Dual Role of NMDAR Containing NR2A and NR2B Subunits in Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
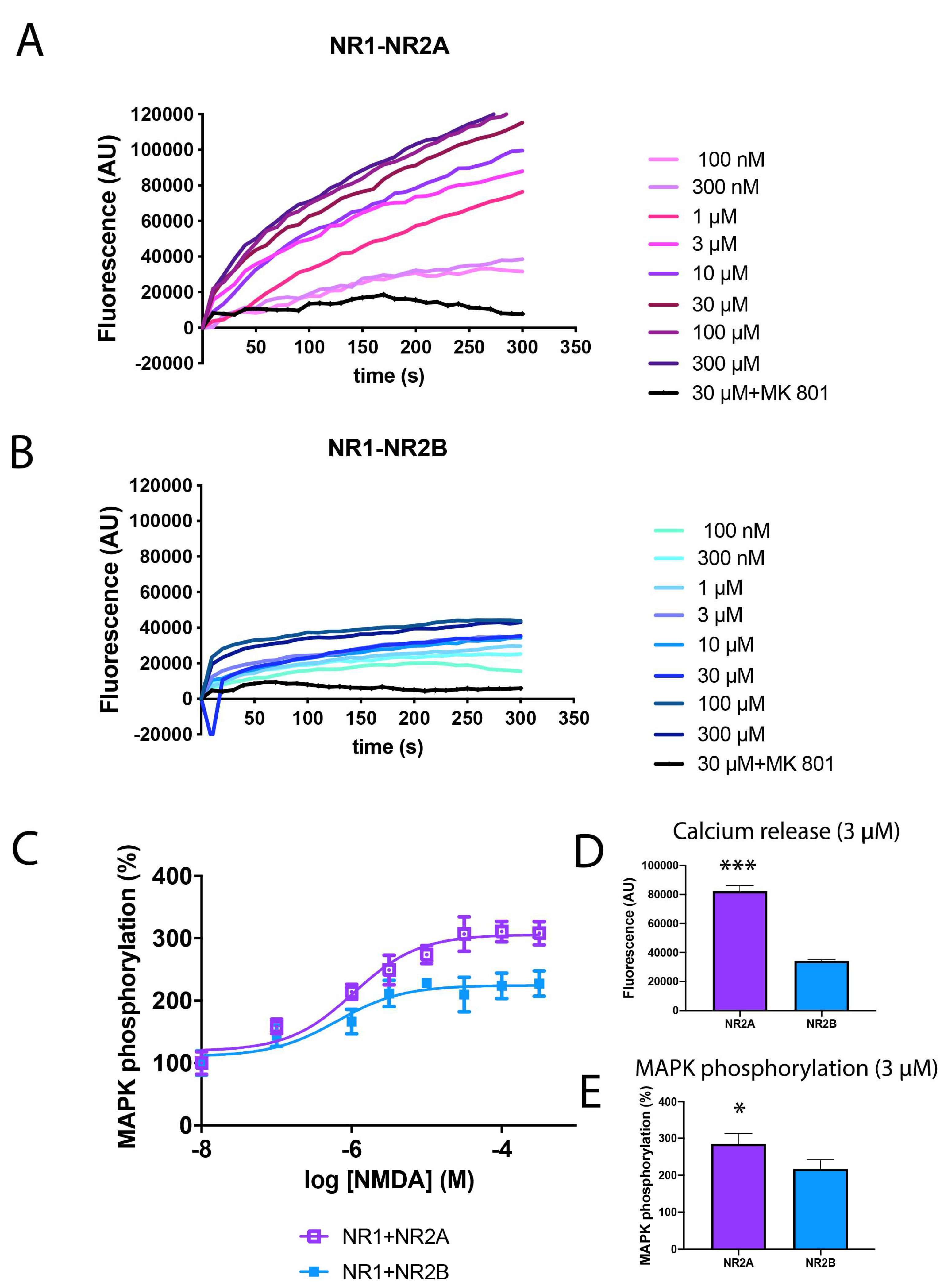
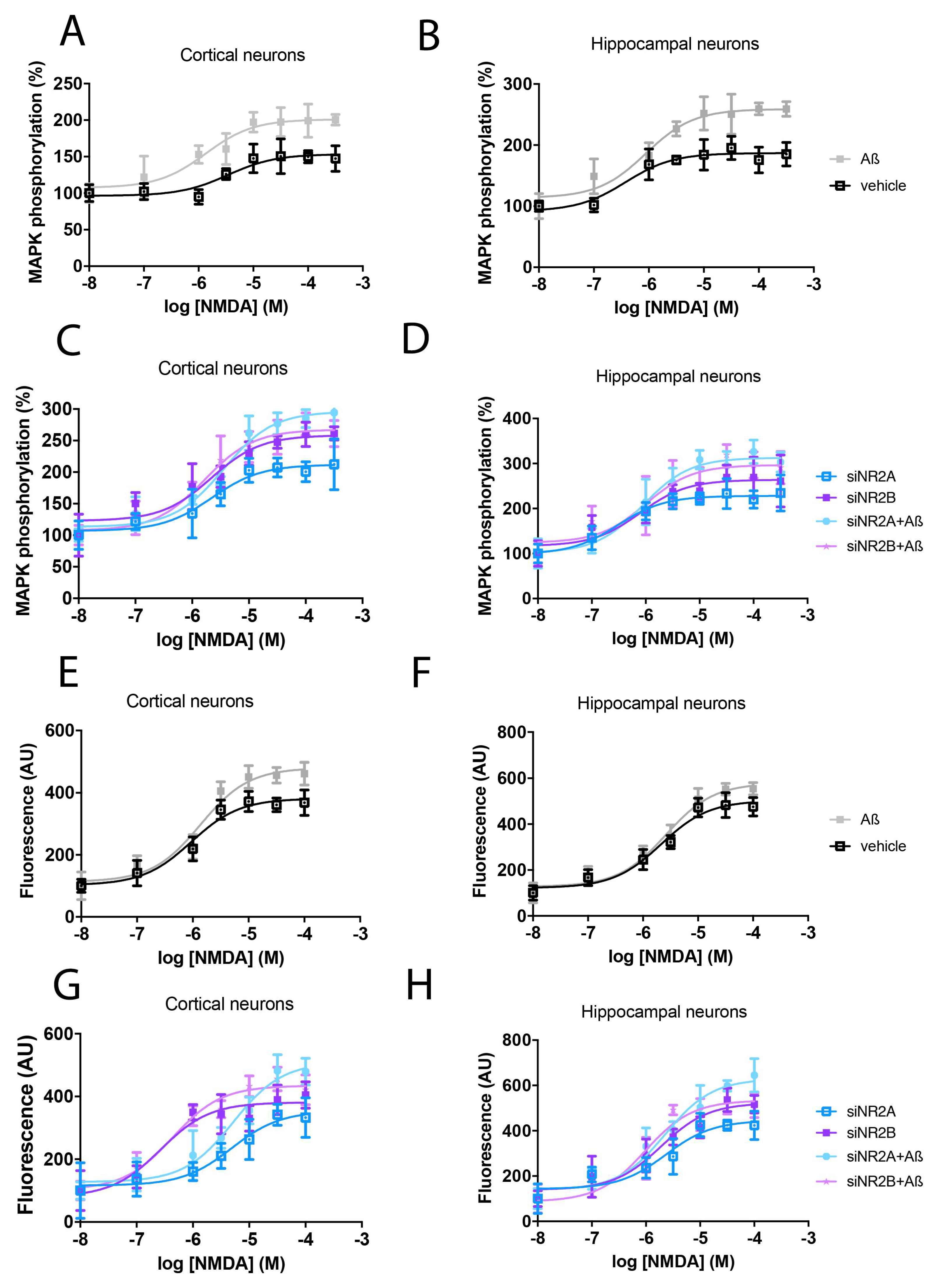
2.1. Activation of NR2A-Containing NMDAR Shows Higher Levels of Calcium Release and MAPK Phosphorylation than NR2B-Containing NMDAR
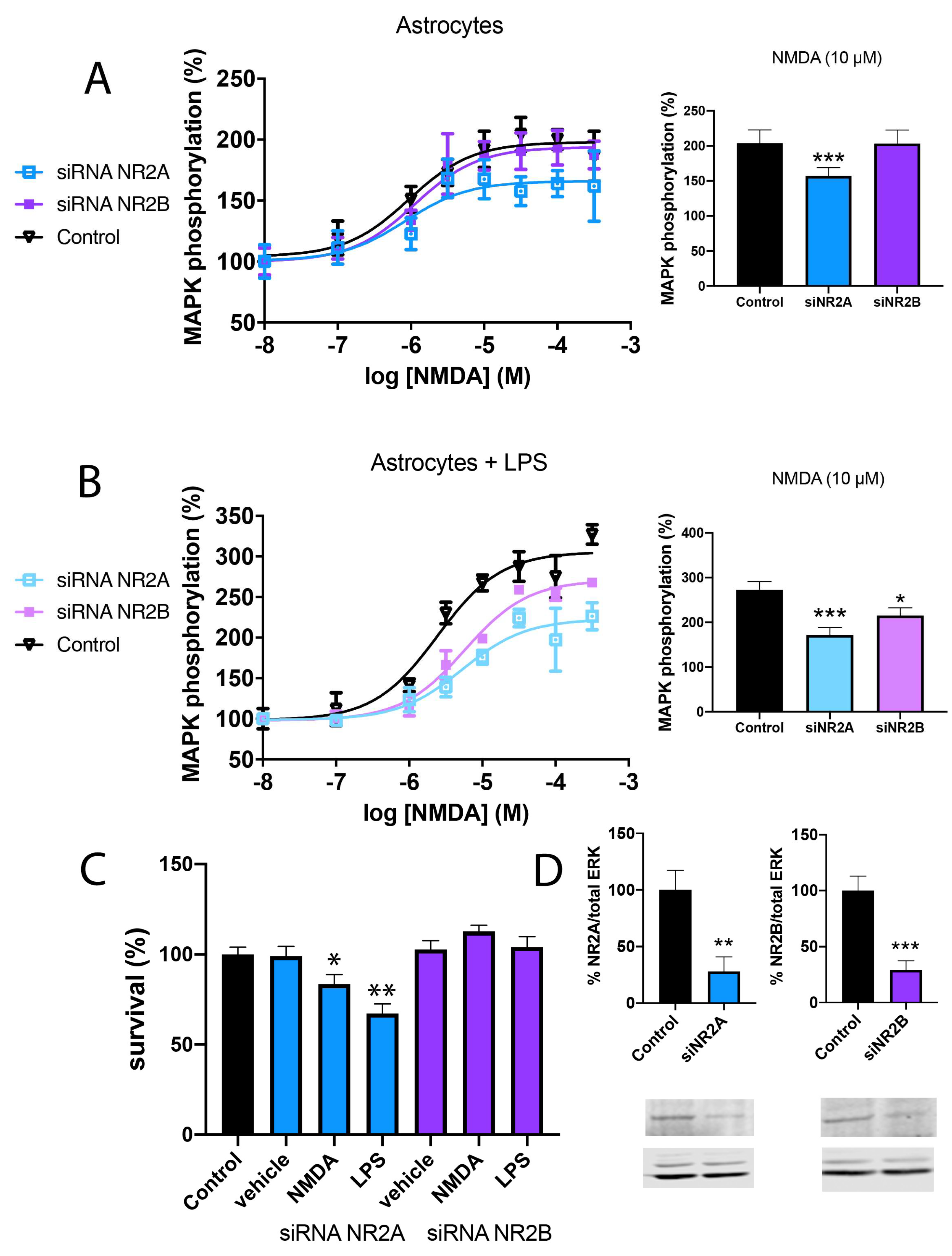
2.2. NMDA-Induced Toxicity in Astroglia Cells Is Due to NR2B-Containing NMDAR
2.3. NMDA-Induced Cytotoxicity Derives from Stimulation of NR2B-Containing NMDAR
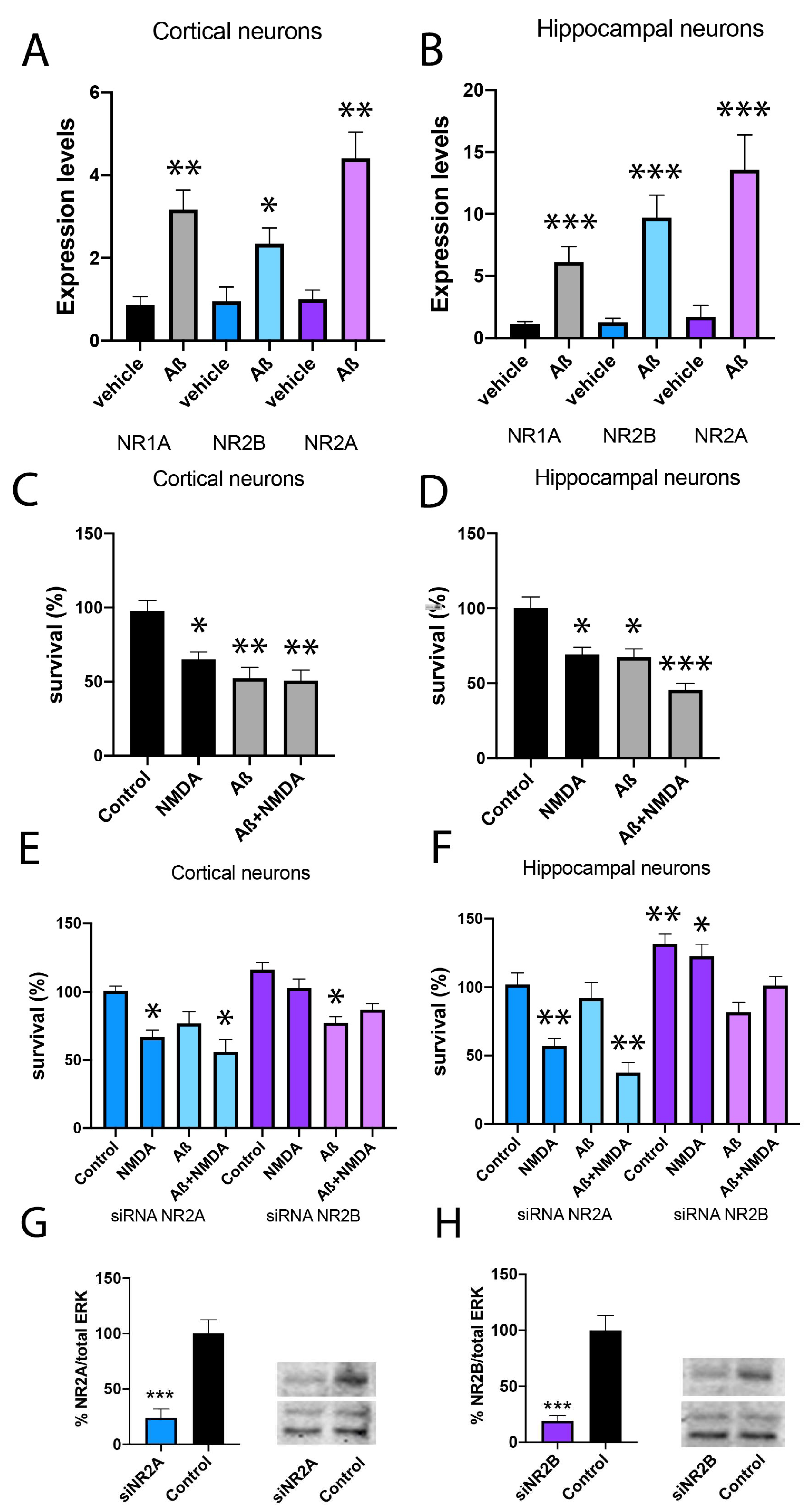
2.4. Aβ1-42 Treatment Potentiates NR2B-Containing NMDAR but Not NR2A-Containing NMDAR in Primary Neurons
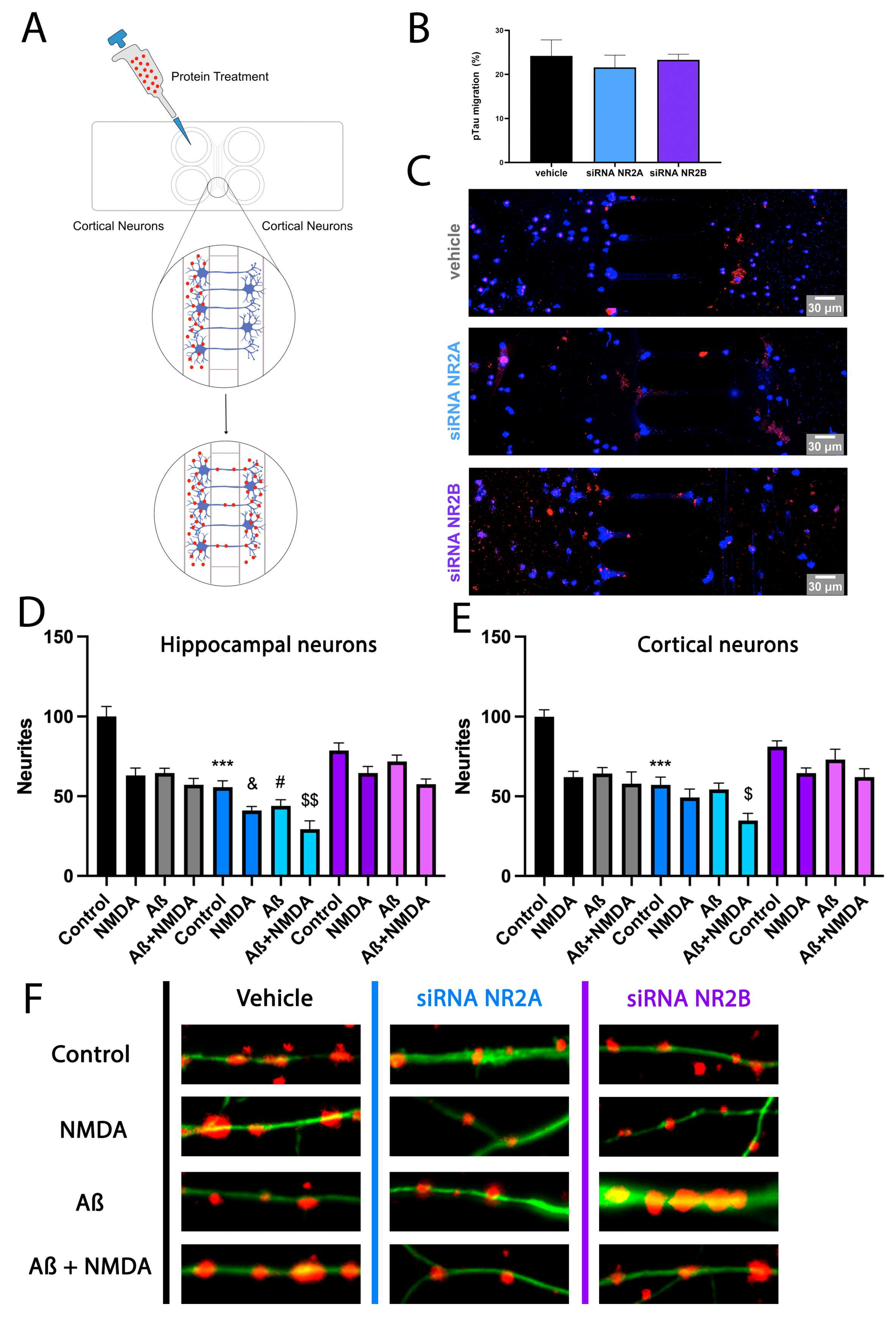
2.5. NMDAR Activation Does Not Affect Aβ1-42 Axonal Transport
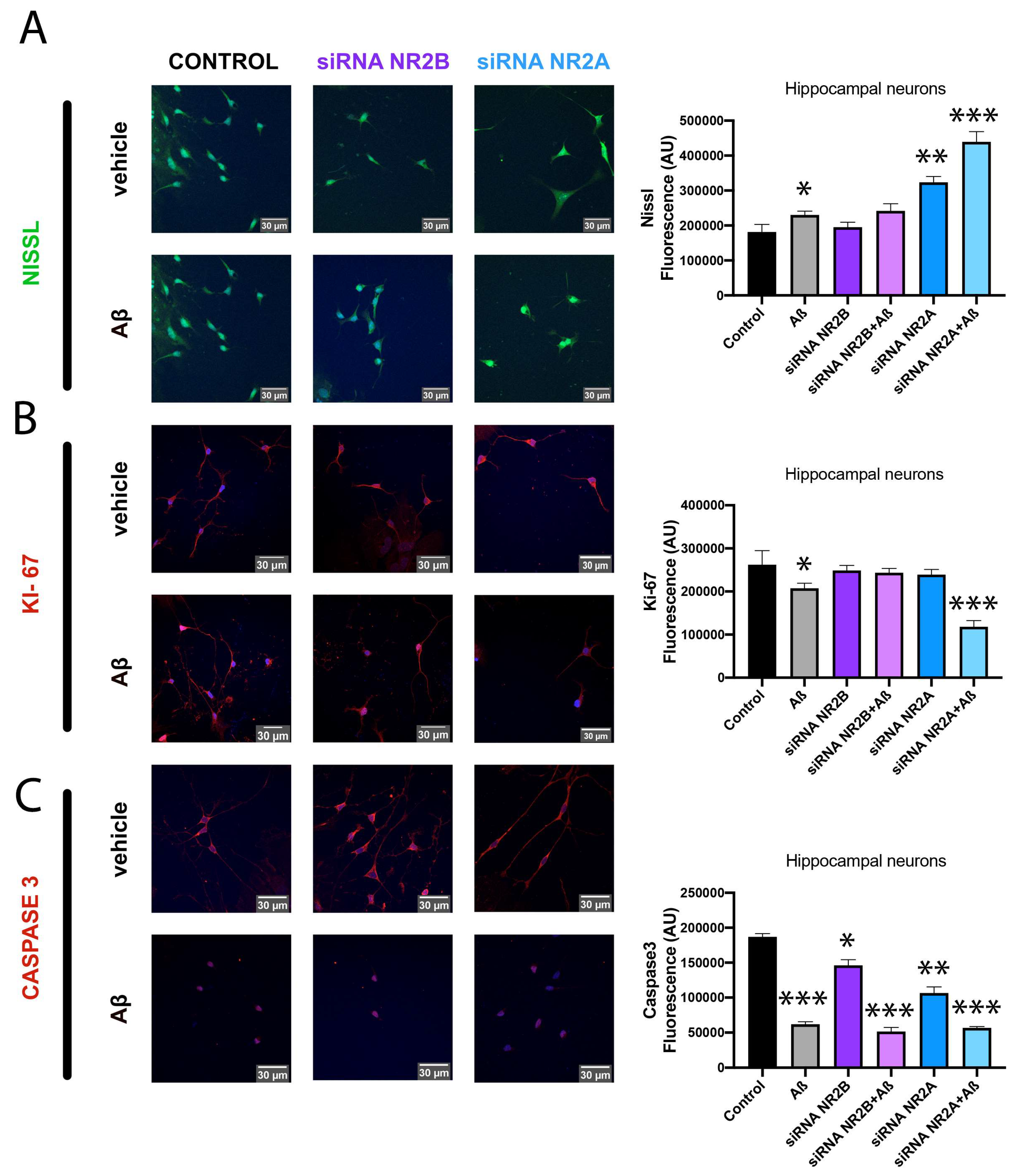
2.6. NR2A-Containing NMDAR Favours Neurite Formation in Comparison to NR2B-Containing NMDAR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Aβ-Oligomer Production
4.3. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.4. Primary Cultures
4.5. Knockdown of Endogenous NR2A or NR2B Subunits of NMDAR in Primary Cultures of Mice Neurons
4.6. Cell Viability
4.7. Detection of Cytoplasmic Calcium Levels
4.8. ERK Phosphorylation Assays
4.9. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
4.10. Immunocytochemistry
4.11. Microfluidics Assays of Tau Trafficking
4.12. Neurite Patterning Determination
4.13. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van der Flier, W.M.; de Vugt, M.E.; Smets, E.M.A.; Blom, M.; Teunissen, C.E. Towards a future where Alzheimer’s disease pathology is stopped before the onset of dementia. Nat. Aging 2023, 3, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, W. Mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes: At the crossroad between familiar and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Synapse 2021, 75, e22196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanzi, R.E. The Genetics of Alzheimer Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, C.; Gauthier, S.; Corbett, A.; Brayne, C.; Aarsland, D.; Jones, E. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2011, 377, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre, M.; Dewachter, I.; Rossner, S.; Bogdanovic, N.; Rosen, E.; Borghgraef, P.; Evert, B.O.; Dumitrescu-Ozimek, L.; Thal, D.R.; Landreth, G.; et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs repress β-secretase gene promoter activity by the activation of PPARγ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Hoeffer, C.A.; Wong, H.; Massaad, C.A.; Zhou, P.; Iadecola, C.; Murphy, M.P.; Pautler, R.G.; Klann, E. Amyloid β-Induced Impairments in Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity Are Rescued by Decreasing Mitochondrial Superoxide. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 5589–5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Yang, Y.; Song, S.S.; Na, J.-H.; Oh, K.J.; Jeong, C.; Yu, Y.G.; Shin, Y.-K. Beta-Amyloid Oligomers Activate Apoptotic BAK Pore for Cytochrome c Release. Biophys. J. 2014, 107, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudher, A.; Lovestone, S. Alzheimer’s disease–Do tauists and baptists finally shake hands? Trends Neurosci. 2002, 25, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zott, B.; Simon, M.M.; Hong, W.; Unger, F.; Chen-Engerer, H.-J.; Frosch, M.P.; Sakmann, B.; Walsh, D.M.; Konnerth, A. A vicious cycle of β amyloid–dependent neuronal hyperactivation. Science 2019, 365, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bading, H. Therapeutic targeting of the pathological triad of extrasynaptic NMDA receptor signaling in neurodegenerations. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardingham, G.E.; Bading, H. Synaptic versus extrasynaptic NMDA receptor signalling: Implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 682–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, M.P.; Raymond, L.A. Extrasynaptic NMDA Receptor Involvement in Central Nervous System Disorders. Neuron 2014, 82, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoletti, P.; Bellone, C.; Zhou, Q. NMDA receptor subunit diversity: Impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaFerla, F.M. Calcium dyshomeostasis and intracellular signalling in alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, T.; Sufian, M.A.; Uddin, S.; Begum, M.M.; Akhter, S.; Islam, A.; Mathew, B.; Islam, S.; Amran, S.; Ashraf, G.M. NMDA Receptor Antagonists: Repositioning of Memantine as a Multitargeting Agent for Alzheimer’s Therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 3506–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiei-Irannejad, V.; Abbaszadeh, S.; Janssen, P.M.L.; Soraya, H. Memantine and its benefits for cancer, cardiovascular and neurological disorders. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 910, 174455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grochowska, K.M.; Gomes, G.M.; Raman, R.; Kaushik, R.; Sosulina, L.; Kaneko, H.; Oelschlegel, A.M.; Yuanxiang, P.; Reyes-Resina, I.; Bayraktar, G.; et al. Jacob-induced transcriptional inactivation of CREB promotes Aβ-induced synapse loss in Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO J. 2023, 42, e112453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.G.; Zukin, R.S. NMDA receptor trafficking in synaptic plasticity and neuropsychiatric disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mony, L.; Kew, J.N.; Gunthorpe, M.J.; Paoletti, P. Allosteric modulators of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 1301–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traynelis, S.F.; Wollmuth, L.P.; McBain, C.J.; Menniti, F.S.; Vance, K.M.; Ogden, K.K.; Hansen, K.B.; Yuan, H.; Myers, S.J.; Dingledine, R. Glutamate Receptor Ion Channels: Structure, Regulation, and Function. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 405–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akazawa, C.; Shigemoto, R.; Bessho, Y.; Nakanishi, S.; Mizuno, N. Differential expression of five N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit mRNAs in the cerebellum of developing and adult rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 1994, 347, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monyer, H.; Burnashev, N.; Laurie, D.J.; Sakmann, B.; Seeburg, P.H. Developmental and regional expression in the rat brain and functional properties of four NMDA receptors. Neuron 1994, 12, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, M.; Cummings, J.; Roldan, L.A.; Jan, Y.N.; Jan, L.Y. Changing subunit composition of heteromeric NMDA receptors during development of rat cortex. Nature 1994, 368, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritschy, J.-M.; Weinmann, O.; Wenzel, A.; Benke, D. Synapse-specific localization of NMDA and GABAA receptor subunits revealed by antigen-retrieval immunohistochemistry. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998, 390, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Huguenard, J.R. Pathway-Specific Differences in Subunit Composition of Synaptic NMDA Receptors on Pyramidal Neurons in Neocortex. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10074–10083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladding, C.M.; Raymond, L.A. Mechanisms underlying NMDA receptor synaptic/extrasynaptic distribution and function. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2011, 48, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovar, K.R.; Westbrook, G.L. Mobile NMDA Receptors at Hippocampal Synapses. Neuron 2002, 34, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groc, L.; Heine, M.; Cousins, S.L.; Stephenson, F.A.; Lounis, B.; Cognet, L.; Choquet, D. NMDA receptor surface mobility depends on NR2A-2B subunits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18769–18774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prybylowski, K.; Fu, Z.; Losi, G.; Hawkins, L.M.; Luo, J.; Chang, K.; Wenthold, R.J.; Vicini, S. Relationship between Availability of NMDA Receptor Subunits and Their Expression at the Synapse. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 8902–8910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroebel, D.; Casado, M.; Paoletti, P. Triheteromeric NMDA receptors: From structure to synaptic physiology. Curr. Opin. Physiol. 2018, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.; Traynelis, S.F.; Hansen, K.B. Selective Cell-Surface Expression of Triheteromeric NMDA Receptors. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1677, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barco, A.; Alarcon, J.M.; Kandel, E.R. Expression of Constitutively Active CREB Protein Facilitates the Late Phase of Long-Term Potentiation by Enhancing Synaptic Capture. Cell 2002, 108, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlezon, W., Jr.; Duman, R.; Nestler, E. The many faces of CREB. Trends Neurosci. 2005, 28, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardingham, G.E.; Fukunaga, Y.; Bading, H. Extrasynaptic NMDARs oppose synaptic NMDARs by triggering CREB shut-off and cell death pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordji, K.; Becerril-Ortega, J.; Nicole, O.; Buisson, A. Activation of Extrasynaptic, But Not Synaptic, NMDA Receptors Modifies Amyloid Precursor Protein Expression Pattern and Increases Amyloid-β Production. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 15927–15942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinow, R. New developments on the role of NMDA receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2012, 22, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, E.M.; Nong, Y.; Almeida, C.G.; Paul, S.; Moran, T.; Choi, E.Y.; Nairn, A.C.; Salter, M.W.; Lombroso, P.J.; Gouras, G.K.; et al. Regulation of NMDA receptor trafficking by amyloid-β. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, B.R.; Reed, M.N.; Su, J.; Penrod, R.D.; Kotilinek, L.A.; Grant, M.K.; Pitstick, R.; Carlson, G.A.; Lanier, L.M.; Yuan, L.-L.; et al. Tau Mislocalization to Dendritic Spines Mediates Synaptic Dysfunction Independently of Neurodegeneration. Neuron 2010, 68, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönicke, R.; Mikhaylova, M.; Rönicke, S.; Meinhardt, J.; Schröder, U.H.; Fändrich, M.; Reiser, G.; Kreutz, M.R.; Reymann, K.G. Early neuronal dysfunction by amyloid β oligomers depends on activation of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 2219–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skowrońska, K.; Obara-Michlewska, M.; Zielińska, M.; Albrecht, J. NMDA Receptors in Astrocytes: In Search for Roles in Neurotransmission and Astrocytic Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grochowska, K.M.; Yuanxiang, P.; Bär, J.; Raman, R.; Brugal, G.; Sahu, G.; Schweizer, M.; Bikbaev, A.; Schilling, S.; Demuth, H.; et al. Posttranslational modification impact on the mechanism by which amyloid-β induces synaptic dysfunction. EMBO Rep. 2017, 18, 962–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskandari, E.; Eaves, C.J. Paradoxical roles of caspase-3 in regulating cell survival, proliferation, and tumorigenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2022, 221, e202201159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver-Rosen, M.S.; Serwer, P. Alzheimer’s Disease: A Molecular Model and Implied Path to Improved Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temido-Ferreira, M.; Ferreira, D.G.; Batalha, V.L.; Marques-Morgado, I.; Coelho, J.E.; Pereira, P.; Gomes, R.; Pinto, A.; Carvalho, S.; Canas, P.M.; et al. Age-related shift in LTD is dependent on neuronal adenosine A2A receptors interplay with mGluR5 and NMDA receptors. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 1876–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibault, O.; Hadley, R.; Landfield, P.W. Elevated Postsynaptic [Ca 2+ ] i and L-Type Calcium Channel Activity in Aged Hippocampal Neurons: Relationship to Impaired Synaptic Plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 9744–9756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombaugh, G.C.; Rowe, W.B.; Chow, A.R.; Michael, T.H.; Rose, G.M. Theta-Frequency Synaptic Potentiation in CA1 In Vitro Distinguishes Cognitively Impaired from Unimpaired Aged Fischer 344 Rats. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 9932–9940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A. NMDA Receptor Function During Senescence: Implication on Cognitive Performance. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameshwaran, K.; Dhanasekaran, M.; Suppiramaniam, V. Amyloid beta peptides and glutamatergic synaptic dysregulation. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 210, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.; Boehm, J.; Sato, C.; Iwatsubo, T.; Tomita, T.; Sisodia, S.; Malinow, R. AMPAR Removal Underlies Aβ-Induced Synaptic Depression and Dendritic Spine Loss. Neuron 2006, 52, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Hong, S.; Shepardson, N.E.; Walsh, D.M.; Shankar, G.M.; Selkoe, D. Soluble Oligomers of Amyloid β Protein Facilitate Hippocampal Long-Term Depression by Disrupting Neuronal Glutamate Uptake. Neuron 2009, 62, 788–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, D.M.; Klyubin, I.; Fadeeva, J.V.; Cullen, W.K.; Anwyl, R.; Wolfe, M.S.; Rowan, M.J.; Selkoe, D.J. Naturally secreted oligomers of amyloid β protein potently inhibit hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo. Nature 2002, 416, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamenetz, F.; Tomita, T.; Hsieh, H.; Seabrook, G.; Borchelt, D.; Iwatsubo, T.; Sisodia, S.; Malinow, R. APP Processing and Synaptic Function. Neuron 2003, 37, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Yamamoto, F.; Amano, A.; Tamaoka, A.; Sanjo, N.; Yokota, T.; Kametani, F.; Araki, W. Amyloid-β oligomers interact with NMDA receptors containing GluN2B subunits and metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 in primary cortical neurons: Relevance to the synapse pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Res. 2022, 180, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, E.; Juhász, G.; Bozsó, Z.; Penke, B.; Fülöp, L.; Szegedi, V. Abeta(1–42) Enhances Neuronal Excitability in the CA1 via NR2B Subunit-Containing NMDA Receptors. Neural Plast. 2014, 2014, 584314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Rosenke, R.; Kronemann, D.; Brim, B.; Das, S.R.; Dunah, A.W.; Magnusson, K.R. The effects of aging on N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunits in the synaptic membrane and relationships to long-term spatial memory. Neuroscience 2009, 162, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, I.L.; Bajouco, L.M.; Mota, S.I.; Auberson, Y.P.; Oliveira, C.R.; Rego, A.C. Amyloid beta peptide 1–42 disturbs intracellular calcium homeostasis through activation of GluN2B-containing N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors in cortical cultures. Cell Calcium 2012, 51, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I.L.; Ferreiro, E.; Schmidt, J.; Cardoso, J.M.; Pereira, C.M.F.; Carvalho, A.L.; Oliveira, C.R.; Rego, A.C. Aβ and NMDAR activation cause mitochondrial dysfunction involving ER calcium release. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, C.; Chen, W.; Kang, Y.; Liu, W.; Qiu, Z.; Hayashi, T.; Mizuno, K.; Hattori, S.; Fujisaki, H.; et al. Inhibition of GluN2B pathway is involved in the neuroprotective effect of silibinin on streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer’s disease models. Phytomedicine 2023, 109, 154594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tackenberg, C.; Grinschgl, S.; Trutzel, A.; Santuccione, A.C.; Frey, M.C.; Konietzko, U.; Grimm, J.; Brandt, R.; Nitsch, R.M. NMDA receptor subunit composition determines beta-amyloid-induced neurodegeneration and synaptic loss. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, K.M.; Sheng, M. NMDA receptors and BAX are essential for Aβ impairment of LTP. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammes, G.; Hasenjäger, A.; Sroka-Saidi, K.; Deussing, J.M.; Parsons, C.G. Therapeutic significance of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors and mGluR5 metabotropic glutamate receptors in mediating the synaptotoxic effects of β-amyloid oligomers on long-term potentiation (LTP) in murine hippocampal slices. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.-W.; Klyubin, I.; Anwyl, R.; Rowan, M.J. GluN2B subunit-containing NMDA receptor antagonists prevent Aβ-mediated synaptic plasticity disruption in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20504–20509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Jin, M.; Koeglsperger, T.; Shepardson, N.E.; Shankar, G.M.; Selkoe, D.J. Soluble Aβ Oligomers Inhibit Long-Term Potentiation through a Mechanism Involving Excessive Activation of Extrasynaptic NR2B-Containing NMDA Receptors. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 6627–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chang, L.; Roselli, F.; Almeida, O.F.X.; Gao, X.; Wang, X.; Yew, D.T.; Wu, Y. Amyloid-β Induces Caspase-Dependent Loss of PSD-95 and Synaptophysin Through NMDA Receptors. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 22, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.-D.; Sun, K.; Hu, R.; Liu, X.-Y.; Hu, Q.-M.; Sun, X.-Y.; Yao, B.; Sun, N.; Hao, J.-R.; Wei, P.; et al. Blocking the Interaction between EphB2 and ADDLs by a Small Peptide Rescues Impaired Synaptic Plasticity and Memory Deficits in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 11959–11973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayordomo-Cava, J.; Yajeya, J.; Navarro-López, J.D.; Jiménez-Díaz, L. Amyloid-β(25–35) Modulates the Expression of GirK and KCNQ Channel Genes in the Hippocampus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoey, S.E.; Williams, R.J.; Perkinton, M.S. Synaptic NMDA Receptor Activation Stimulates α-Secretase Amyloid Precursor Protein Processing and Inhibits Amyloid-β Production. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 4442–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.E.; Ma, K.; Elstrott, J.; Weber, M.; Saillet, S.; Khan, A.S.; Simms, J.; Liu, B.; Kim, T.A.; Yu, G.-Q.; et al. GluN2A NMDA Receptor Enhancement Improves Brain Oscillations, Synchrony, and Cognitive Functions in Dravet Syndrome and Alzheimer’s Disease Models. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 381–396.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, R.; Aguinaga, D.; Reyes, I.; Canela, E.I.; Lillo, J.; Tarutani, A.; Hasegawa, M.; del Ser-Badia, A.; del Rio, J.A.; Kreutz, M.R.; et al. N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Link to the MAP Kinase Pathway in Cortical and Hippocampal Neurons and Microglia Is Dependent on Calcium Sensors and Is Blocked by α-Synuclein, Tau, and Phospho-Tau in Non-transgenic and Transgenic APPSw, Ind Mice. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, G.; Aguinaga, D.; Moreno, E.; Hradsky, J.; Reddy, P.P.; Cortés, A.; Mallol, J.; Casadó, V.; Mikhaylova, M.; Kreutz, M.R.; et al. Intracellular Calcium Levels Determine Differential Modulation of Allosteric Interactions within G Protein-Coupled Receptor Heteromers. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas-Santisteban, R.; Raïch, I.; Aguinaga, D.; Saura, C.A.; Franco, R.; Navarro, G. The Expression of Cellular Prion Protein, PrPC, Favors pTau Propagation and Blocks NMDAR Signaling in Primary Cortical Neurons. Cells 2023, 12, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raïch, I.; Lillo, J.; Rebassa, J.B.; Capó, T.; Cordomí, A.; Reyes-Resina, I.; Pallàs, M.; Navarro, G. Dual Role of NMDAR Containing NR2A and NR2B Subunits in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094757
Raïch I, Lillo J, Rebassa JB, Capó T, Cordomí A, Reyes-Resina I, Pallàs M, Navarro G. Dual Role of NMDAR Containing NR2A and NR2B Subunits in Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(9):4757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094757
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaïch, Iu, Jaume Lillo, Joan Biel Rebassa, Toni Capó, Arnau Cordomí, Irene Reyes-Resina, Mercè Pallàs, and Gemma Navarro. 2024. "Dual Role of NMDAR Containing NR2A and NR2B Subunits in Alzheimer’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 9: 4757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094757





