1
College of Earth Sciences, Jilin University, Changchun 130061, China
2
School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, Shandong University of Technology, Zibo 255000, China
3
College of Geology and Mining Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830047, China
4
School of Resources, Environment and Architectural Engineering, Chifeng University, Chifeng 024000, China
Minerals 2022, 12(6), 708; https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060708 - 1 Jun 2022
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2331
Abstract
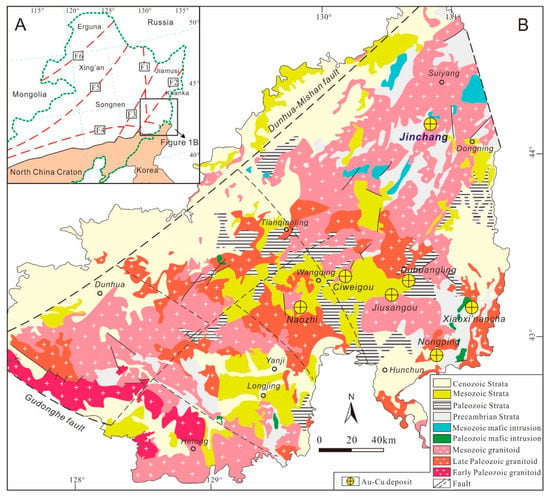
The Jinchang deposit is a large Au deposit in the Yanbian–Dongning region, in Northeast China, and is the product of magmatic–hydrothermal activities related to Early Cretaceous concealed igneous intrusions. However, these Early Cretaceous ore-causative igneous intrusions and the ore-hosting rocks in the Jinchang
[...] Read more.
The Jinchang deposit is a large Au deposit in the Yanbian–Dongning region, in Northeast China, and is the product of magmatic–hydrothermal activities related to Early Cretaceous concealed igneous intrusions. However, these Early Cretaceous ore-causative igneous intrusions and the ore-hosting rocks in the Jinchang ore district have rarely been studied, with their magma sources and tectonic settings being ambiguous. Here, we integrate new geochemical, zircon U–Pb and Hf isotopic data from the concealed ore-hosting monzogranite and the ore-causative granodiorite to constrain their magma sources and tectonic settings. Zircon U–Pb dating indicates that the two monzogranites from the drill holes JIZKN01 and J18ZK0303 have similar crystallization ages of 202.0 ± 1.6 and 200.9 ± 1.2 Ma, respectively, whereas the granodiorite from the drill hole JXI-1ZK1001 was formed in the Early Cretaceous period (107.0 ± 3.0 Ma). They are all enriched in large-ion lithophile elements (e.g., Rb, Th, and K) and light rare-earth elements, depleted in high field strength elements (e.g., Nb, Ta, and Ti) and heavy rare-earth elements, and yield similar positive εHf(t) values of +4.4 to +11.5, with their two-stage model ages ranging from 799 to 389 Ma. These results indicate that the concealed Early Jurassic ore-hosting monzogranite was derived from the partial melting of the Neoproterozoic–Paleozoic continental crust in a continental arc setting related to the Paleo-Pacific subduction. The ore-causative granodiorite originated from the partial melting of both the mantle wedge and the overlying continental crust, most likely caused by the dehydration and metasomatism of the subducted Paleo-Pacific slab involved in the rollback in the Early Cretaceous period.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Isotopic Tracers of Mantle and Magma Evolution)
▼
Show Figures