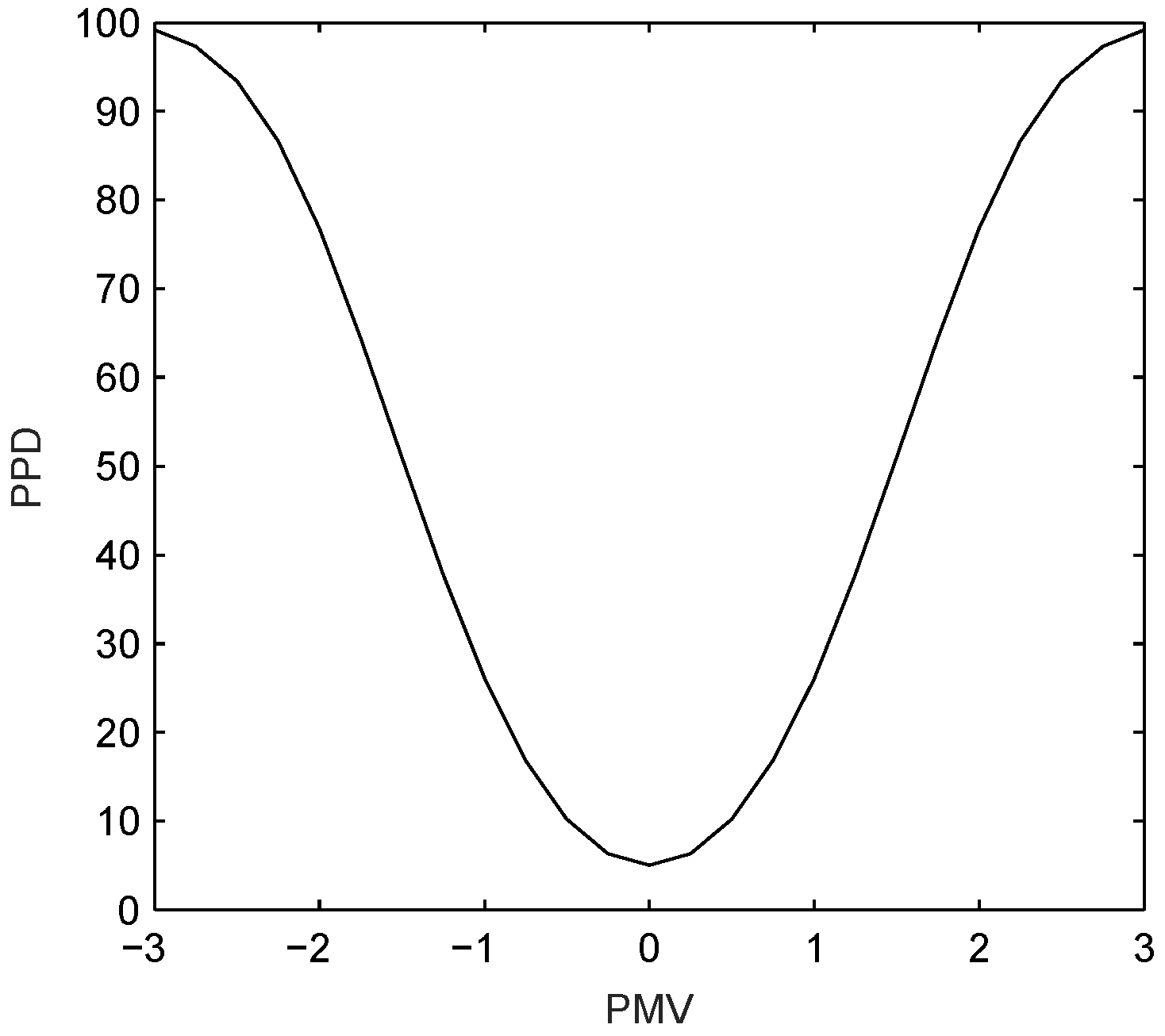
4. Application to Energy Management of HVAC Systems
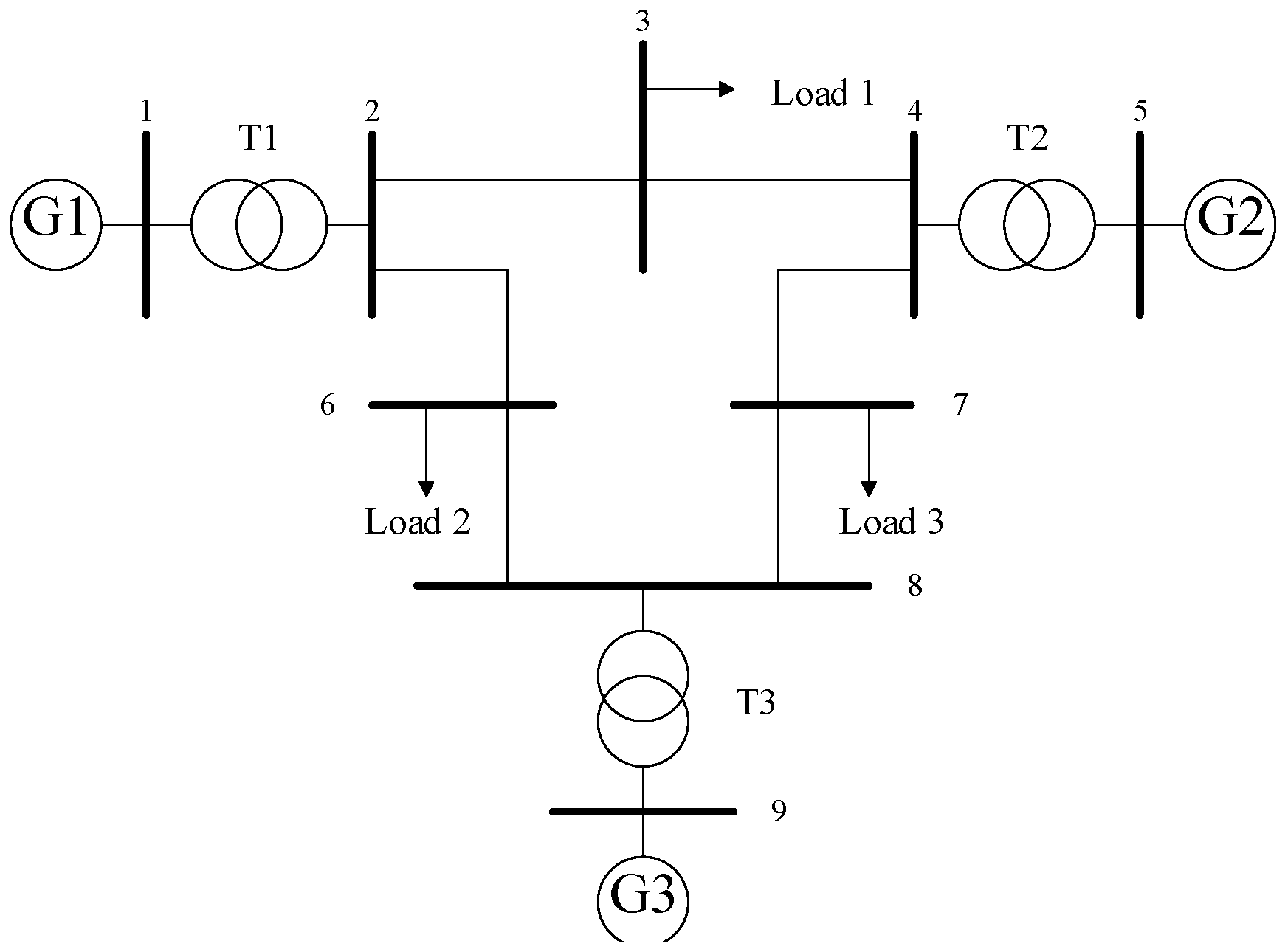
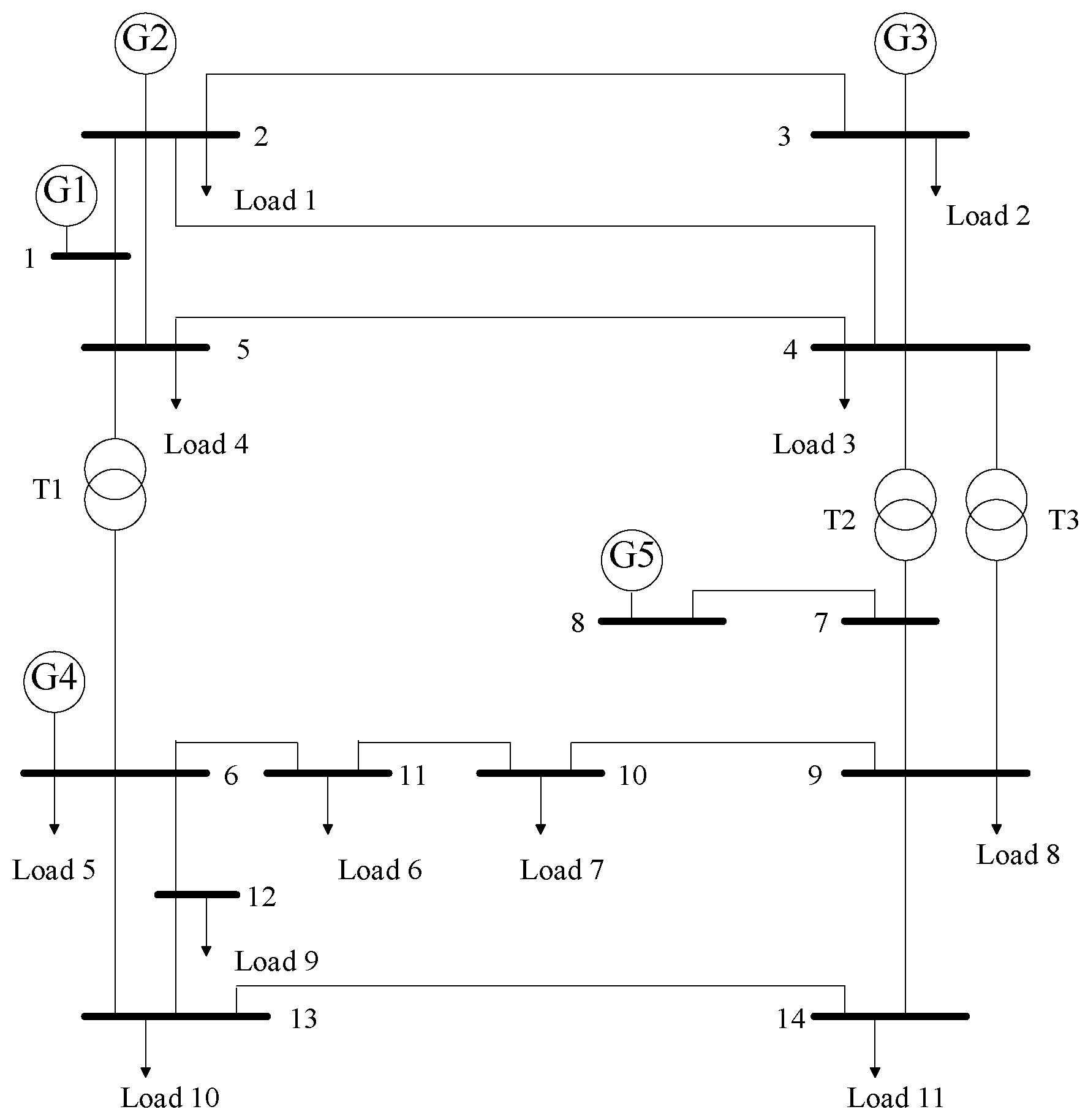
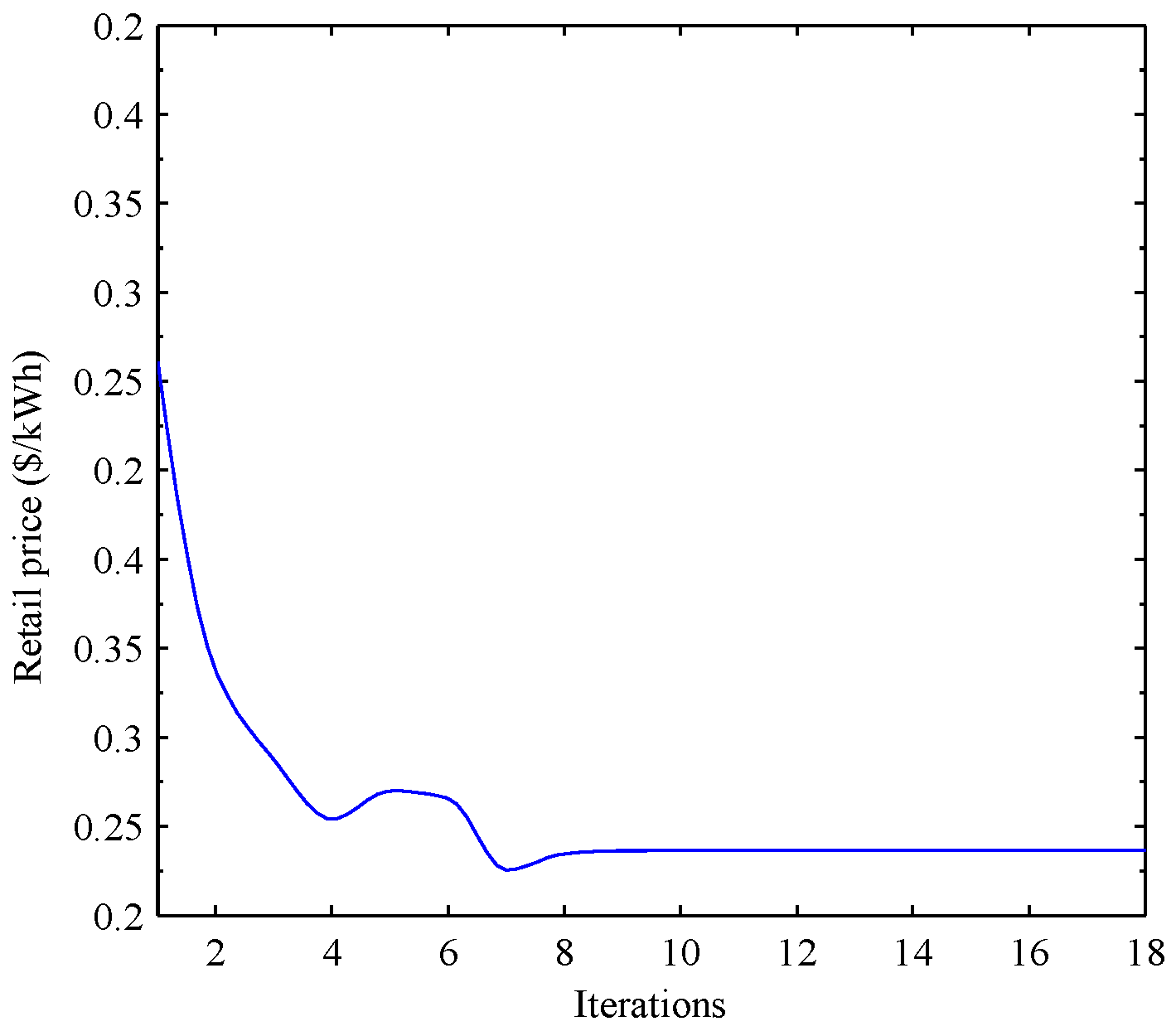
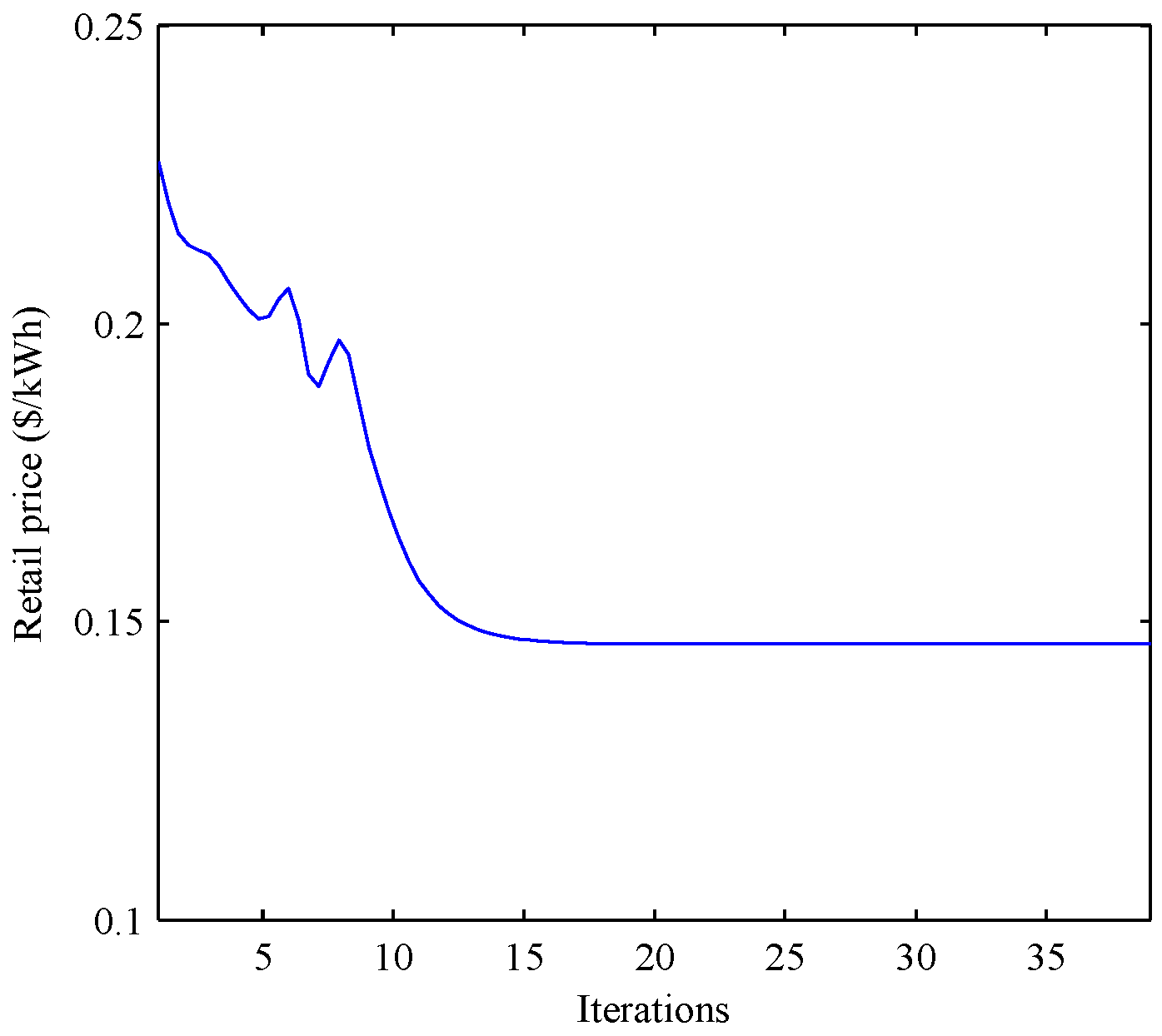
5. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HVAC | Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning |
| EER | Energy Efficient Ratio |
| EEG | Energy Efficient Grade |
| PHR | Powell-Hestenes-Rockafellar |
| PMV | Predicted Mean Vote |
| PPD | Predicted Percentage of Dissatisfied |
References
- Zaballos, A.; Vallejo, A.; Selga, J.M. Heterogeneous communication architecture for the smart grid. IEEE Netw. 2011, 25, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.X.; Luan, W.P. Smart grid and its implementations. Proc. CSEE 2009, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Elaiw, A.M.; Xia, X.; Shehata, A.M. Hybrid DE-SQP and hybrid PSO-SQP methods for solving dynamic economic emission dispatch problem with valve-point effects. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2013, 103, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschae, R.; Kato, T.; Matsuyama, T. Energy Management in Prosumer Communities: A Coordinated Approach. Energies 2016, 9, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divshali, P.H.; Choi, B. Electrical Market Management Considering Power System Constraints in Smart Distribution Grids. Energies 2016, 9, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Tang, Y. Autonomous Household Energy Management Based on a Double Cooperative Game Approach in the Smart Grid. Energies 2015, 8, 7326–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, R. Energy Management and Smart Grids. Energies 2013, 6, 2262–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albadi, M.H.; El-Saadany, E.F. A summary of demand response in electricity markets. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2008, 78, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.T.; Zhu, Z.Z.; Yu, E.K. Study on demand response markets and programs in electricity markets. Power Syst. Technol. 2010, 34, 146–153. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, Y. Optimal Power Allocation for a Relaying-Based Cognitive Radio Network in a Smart Grid. Energies 2017, 10, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, J.L.; Koch, S.; Callaway, D.S. State Estimation and Control of Electric Loads to Manage Real-Time Energy Imbalance. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.H.; Min, X.U. Researches on spot price based on optimal power flow and its algorithm. Relay 2006, 34, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Sanduleac, M.; Lipari, G.; Monti, A.; Voulkidis, A.; Zanetto, G.; Corsi, A.; Toma, L.; Fiorentino, G.; Federenciuc, D. Next Generation Real-Time Smart Meters for ICT Based Assessment of Grid Data Inconsistencies. Energies 2017, 10, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottondi, C.; Duchon, M.; Koss, D.; Palamarciuc, A.; Pití, A.; Verticale, G.; Schätz, B. An Energy Management Service for the Smart Office. Energies 2015, 8, 11667–11684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agnetis, A.; de Pascale, G.; Detti, P.; Vicino, A. Load Scheduling for Household Energy Consumption Optimization. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 2364–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K.; Gibtner, A.K.; Duchon, M.; Koss, D.; Schätz, B. Using knowledge discovery for autonomous decision making in smart grid nodes. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, Seville, Spain, 17–19 March 2015; pp. 3134–3139. [Google Scholar]
- Gatsis, N.; Giannakis, G.B. Residential demand response with interruptible tasks: Duality and algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2011 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–15 Dcember 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Barbato, A.; Bolchini, C.; Geronazzo, A.; Quintarelli, E.; Palamarciuc, A.; Pitì, A.; Rottondi, C.; Verticale, G. Energy Optimization and Management of Demand Response Interactions in a Smart Campus. Energies 2016, 9, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, K.; Hu, G.; Spanos, C.J. Distributed Energy Consumption Control via Real-Time Pricing Feedback in Smart Grid. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2014, 22, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsenian-Rad, A.H.; Wong, V.W.S.; Jatskevich, J.; Schober, R.; Leon-Garcia, A. Autonomous Demand-Side Management Based on Game-Theoretic Energy Consumption Scheduling for the Future Smart Grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2010, 1, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; Asr, N.R.; Chow, M.Y. Residential Energy Consumption Scheduling: A Coupled-Constraint Game Approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Demand Response Management with Multiple Utility Companies: A Two-Level Game Approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, B.; Guan, X. Optimal demand response scheduling with Stackelberg game approach under load uncertainty for smart grid. In Proceedings of the IEEE Third International Conference on Smart Grid Communications, Tainan, Taiwan, 5–8 November 2012; pp. 546–551. [Google Scholar]
- Tushar, W.; Chai, B.; Yuen, C.; Smith, D.B. Three-Party Energy Management With Distributed Energy Resources in Smart Grid. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 62, 2487–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, P.; Mohsenian-Rad, A.H.; Schober, R.; Wong, V.W.S.; Jatskevich, J. Optimal Real-Time Pricing Algorithm Based on Utility Maximization for Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the First IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications, Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 4–6 October 2010; pp. 415–420. [Google Scholar]
- Roozbehani, M.; Dahleh, M.A.; Mitter, S.K. Volatility of Power Grids Under Real-Time Pricing. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 27, 1926–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenian-Rad, A.H.; Leon-Garcia, A. Optimal Residential Load Control With Price Prediction in Real-Time Electricity Pricing Environments. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2010, 1, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Giannakis, G.B. Real-Time Load Elasticity Tracking and Pricing for Electric Vehicle Charging. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Ye, M.; Sun, C.; Hu, G. Distributed control for economic dispatch via saddle point dynamics and consensus algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 12–14 Dcember 2016; pp. 6934–6939. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.; Hu, G.; Spanos, C.J. Energy Management Considering Load Operations and Forecast Errors with Application to HVAC Systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, PP, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Yuan, Y.X. Optimization Theory and Methods—Nonlinear Programming; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Van, H.J. Forty years of Fanger’s model of thermal comfort: Comfort for all? Indoor Air 2008, 18, 182–201. [Google Scholar]
- De Donato, S.R.; Graziani, M.; Mainetti, S. Evaluation of the predictive value of Fanger’s PMV index study in a population of school children. Predicted mean vote. Med. Lav. 1996, 87, 51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gilani, I.U.H.; Khan, M.H.; Ali, M. Revisiting Fanger’s thermal comfort model using mean blood pressure as a bio-marker: An experimental investigation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 109, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.J.; Wollenberg, B. 96/02779—Power generation operation and control, 2nd edition. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 1996, 37, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, J.; Xia, X. Energy consumption of air conditioners at different temperature set points. Energy Build. 2013, 65, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameters | Explanation |
|---|---|
| M | Human body’s energy metabolic rate () |
| W | Human body’s mechanical work () |
| Pa | Vapour pressure around body (Pa) |
| Air temperature (°C) | |
| Area coefficient of clothing | |
| Ttemperature of clothes (°C) | |
| Indoor’s mean radiant temperature (°C) | |
| Convective heat transfer coefficient (W/(K)) | |
| Heat resistance of clothes ((K)/W) | |
| Air velocity (m/s) |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Outdoor temperature (°C) | |
| Transmission area () | |
| Heat transfer constant () | |
| Specific heat of air (°C) | |
| Air density () | |
| Wind speed coefficient | |
| Outdoor heat coefficient | |
| Effective infiltration area () | |
| Building height (m) | |
| Solar and internal load (W) |
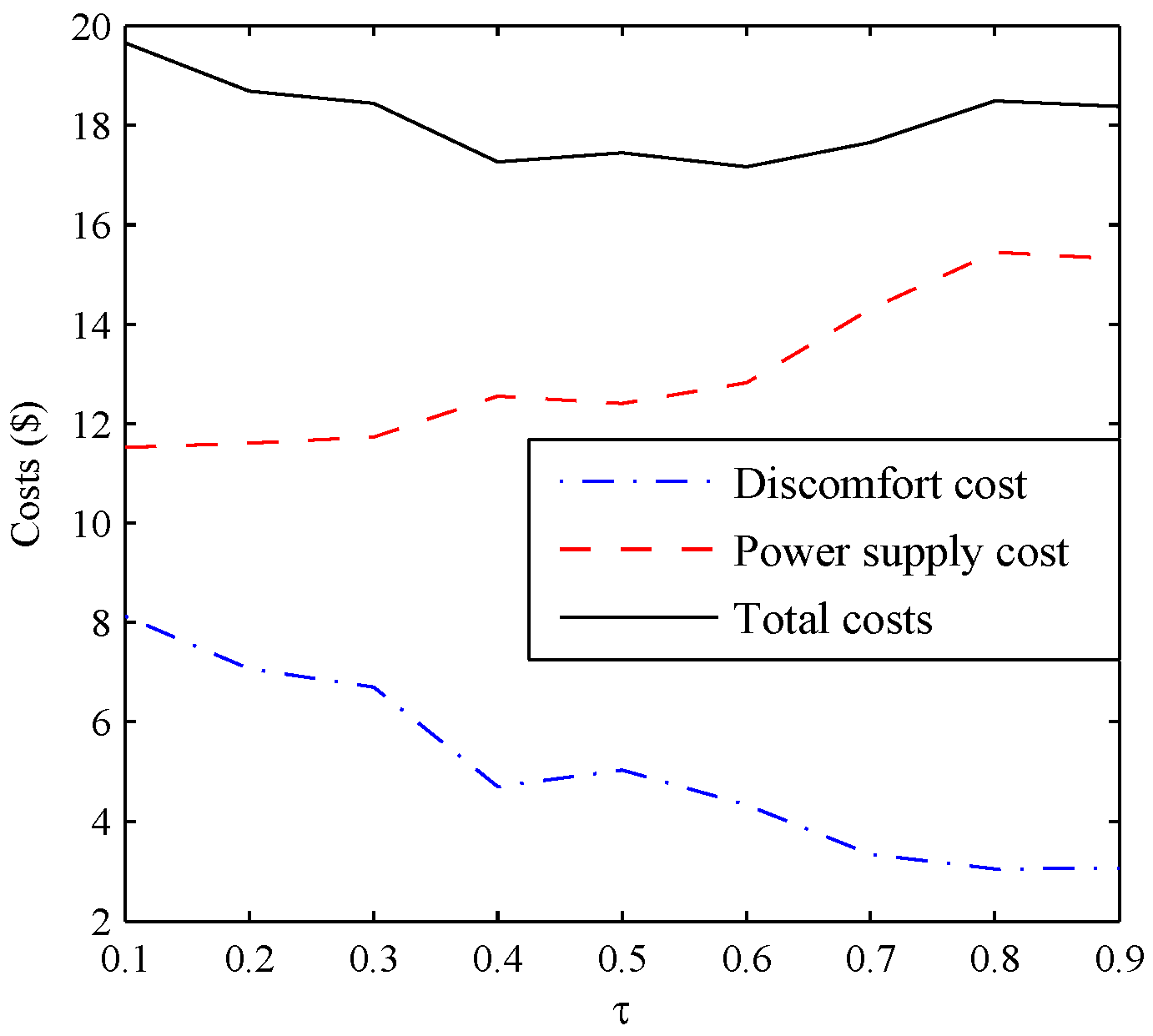
| Discomfort Cost ($) | Generation Cost ($) | Total Costs ($) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 8.1279 | 11.5264 | 19.6543 |
| 0.2 | 7.0753 | 11.6035 | 18.6788 |
| 0.3 | 6.7075 | 11.7344 | 18.4419 |
| 0.4 | 4.7092 | 12.5458 | 17.2550 |
| 0.5 | 5.0396 | 12.4054 | 17.4450 |
| 0.6 | 4.3398 | 12.8159 | 17.1557 |
| 0.7 | 3.3431 | 14.3050 | 17.6481 |
| 0.8 | 3.0488 | 15.4414 | 18.4902 |
| 0.9 | 3.0605 | 15.3121 | 18.3726 |
| Consumer i | Temperature (°C) | Power Consumption (kW) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25.4534 | 0.6986 |
| 2 | 25.0573 | 1.6701 |
| 3 | 24.5559 | 3.6015 |
| 1–3 | / | 5.9702 |
| Buses i | Power Supply (W) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 663.3679 |
| 2 | 663.3646 |
| 3 | 663.3654 |
| 4 | 663.3676 |
| 5 | 663.3669 |
| 6 | 663.3692 |
| 7 | 663.3686 |
| 8 | 663.3693 |
| 9 | 663.3683 |
| 1–9 | 59702 |
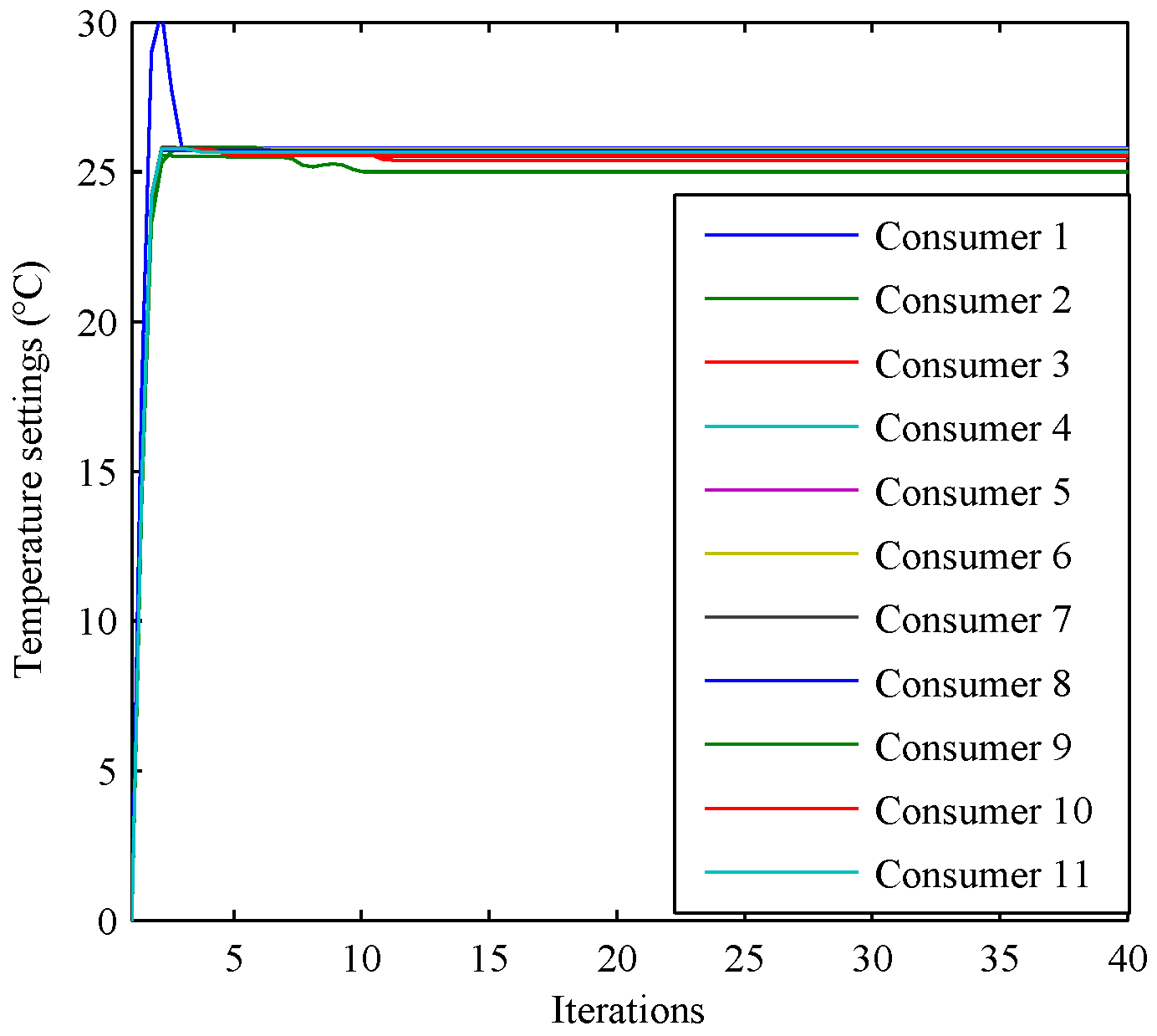
| Consumer i | Temperature (°C) | Power Consumption (kW) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25.7925 | 0.3526 |
| 2 | 25.5883 | 0.6228 |
| 3 | 25.3969 | 0.9958 |
| 4 | 25.7143 | 0.7118 |
| 5 | 25.7578 | 0.7356 |
| 6 | 25.7708 | 0.7896 |
| 7 | 25.5143 | 1.2350 |
| 8 | 25.7187 | 1.0332 |
| 9 | 25.0050 | 2.2812 |
| 10 | 25.5317 | 1.5131 |
| 11 | 25.6491 | 1.4117 |
| 1–11 | / | 11.6825 |
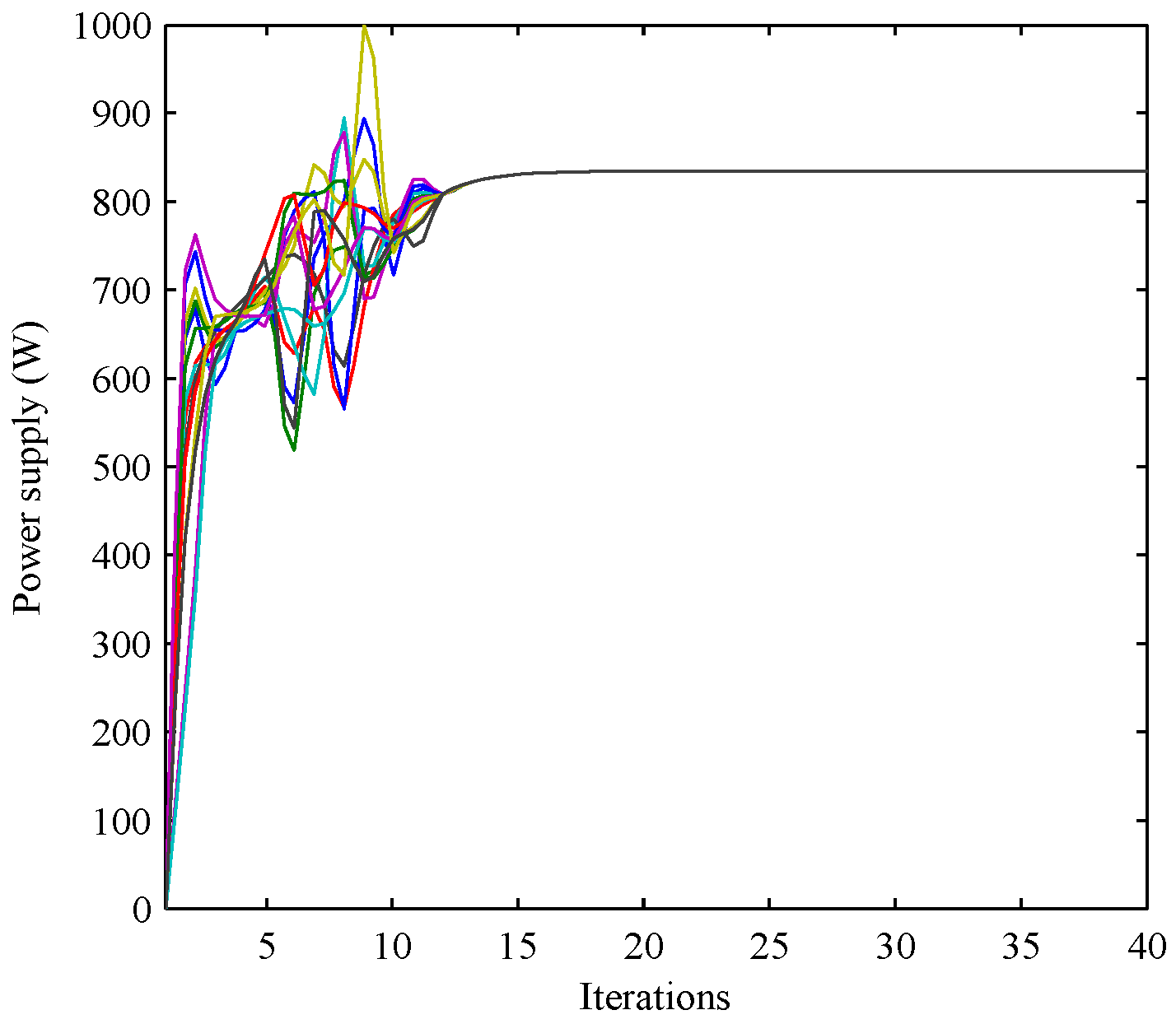
| Buses i | Power Supply (W) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 834.4625 |
| 2 | 834.4609 |
| 3 | 834.4616 |
| 4 | 834.4629 |
| 5 | 834.4693 |
| 6 | 834.4612 |
| 7 | 834.4625 |
| 8 | 834.4650 |
| 9 | 834.4621 |
| 10 | 834.4595 |
| 11 | 834.4648 |
| 12 | 834.4673 |
| 13 | 834.4591 |
| 14 | 834.4637 |
| 1–14 | 11682 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, K.; Bai, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Q. Demand-Side Energy Management Based on Nonconvex Optimization in Smart Grid. Energies 2017, 10, 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10101538
Ma K, Bai Y, Yang J, Yu Y, Yang Q. Demand-Side Energy Management Based on Nonconvex Optimization in Smart Grid. Energies. 2017; 10(10):1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10101538
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Kai, Yege Bai, Jie Yang, Yangqing Yu, and Qiuxia Yang. 2017. "Demand-Side Energy Management Based on Nonconvex Optimization in Smart Grid" Energies 10, no. 10: 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10101538





