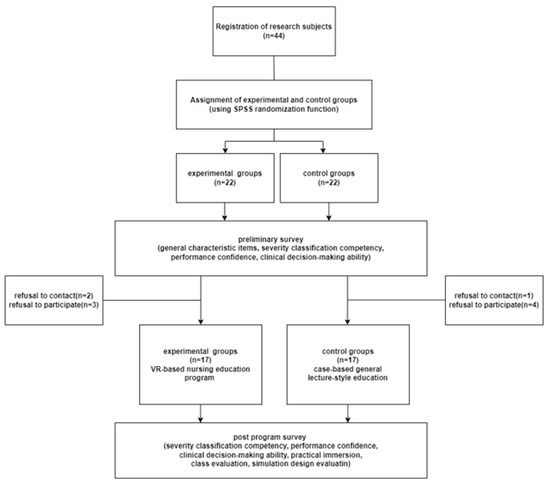
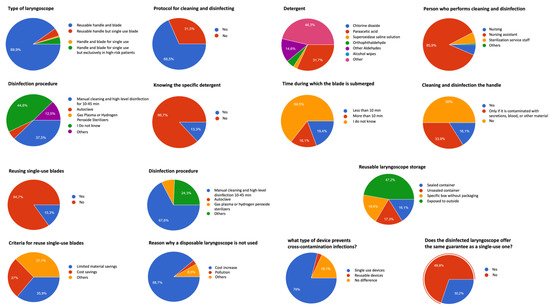
Healthcare 2023, 11(8), 1127; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11081127 - 14 Apr 2023
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2453
Abstract
►
Show Figures
The purpose of the study is to determine the influence of lateral-heel-worn shoes (LHWS) on balance control ability through the single-leg drop jump test. The results could be beneficial by preventing lower limb injuries. Eighteen healthy participants performed the single-leg drop jump test.
[...] Read more.
The purpose of the study is to determine the influence of lateral-heel-worn shoes (LHWS) on balance control ability through the single-leg drop jump test. The results could be beneficial by preventing lower limb injuries. Eighteen healthy participants performed the single-leg drop jump test. Times to stabilization for ground reaction forces (TTSG) in the anterior/posterior, medial/lateral, and vertical directions were calculated to quantify dynamic balance control ability. Outcome variables of the center of pressure (COP) were used to examine the main effect of LHWS during the static phase. The postural control ability was assessed through time to stabilization for the center of mass (TTSC) in the three directions. TTSG and TTSC for the LHWS group were found to be longer than those for the new shoes (NS) group in the M/L direction (p < 0.05). An increase in the TTS revealed an increased risk of falls during physical activities. However, no significant effects for both TTSG and TTSC were found in the other two directions between LHWS and NS groups. A static phase was cropped using TTSG for each trial, which indicated a phase after participants obtained balance. Outcome measures derived from COP showed no significant effects in the static phase. In conclusion, LHWS weakened balance control ability and postural stability in the M/L direction when compared to the NS group. During the static phase, no significant differences were found between the LHWS group and the NS group in balance control ability and postural stability. Consequently, lateral-worn shoes might increase the risk of fall injuries. The results could serve as an evaluation of shoe degradation for individuals with the aim of avoiding the risk of falls.
Full article