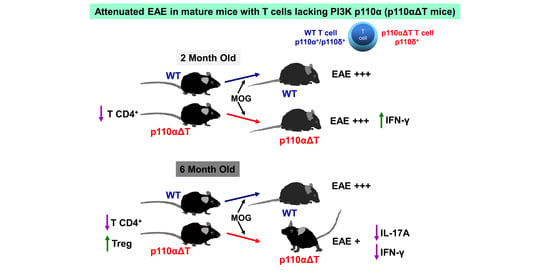
PI3-Kinase p110α Deficiency Modulates T Cell Homeostasis and Function and Attenuates Experimental Allergic Encephalitis in Mature Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Altered Cell Populations in Secondary Lymphoid Organs from Mice with PI3-K p110α-Deficient T Cells
2.2. Development of Experimental Allergic Encephalitis in Young and Mature p110αΔT Mice
2.3. Cytokine Production by Lymph Node Cells from Young and Mature MOG-Immunized Mice
2.4. Early Anti-MOG Responses in Mature p110αΔT Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. EAE Induction and Measurement
4.3. Antigen Activation Ex Vivo
4.4. CD4+ T Cell Isolation and Activation
4.5. Cytokine Determination
4.6. Antibodies
4.7. Flow Cytometry
4.8. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dendrou, C.A.; Fugger, L.; Friese, M.A. Immunopathology of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baecher-Allan, C.; Kaskow, B.J.; Weiner, H.L. Multiple Sclerosis: Mechanisms and immunotherapy. Neuron 2018, 97, 742–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Procaccini, C.; De Rosa, V.; Pucino, V.; Formisano, L.; Matarese, G. Animal models of Multiple Sclerosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 759, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.A.; Roqué, P.J.; Goverman, J.M. Pathogenic T cell cytokines in multiple sclerosis. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petermann, F.; Korn, T. Cytokines and effector T cell subsets causing autoimmune CNS disease. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 3747–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGeachy, M.J.; Stephens, L.A.; Anderton, S.M. Natural recovery and protection from Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis: Contribution of CD4+CD25+ regulatory cells within the central nervous system. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 3025–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Reddy, J.; Ochi, H.; Frenkel, D.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Weiner, H.L. Recovery from experimental allergic encephalomyelitis is TGF-β dependent and associated with increases in CD4+LAP+ and CD4+CD25+ T cells. Int. Immunol. 2006, 18, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileiadis, G.K.; Dardiotis, E.; Mavropoulos, A.; Tsouris, Z.; Tsimourtou, V.; Bogdanos, D.P.; Sakkas, L.I.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M. Regulatory B and T lymphocytes in multiple sclerosis: Friends or foes? Auto. Immun. Highlights 2018, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, A.C.; Reddy, J.; Nazareno, R.; Sobel, R.A.; Nicholson, L.B.; Kuchroo, V.K. IL-10 plays an important role in the homeostatic regulation of the autoreactive repertoire in naive mice. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greve, B.; Vijayakrishnan, L.; Kubal, A.; Sobel, R.A.; Peterson, L.B.; Wicker, L.S.; Kuchroo, V.K. The diabetes susceptibility locus Idd5.1 on mouse chromosome 1 regulates ICOS expression and modulates murine Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyamoto, K.; Kingsley, C.I.; Zhang, X.; Jabs, C.; Izikson, L.; Sobel, R.A.; Weiner, H.L.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Sharpe, A.H. The ICOS molecule plays a crucial role in the development of mucosal tolerance. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 7341–7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzgerald, D.C.; Zhang, G.-X.; El-Behi, M.; Fonseca-Kelly, Z.; Li, H.; Yu, S.; Saris, C.J.; Gran, B.; Ciric, B.; Rostami, A. Suppression of autoimmune inflammation of the central nervous system by interleukin 10 secreted by interleukin 27-stimulated T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pot, C.; Jin, H.; Awasthi, A.; Liu, S.M.; Lai, C.-Y.; Madan, R.; Sharpe, A.H.; Karp, C.L.; Miaw, S.-C.; Ho, I.C.; et al. IL-27 induces the transcription factor c-Maf, cytokine IL-21, and the costimulatory receptor ICOS that coordinately act together to promote differentiation of IL-10-producing Tr1 cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojo, J.M.; Pini, E.; Ojeda, G.; Bello, R.; Dong, C.; Flavell, R.A.; Dianzani, U.; Portoles, P. CD4+ICOS+ T lymphocytes inhibit T cell activation ‘in vitro’ and attenuate autoimmune encephalitis ‘in vivo’. Int. Immunol. 2008, 20, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adefemi, F.; Fruman, D.A.; Marshall, A.J. A case for Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase–targeted therapy for infectious disease. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 3237–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, A.-K.; Sriskantharajah, S.; Hessel, E.M.; Okkenhaug, K. PI3K inhibitors in inflammation, autoimmunity and cancer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 23, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banham-Hall, E.; Clatworthy, M.R.; Okkenhaug, K. The therapeutic potential for PI3K inhibitors in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Open Rheumatol. J. 2012, 6, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Guillermet-Guibert, J.; Graupera, M.; Bilanges, B. The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 11, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Sauer, K. Lipid signaling in T-cell development and function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a002428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fruman, D.A.; Bismuth, G. Fine tuning the immune response with PI3K. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 228, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommel, C.; Camps, M.; Ji, H. PI3Kδ and PI3Kγ: Partners in crime in inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis and beyond? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, J.A.; Fruman, D.A. Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase: Diverse roles in immune cell activation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 563–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyasu, S. The role of PI3K in immune cells. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okkenhaug, K.; Patton, D.T.; Bilancio, A.; Garcon, F.; Rowan, W.C.; Vanhaesebroeck, B. The p110δ isoform of Phosphoinositide 3-kinase controls clonal expansion and differentiation of Th cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 5122–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, H.; Rintelen, F.; Waltzinger, C.; Bertschy Meier, D.; Bilancio, A.; Pearce, W.; Hirsch, E.; Wymann, M.P.; Ruckle, T.; Camps, M.; et al. Inactivation of PI3Kγ and PI3Kδ distorts T-cell development and causes multiple organ inflammation. Blood 2007, 110, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, T.; Marshall, A.J.; Okkenhaug, K.; Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Uzonna, J.E. The p110δ isoform of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase controls susceptibility to Leishmania major by regulating expansion and tissue homing of regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 1921–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Utsugi, M.; Dobashi, K.; Ono, A.; Ishizuka, T.; Matsuzaki, S.-i.; Hisada, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Kawata, T.; Aoki, H.; Kamide, Y.; et al. PI3K p110β positively regulates Lipopolysaccharide-induced IL-12 production in human macrophages and dendritic cells and JNK1 plays a novel role. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5225–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haylock-Jacobs, S.; Comerford, I.; Bunting, M.; Kara, E.; Townley, S.; Klingler-Hoffmann, M.; Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Puri, K.D.; McColl, S.R. PI3Kδ drives the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhibiting effector T cell apoptosis and promoting Th17 differentiation. J. Autoimmun. 2011, 36, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, E.C.; Kobayashi, T.; Russo, S.M.; Sheikh, S.Z.; Gipson, G.R.; Kennedy, S.T.; Uno, J.K.; Mishima, Y.; Borst, L.B.; Liu, B.; et al. Innate PI3K p110δ regulates Th1/Th17 development and microbiota-dependent colitis. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3958–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aragoneses-Fenoll, L.; Montes-Casado, M.; Ojeda, G.; Acosta, Y.Y.; Herranz, J.; Martínez, S.; Blanco-Aparicio, C.; Criado, G.; Pastor, J.; Dianzani, U.; et al. ETP-46321, a dual p110α/δ class IA phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor modulates T lymphocyte activation and collagen-induced arthritis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 106, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aragoneses-Fenoll, L.; Ojeda, G.; Montes-Casado, M.; Acosta-Ampudia, Y.; Dianzani, U.; Portolés, P.; Rojo, J.M. T-cell specific loss of the PI-3 kinase p110α catalytic subunit results in enhanced cytokine production and anti tumor response. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, e332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Zheng, N.; Sun, L.; Pang, G.; Wang, S.; Jia, P.; Uzonna, J.; Bai, H.; Yang, X. The p110δ Isoform of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase plays an important role in host defense against Chlamydial lung infection through influencing CD4+ T cell function. Pathog. Dis. 2018, 76, fty053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Chen, X.; Wei, Z.; Xiao, J.; Chen, W.; Shang, Y.; Liu, J. Targeting the class IA PI3K isoforms p110α/δ attenuates heart allograft rejection in mice by suppressing the CD4+ T lymphocyte response. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, D.T.; Garden, O.A.; Pearce, W.P.; Clough, L.E.; Monk, C.R.; Leung, E.; Rowan, W.C.; Sancho, S.; Walker, L.S.K.; Vanhaesebroeck, B.; et al. Cutting edge: The phosphoinositide 3-kinase p110δ is critical for the function of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 6598–6602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, K.; Soond, D.R.; Pineiro, R.; Hagemann, T.; Pearce, W.; Lim, E.L.; Bouabe, H.; Scudamore, C.L.; Hancox, T.; Maecker, H.; et al. Inactivation of PI(3)K p110δ breaks regulatory T-cell-mediated immune tolerance to cancer. Nature 2014, 510, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, E.L.; Cugliandolo, F.M.; Rosner, D.R.; Gyori, D.; Roychoudhuri, R.; Okkenhaug, K. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase δ inhibition promotes antitumor responses but antagonizes checkpoint inhibitors. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e120626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellappa, S.; Kushekhar, K.; Munthe, L.A.; Tjønnfjord, G.E.; Aandahl, E.M.; Okkenhaug, K.; Taskén, K. The PI3K p110δ isoform inhibitor Idelalisib preferentially inhibits human regulatory T cell function. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.S.; Dominik, A.; Christopher, A.L.; Krishnendu, C.; Jonathan, C.; Sumeet, P.; Karin, R.E.; Rui, C.; Athena, C.; Yuchun, D.; et al. Immunodeficiency, autoimmune thrombocytopenia and enterocolitis caused by autosomal recessive deficiency of PIK3CD-encoded phosphoinositide 3-kinase δ. Haematologica 2019, 104, e483–e486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stark, A.-K.; Davenport, E.C.M.; Patton, D.T.; Scudamore, C.L.; Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Veldhoen, M.; Garden, O.A.; Okkenhaug, K. Loss of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in regulatory T cells leads to neuronal inflammation. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, P.T.; Anderson, K.E.; Davidson, K.; Stephens, L.R. Signalling through Class I PI3Ks in mammalian cells. Biochem. Soc. Transac. 2006, 34, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acosta, Y.; Zafra, M.; Ojeda, G.; Bernardone, I.; Dianzani, U.; Portolés, P.; Rojo, J. Biased binding of class IA phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase subunits to inducible costimulator (CD278). Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 3065–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graupera, M.; Guillermet-Guibert, J.; Foukas, L.C.; Phng, L.-K.; Cain, R.J.; Salpekar, A.; Pearce, W.; Meek, S.; Millan, J.; Cutillas, P.R.; et al. Angiogenesis selectively requires the p110α isoform of PI3K to control endothelial cell migration. Nature 2008, 453, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, Y.Y.; Montes-Casado, M.; Aragoneses-Fenoll, L.; Dianzani, U.; Portolés, P.; Rojo, J.M. Suppression of CD4+ T lymphocyte activation “in vitro” and experimental encephalomyelitis “in vivo” by the phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase inhibitor PIK-75. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2014, 27, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matejuk, A.; Hopke, C.; Vandenbark, A.A.; Hurn, P.D.; Offner, H. Middle-Age male mice have increased severity of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and are unresponsive to testosterone therapy. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-E.; Hasan, M.; Han, J.-S.; Kang, M.-J.; Jung, B.-H.; Kwok, S.-K.; Kim, H.-Y.; Kwon, O.-S. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and age-related correlations of NADPH oxidase, MMP-9, and cell adhesion molecules: The increased disease severity and blood–brain barrier permeability in middle-aged mice. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 287, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peferoen, L.A.N.; Breur, M.; van de Berg, S.; Peferoen-Baert, R.; Boddeke, E.H.W.G.M.; van der Valk, P.; Pryce, G.; van Noort, J.M.; Baker, D.; Amor, S. Ageing and recurrent episodes of neuroinflammation promote progressive experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in Biozzi ABH mice. Immunology 2016, 149, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crawford, A.; Angelosanto, J.M.; Kao, C.; Doering, T.A.; Odorizzi, P.M.; Barnett, B.E.; Wherry, E.J. Molecular and transcriptional basis of CD4+ T cell dysfunction during chronic infection. Immunity 2014, 40, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lupar, E.; Brack, M.; Garnier, L.; Laffont, S.; Rauch, K.S.; Schachtrup, K.; Arnold, S.J.; Guéry, J.-C.; Izcue, A. Eomesodermin expression in CD4+ T cells restricts peripheral Foxp3 induction. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, W.; Liu, X.; Lin, X.; Feng, H.; Sun, L.; Li, S.; Chen, H.; Tang, H.; Lu, L.; Jin, W.; et al. Deficiency in T follicular regulatory cells promotes autoimmunity. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burmeister, Y.; Lischke, T.; Dahler, A.C.; Mages, H.W.; Lam, K.-P.; Coyle, A.J.; Kroczek, R.A.; Hutloff, A. ICOS controls the pool size of effector-memory and regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, T.; Hanabuchi, S.; Wang, Y.-H.; Park, W.R.; Arima, K.; Bover, L.; Qin, F.X.-F.; Gilliet, M.; Liu, Y.-J. Two functional subsets of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in human thymus and periphery. Immunity 2008, 28, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Channappanavar, R.; Twardy, B.S.; Krishna, P.; Suvas, S. Advancing age leads to predominance of inhibitory receptor expressing CD4 T cells. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2009, 130, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, L.M.; Salinas, V.H.; Brown, K.E.; Vanguri, V.K.; Freeman, G.J.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-L1 regulates the development, maintenance, and function of induced regulatory T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 3015–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.L.; Kuchroo, J.R.; Sage, P.T.; Liang, D.; Francisco, L.M.; Buck, J.; Thaker, Y.R.; Zhang, Q.; McArdel, S.L.; Juneja, V.R.; et al. PD-1 restraint of regulatory T cell suppressive activity is critical for immune tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20182232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelsteadt, K.L.; Hayes, E.T.; Campbell, D.J. ICOS signaling limits regulatory T cell accumulation and function in visceral adipose tissue. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20201142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Casado, M.; Ojeda, G.; Criado, G.; Rojo, J.M.; Portolés, P. The PI-3-kinase p110α catalytic subunit of T lymphocytes modulates Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, L.; Sasaki, Y.; Calado, D.P.; Zhang, B.; Paik, J.H.; DePinho, R.A.; Kutok, J.L.; Kearney, J.F.; Otipoby, K.L.; Rajewsky, K. PI3 kinase signals BCR-dependent mature B cell survival. Cell 2009, 139, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramadani, F.; Bolland, D.J.; Garcon, F.; Emery, J.L.; Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Corcoran, A.E.; Okkenhaug, K. The PI3K isoforms p110α and p110δ are essential for pre-B cell receptor signaling and B cell development. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huber, S.; Gagliani, N.; Esplugues, E.; O’Connor, W.; Huber, F.J.; Chaudhry, A.; Kamanaka, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Booth, C.J.; Rudensky, A.Y.; et al. Th17 cells express Interleukin-10 receptor and are controlled by Foxp3- and Foxp3+ regulatory CD4+ T cells in an Interleukin-10-dependent manner. Immunity 2011, 34, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaudhry, A.; Samstein, R.M.; Treuting, P.; Liang, Y.; Pils, M.C.; Heinrich, J.-M.; Jack, R.S.; Wunderlich, F.T.; Brüning, J.C.; Müller, W.; et al. Interleukin-10 signaling in regulatory T cells is required for suppression of Th17 cell-mediated inflammation. Immunity 2011, 34, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, P.P.; Fitzpatrick, D.R.; Beard, C.; Jessup, H.K.; Lehar, S.; Makar, K.W.; Pérez-Melgosa, M.; Sweetser, M.T.; Schlissel, M.S.; Nguyen, S.; et al. A critical role for Dnmt1 and DNA methylation in T cell development, function, and survival. Immunity 2001, 15, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suen, W.E.; Bergman, C.M.; Hjelmstrom, P.; Ruddle, N.H. A critical role for Lymphotoxin in Experimental Allergic Encephalomyelitis. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Portoles, P.; Rojo, J.; Golby, A.; Bonneville, M.; Gromkowski, S.; Greenbaum, L.; Janeway, C.A., Jr.; Murphy, D.B.; Bottomly, K. Monoclonal antibodies to murine CD3 epsilon define distinct epitopes, one of which may interact with CD4 during T cell activation. J. Immunol. 1989, 142, 4169–4175. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rojo, J.M.; Montes-Casado, M.; Aragoneses-Fenoll, L.; Ojeda, G.; Dianzani, U.; Portolés, P. PI3-Kinase p110α Deficiency Modulates T Cell Homeostasis and Function and Attenuates Experimental Allergic Encephalitis in Mature Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168698
Rojo JM, Montes-Casado M, Aragoneses-Fenoll L, Ojeda G, Dianzani U, Portolés P. PI3-Kinase p110α Deficiency Modulates T Cell Homeostasis and Function and Attenuates Experimental Allergic Encephalitis in Mature Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(16):8698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168698
Chicago/Turabian StyleRojo, José M., María Montes-Casado, Laura Aragoneses-Fenoll, Gloria Ojeda, Umberto Dianzani, and Pilar Portolés. 2021. "PI3-Kinase p110α Deficiency Modulates T Cell Homeostasis and Function and Attenuates Experimental Allergic Encephalitis in Mature Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 16: 8698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168698
APA StyleRojo, J. M., Montes-Casado, M., Aragoneses-Fenoll, L., Ojeda, G., Dianzani, U., & Portolés, P. (2021). PI3-Kinase p110α Deficiency Modulates T Cell Homeostasis and Function and Attenuates Experimental Allergic Encephalitis in Mature Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(16), 8698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168698