Immunomodulatory Aspects of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange in Neurological Disorders—A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study Population
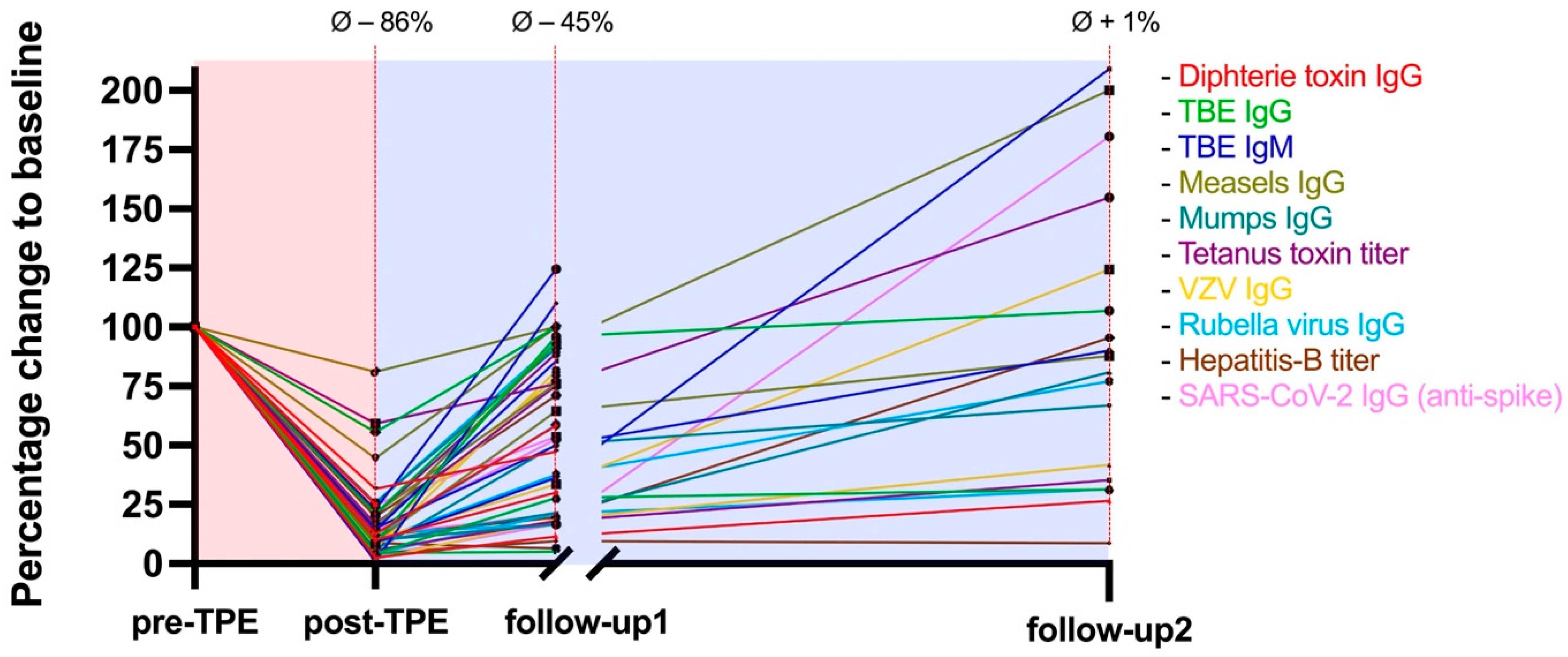
2.2. Washout of Pathogen-Specific Antibodies
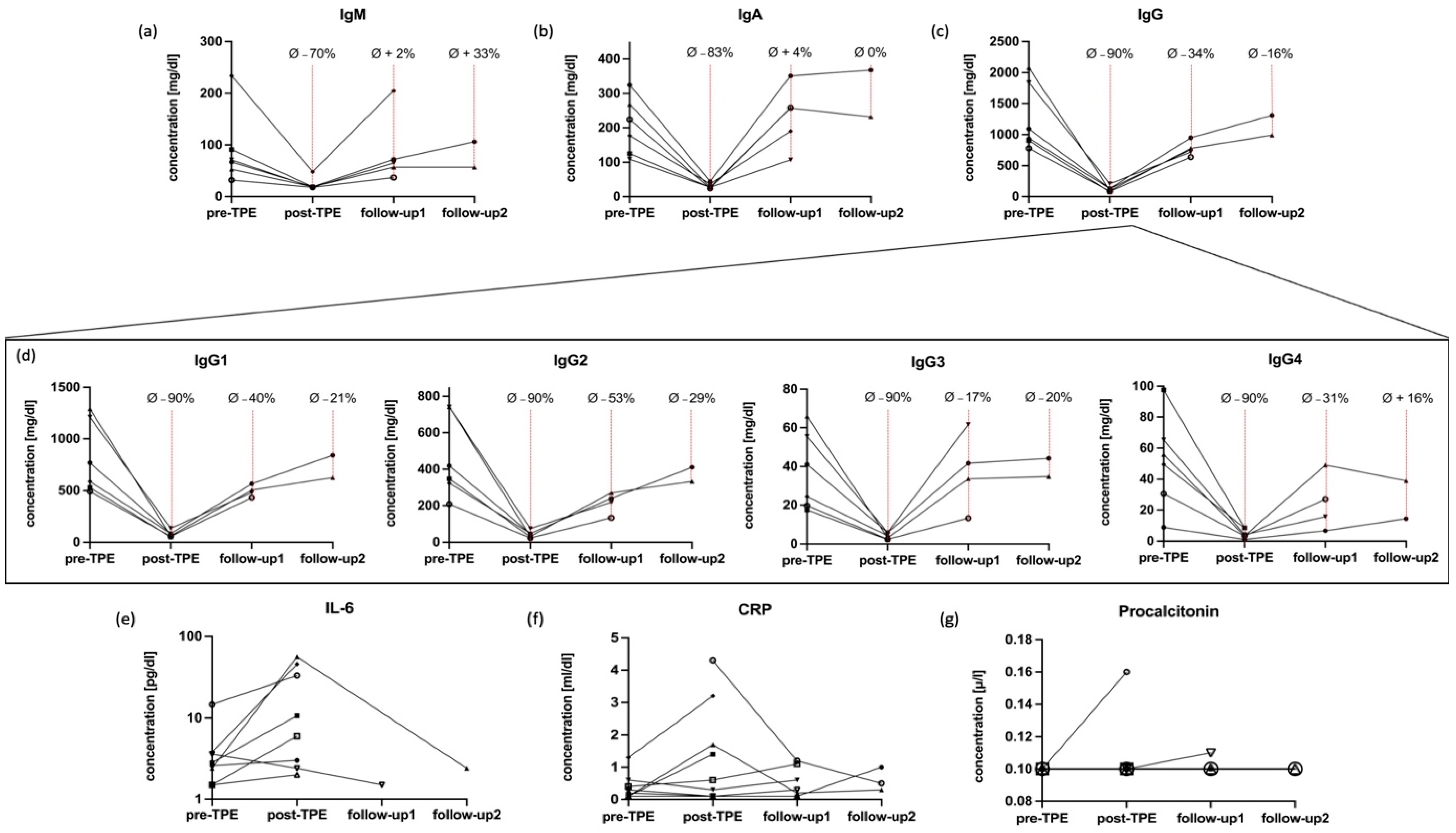
2.3. Dynamics of Immunoglobulins
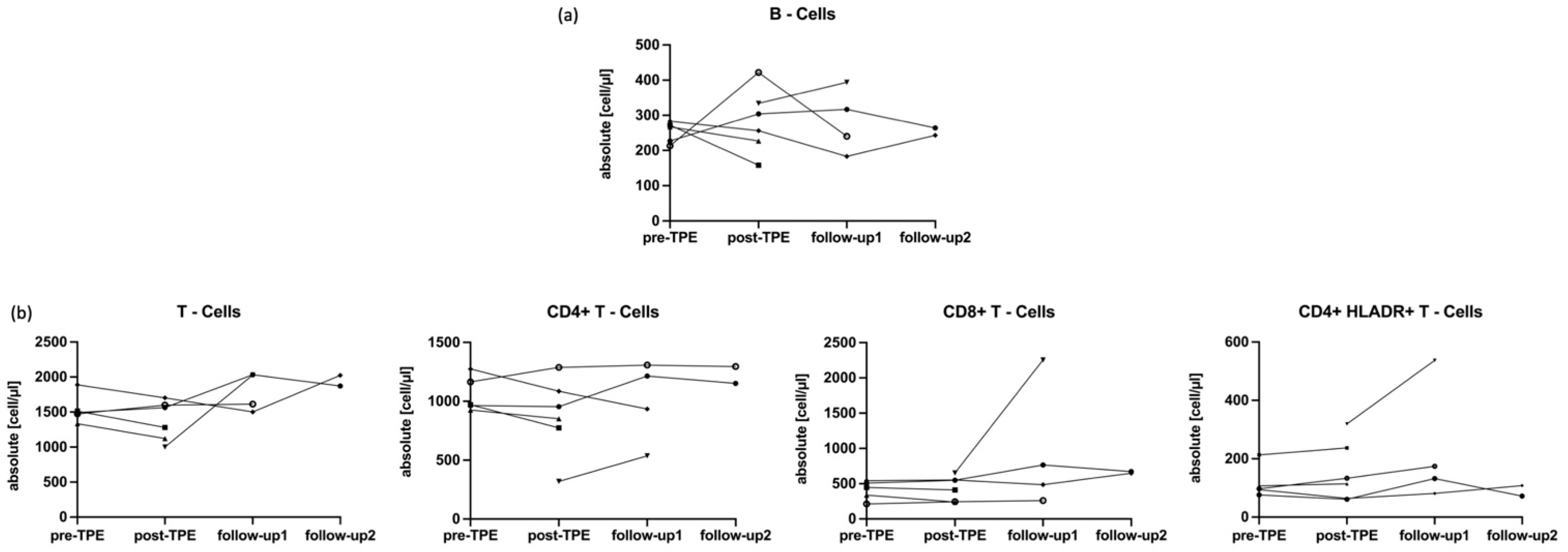
2.4. Impact of TPE on IL-6 and CRP and Main Lymphocytes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population and Recruitment
4.2. Therapeutic Plasma Exchange
4.3. Sample Collection and Laboratory Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Time | Cut Off | Kit | Manufacturer | Instrument | Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measles | >150 mIU/mL | Anti-Masern ELISA (IgG) | Euroimmun (Luebeck, Germany) | Euroimmun Analyzer I | ELISA |
| Mumps | >1:231 | Anti-Mumps ELISA (IgG) | Euroimmun (Luebeck, Germany) | Euroimmun Analyzer I | ELISA |
| VZV | >50 mIU/mL | Anti-VZV ELISA (IgG) | Euroimmun (Luebeck, Germany) | Euroimmun Analyzer I | ELISA |
| Rubella | >5 IU/mL | Alinity Rubella IgG assay | Abbott Diagnostics (Abbott Park, IL, USA) | Architect i2000SR | CMIA |
| Hepatitis B | >100 U/L | Alinity Anti-HBs assay | Abbott Diagnostics (Abbott Park, IL, USA) | Architect i2000SR | CMIA |
| Diphtheria | >0.01 U/mL | Anti-Diphteria Toxin ELISA (IgG) | Euroimmun (Luebeck, Germany) | Euroimmun Analyzer I | ELISA |
| Measles | >150 mIU/mL | Anti-Masern ELISA (IgG) | Euroimmun (Luebeck, Germany) | Euroimmun Analyzer I | ELISA |
| SARS-CoV-2 | >7 BAU/mL | Anti-SARS-CoV 2 (IgG) | Abbott Diagnostics (Abbott Park, IL, USA) | Architect i2000SR | CMIA |
References
- Pruss, H. Autoantibodies in neurological disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 798–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagavati, S. Autoimmune Disorders of the Nervous System: Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, and Therapy. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 664664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, S.; Mazibrada, G.; Irani, S.R.; Jacob, A.; Yudina, A. The Role of Plasma Exchange in the Treatment of Refractory Autoimmune Neurological Diseases: A Narrative Review. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021, 16, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortese, I.; Chaudhry, V.; So, Y.T.; Cantor, F.; Cornblath, D.R.; Rae-Grant, A. Evidence-based guideline update: Plasmapheresis in neurologic disorders: Report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2011, 76, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chevret, S.; Hughes, R.A.; Annane, D. Plasma exchange for Guillain-Barre syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2, CD001798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, T.; Harutyunyan, G.; Karamyan, A.; Otto, F.; Bacher, C.; Chroust, V.; Leitinger, M.; Novak, H.F.; Trinka, E.; Sellner, J. Therapeutic Plasma Exchange in Multiple Sclerosis and Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Comparative Study of Indication, Efficacy and Safety. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moser, T.; Akgün, K.; Proschmann, U.; Sellner, J.; Ziemssen, T. The role of TH17 cells in multiple sclerosis: Therapeutic implications. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dau, P.C. Immunologic rebound. J. Clin. Apher. 1995, 10, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystryn, J.C.; Graf, M.W.; Uhr, J.W. Regulation of antibody formation by serum antibody. II. Removal of specific antibody by means of exchange transfusion. J. Exp. Med. 1970, 132, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derksen, R.H.; Schuurman, H.J.; Meyling, F.H.G.; Struyvenberg, A.; Kater, L. Rebound and overshoot after plasma exchange in humans. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1984, 104, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-H.; Kim, W.; Huh, S.-Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Jung, I.J.; Kim, H.J. Clinical efficacy of plasmapheresis in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder and effects on circulating anti-aquaporin-4 antibody levels. J. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 9, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guptill, J.T.; Juel, V.C.; Massey, J.M.; Anderson, A.C.; Chopra, M.; Yi, J.S.; Esfandiari, E.; Buchanan, T.; Smith, B.; Atherfold, P.; et al. Effect of therapeutic plasma exchange on immunoglobulins in myasthenia gravis. Autoimmunity 2016, 49, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- James, L.K. B cells defined by immunoglobulin isotypes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 210, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, R.J.; Churchill, W.H. Therapeutic Plasma Exchange. In Office Practice of Neurology; Office Practice of Neurology: London, UK, 2003; pp. 238–243. [Google Scholar]
- Fujihara, K.; Bennett, J.L.; de Seze, J.; Haramura, M.; Kleiter, I.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Kang, D.; Mughal, T.; Yamamura, T. Interleukin-6 in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder pathophysiology. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciron, J.; Audoin, B.; Bourre, B.; Brassat, D.; Durand-Dubief, F.; Laplaud, D.; Maillart, E.; Papeix, C.; Vukusic, S.; Zephir, H.; et al. Recommendations for the use of Rituximab in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 174, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damato, V.; Theorell, J.; Al-Diwani, A.; Kienzler, A.-K.; Makuch, M.; Sun, B.; Handel, A.; Akdeniz, D.; Berretta, A.; Ramanathan, S.; et al. Rituximab abrogates aquaporin-4-specific germinal center activity in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2121804119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, T.; O’Sullivan, C.; Otto, F.; Hitzl, W.; Pilz, G.; Schwenker, K.; Mrazek, C.; Haschke-Becher, E.; Trinka, E.; Wipfler, P.; et al. Long-term immunological consequences of anti-CD20 therapies on humoral responses to COVID-19 vaccines in multiple sclerosis: An observational study. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2022, 15, 17562864221092092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, T.; Otto, F.; O’Sullivan, C.; Hitzl, W.; Pilz, G.; Harrer, A.; Trinka, E.; Wipfler, P. Recall response to COVID-19 antigen is preserved in people with multiple sclerosis on anti-CD20 medications—A pilot study. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 59, 103560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feige, J.; Berek, K.; Seiberl, M.; Hilpold, P.; Hitzl, W.; Di Pauli, F.; Hegen, H.; Deisenhammer, F.; Trinka, E.; Harrer, A.; et al. Humoral Response to SARS-CoV-2 Antigen in Patients Treated with Monoclonal Anti-CD20 Antibodies: It Is Not All about B Cell Recovery. Neurol. Int. 2022, 14, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ontaneda, D.; Rae-Grant, A.D. Management of acute exacerbations in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2009, 12, 264–272. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.H.; Rempe, T.; Whitmire, N.; Dunn-Pirio, A.; Graves, J.S. Therapeutic Advances in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 824926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.; Marta, M.; Pryce, G.; Giovannoni, G.; Schmierer, K. Memory B Cells are Major Targets for Effective Immunotherapy in Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis. EBioMedicine 2017, 16, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Höftberger, R.; Lassmann, H.; Berger, T.; Reindl, M. Pathogenic autoantibodies in multiple sclerosis—From a simple idea to a complex concept. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 18, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stork, L.; Ellenberger, D.; Beißbarth, T.; Friede, T.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Brück, W.; Metz, I. Differences in the Reponses to Apheresis Therapy of Patients With 3 Histopathologically Classified Immunopathological Patterns of Multiple Sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, I.; Ribeiro, J.J.; Isidoro, L.; Batista, S.; Nunes, C.; Macário, C.; Borges, C.; Tomaz, J.; Sousa, L. Plasma exchange in severe acute relapses of multiple sclerosis—Results from a Portuguese cohort. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2018, 19, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, T.; Hoepner, L.; Schwenker, K.; Seiberl, M.; Feige, J.; Akgün, K.; Haschke-Becher, E.; Ziemssen, T.; Sellner, J. Cladribine Alters Immune Cell Surface Molecules for Adhesion and Costimulation: Further Insights to the Mode of Action in Multiple Sclerosis. Cells 2021, 10, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudick, R.A.; Sandrock, A. Natalizumab: Alpha 4-integrin antagonist selective adhesion molecule inhibitors for MS. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2004, 4, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesař, V.; Jelínková, E.; Mašek, Z.; Jirsa, M., Jr.; Žabka, J.; Bartůňková, J.; Stejskalová, A.; Janatková, I.; Zima, T. Influence of plasma exchange on serum levels of cytokines and adhesion molecules in ANCA-positive renal vasculitis. Blood Purif. 1998, 16, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.H.; Wang, S.H.; Chien, P.J.; Shih, C.M.; Chiu, H.C. Changes in serum cytokine levels during plasmapheresis in patients with myasthenia gravis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2009, 16, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatmadar, S.; Nassiri, M.; Vincek, V. Effect of plasma exchange on cytokines measured by multianalyte bead array in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am. J. Hematol. 2005, 79, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chu, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; George, J.; Young, H.A.; Liu, G. Cytokines: From Clinical Significance to Quantification. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2004433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, A.; Connelly-Smith, L.; Aqui, N.; Balogun, R.A.; Klingel, R.; Meyer, E.; Pham, H.P.; Schneiderman, J.; Witt, V.; Wu, Y.; et al. Guidelines on the Use of Therapeutic Apheresis in Clinical Practice—Evidence-Based Approach from the Writing Committee of the American Society for Apheresis: The Eighth Special Issue. J. Clin. Apher. 2019, 34, 171–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age in Years, Median (IQR) | 53 (36–72) |
|---|---|
| Female, n (%) | 3 (30) |
| Caucasian, n (%) | 10 (100) |
| Neurologic disorders: | |
| Steroid-refractory ON, n (%) | 3 (30) |
| CIDP, n (%) | 2 (20) |
| GBS, n (%) | 2 (20) |
| NMDARE, n (%) | 1 (10) |
| MG, n (%) | 1 (10) |
| ADEM, n (%) | 1 (10) |
| Number of TPE cycles: | |
| 5 | 8 |
| 4 | 1 * |
| 3 | 1 ** |
| Average time of symptom onset or relapse to TPE, in days (SD) | 22 (±15) |
| Patients with steroid therapy prior to TPE, n (%): | 6 (60) |
| Average time of steroid therapy to TPE, in days (SD) | 6 (±5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Foettinger, F.; Pilz, G.; Wipfler, P.; Harrer, A.; Kern, J.M.; Trinka, E.; Moser, T. Immunomodulatory Aspects of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange in Neurological Disorders—A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076552
Foettinger F, Pilz G, Wipfler P, Harrer A, Kern JM, Trinka E, Moser T. Immunomodulatory Aspects of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange in Neurological Disorders—A Pilot Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(7):6552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076552
Chicago/Turabian StyleFoettinger, Fabian, Georg Pilz, Peter Wipfler, Andrea Harrer, Jan Marco Kern, Eugen Trinka, and Tobias Moser. 2023. "Immunomodulatory Aspects of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange in Neurological Disorders—A Pilot Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 7: 6552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076552






