Barium Oxalates Combined with Oxo-Anions and Organic Cations: Syntheses and Structures of Ba2(C2O4)(H2PO3)2 and C2H10N2·Ba(H2O)2(HC2O4)4
Abstract
: The syntheses and single-crystal structures of Ba2(C2O4)(H2PO3)2 (1) and C2H10N2·Ba(H2O)2(HC2O4)4 (2) are described. Compound 1 is a three-dimensional mixed-anion framework containing BaO9 coordination polyhedra, which approximate to monocapped square anti-prisms: the connectivity of the BaO9 units via edges and triangular faces leads to a sheet structure. The oxalate ion in 1 is substantially twisted about its C–C bond [dihedral angle between the CO2 groups = 33.8 (3)°]. Compound 2 is a molecular salt containing ethylenediammonium dications and [Ba(HC2O4)4(H2O)2]2– dianions, which are linked by O–H⋯O and N–H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The BaO10 coordination polyhedron can be described as a distorted pentagonal anti-prism. Crystal data: 1 (C2H4Ba2O10P2), Mr = 524.68, monoclinic, C2/c (No. 15), Z = 4, a = 12.3829 (3) Å, b = 7.9124 (2) Å, c = 11.0858 (3) Å, β = 114.788 (2)°, V = 986.10 (4) Å3, R(F) = 0.016, wR(F2) = 0.040. 2 (C10H18BaN2O10), Mr = 591.60, monoclinic, C2/m (No. 12), Z = 2, a = 12.7393 (7) Å, b = 13.0111 (7) Å, c = 5.6050 (3) Å, β = 104.208 (4)°, V = 900.62 (8) Å3, R(F) = 0.027, wR(F2) = 0.054.1. Introduction
Hydrated barium oxalates including Ba(C2O4)·½H2O [1], Ba(C2O4)·H2O [2], Ba(C2O4)·2H2O [3] and Ba(C2O4)·3½H2O [4], which feature various bridging and coordination modes of the oxalate ions, are a well studied family of inorganic compounds [5]. Of particular interest is the topotactic dehydration of Ba(C2O4)(H2C2O4)·2H2O to yield the polymorphs α-Ba(C2O4)(H2C2O4) and β-Ba(C2O4)(H2C2O4), which serves as a model system for this type of reaction [6,7]. Barium oxalate is used to prepare barium titanyl oxalate, which is an important molecular precursor to barium titanate, BaTiO3 [8]. A more exotic application for barium oxalates is to impart a green color to pyrotechnics [9]. A quite different crystallochemical aspect of the oxalate ion is its structural role in forming organically-templated oxalate/oxo-anion open frameworks such as C4H12N2· [Fe4(HPO3)2(C2O4)3] [10] or C6H14N2·[In2(HPO3)3(C2O4)] [11].
Although these types of metal–mixed-anion frameworks have been reported for a number of transition and main-group metals and rare earths [12], similar studies of barium oxalates either in combination with oxo-anions such as hydrogen phosphite or with organic cations are in their infancy. In this paper, we describe the syntheses and crystal structures of two new representative compounds in this family, namely Ba2(C2O4)(H2PO3)2 (1) and C2H10N2·Ba(H2O)2(HC2O4)4 (2).
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Crystal structure of Ba2(C2O4)(H2PO3)2 (1)
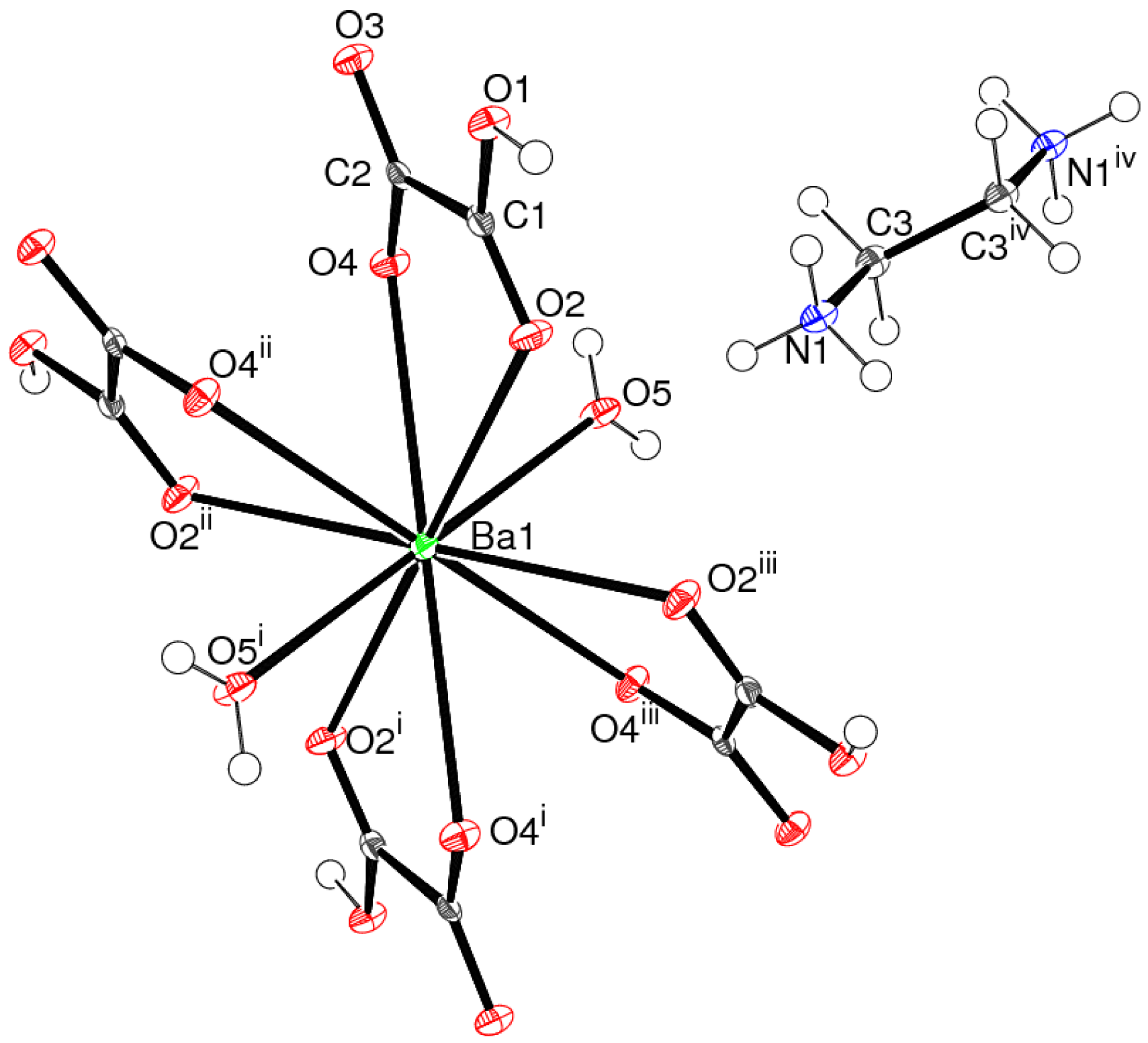
The asymmetric unit of 1 (Figure 1) contains a barium cation, an (H2PO3)– dihydrogen phosphite (dhp) ion and half an oxalate ion: the latter is completed by crystallographic 2-fold symmetry.
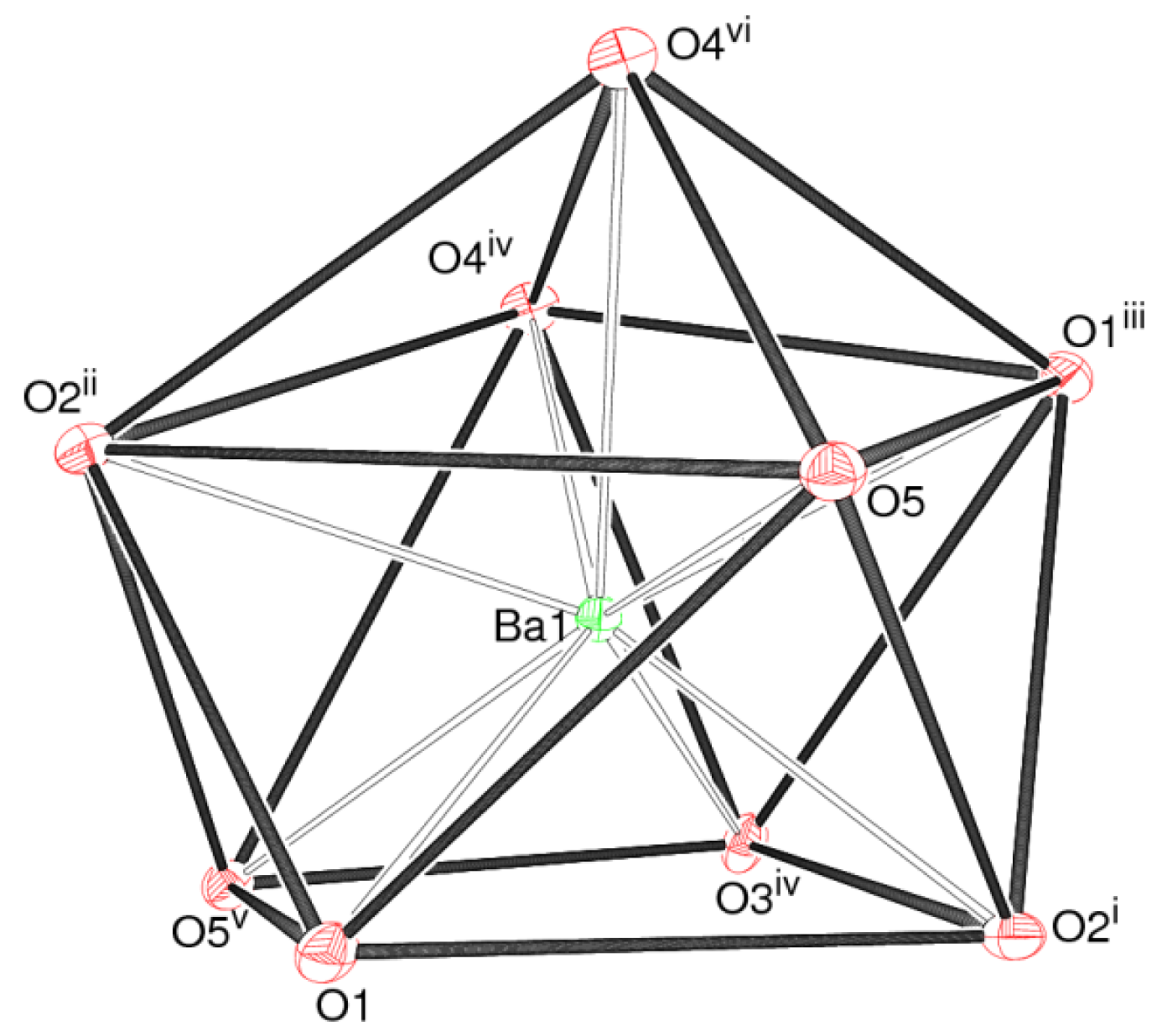
The barium ion in 1 is coordinated by nine oxygen atoms, with a mean Ba–O separation of 2.824 Å (Table 1): the next-nearest O atom is over 3.9 Å from the metal ion. The bond valence sum (BVS) value for Ba1, as calculated by the Brown-Altermatt formalism [13], is 2.16, compared to an expected value of 2.00. Four of the O atoms are parts of oxalate ions and five are from adjacent dhp ions. The polyhedral geometry of the metal ion (Figure 2) is quite well described as a monocapped square anti-prism [14], with O1/O2i/O3iv/O5v (see Table 1 for symmetry codes) forming one square face (r.m.s. deviation = 0.045 Å) and O1iii/O2ii/O4iv/O5 (r.m.s. deviation = 0.097 Å) the other: the dihedral angle between the two mean planes is 10.78 (6)°. Atom O4vi projects through the second of these faces to provide the cap. The Ba atom is displaced by 1.4843 (9) Å from the first plane and by −1.1191 (8) Å from the second.
The dhp anion in 1 adopts its normal tetrahedral geometry [15]: the phosphorus(III) atom is displaced by 0.4268 (13) Å from its three attached O atoms and the fourth vertex is occupied by the P–H grouping. The P1–O3 bond length is substantially longer than the other two P–O bonds, due to its protonation: the P–OH group forms an O–H⋯O hydrogen bond to an acceptor oxalate O atom (Figure 1, Table 1). As usual, the P–H vertex does not participate in hydrogen bonding interactions [16].
The C–O bonds in the oxalate dianion in 1 show slightly different lengths, possibly due to packing effects or because O5 is the hydrogen-bond acceptor. The dihedral angle between the two −CO2 groups is 33.8 (3)°, indicating a substantial degree of twisting about the central C–C bond. Oxalate ions in crystal structures are more commonly close to planar [17], although a similar degree of twist has long been known in (NH4)2(C2O4)·H2O [18]. Interestingly, this twisting renders the isolated oxalate ion an enantiomorphous (chiral) object [19], with local C2 symmetry. This 2-fold symmetry is crystallographically imposed for the oxalate ion in 1, but of course, the presence of crystallographic inversion symmetry in space group C2/c leads to a racemic overall structure. The C–C bond length is 1 is notably long at 1.550 (5) Å, a feature also seen in the ammonium compound [18].
The connectivity of the polyhedral building units in 1 leads to a three-dimensional framework constructed from BaO9, H2PO3 and C2O4 building blocks. Considered by themselves, the BaO9 polyhedra share both edges (via O4/O4) in the c direction and faces (via O1/O2/O5) in the b direction to generate (100) sheets (Figure 3). The oxalate ions and dhp ions complete the packing to generate a dense three-dimensional network, without any indication of channels or pores.
2.2. Structure of C2H10N2·Ba(H2O)2(HC2O4)4 (2)
Compound 2 (Figure 4) is a molecular salt built up from a barium ion lying on a special position at the origin with 2/m site symmetry, an (HC2O4)– hydrogen oxalate monoanion, a water molecule (O atom site symmetry m) and half a [C2H10N2]2+ ethylenediammonium cation, with both the N and the C atom lying on a crystallographic mirror plane. The complete organic cation is completed by inversion symmetry.
The barium ion in 2 is 10-coordinated by four bidentate hydrogen oxalate anions and two water molecules (Table 2) as a [Ba(H2O)2(HC2O4)4]2– dianion: the mean Ba–O separation is 2.867 Å and BVS(Ba1) = 2.12 The polyhedral geometry about the metal ion can be described as a pentagonal antiprism [20] (Figure 5), although the pentagonal faces are significantly puckered into envelopes with O5 at the flap position pointing away from the barium ion. The dihedral angle between the mean planes is constrained by symmetry to be zero and Ba is displaced from each plane by 1.271 (2) Å.
The hydrogen oxalate ion is 2 is almost planar, as indicated by the C1/O1/O2–C2/O3/O4 dihedral angle of 1.0 (3)°. Unlike the case in 1, the oxalate C–C bond length in 2 of 1.501 (7) Å is quite typical for a carbon–carbon single bond. The [C2H10N2]2+ ethyl enedi ammonium ion in 2 shows no unusual features; the N–C–C–N torsion angle is constrained by symmetry to be −180°.
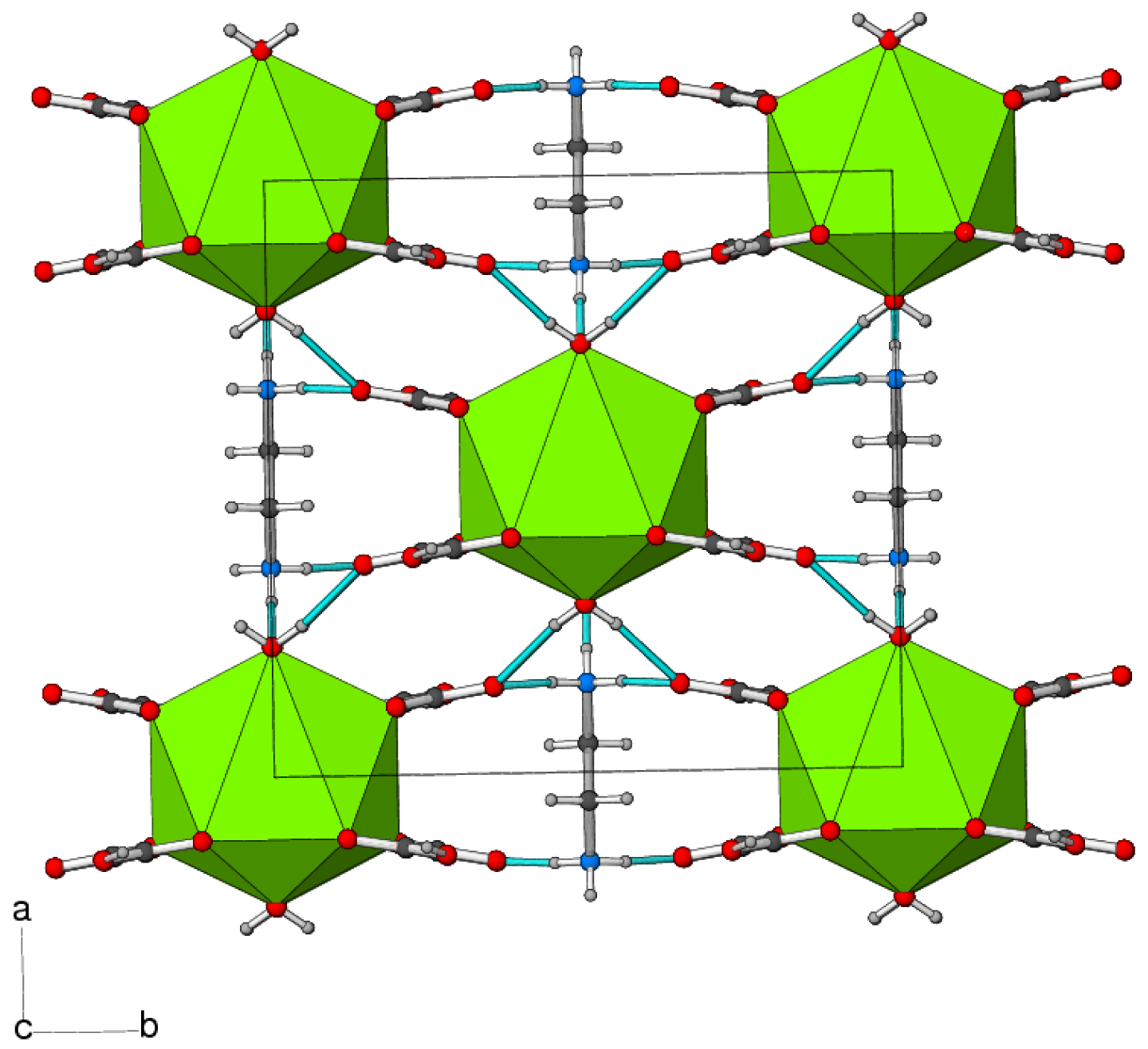
In the crystal of 2, the components are linked by N–H⋯O and O–H⋯O hydrogen bonds (Table 2, Figure 6). The length of the O–H bond (1.00 Å) of the hydrogen oxalate anion is slightly longer than expected, which may correlate with its participation in a strong hydrogen bond. Similar O–H bond lengths have been seen in related compounds [21]. Overall, this leads to a connectivity of the complex anions in the ab plane with the N–H⋯O bonds serving to link the anions in the c direction.
3. Experimental Section
Compound 1 was prepared from 2.77 g BaC2O4, 3.6 g H3PO3, and 1.3 mL diethylamine in 20 mL of water. The components were placed in a PTFE bottle, shaken well to form a milky slurry, and placed in an oven at 80 °C for two days. Product recovery by vacuum filtration yielded colorless blocks and bars of 1. IR (KBr, cm−1): 2461w, 2157w, 2017w, 1589vs, 1309s, 1221m, 1156m, 1068m, 892m, 771m, 662w. The band at 2461 cm−1 is the characteristic phosphite P–H stretch [22] and the various bands in the region 900–1200 cm−1 have been associated with PO3 modes [22]. The bands at 771, 1309 and 1589 cm−1 probably correspond to the δ(O–C–O), νsym(COO) and νasym(COO) deformations respectively of the oxalate −CO2 groups [23]. The X-ray powder pattern for 1 could be matched to a simulation of the single-crystal structure, indicating phase purity.
Compound 2 was prepared by the same procedure, with ethylenediamine (2.0 mL) replacing diethylamine. Product recovery as above led to a mass of small colorless blocks and rods of 2. IR (KBr, cm−1): ∼3200m, 1583s, 1303m, 1217m, 1150m, 1063s, 887m, 772w. The characteristic 772, 1303 and 1583 cm−1 oxalate bands are assigned as above. Powder diffraction indicated that the product was almost phase pure with possibly a trace of barium oxalate.
The single-crystal data for 1 and 2 were collected on a Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer (graphite monochromated Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å) at 120 K. Data reduction with DENZO/HKL [24] then routinely proceeded in each case and empirical (multi-scan) absorption corrections were applied with SADABS [25], as summarized in the paragraphs below. For 1, the structure was solved by direct methods with SHELXS in space group C2/c and the atomic model refined against |F|2 with SHELXL [26]. For 2, attempts to solve the structure in space group C2/m either by direct methods or Patterson maps were not successful and lower symmetry space groups were tried. The structure solved easily in space group Cm but a symmetry check with PLATON [27] indicated that C2/m was the most appropriate symmetry and the atomic model was transformed to the latter space group. Full-matrix least-squares refinement then proceeded as for 1. The “observed data” threshold for calculating the R(F) residuals was set as I > 2σ(I). For 1, the H atoms were located in difference maps and freely refined with the constraint Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(carrier) applied. For 2, the H atoms of the organic cation were geometrically placed (C–H = 0.97, N–H = 0.89 Å) and refined as riding atoms. The water and oxalate H atoms were located in difference maps and refined as riding atoms in their as-found relative positions. The constraint Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(carrier) was applied in all cases. Full details are given in the deposited cifs.
Crystal data for 1: colorless block, 0.09 × 0.06 × 0.05 mm, C2H4Ba2O10P2, Mr = 531.38, monoclinic, C2/c (No. 15), a = 12.3829 (3) Å, b = 7.9124 (2) Å, c = 11.0858 (3) Å, β = 114.788 (2)°, V = 986.10 (4) Å3, Z = 4, F(000) = 952, T = 120 K, ρcalc = 3.534 g cm−3, μ = 8.304 mm−1, Tmin = 0.522, Tmax = 0.682, 5117 reflections measured (−16 ≤ h ≤ 15, −10 ≤ k ≤ 10, −14 ≤ l ≤ 14; 6.30° ≤ 2θ ≤ 54.98°), RInt = 0.034, 1133 merged reflections, 1115 with I > 2σ(I), 79 parameters, R(F) = 0.016, wR(F2) = 0.040, S (goodness-of-fit) = 1.143, w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + 3.6002P], where P = (Fo2 + 2 Fc2)/3, min./max. Δρ = −0.53, +0.59 e Å−3. Cambridge Database deposition number: CSD-826099.
Crystal data for 2: colorless block, 0.12 × 0.08 × 0.05 mm, C10H18BaN2O18, Mr = 591.6, monoclinic, C2/m (No. 12), a = 12.7393 (7) Å, b = 13.0111 (7) Å, c = 5.6050 (3) Å, β = 104.208 (4)°, V = 900.62 (8) Å3, Z = 2, F(000) = 584, T = 120 K, ρcalc = 2.182 g cm−3, μ = 2.310 mm−1, Tmin = 0.769, Tmax = 0.893, 5144 reflections measured (−15 ≤ h ≤ 16, −16 ≤ k ≤ 16, −7 ≤ l ≤ 7; 6.26° ≤ 2θ ≤ 55.02°), RInt = 0.048, 1084 merged reflections, 1056 with I > 2σ(I), 77 parameters, R(F) = 0.027, wR(F2) = 0.054, S (goodness-of-fit) = 1.091, w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + 0.0083P2 + 2.0292P], where P = (Fo2 + 2 Fc2)/3, min./max. Δρ = −0.69, +0.78 e Å−3. Cambridge Database deposition number: CSD-826100.
4. Conclusions
We have prepared and structurally characterized the new phases Ba2(C2O4)(H2PO3)2 and C2H10N2·Ba(H2O)2(HC2O4)4. So far as we can ascertain, they are the first examples of barium oxalates in combination with oxo-anions or organic cations. The deposition of the oxalate ion in 1 is notably twisted, whereas it is almost planar in 2. The barium ions show different, distinctive coordination polyhedra in these structures. The number of crystal structures containing nine- and ten-coordinate barium complexes in the Cambridge Structural Database (version 5.32 of November 2010 with two updates) [28] is almost the same, at 73 and 75, respectively.



| Ba1–O2i | 2.6927 (18) | Ba1–O1 | 2.7322 (18) |
| Ba1–O2ii | 2.7519 (18) | Ba1–O1iii | 2.7894 (18) |
| Ba1–O4iv | 2.7929 (19) | Ba1–O5 | 2.8818 (17) |
| Ba1–O5v | 2.9101 (18) | Ba1–O4vi | 2.9202 (18) |
| Ba1–O3iv | 2.9453 (19) | P1–O2 | 1.5013 (17) |
| P1–O1 | 1.5015 (19) | P1–O3 | 1.595 (2) |
| P1–H1 | 1.25 (3) | C1–O4 | 1.244 (3) |
| C1–O5 | 1.269 (3) | C1–C1vi | 1.550 (5) |
| O2–P1–O1 | 117.92 (10) | O2–P1–O3 | 108.92 (11) |
| O1–P1–O3 | 110.65 (11) | O4–C1–O5 | 126.5 (2) |
| O4–C1–C1vi | 117.0 (2) | O5–C1–C1vi | 116.3 (3) |
| O3–H2⋯O5 | 0.79 (4) | 1.87 (4) | 2.647 (3) | 168 (3) |
Symmetry codes:(i)½−x, ½−y, 1−z;(ii)x, 1−y, ½+z;(iii)½−x, y−½, 1½−z;(iv)½+x, ½−y, ½+z;(v)½−x, ½+y, 1½−z;(vi)−x, y, 1½−z.
| Ba1–O5 | 2.781 (2) | Ba1–O2 | 2.8178 (17) |
| Ba1–O4 | 2.9586 (17) | C1–O2 | 1.215 (3) |
| C1–O1 | 1.301 (3) | C1–C2 | 1.548 (2) |
| C2–O3 | 1.240 (3) | C2–O4 | 1.265 (3) |
| C3–N1 | 1.493 (5) | C3–C3iv | 1.501 (7) |
| O2–C1–O1 | 125.6 (2 | O2–C1–C2 | 121.4 (2) |
| O1–C1–C2 | 113.0 (2) | O3–C2–O4 | 127.2 (2) |
| O3–C2–C1 | 118.3 (2) | O4–C2–C1 | 114.4 (2) |
| N1–C3–C3iv | 109.5 (4) |
| O1–H1⋯O4v | 1.00 | 1.50 | 2.504 (2) | 176 |
| O5–H5⋯O3vii | 0.85 | 2.00 | 2.841 (2) | 172 |
| N1–H2⋯O5 | 0.89 | 1.99 | 2.824 (4) | 156 |
| N1–H3⋯O3vi | 0.89 | 1.98 | 2.839 (3) | 163 |
| N1–H3⋯O1vi | 0.89 | 2.40 | 2.9765 (17) | 123 |
Symmetry codes:(iv)1−x, −y, 1−z;(v)x, y, 1+z;(vi)½−x, ½−y, 1−z;(vii)½−z, ½−y, −z.
Acknowledgments
We thank the EPSRC national Crystallography Service (University of Southampton, England) for the X-ray data collections.
References and Notes
- Mutin, J.-C.; Dusausoy, Y.; Protas, J. Structural description of endothermic decompositions in the form solid-1 → solid-2 + gas 1. Crystal structure of barium oxalate, 2BaC2O4·H2O. J. So/id State Chem. 1981, 36, 356–364. [Google Scholar]
- Mutin, J.-C.; Aubry, A.; Bertrand, G.; Joly, E.; Protas, J. Determination of crystal-structure of BaC2O4·H2O. C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris), Ser. C. 1974, 278, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Mutin, J.-C.; Courtois, A.; Bertrand, G.; Protas, J.; Watelle-Marion, G. Determination of crystal-structure of BaC2O4·2H2O. C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris), Ser. C. 1971, 273, 1512. [Google Scholar]
- Neder, R.; Burghammer, M.; Schulz, H.; Christensen, A.N.; Krane, H.G.; Bell, A.M.T.; Hewat, A.W.; Altomare, A. Crystal structure determination of BaC2O4·3.5H2O/D2O. Zeit. Kristallogr. 1997, 212, 305–309. [Google Scholar]
- Borel, C.; Ghazzali, M.; Langer, V.; Ohrstrom, L. Network analysis of barium oxalates Ba(C2O4)m(HC2O4)n(H2C2O4)p(H2O)q, including the new, uniform, five-connected loh net. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2009, 12, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Mutin, J.-C.; Watelle, G.; Dusausoy, Y. Study of a lacunary solid phase I—thermodynamic and crystallographic characteristics of its formation. J. Solid State Chem. 1979, 27, 407–421. [Google Scholar]
- Mutin, J.-C.; Watelle, G. Study of a lacunary solid phase II—morphological and kinetic characteristics of its formation. J. Solid State Chem. 1979, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, W.-S.; Min, B.-K.; Park, J.; Yoon, D.-H. Formation mechanism of barium titanate by thermal decomposition of barium titanyl oxalate. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 669–672. [Google Scholar]
- Kosanke, K.; Kosanke, B.J.; von Maltitz, I.; Sturman, B.; Shimizu, T.; Wilson, M.A.; Kubota, N.; Jennings-White, C.; Chapman, D. Pyrotechnic Chemistry; Journal of Pyrotechnics, Inc.: Whitewater, CO, USA, 2004; Chapter 14; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, S.; Pati, S.K.; Green, M.A.; Natarajan, S. Inorganic–organic hybrid compounds: synthesis, structure, and magnetic properties of the first organically templated iron oxalate-phosphite, [C4N2H12[Fe4II(HPO3)2(C2O4)3], possessing infinite Fe–O–Fe chains. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 2912–2917. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Jiang, T.; Yu, Y.; Li, G.; Huo, Q.; Liu, Y. Organic template-directed indium phosphite-oxalate hybrid material: synthesis and characterization of a novel 3D [C6H14N2][In2(HPO3)3(C2O4)] compound with intersecting channels. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2009, 12, 1020–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, N.; Liu, L.; Tong, F. Synthesis, crystal structures and luminescence properties of lanthanide oxalatophosphonates with a three dimensional framework structure. New J. Chem. 2009, 33, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, I.D.; Altermatt, D. Bond-valence parameters obtained from a systematic analysis of the Inorganic Crystal Structure Database. Acta Cryst. 1985, B41, 244–247. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Martínez, A.; Casanova, D.; Alvarez, S. Polyhedral structures with an odd number of vertices: nine-atom clusters and supramolecular architectures. Dalton Trans. 2008, 2583–2591. [Google Scholar]
- Corbridge, D.E.C. The crystal structure of magnesium phosphite hexahydrate, MgHPO3·6H2O. Acta Cryst. 1956, 9, 991–994. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, D.R.; Smith, S.K.; Farrar, T.C.; Ross, F.K. Neutron and X-ray diffraction study of magnesium phosphite hexahydrate, [Mg(H2O)6]2+[HPO3]2–. Acta Cryst. 1994, C50, 342–346. [Google Scholar]
- Dewar, M.J.S.; Zheng, Y.-J. Structure of the oxalate ion. J. Mol. Struct. Theochem 1990, 209, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, J.H. Ammonium oxalate monohydrate: structure refinement at 30 K. Acta Cryst. 1965, 18, 410–417. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, J.H. Enantiomorphism of the oxalate ion in ammonium oxalate monohydrate. Acta Cryst. 1965, 18, 417–419. [Google Scholar]
- Green, E.A.; Daux, W.L.; Smith, G.M.; Wudl, F. Coordination complexes of groups 1 and 2. Potassium O,O′-catecholdiacetate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 6689–6692. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, N.G.; Tellgren, R. Ammonium hydrogen oxalate hemihydrate: X-ray and neutron diffraction studies. Acta Cryst. 1989, C45, 499–504. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, K.J.; Zhang, Y.; Clearfield, A. The synthesis and characterization of lanthanum phosphite phenylphosphonate mixed derivatives. Polyhedron 1994, 13, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar]
- Trpkovska, M.; Šoptrajanov, B.; Pejov, L. Reinvestigation of the infrared spectra of calcium oxalate monohydrate and its partially deuterated analogues. Bull. Chem. Technol. Macedonia 2002, 21, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Otwinowski, Z.; Minor, W. Processing of X-ray Diffraction Data Collected in Oscillation Mode. Methods in Enzymology; Carter, C.W., Jr., Sweet, R.M., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, part A; pp. 307–326. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SADABS: Program for Empirical Absorption Correction of Area Detector Data; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. 2008, A64, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Spek, A.L. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Cryst. 2009, D65, 148–155. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, F.H.; Motherwell, W.D.S. Applications of the Cambridge Structural Database in organic chemistry and crystal chemistry. Acta Cryst. 2002, B58, 407–422. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Iveson, S.J.; Johnston, C.B.; Harrison, W.T.A. Barium Oxalates Combined with Oxo-Anions and Organic Cations: Syntheses and Structures of Ba2(C2O4)(H2PO3)2 and C2H10N2·Ba(H2O)2(HC2O4)4. Crystals 2011, 1, 59-68. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst1020059
Iveson SJ, Johnston CB, Harrison WTA. Barium Oxalates Combined with Oxo-Anions and Organic Cations: Syntheses and Structures of Ba2(C2O4)(H2PO3)2 and C2H10N2·Ba(H2O)2(HC2O4)4. Crystals. 2011; 1(2):59-68. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst1020059
Chicago/Turabian StyleIveson, Samuel J., Chloe B. Johnston, and William T.A. Harrison. 2011. "Barium Oxalates Combined with Oxo-Anions and Organic Cations: Syntheses and Structures of Ba2(C2O4)(H2PO3)2 and C2H10N2·Ba(H2O)2(HC2O4)4" Crystals 1, no. 2: 59-68. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst1020059




