Effects of Moderate- and High-Intensity Chronic Exercise on the Adiponectin Levels in Slow-Twitch and Fast-Twitch Muscles in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Animals and Experimental Protocol
2.3. Training Schedule
2.4. Skeletal Muscle Sample
2.5. Measurement of Adiponectin Levels in Serum and Muscle Tissue
2.6. Adiponectin Receptor 1 and Adiponectin mRNA Expression in Muscle Samples Based on RT-qPCR
2.7. Data Presentation and Statistical Analysis
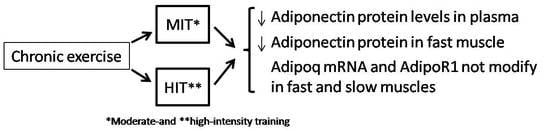
3. Results
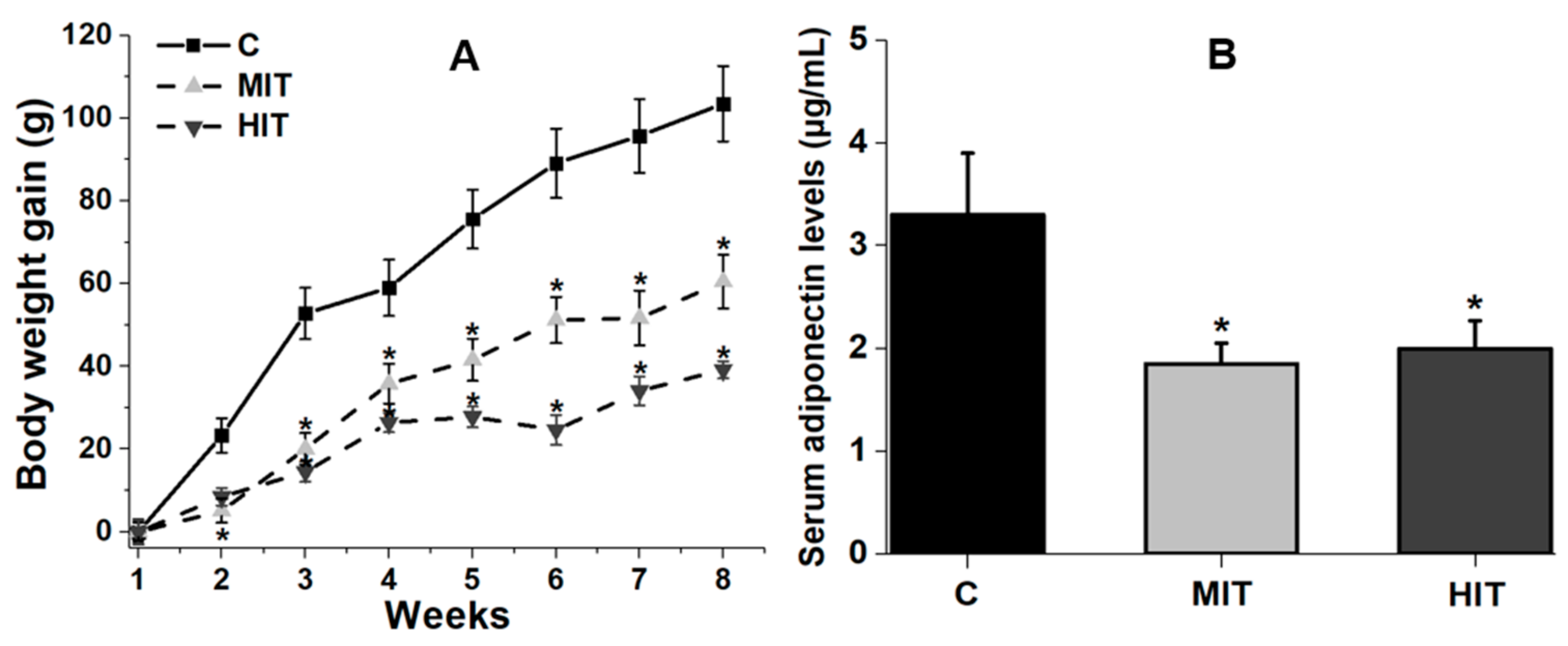
3.1. Effect of Chronic Exercise on Body Weight and Serum Adiponectin
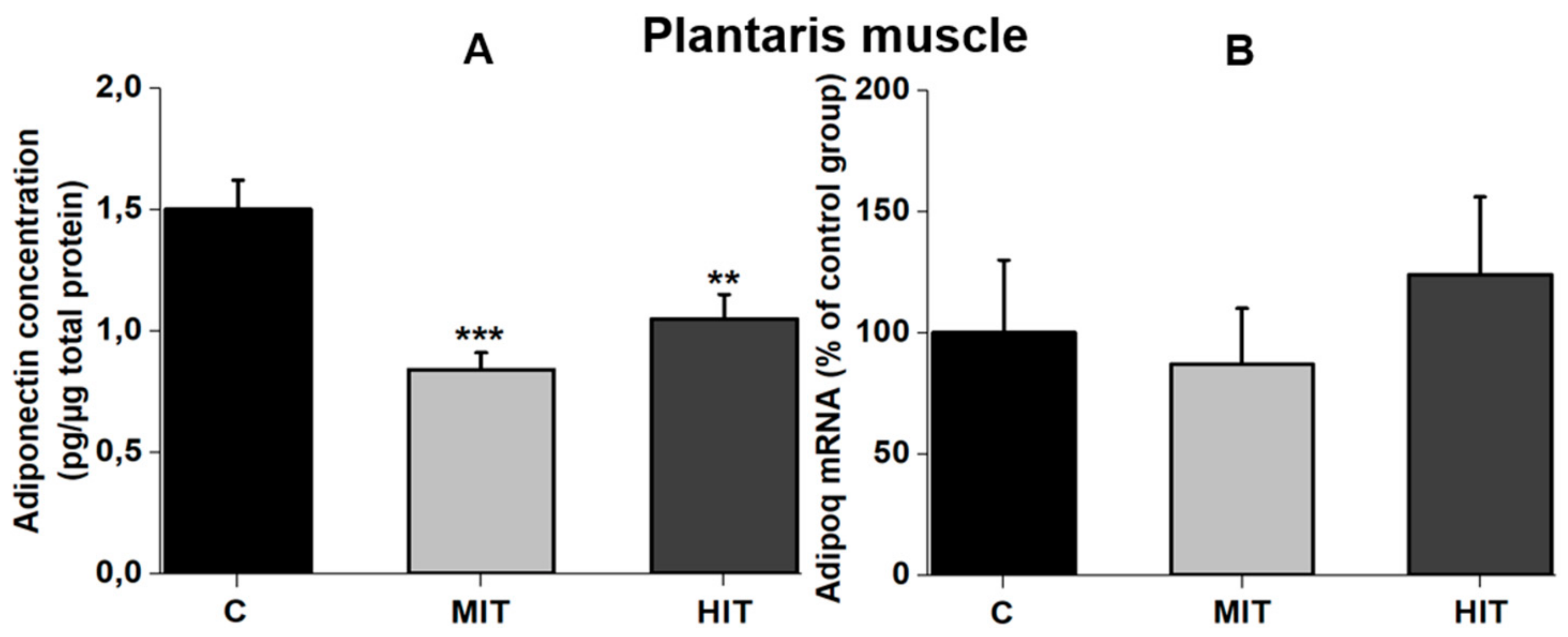
3.2. Effect of Training Intensity on Adiponectin Protein Content and Adiponectin mRNA Expression in Fast-Twitch Muscle
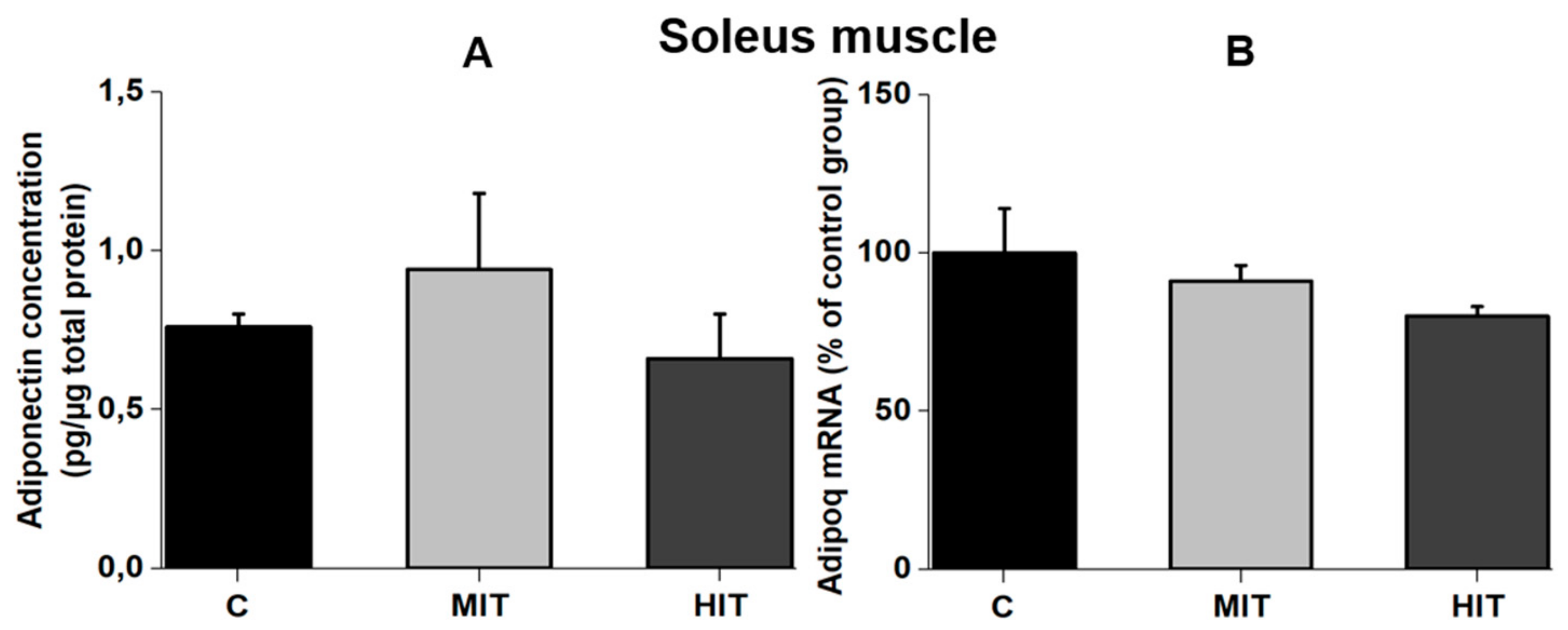
3.3. Effect of Training Intensity on Adiponectin Protein Content and Adiponectin mRNA Expression in Slow-Twitch Muscle
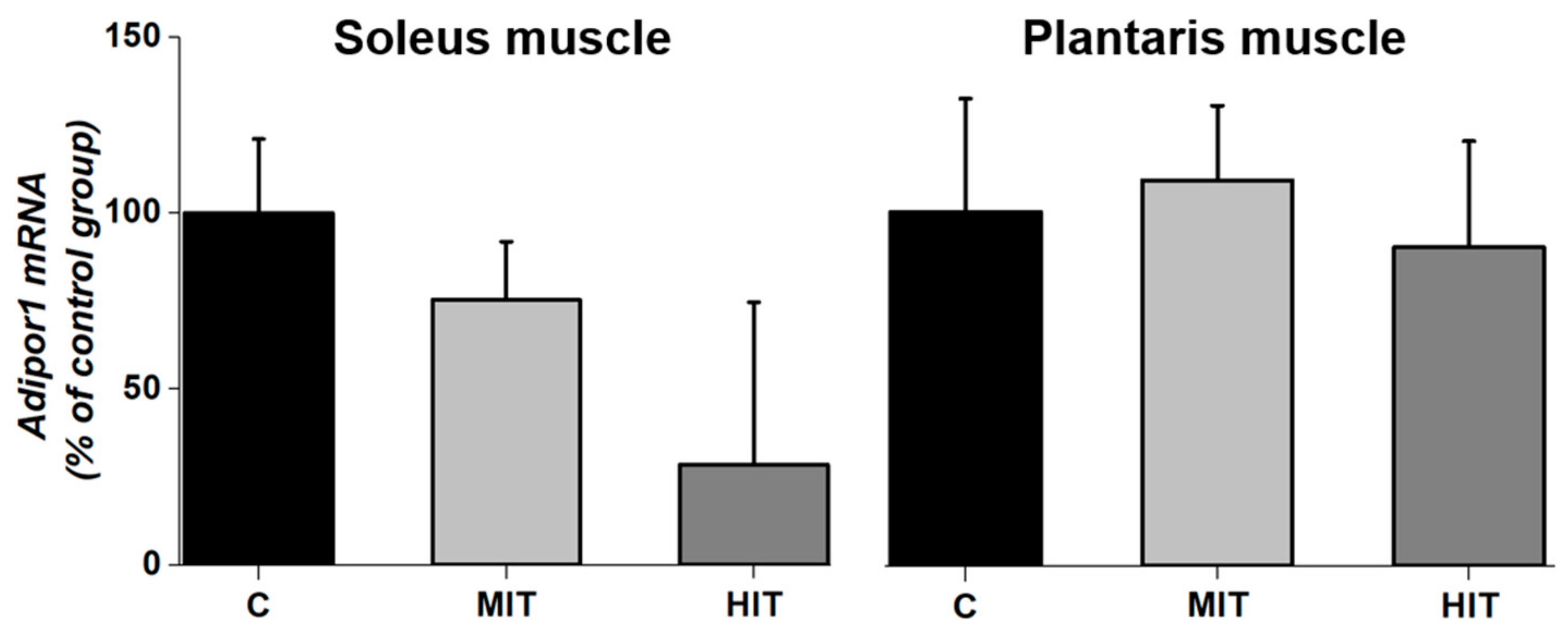
3.4. Adipor1 mRNA Expression after Chronic Exercise in Fast-Twitch and Slow-Twitch Muscles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, Y.; Luo, N.; Klein, R.L.; Garvey, W.T. Adiponectin promotes adipocyte differentiation, insulin sensitivity, and lipid accumulation. J. Lipid. Res. 2005, 46, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Yokomizo, T.; Kita, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Hara, K.; Tsunoda, M.; et al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 2003, 423, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Isobe, K.; Fu, L.; Ohkoshi, N.; Ohmori, H.; Takekoshi, K.; Kawakami, Y. Effects of exercise on adiponectin and adiponectin receptor levels in rats. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Berendoncks, A.M.; Garnier, A.; Beckers, P.; Hoymans, V.Y.; Possemiers, N.; Fortin, D.; Martinet, W.; Van Hoof, V.; Vrints, C.J.; Ventura–Clapier, R.; et al. Functional adiponectin resistance at the level of the skeletal muscle in mild to moderate chronic heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2010, 3, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, E.; Liang, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. AdipoQ is a novel adipose-specific gene dysregulated in obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 10697–10703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, M.P.; Liu, Y.; Vu, V.; Chan, L.; Xu, A.; Riddell, M.C.; Sweeney, G.; Hawke, T.J. Adiponectin is expressed by skeletal muscle fibers and influences muscle phenotype and function. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2008, 295, C203–C212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, A.; Ohno, Y.; Ikuta, A.; Suzuki, M.; Ohira, T.; Egawa, T.; Sugiura, T.; Yoshioka, T.; Ohira, Y.; Goto, K. Up–regulation of adiponectin expression in antigravitational soleus muscle in response to unloading followed by reloading, and functional overloading in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, H.; Nguyen, M.T.; Trujillo, M.; Imamura, T.; Usui, I.; Scherer, P.E.; Olefsky, J.M. Adenovirus–mediated adiponectin expression augments skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity in male Wistar rats. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safwat, Y.; Yassin, N.; Gamal, E.l.; Din, M.; Kassem, L. Modulation of skeletal muscle performance and SERCA by exercise and adiponectin gene therapy in insulin–resistant rat. DNA Cell Biol. 2013, 32, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jortay, J.; Senou, M.; Abou–Samra, M.; Noel, L.; Robert, A.; Many, M.C.; Brichard, S.M. Adiponectin and skeletal muscle: pathophysiological implications in metabolic stress. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 18, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jortay, J.; Senou, M.; Abou–Samra, M.; Noel, L.; Robert, A.; Many, M.C.; Brichard, S.M. Involvement of adiponectin in the pathogenesis of dystrophinopathy. Skelet Muscle 2015, 7, 5–25. [Google Scholar]
- Civitarese, A.E.; Ukropcova, B.; Carling, S.; Hulver, M.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Mandarino, L.; Ravussin, E.; Smith, S.R. Role of adiponectin in human skeletal muscle bioenergetics. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leiter, J.R.; Peeler, J.; Anderson, J.E. Exercise–induced muscle growth is muscle-specific and age–dependent. Muscle Nerve 2011, 43, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez–Maldonado, A.; Cerna–Cortés, J.; Castro–Rodríguez, E.M.; Montero, S.A.; Muñiz, J.; Rodríguez–Hernández, A.; Lemus, M.; De Álvarez–Buylla, E.R. Effects of moderate and high–intensity chronic exercise on brain–derived neurotrophic factor expression in fast and slow muscles. Muscle Nerve 2016, 53, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guhad, F. Introduction to the 3Rs (Refinement, Reduction and Replacement). Contemp. Top. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2005, 44, 58–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wisløff, U.; Helgerud, J.; Kemi, O.J.; Ellingsen, O. Intensity–controlled treadmill running in rats: VO(2 max) and cardiac hypertrophy. Am. J. Physio. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001, 280, H1301–H1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leandro, C.G.; Levada, A.C.; Hirabara, F.M.; Manhães–de–Castro, R.; De–Castro, C.B.; Curi, R.; Pithon–Curi, T.C. A programof moderate physical training for Wistar rats based on maximal oxygen consumption. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garekani, E.T.; Mohebbi, H.; Kraemer, R.R.; Fathi, R. Exercise training intensity/volume affects plasma and tissue adiponectin concentrations in the male rat. Peptides 2011, 32, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, I.R.; MacDonald, T.L.; Wright, D.C.; Dyck, D.J. Adiponectin is sufficient, but not required, for exercise-induced increases in the expression of skeletal muscle mitochondrial enzymes. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 2653–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, A.; Monaco, M.L.; Capasso, M.; Forestieri, P.; Pilone, V.; Nardelli, C.; Buono, P.; Daniele, A. Adiponectin oligomers as potential indicators of adipose tissue improvement in obese subjects. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 69, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy–Matos, A.F.; Bahia, L.R.; Domingues, R.C.; Sicuro, F.; Tambascia, M.; Geloneze, B.; Kraemer–Aguiar, L.G.; Bouskela, E. Adiponectin is related to intramyocellular lipid content in non–diabetic adults. Endocrinol. Invest. J. 2010, 33, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Matsushita, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Hayashi, T.; Noda, M.; Mizoue, T. Circulating adiponectin levels and risk of type 2 diabetes in the Japanese. Nutr. Diabetes 2014, 4, e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez–Merino, D.; Drogou, C.; Guezennec, C.Y.; Chennaoui, M. Effects of chronic exercise on cytokine production in white adipose tissue and skeletal muscle of rats. Cytokine 2007, 40, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, K.A.; Singh, M.A. Effects of exercise on adiponectin: A systematic review. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008, 16, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfahani, M.; Movahedian, A.; Baranchi, M.; Goodarzi, MT. Adiponectin: An adipokine with protective features against metabolic syndrome. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2015, 18, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nunes, R.; Silva, P.; Alves, J.; Stefani, G.; Petry, M.; Rhoden, C.; Dal Lago, P.; Schneider, C.D. Effects of resistance training associated with whey protein supplementation on liver and kidney biomarkers in rats. Appl. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 38, 1166–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerosa–Neto, J.; Antunes, B.M.M.; Campos, E.Z.; Rodrigues, J.; Ferrari, G.D.; Rosa Neto, J.C.; Bueno, C.R., Jr.; Lira, F.S. Impact of long-term high-intensity interval and moderate-intensity continuous training on subclinical inflammation in overweight/obese adults. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2016, 12, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadizad, S.; Haghighi, A.H.; Hamedinia, M.R. Effects of resistance versus endurance training on serum adiponectin and insulin resistance index. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 157, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirico, F.; Bianco, A.; D’Alicandro, G.; Castaldo, C.; Montagnani, S.; Spera, R.; Di Meglio, F.; Nurzynska, D. Effects of physical exercise on adiponectin, leptin, and inflammatory markers in childhood obesity: Systematic review and meta–analysis. Child. Obes. 2018, 14, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, K.I.; Goodyear, L.J. Exercise regulation of adipose tissue. Adipocyte 2016, 5, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez–Huenchullan, S.F.; Maharjan, B.R.; Williams, P.F.; Tam, C.S.; Mclennan, S.V.; Twigg, S.M. Skeletal muscle adiponectin induction depends on diet, muscle type/activity, and exercise modality in C57BL/6 mice. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Hattori, M. Intramyocellular lipids of muscle type in athletes of different sport discipline. Open. Acc. J. Ports. Med. 2017, 11, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kwak, H.B. Effects of interventions on adiponectin and adiponectin receptors. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2014, 10, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiménez-Maldonado, A.; Virgen-Ortiz, A.; Lemus, M.; Castro-Rodríguez, E.; Cerna-Cortés, J.; Muñiz, J.; Montero, S.; Roces, E. Effects of Moderate- and High-Intensity Chronic Exercise on the Adiponectin Levels in Slow-Twitch and Fast-Twitch Muscles in Rats. Medicina 2019, 55, 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55060291
Jiménez-Maldonado A, Virgen-Ortiz A, Lemus M, Castro-Rodríguez E, Cerna-Cortés J, Muñiz J, Montero S, Roces E. Effects of Moderate- and High-Intensity Chronic Exercise on the Adiponectin Levels in Slow-Twitch and Fast-Twitch Muscles in Rats. Medicina. 2019; 55(6):291. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55060291
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiménez-Maldonado, Alberto, Adolfo Virgen-Ortiz, Mónica Lemus, Elena Castro-Rodríguez, Joel Cerna-Cortés, Jesús Muñiz, Sergio Montero, and Elena Roces. 2019. "Effects of Moderate- and High-Intensity Chronic Exercise on the Adiponectin Levels in Slow-Twitch and Fast-Twitch Muscles in Rats" Medicina 55, no. 6: 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55060291