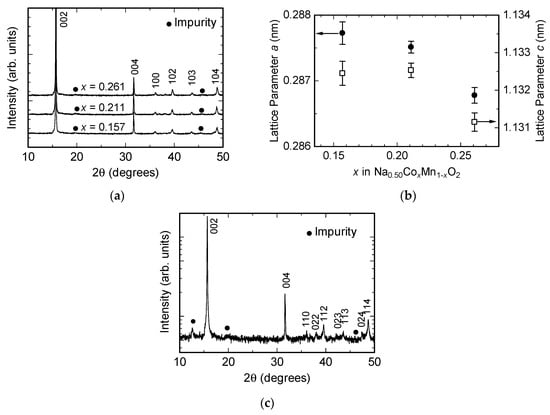
Nanomaterials 2017, 7(10), 300; https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7100300 - 29 Sep 2017
Cited by 44 | Viewed by 6005
Abstract
The growing use of silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) in consumer products raises concerns about their toxicological potential. The purpose of the study was to investigate the size- and coating-dependent pulmonary toxicity of Ag-NPs in vitro and in vivo, using an ovalbumin (OVA)-mouse allergy model.
[...] Read more.
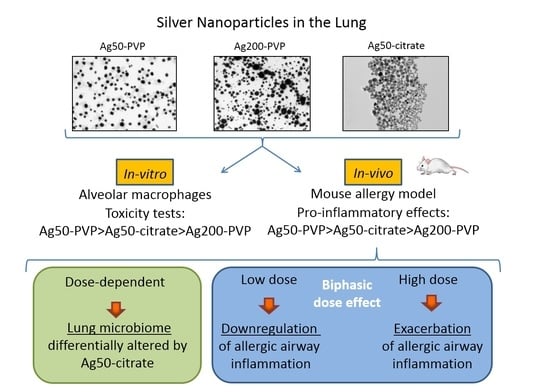
The growing use of silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) in consumer products raises concerns about their toxicological potential. The purpose of the study was to investigate the size- and coating-dependent pulmonary toxicity of Ag-NPs in vitro and in vivo, using an ovalbumin (OVA)-mouse allergy model. Supernatants from (5.6–45 µg/mL) Ag50-PVP, Ag200-PVP or Ag50-citrate-treated NR8383 alveolar macrophages were tested for lactate dehydrogenase and glucuronidase activity, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α release and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. For the in vivo study, NPs were intratracheally instilled in non-sensitized (NS) and OVA-sensitized (S) mice (1–50 µg/mouse) prior to OVA-challenge and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) inflammatory infiltrate was evaluated five days after challenge. In vitro results showed a dose-dependent cytotoxicity of Ag-NPs, which was highest for Ag50-polyvinilpyrrolidone (PVP), followed by Ag50-citrate, and lowest for Ag200-PVP. In vivo 10–50 µg Ag50-PVP triggered a dose-dependent pulmonary inflammatory milieu in NS and S mice, which was significantly higher in S mice and was dampened upon instillation of Ag200-PVP. Surprisingly, instillation of 1 µg Ag50-PVP significantly reduced OVA-induced inflammatory infiltrate in S mice and had no adverse effect in NS mice. Ag50-citrate showed similar beneficial effects at low concentrations and attenuated pro-inflammatory effects at high concentrations. The lung microbiome was altered by NPs instillation dependent on coating and/or mouse batch, showing the most pronounced effects upon instillation of 50 µg Ag50-citrate, which caused an increased abundance of operational taxonomic units assigned to Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes and Proteobacteria. However, no correlation with the biphasic effect of low and high Ag-NPs dose was found. Altogether, both in vitro and in vivo data on the pulmonary effects of Ag-NPs suggest the critical role of the size, dose and surface functionalization of Ag-NPs, especially in susceptible allergic individuals. From the perspective of occupational health, care should be taken by the production of Ag-NPs-containing consumer products.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nanoparticles in Vivo and in Vitro Studies: A Collection of Parallel Approaches)
►
Show Figures