Agriculture 2021, 11(12), 1224; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11121224 - 3 Dec 2021
Cited by 24 | Viewed by 4045
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Chinese goldthread (Coptis chinensis Franch.) represents one of the most important medicinal plants with diverse medicinal applications, but it easily suffers from continuous cropping obstacles in the plantation. In this study, we have selected eight different continuously cropped fields with C. chinensis
[...] Read more.
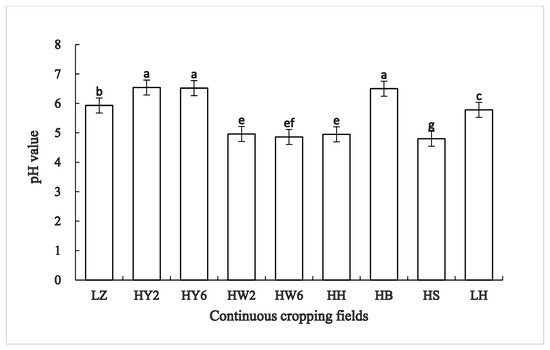
Chinese goldthread (Coptis chinensis Franch.) represents one of the most important medicinal plants with diverse medicinal applications, but it easily suffers from continuous cropping obstacles in the plantation. In this study, we have selected eight different continuously cropped fields with C. chinensis and fallow field, providing detailed information regarding the diversity and composition of the rhizospheric bacterial communities. We have found a significant difference between fallow field (LH) and other continuously cropped fields in soil pH; the total content of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium; and soil enzyme activities. The results indicate that continuous cropping had a significant effect on soil physicochemical properties and enzyme activities under different plant cultivations. The relative abundance of bacterial phyla was significantly altered among the fields; for example, proteobacteria and Actinobacteria were observed to be higher in continuous cropping of maize (HY6) and lower in sweet potato continuous cropping (HH). Alpha diversity analysis showed that different plants with different years of continuous cropping could change the diversity of bacterial communities, among which the effect of maize and Polygonum multiflorum continuous cropping were most significant. Principle coordinate analysis (PCoA) showed that continuously cropped C. chinensis (LZ) and cabbage continuously cropped for 2 years (HS) were slightly clustered together and separated from LH and others. The results showed that the similarity of the bacterial community in the same crop rotation was higher, which further indicated that the bacterial community structure was significantly altered by the continuous cropping system and plant species. Our study provides a foundation for future agricultural research to improve microbial activity and increase crops/cash-crops productivity under a continuous cropping system and mitigate continuous cropping obstacles.
Full article