1
Faculty of Engineering, University of the Ryukyus, 1 Senbaru Nishihara-cho Nakagami, Okinawa 903-0213, Japan
2
Department of Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Science and Technology, Tokyo University of Science, 2641 Yamazaki Noda, Chiba 278-8510, Japan
3
Hawaii Natural Energy Institute, University of Hawaii, Manoa Honolulu, HI 96822, USA
†
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Sustainability 2017, 9(1), 117; https://doi.org/10.3390/su9010117 - 13 Jan 2017
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 5282
Abstract
Recently, the off-grid smart house has been attracting attention in Japan for considering global warming. Moreover, the selling price of surplus power from the renewable energy system by Feed-In Tariff (FIT) has declined. Therefore, this paper proposes an off-grid smart house with the
[...] Read more.
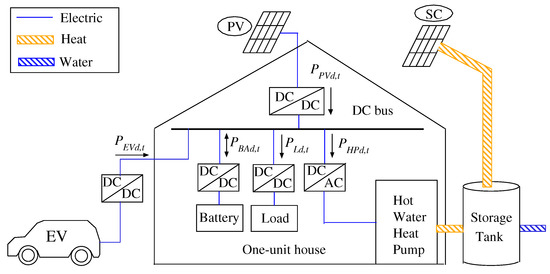
Recently, the off-grid smart house has been attracting attention in Japan for considering global warming. Moreover, the selling price of surplus power from the renewable energy system by Feed-In Tariff (FIT) has declined. Therefore, this paper proposes an off-grid smart house with the introduced Photovoltaic (PV) system, Solar Collector (SC) system, Hot Water Heat Pump (HWHP), fixed battery and Electric Vehicle (EV). In this research, a multi-objective optimization problem is considered to minimize the introduced capacity and shortage of the power supply in the smart house. It can perform the electric power procurement from the EV charging station for the compensation of a shortage of power supply. From the simulation results, it is shown that the shortage of the power supply can be reduced by the compensation of the EV power. Furthermore, considering the uncertainty for PV output power, reliable simulation results can be obtained.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Electric Power Systems Research)
▼
Show Figures