Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19(10), 6157; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106157 - 18 May 2022
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 4982
Abstract
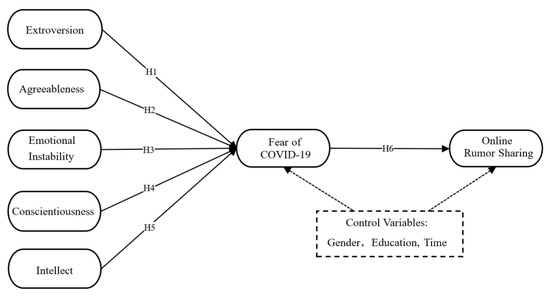
This study aims to explore the effects of personality traits on online rumor sharing during the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic and the mediating role of the fear of COVID-19 between them. We conducted this research using a web-based questionnaire distributed to 452 university
[...] Read more.
This study aims to explore the effects of personality traits on online rumor sharing during the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic and the mediating role of the fear of COVID-19 between them. We conducted this research using a web-based questionnaire distributed to 452 university students who were invited to fill it out. The partial least square structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) method was used to test the data and model, with the yielded results demonstrating that three—extroversion, emotional instability, and conscientiousness—of the Big Five personality traits are positively related to a fear of COVID-19, with this fear positively affecting online rumor sharing. Moreover, fear of COVID-19 was found to act as a mediator between personality traits and online rumor sharing; thus, we can conclude that persons with high levels of extroversion, emotional instability, and conscientiousness are more likely to share rumors online due to a fear of COVID-19. This study furthers our understanding of the psychological mechanism by which personality traits influence online rumor sharing and provides references for anti-rumor campaigns taking place during the COVID-19 pandemic, as it identifies key groups and sheds light on the necessity of reducing people’s fear of COVID-19.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Effects of Media Content on Public Health)
►
Show Figures